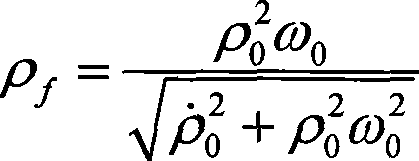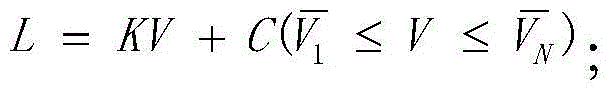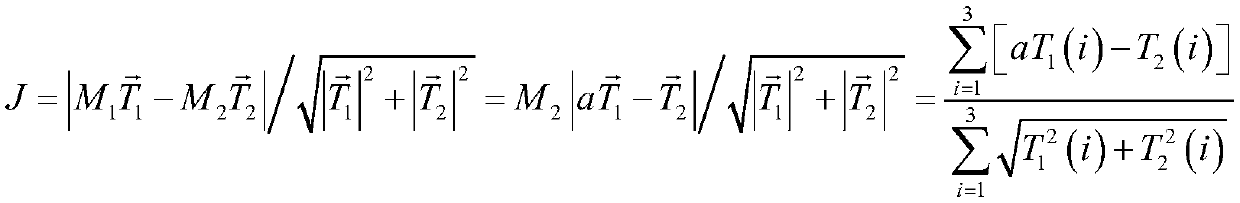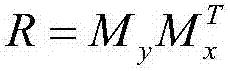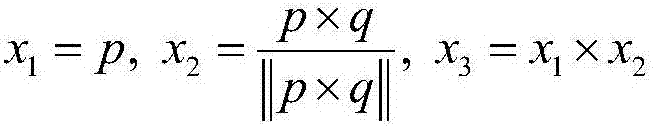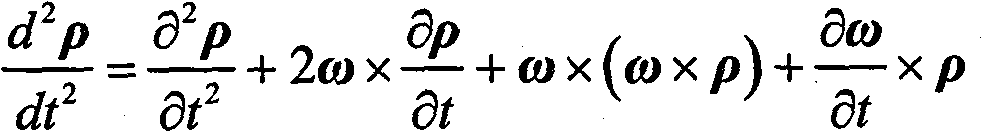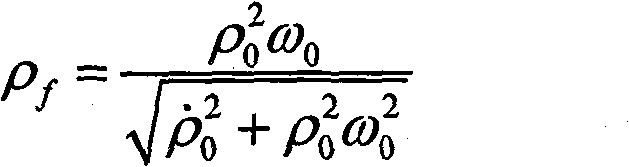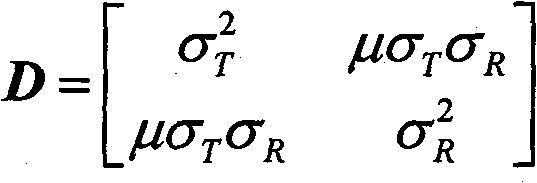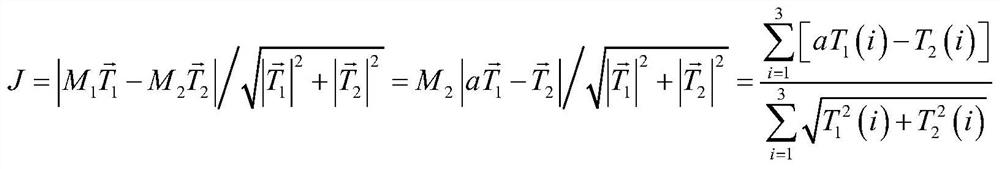Patents
Literature
64 results about "Orbit correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
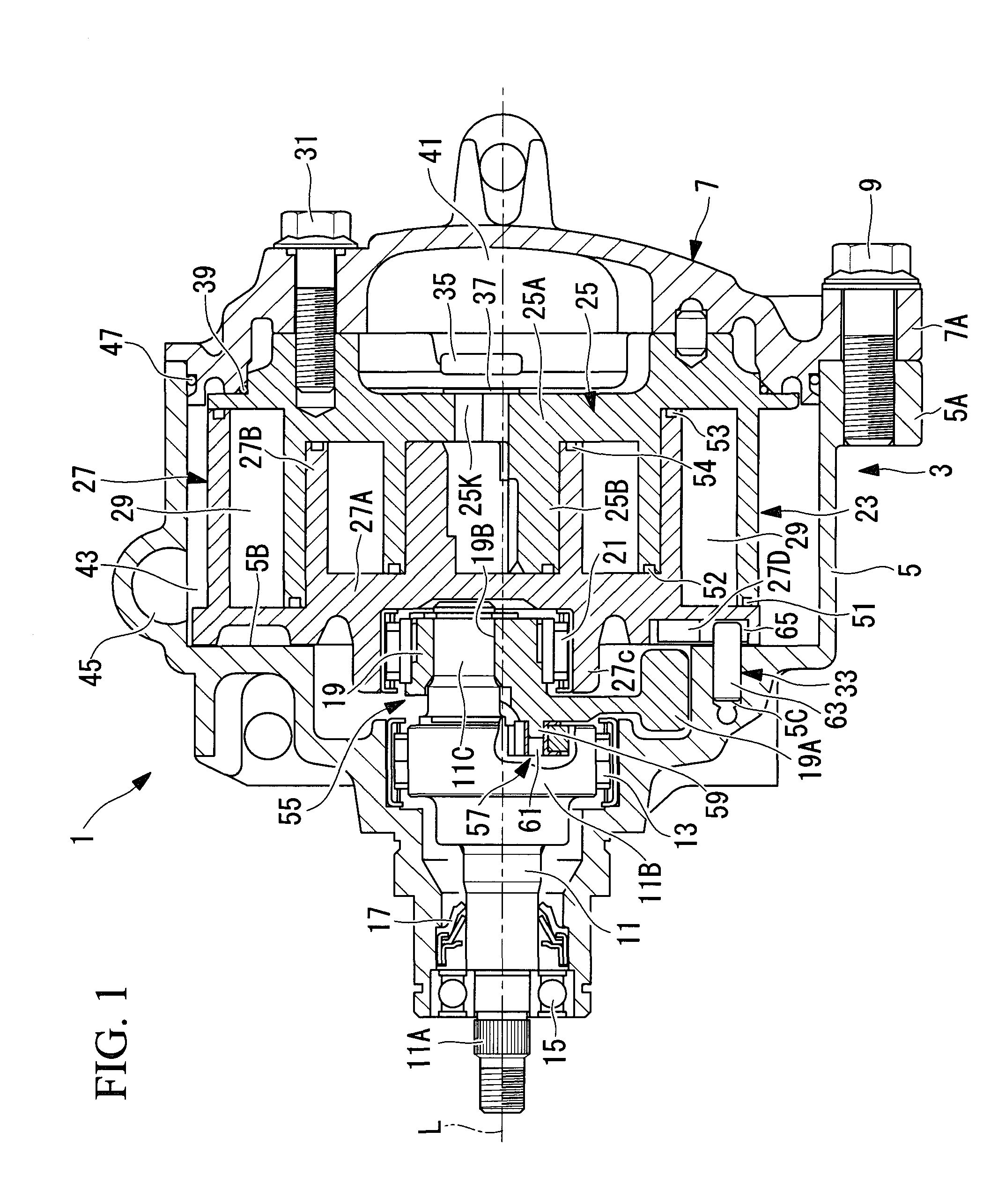
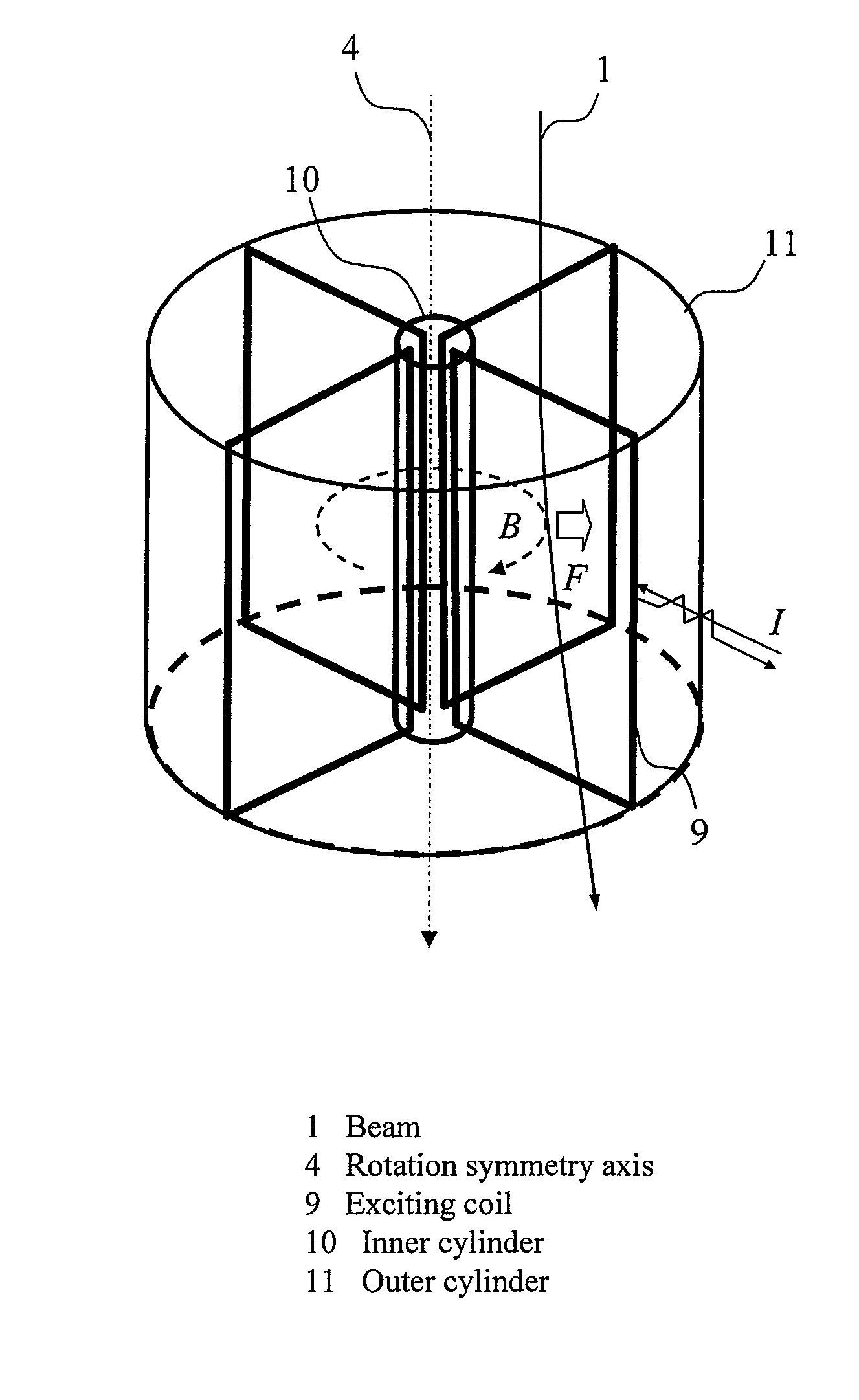
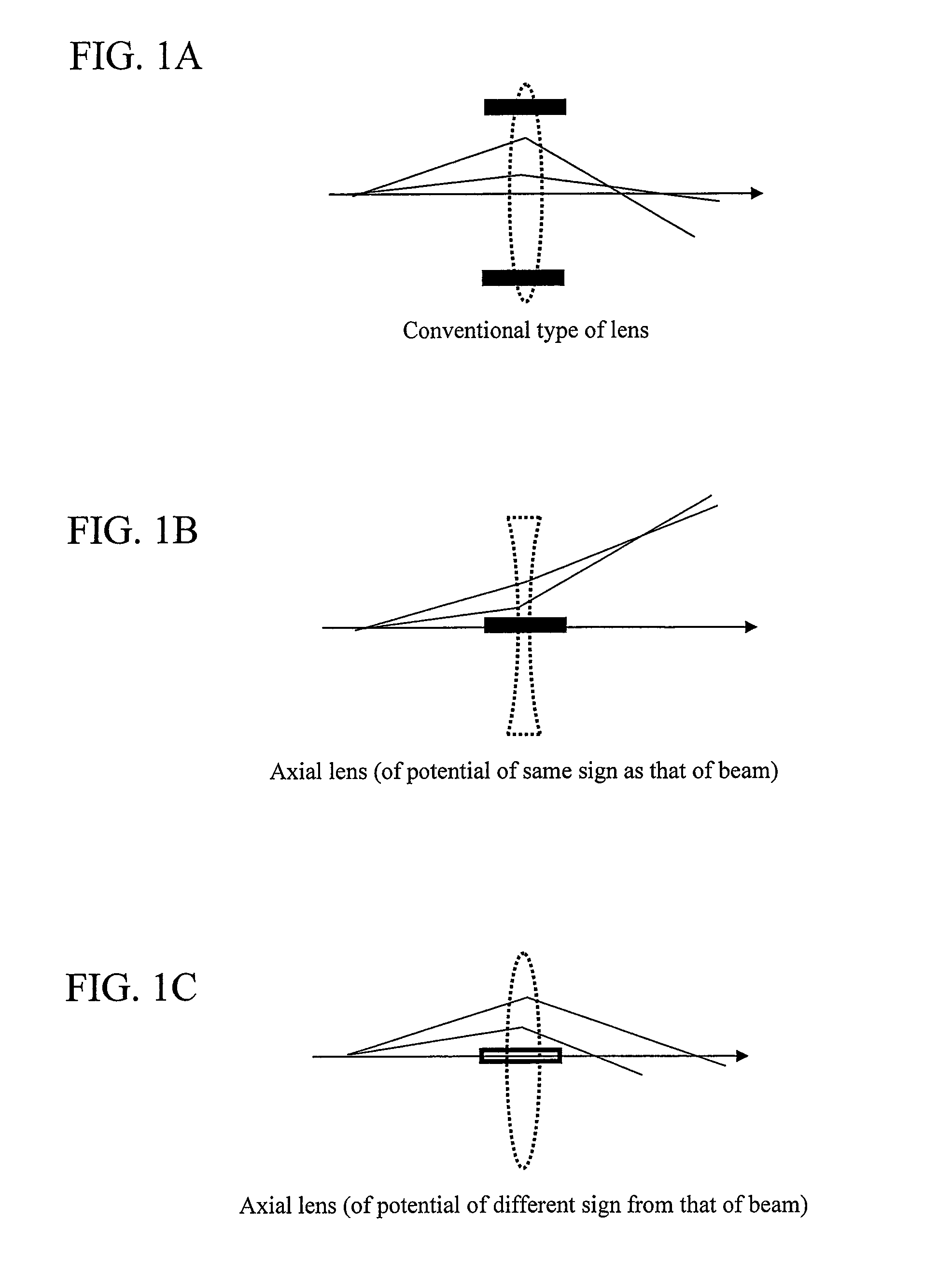
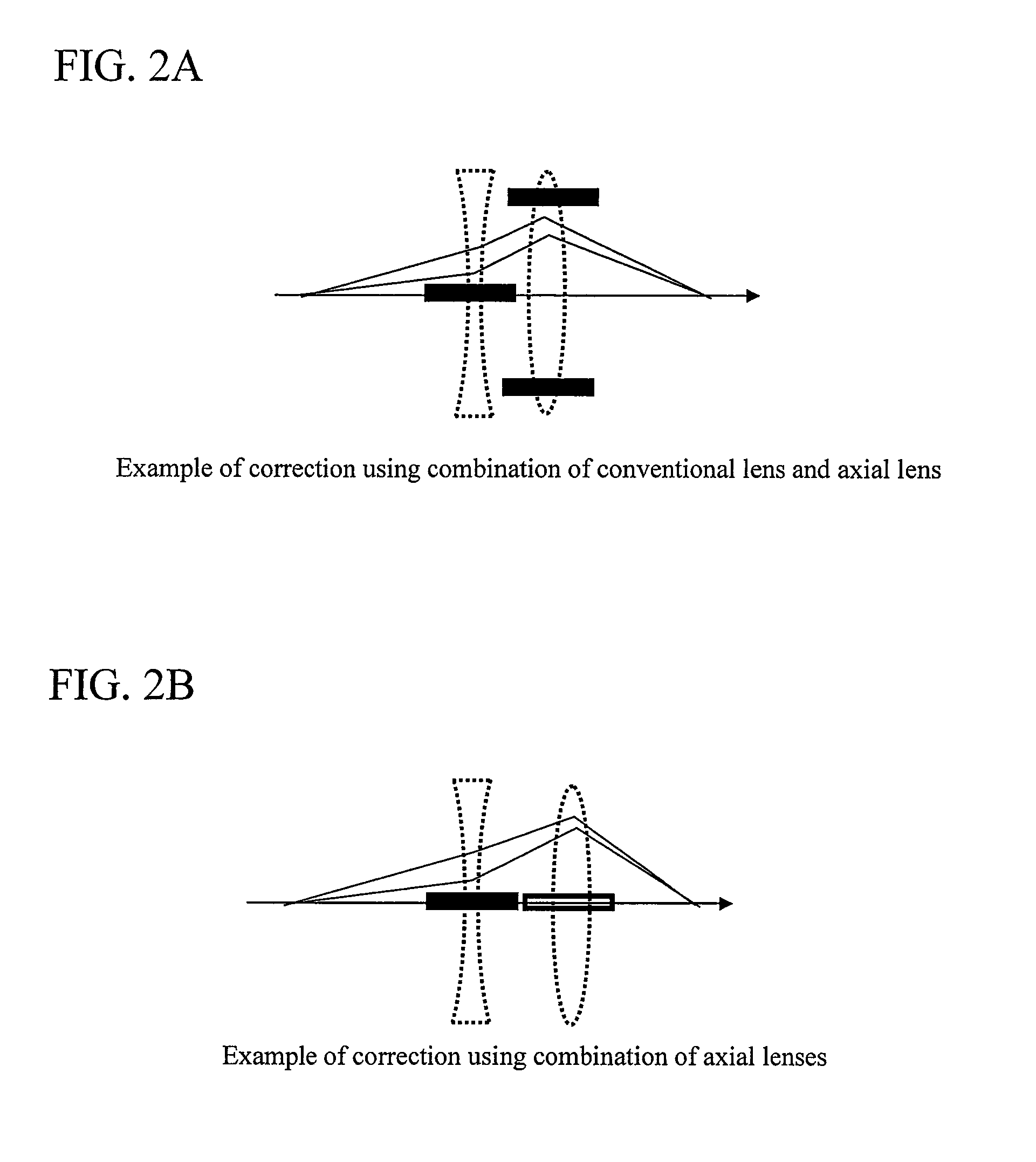
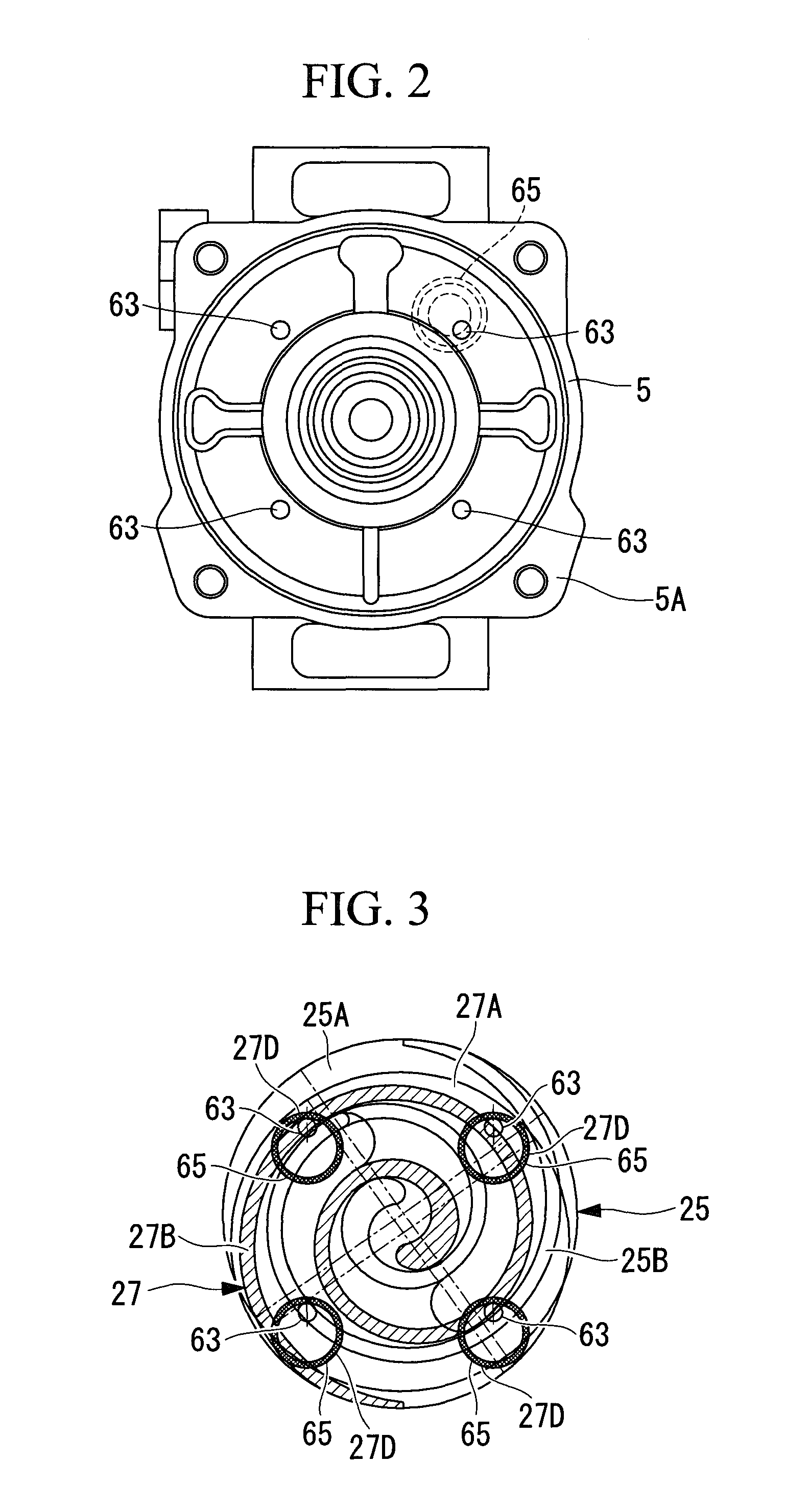
Charged Particle Beam Orbit Corrector and Charged Particle Beam Apparatus
ActiveUS20080116391A1High degreeLow costStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOrbit correctionElectromagnetic field
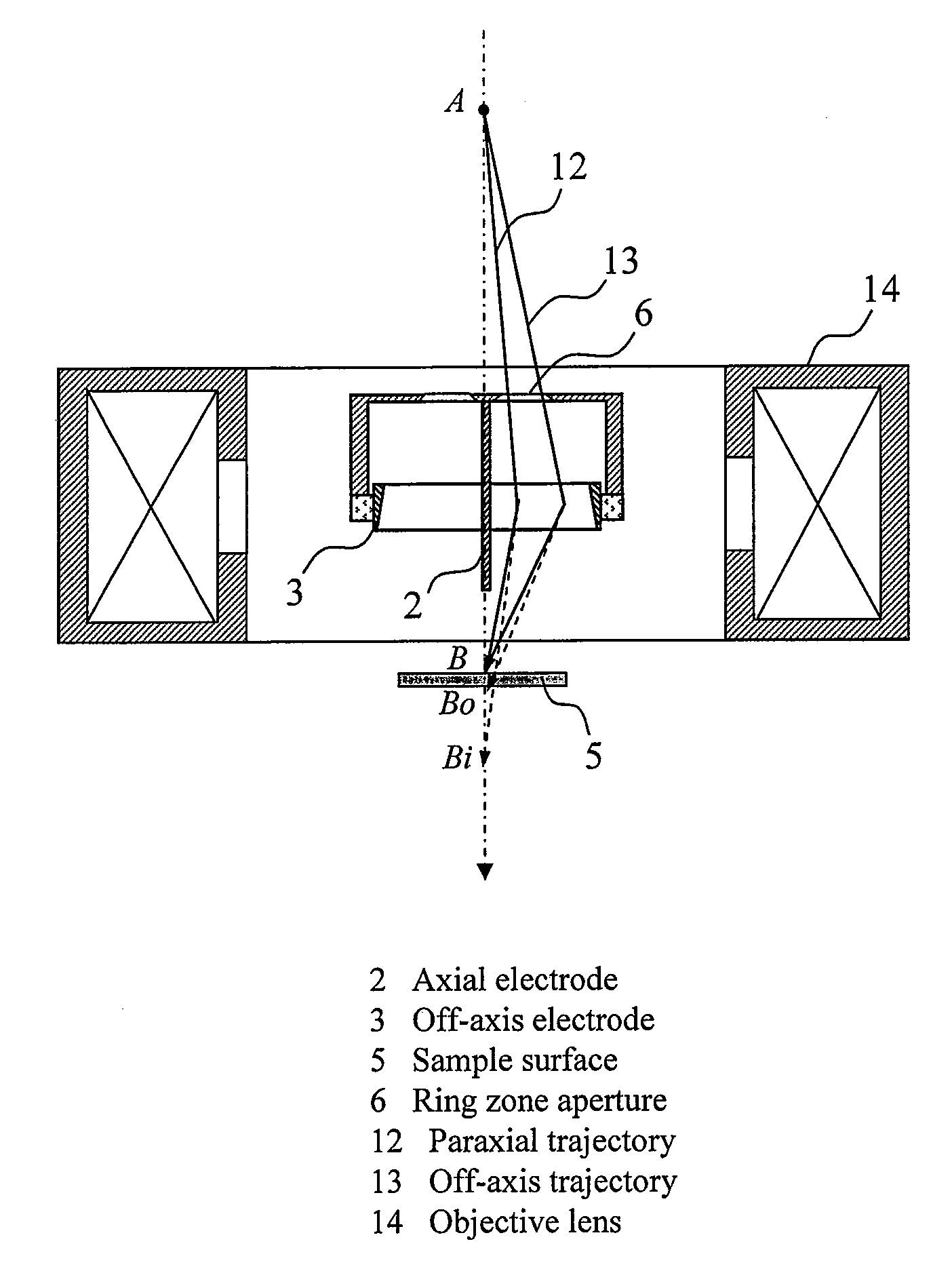
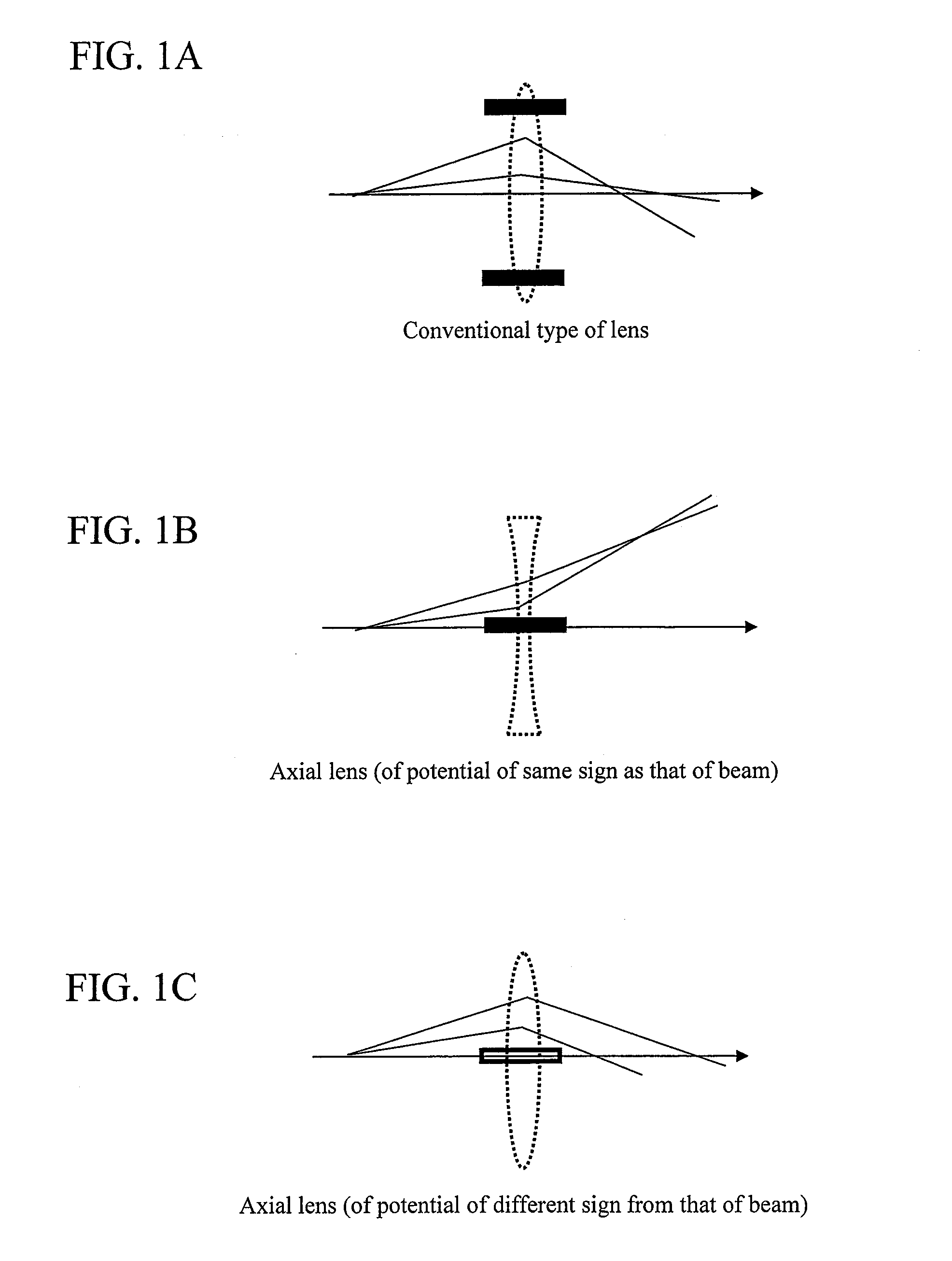
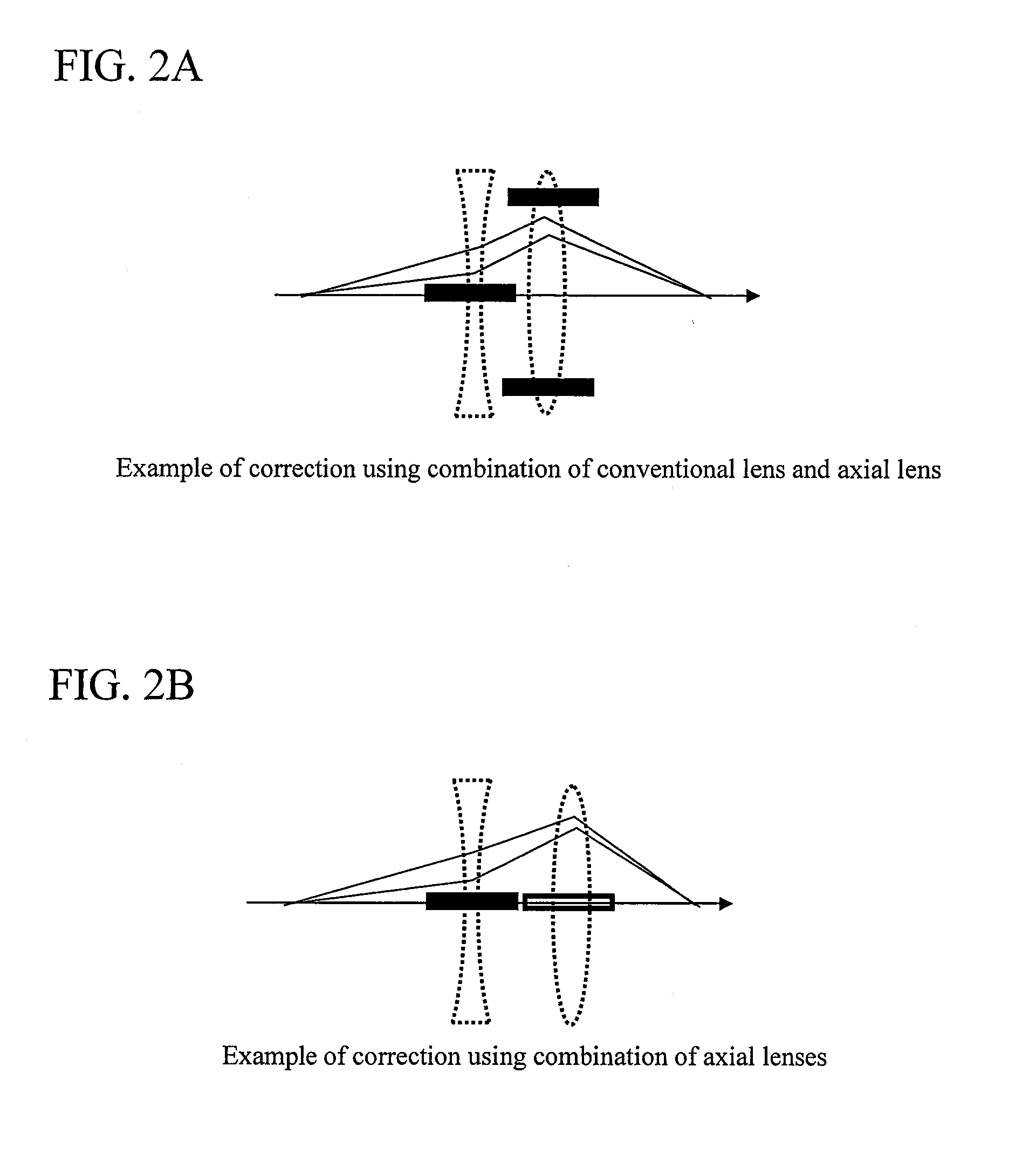
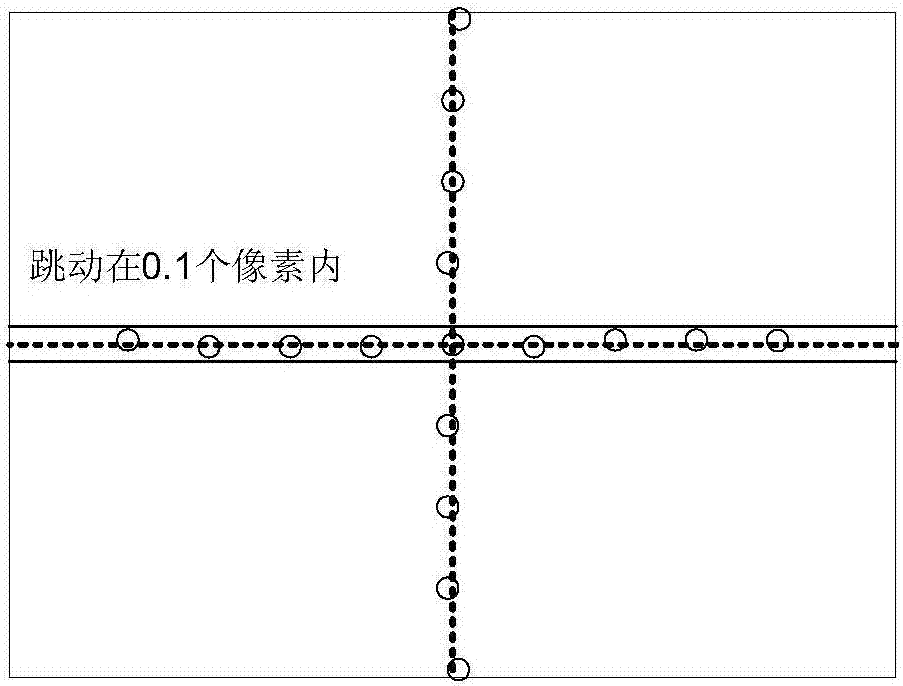
The present invention relates to an orbit correction method for a charged particle beam, and aims to solve problems inherent in conventional aberration correction systems and to provide a low-cost, high-precision, high-resolution optical converging system for a charged particle beam. To this end, employed is a configuration in which a beam orbit is limited in ring zone form to form a distribution of electromagnetic field converging toward the center of a beam orbit axis. Consequently, a nonlinear action outwardly augmented, typified by spherical aberration of an electron lens, can be cancelled out. Specifically, this effect can be achieved by an electron disposed on the axis and subjected to a voltage to facilitate the occurrence of electrostatic focusing. For a magnetic field, this effect can be achieved by forming a coil radially distributed-wound on a surface equiangularly divided in the direction of rotation to control convergence of a magnetic flux density.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
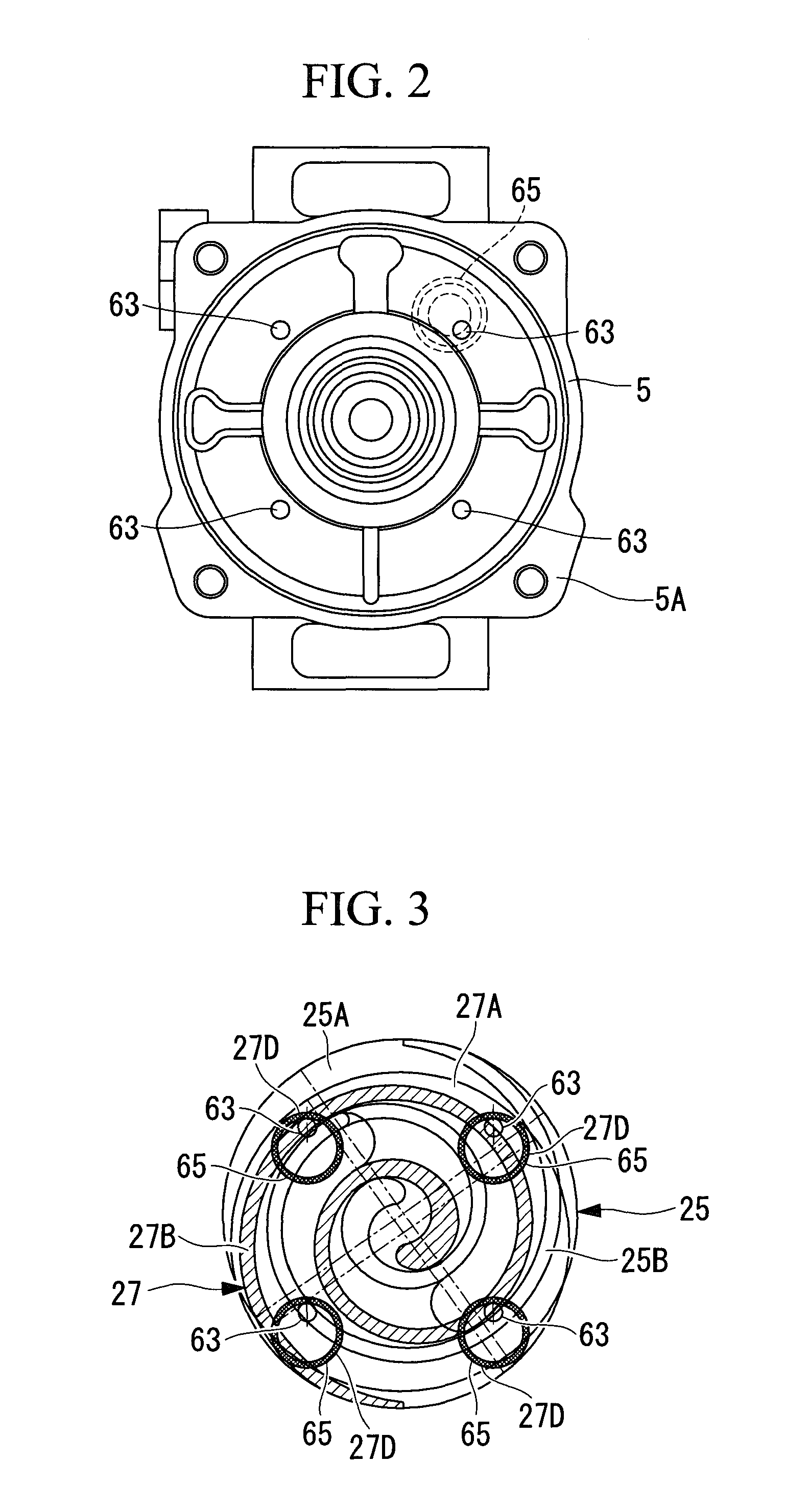
Scroll compressor
ActiveUS20100172781A1Prevent rotationReduce noiseEngine of arcuate-engagement typeOscillating piston enginesEngineeringOrbit correction
To provide a scroll compressor capable of reducing a noise occurring in a pin-and-ring type self rotation preventing mechanism and improving compression performance. In a scroll compressor comprising: a fixed scroll member and a revolving scroll member; a driven crank mechanism for driving the revolving scroll member to revolutionary turn; and a pin-and-ring type self rotation preventing mechanism provided in plural places for preventing self rotation of a revolving scroll member, at least one of the self rotation preventing pin, the self rotation preventing ring and the self rotation preventing ring hole, which form the pin-and-ring type self rotation preventing mechanism, is provided with an orbit correction part for reducing a maximum displacement R in a direction of self rotation of the revolving scroll member to smooth a change of an orbit of the revolving scroll member in changing a pin and a ring in a section of prevention of self rotation by means of a corresponding pin and ring part.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
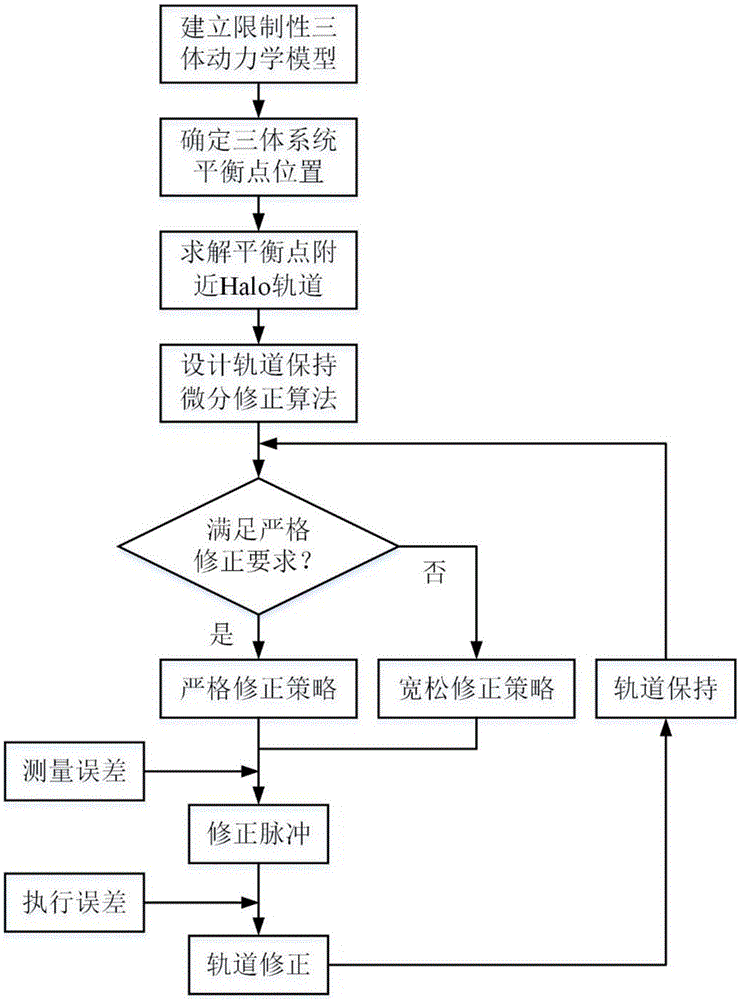
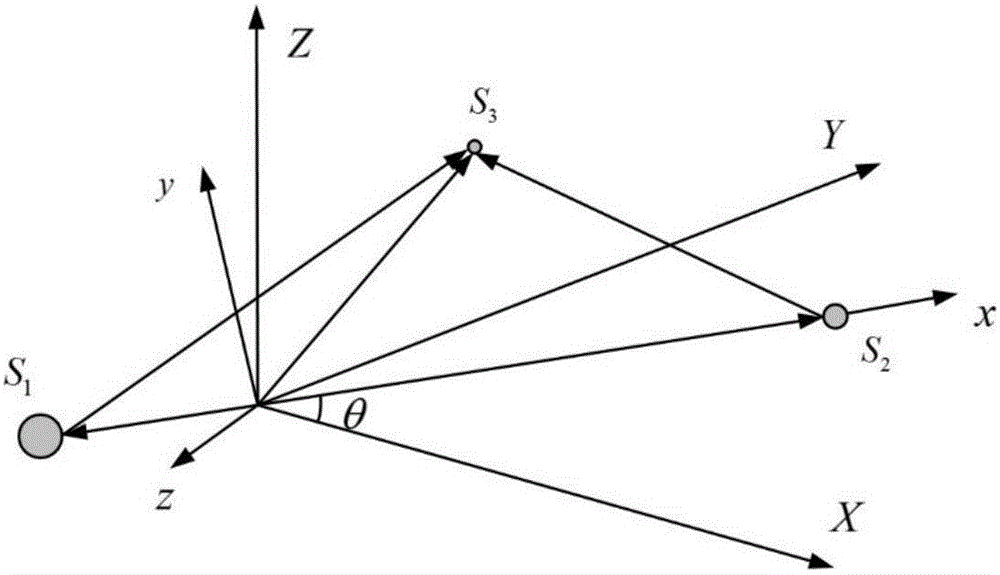
Halo orbit on-orbit keeping method considering amplitude constraint
InactiveCN106682274AStay fit in orbitSimple calculationCosmonautic condition simulationsDesign optimisation/simulationObservational errorAviation
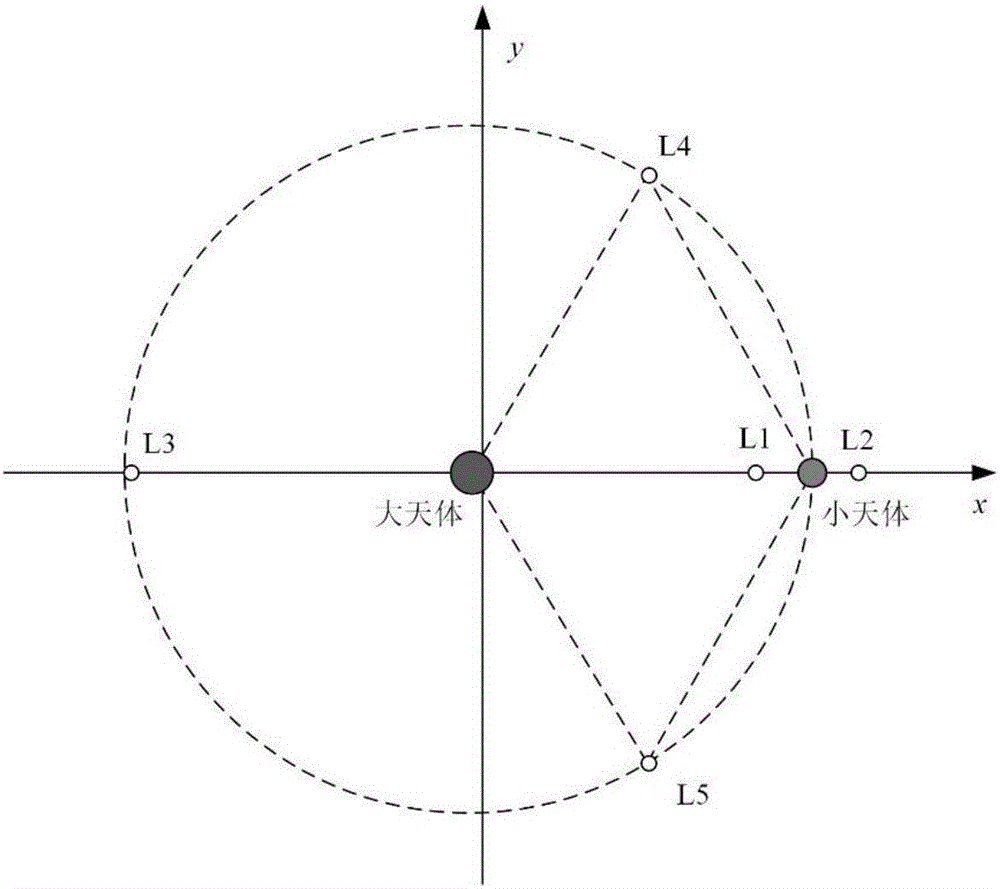
The invention provides a Halo orbit on-orbit keeping method considering amplitude constraint, and belongs to the aerospace technology field. The method comprises the steps that by establishing a kinetic equation under a limited three-body model composed of two main celestial bodies and a detector, the position of a balance point of a three-body system composed of the two celestial bodies and the detector is determined; a Halo orbit, near the balance point, in the three-body system composed of the big and small celestial bodies and the detector is determined; a differential correction algorithm for Halo orbit keeping is designed according to the disturbance variable; a Halo orbit on-orbit keeping strategy is designed according to the differential correction algorithm; in a real ephemeris environment, measurement errors and execution errors are considered, the speed increment of each time of orbit correction is obtained according to the orbit keeping strategy through the differential correction algorithm, orbit correction control is conducted according to the speed increments. Accordingly, Halo orbit on-orbit keeping considering amplitude constraint can be achieved, and consumption of fuel needed in orbit keeping can be reduced as much as possible.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Medication maneuvering time selecting method for deep space detector approaching orbit
InactiveCN101462597AMeet the requirements of brake implementationReduce consumptionArtificial satellitesNavigation by astronomical meansAviationCelestial body
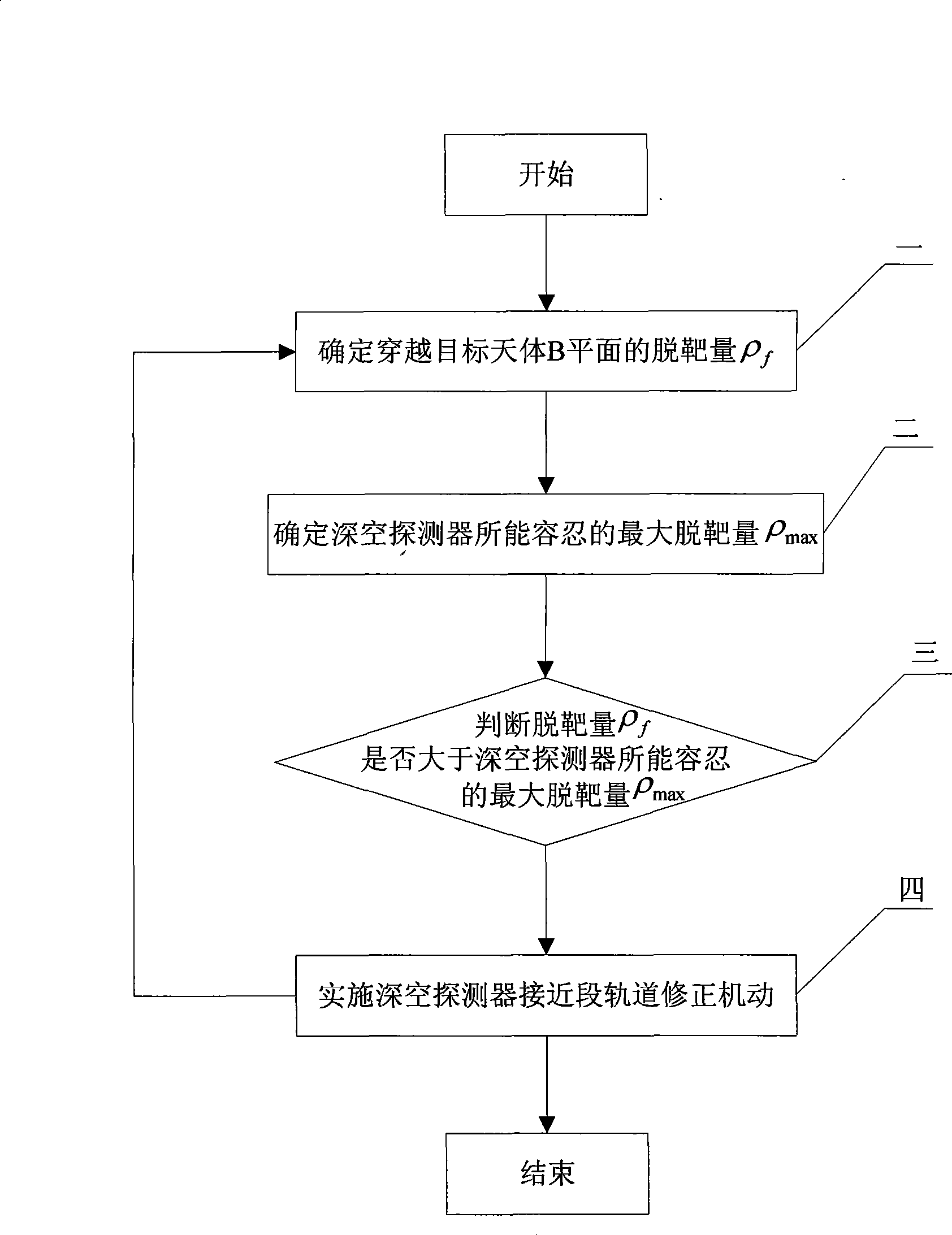
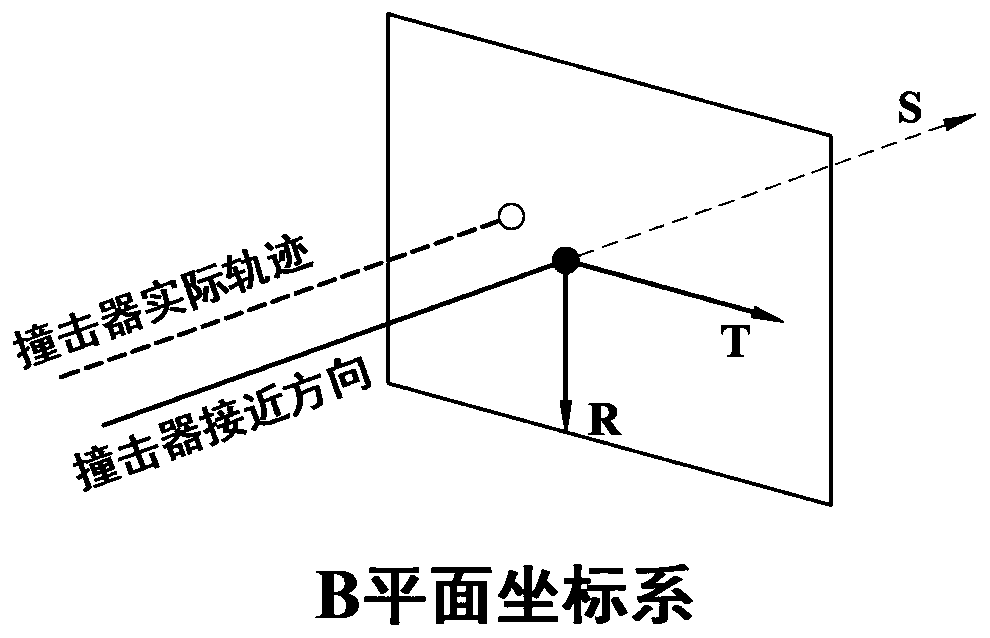
The invention relates to a method for selecting time of deep space probe approach orbit correction maneuver, which belongs to the field of spaceflight and aviation and solves the problems of deep space probe approach orbit correction maneuvering time including low control precision, great calculation amount and poor independency in the prior method for selecting time of deep space probe approach section orbit correction maneuver. The method comprises: 1, determining miss distance rhof passing through the B plane of an object celestial body; 2, determining the acceptable maximum miss distance rhomax of a deep space probe; 3, judging whether the miss distance rhof is more than the acceptable maximum miss distance rhomax, if yes, executing step 4; otherwise, returning to step 1; and 4, executing deep space probe approach section orbit correction maneuver. The method not only can save fuel at a rate of 6m / s, but also can ensure that final passing-through precision is increased by more than 100m as compared with ground station designated maneuver time precision under the same condition and reaches within 250m.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
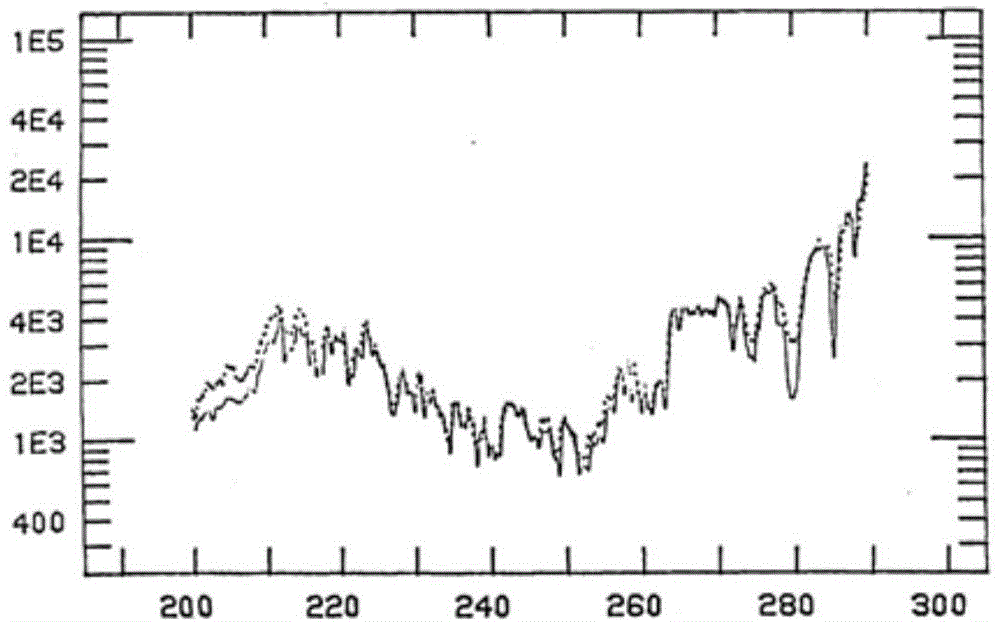
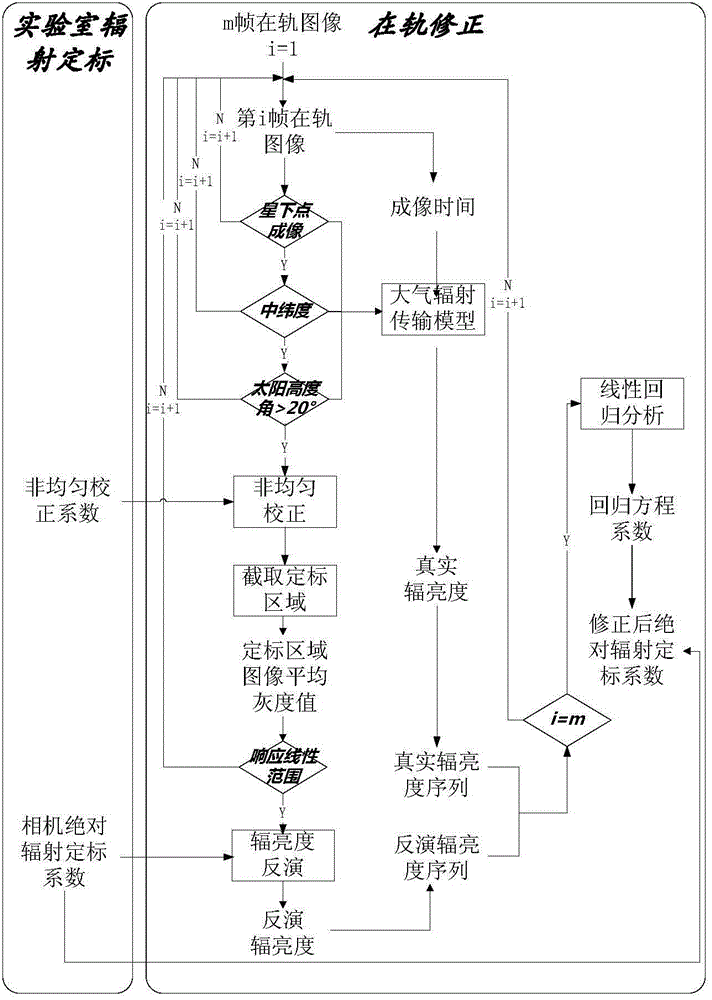
Solar blind ultraviolet remote sensing camera absolute radiometric calibration coefficient in-orbit correction method
ActiveCN104977024ARadiation calibration accuracy cannot be guaranteedMeet the high-frequency on-orbit calibration requirementsMeasurement devicesUltravioletLinear regression
The present invention relates to a solar blind ultraviolet camera absolute radiometric calibration equation coefficient in-orbit correction method, wherein a camera is subjected to laboratory absolute radiometric calibration to obtain the absolute radiometric calibration coefficient and the non-uniformity correction coefficient of the camera, the atmosphere background radiation value calculated based on the atmosphere radiation transmission model can be considered as the true background radiance when the camera in-orbit operating meets a certain constraint of the imaging mode, the location and the illumination condition, the background radiance is inverted according to the laboratory absolute radiometric calibration coefficient and the image local gray mean, and a linear regression method is used to analyze the inverted radiance value and the true radiance value so as to achieve the in-orbit correction of the calibration equation coefficient. According to the present invention, according to the solar blind ultraviolet spectrum atmosphere background radiation characteristic, the high-frequency and operational in-orbit absolute radiometric calibration of the solar blind ultraviolet spectrum remote sensor can be supported, and the blank of the in-orbit absolute radiometric calibration method of the domestic camera at the spectrum is filled.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
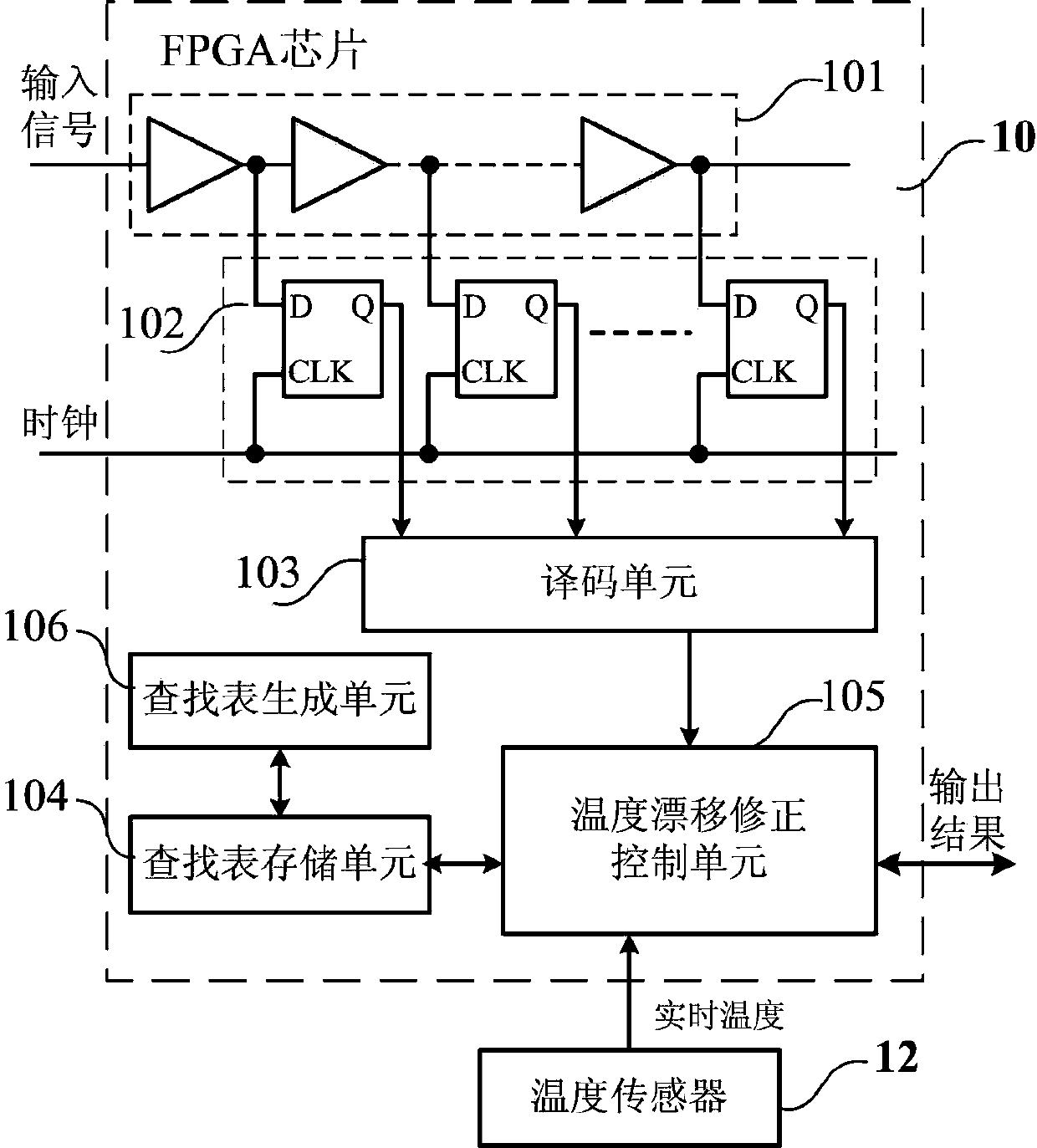
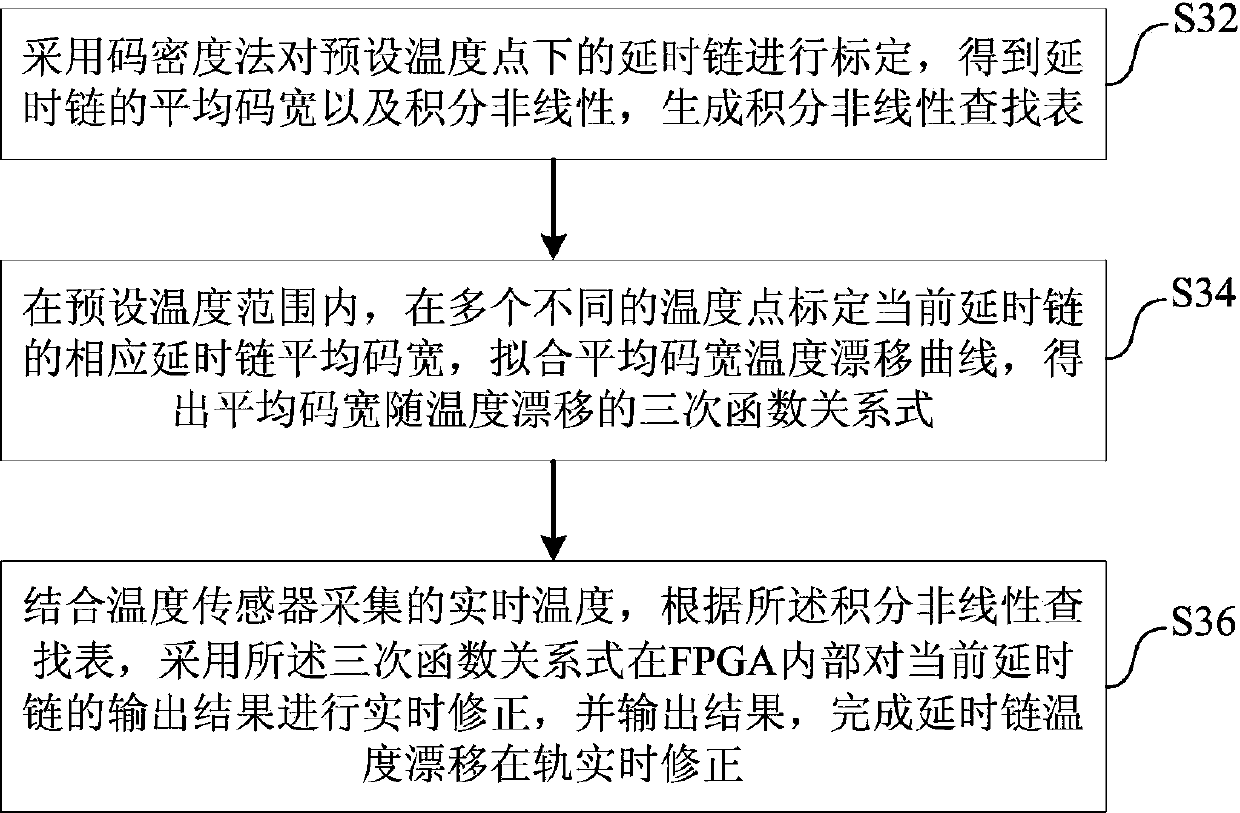
Delay chain temperature drift on-orbit correction device and method based on FPGA
InactiveCN104199481AUpload in real timeFlexible useTemperatue controlTime informationOrbit correction
The invention discloses a delay chain temperature drift on-orbit correction device and a delay chain temperature drift on-orbit correction method based on FPGA. The device comprises a temperature sensor, a delay chain, a D trigger array, a decoding unit, a lookup table storage unit and a temperature drift correction control unit, wherein the temperature sensor is used for collecting real-time temperature; the delay chain is used for reading out time information of an input signal relating to a clock edge; the D trigger array is connected to the delay chain, for locking an output state of each delay unit in the delay chain when arriving the clock edge and outputting temperature coding data; the decoding unit is connected to the D trigger array, for converting the temperature coding data into binary code data and outputting; the lookup table storage unit is used for storing integral nonlinear lookup table data of the delay chain marked at a preset temperature point; the temperature drift correction control unit is connected to the temperature sensor, the decoding unit and the lookup table storage unit respectively, for achieving on-orbit correction of delay chain temperature drift. According to the delay chain temperature drift on-orbit correction device and method based on FPGA, correction of the delay chain temperature drift is achieved by fewer sources, and high time resolution capacity is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
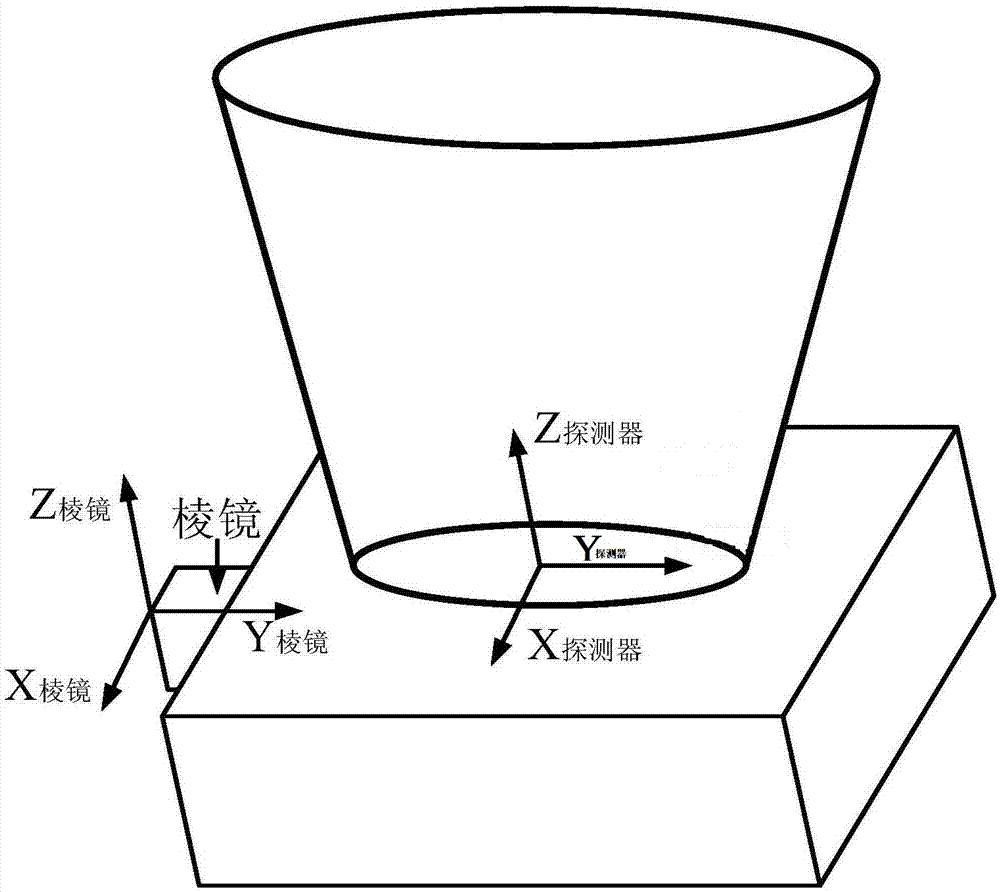
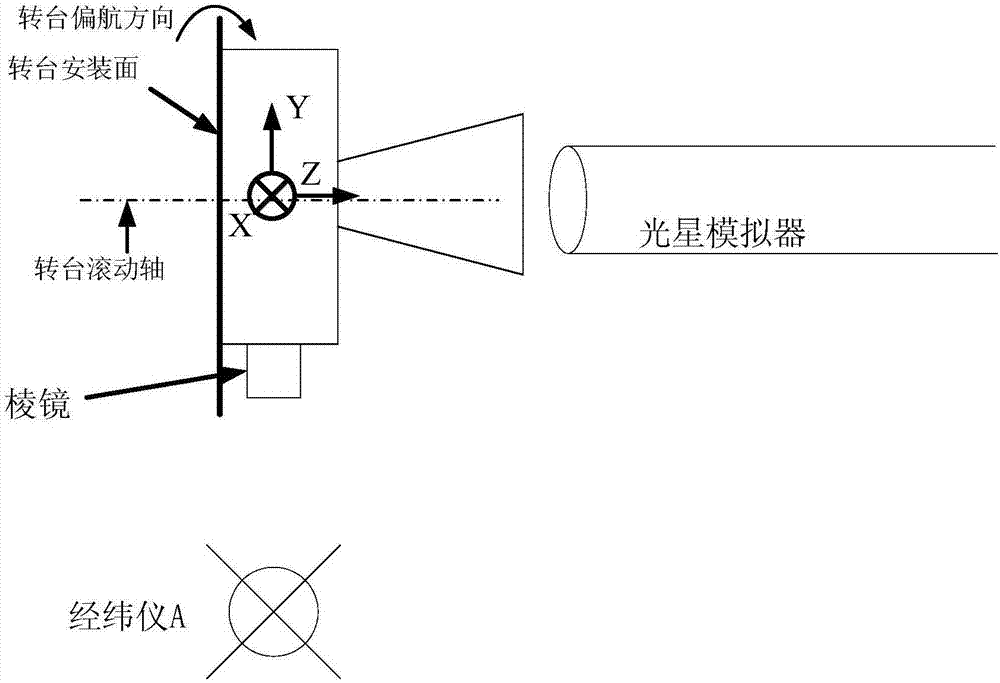
Method for measuring relationship between surveying coordinate system and prism coordinate system of star sensor
InactiveCN106871929AImprove reliabilityIncrease credibilityNavigation by astronomical meansTheodoliteControl system
The invention relates to a method for measuring a relationship between a surveying coordinate system and a prism coordinate system of a star sensor. According to the method, the star sensor is mounted on a high-precision three-axle turntable and is subjected to irradiating by using a photostar simulator, a deviation of a Z axis of the prism coordinate system of the star sensor relative to a Z axis of the surveying coordinate system is measured by using a theodolite, and meanwhile, a deviation of an X axis of the prism coordinate system of the star sensor relative to an X axis of the surveying coordinate system and a deviation of a Y axis of the prism coordinate system of the star sensor relative to a Y axis of the surveying coordinate system are measured by using two theodolites. According to the method, a surveying coordinate system and a prism coordinate system of a detector cover glass are correlated by means of light measurement, coordinate system relationship measurement is completed on the ground, and the measured deviations between the coordinate systems can be directly applied to entire star loading and the direct correction of in-orbit surveying coordinate systems of an attitude and orbit control system; the method is high in reliability, high in dependability and high in implementation performance, and the problems that in-orbit data deviation is large, in-orbit correction is complicated, and the like can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Pulsed detonation engines for reaction control systems
InactiveUS7278611B2Improve performanceEffective controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl systemMissile defense
Owner:LEIDOS
DGNSS satellite orbit deviation correction method
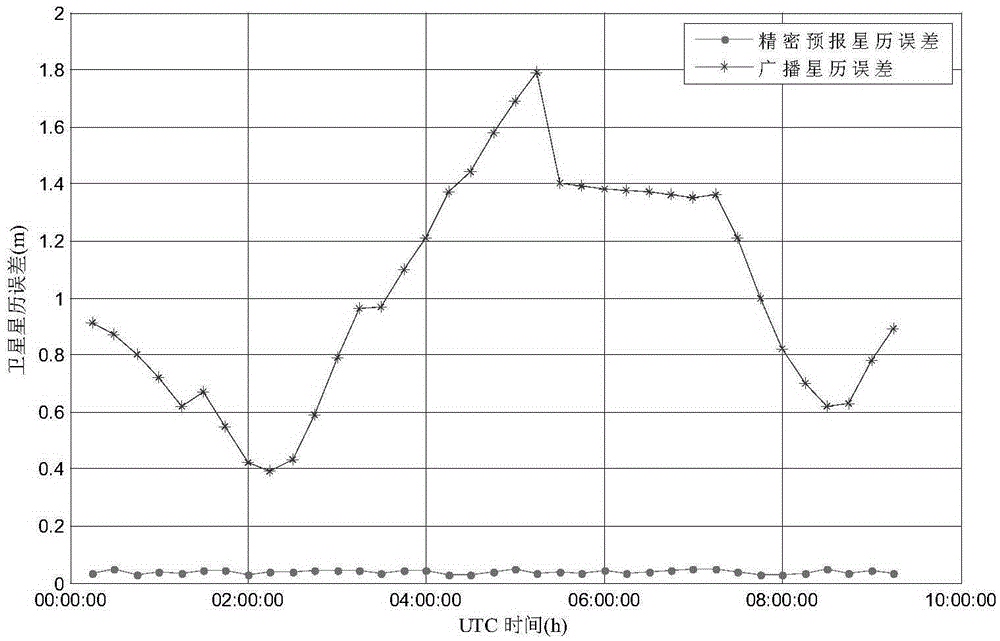
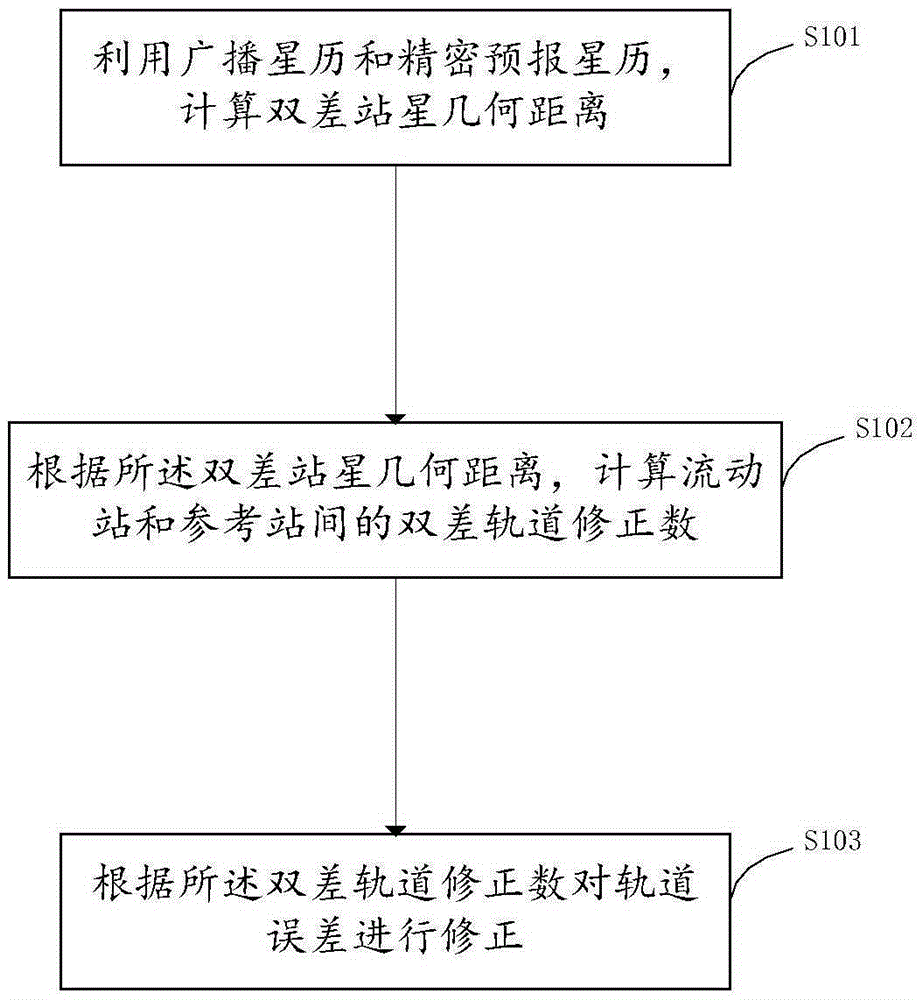
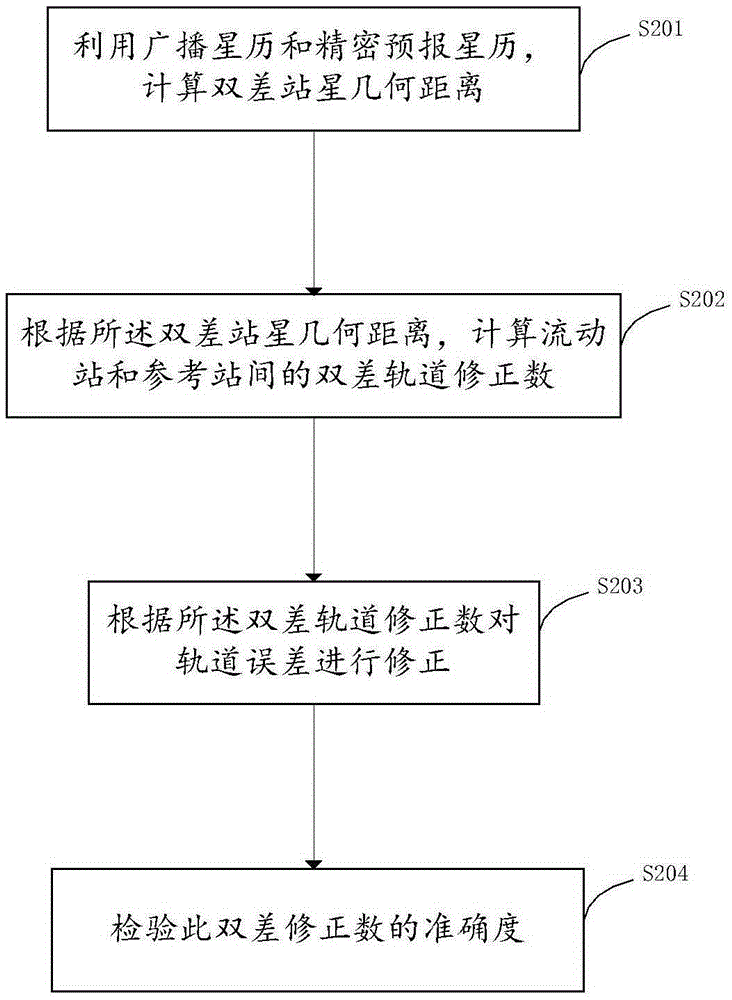
InactiveCN105403901AAchieve separationEffective monitoringSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceEphemeris
The invention belongs to the satellite navigation field and provides a DGNSS satellite orbit deviation correction method. The method includes the following steps that: broadcast ephemeris and precise prediction ephemeris are utilized to calculate double-difference station-satellite geometric distances; a double-difference orbit correction number of a mobile station and a reference station is calculated according to the double-difference station-satellite geometric distances; an orbit error is corrected according to the double-difference orbit correction number. With the DGNSS satellite orbit deviation correction method adopted, the separation of the orbit error from other distance related errors such as tropospheric and ionospheric delay errors can be realized, and the quality of the orbit deviation correction number can be monitored and controlled more effectively; and correction accuracy and stability are significantly improved. The method has a wider application range. The DGNSS satellite orbit deviation correction method can satisfy the requirements of the correction of orbits of baselines of different lengths such as medium-short baselines, medium-long baselines and ultra-long baselines.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HI TARGET NAVIGATION TECH
Dual-mode GNSS carrier precise single-point positioning method and system for intelligent terminal
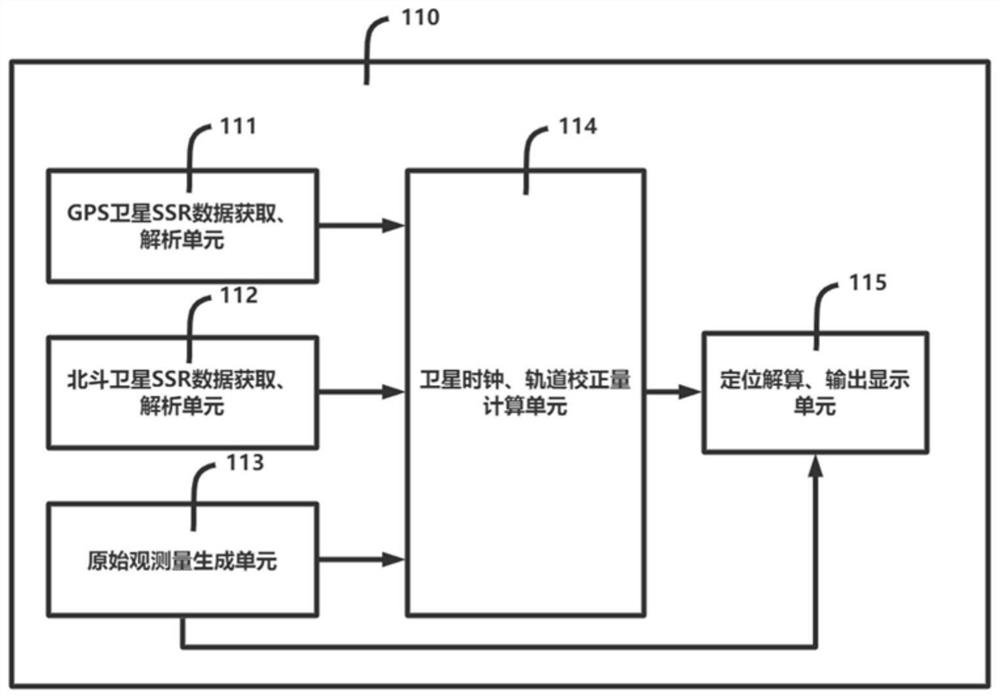
PendingCN111856534ASSR data augmentationMany satellitesSatellite radio beaconingSatellite dataData acquisition
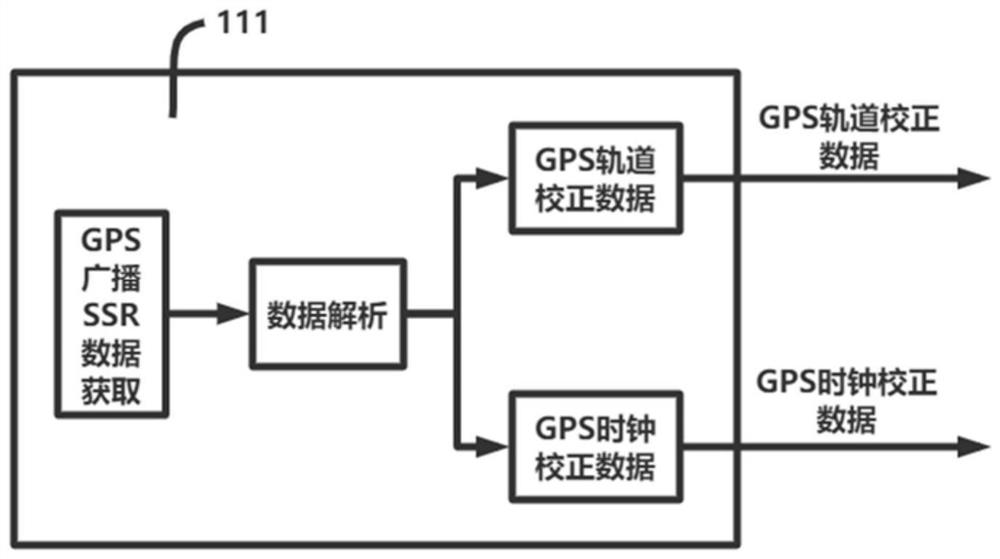
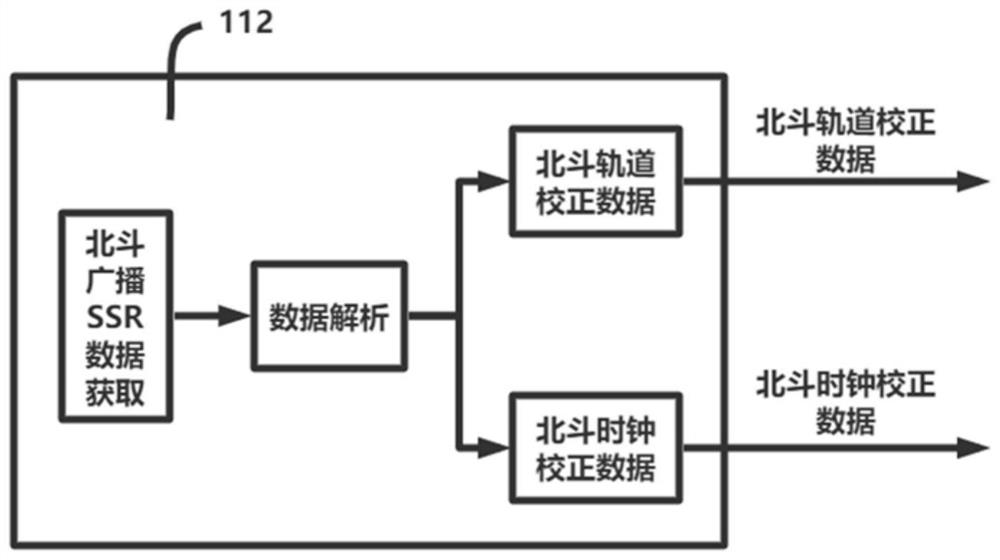
The invention provides a dual-mode GNSS carrier precision single-point positioning method and system for an intelligent terminal. The system comprises a GPS satellite SSR data acquisition and analysisunit (111), a Beidou satellite SSR data acquisition and analysis unit (112), an original observed quantity generation unit (113), a satellite clock, an orbit correction value calculation unit (114) and a positioning calculation and output display unit (115). According to the method, the SSR data of the GPS and Beidou dual-mode system is used for enhancement, the number of satellites is large, theconvergence rate of carrier phase ambiguity calculation is high, and the positioning precision is high and stable.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
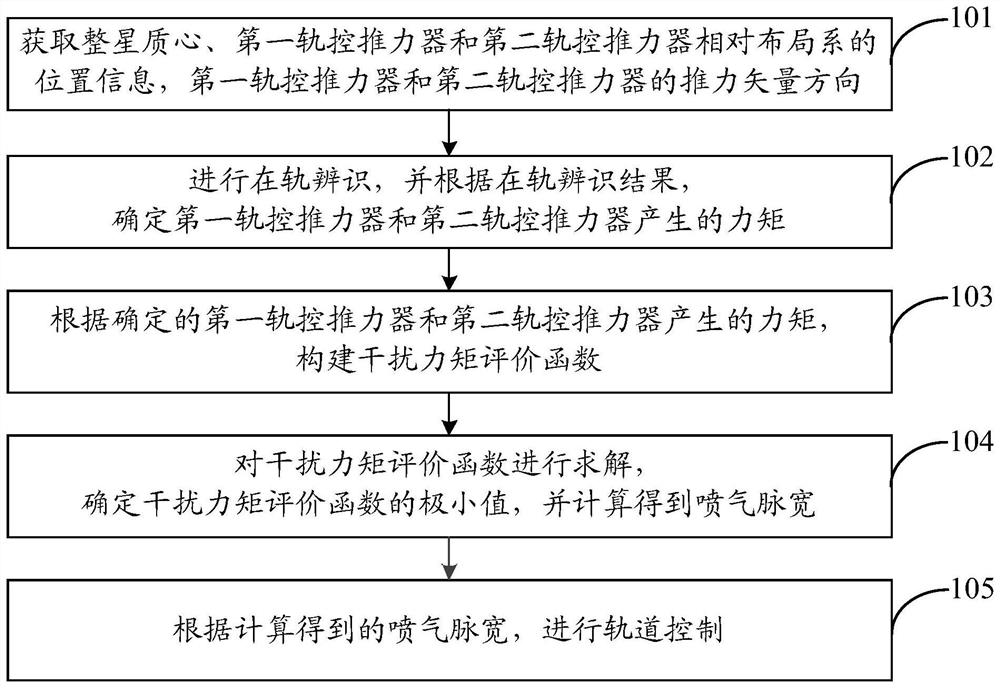
Trajectory control strategy on-orbit correction method and system based on thruster deviation estimation
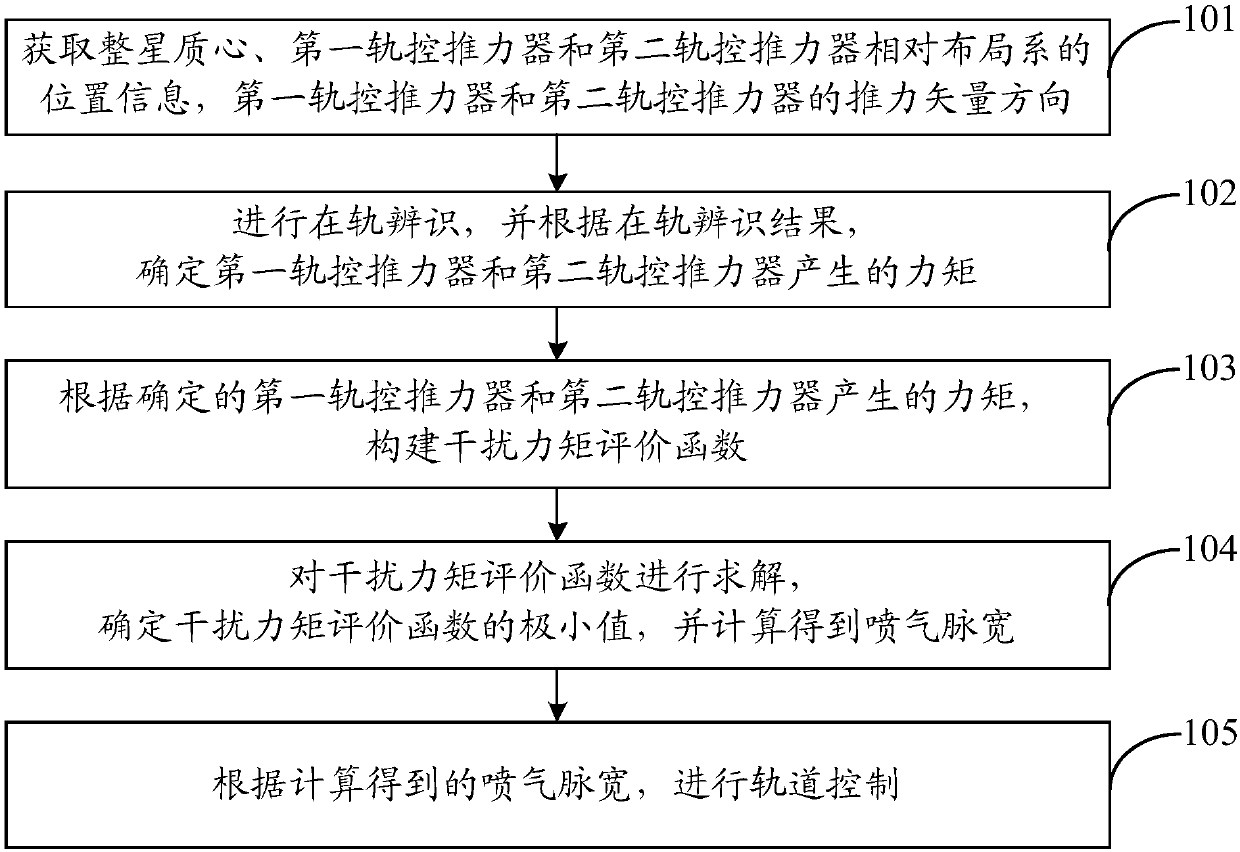
ActiveCN109649692AExtended life on orbitReduce consumptionCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusEngineeringOrbit correction
The invention discloses a method and system for on-orbit correction of a track control strategy based on thruster deviation estimation. The method comprises the following steps: respectively acquiringthe position information of the center of mass of a whole satellite, a first orbit control thruster and a second orbit control thruster relative to a layout system; acquiring thrust vector directionsof the first orbit control thruster and the second orbit control thruster; carrying out on-orbit identification, and determining moments generated by the first orbit control thruster and the second orbit control thruster according to an on-orbit identification result; constructing an interference torque evaluation function; solving the interference torque evaluation function, determining the minimum value of the interference torque evaluation function, and calculating to obtain jet pulse width; and performing orbit control according to the calculated jet pulse width. According to the invention, an orbit control thrust distribution strategy is updated on orbit by adopting an energy optimization principle, and the minimization of orbit control interference is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Spaceborne radar clock drifting on-orbit correction method based on active calibrator
ActiveCN103792519AAccurately measure clock driftStrong spatiotemporal flexibilityWave based measurement systemsRadio-controlled time-piecesAnalysis dataClock drift
The invention provides a spaceborne radar clock drifting on-orbit correction method based on an active calibrator. The spaceborne radar clock drifting on-orbit correction method based on the active calibrator comprises the steps that spaceborne radar pulse signals are tracked, received and transmitted through the active calibrator, the clock drifting distance of spaceborne radar is obtained by comparing an active calibrator distance parabola and a spaceborne radar distance parabola, and real-time quantitative monitoring of the operating state of a spaceborne radar clock is achieved based on the clock drifting distance of the spaceborne radar. According to the spaceborne radar clock drifting on-orbit correction method based on the active calibrator, the clock drifting distance of the spaceborne radar is measured accurately with an independent method for the first time, testing can be conducted in any position within the coverage of wave beams of the spaceborne radar and at any time when the spaceborne radar is in transit according to the method, the space-time flexibility is high, and the requirement for absolute timing reference for the active calibrator does not exist due to the fact that the pulse intervals are received by the active calibrator on the ground to serve as analysis data; meanwhile, path errors caused by the air when the spaceborne radar signals are transmitted are eliminated, and the clock drifting distance of the spaceborne radar can be measured accurately in real time.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Charged particle beam orbit corrector and charged particle beam apparatus
ActiveUS7947964B2Increase rangeHigh currentStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectromagnetic fieldOrbit correction
The present invention relates to an orbit correction method for a charged particle beam, and aims to solve problems inherent in conventional aberration correction systems and to provide a low-cost, high-precision, high-resolution optical converging system for a charged particle beam. To this end, employed is a configuration in which a beam orbit is limited in ring zone form to form a distribution of electromagnetic field converging toward the center of a beam orbit axis. Consequently, a nonlinear action outwardly augmented, typified by spherical aberration of an electron lens, can be cancelled out. Specifically, this effect can be achieved by an electron disposed on the axis and subjected to a voltage to facilitate the occurrence of electrostatic focusing. For a magnetic field, this effect can be achieved by forming a coil radially distributed-wound on a surface equiangularly divided in the direction of rotation to control convergence of a magnetic flux density.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
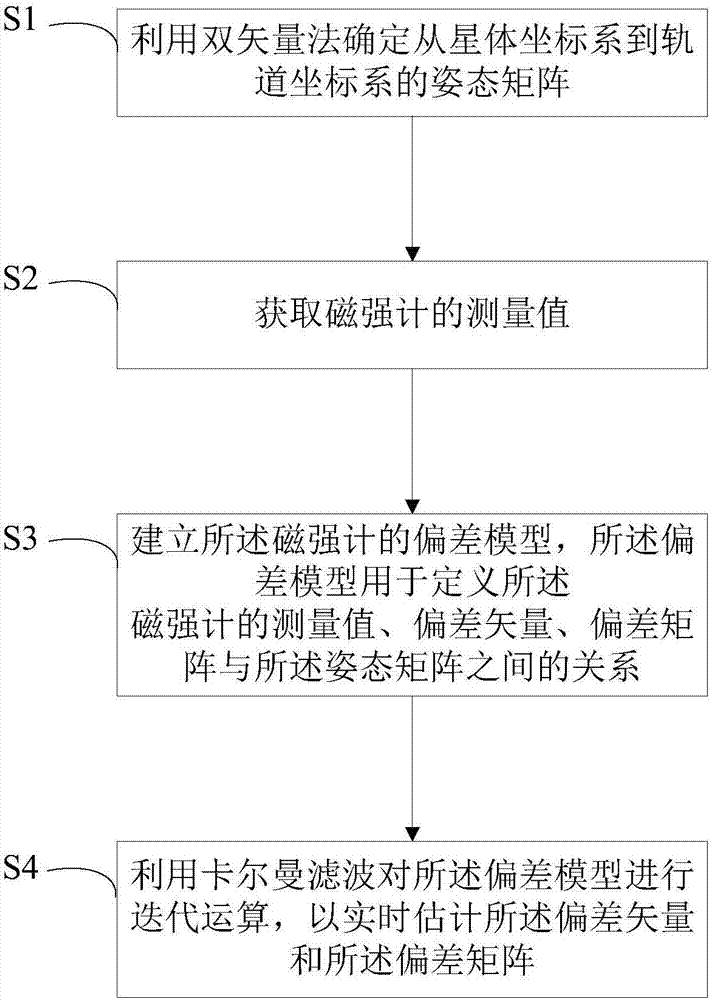
Method for estimating output deviations of triaxial magnetometer
InactiveCN107270940ACalculation convergence is fastHigh precisionMeasurement devicesDeviation vectorOrbit correction
The invention provides a method for estimating the output deviations of a triaxial magnetometer. The method is applied to spacecrafts. The output deviations of the triaxial magnetometer comprise a deviation vector and a deviation matrix. The method comprises the following steps: determining an attitude matrix from star coordinate system to track coordinate system by using a double-vector method; acquiring the measured value of the magnetometer; establishing a deviation model of the magnetometer which is used for defining the relationship among the measured value of the magnetometer, the deviation vector, the deviation matrix and the attitude matrix; and subjecting the deviation model to iterative operation in virtue of Kalman filtering so as to estimate the deviation vector and the deviation matrix in real time. The method provided by the invention is fast in calculation convergence, high in precision and applicable to spacecrafts with stable attitudes and has reference significance to error analysis, in-orbit correction and subsequent designing of the triaxial magnetometer and other triaxial vector sensors with similar measuring principles.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Orbit correction method and system of space laser interference gravitational wave detector
ActiveCN110077627AReduce consumptionExtend mission lifeCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusStability indexClassical mechanics
The embodiments of the invention provide an orbit correction method and system of a space laser interference gravitational wave detector. The orbit correction method comprises the steps: nominal orbitelements and actual orbit elements of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector are obtained, and the average orbit element deviation value of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector is calculated; the nominal orbit elements of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector and perturbation magnitude information of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector are obtained, and an average orbit element perturbation equation of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector is calculated; and according to the geometrical relationship between the virtual formation configuration envelope radius and orbit configuration stability indexes of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector, by combining with the average orbit element perturbation equation, the expected value of the average orbit element deviation value of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector is obtained, and then the average orbit element correction of the space laser interference gravitational wave detector is calculated. According to the orbit correction method, fuel consumption can be reduced, and the mission life is prolonged.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
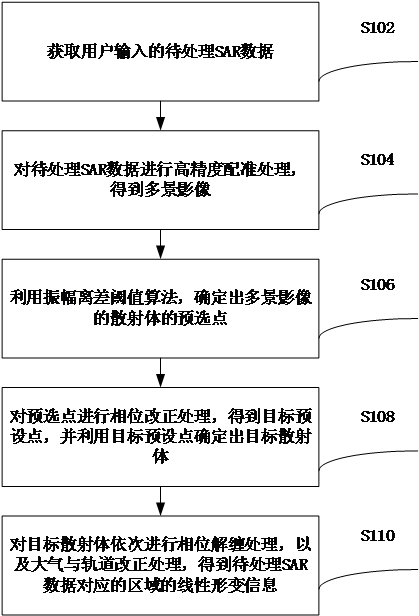
High-precision settlement monitoring method and device for SAR data
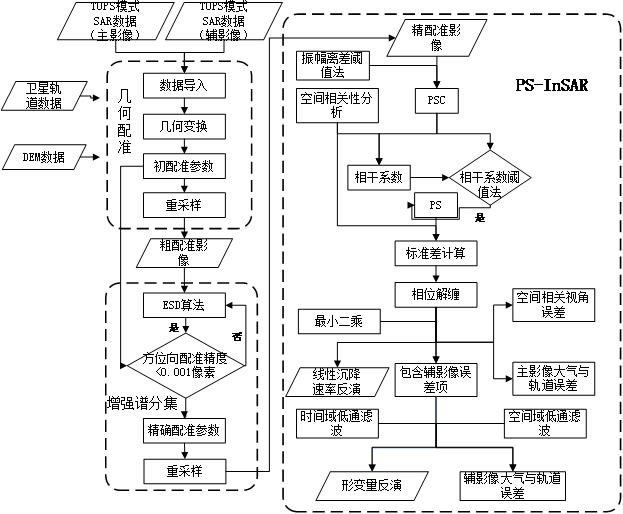
InactiveCN112034463ASolve the technical problem of low monitoring accuracyHeight/levelling measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionEngineering
The invention provides a high-precision settlement monitoring method and device for SAR data, and relates to the technical field of data processing. The method comprises the steps: obtaining to-be-processed SAR data inputted by a user, and enabling the to-be-processed SAR data to be SAR data in a TOPS mode; performing high-precision registration processing on the to-be-processed SAR data to obtaina multi-scene image; determining a pre-selected point of a scatterer of the multi-scene image by utilizing an amplitude deviation threshold algorithm; performing phase correction processing on the pre-selected point to obtain a target preset point, and determining a target scatterer by using the target preset point; and performing phase unwrapping processing and atmosphere and orbit correction processing sequentially on the target scatterer to obtain linear deformation information of the area corresponding to the to-be-processed SAR data. The technical problem that an existing SAR data settlement monitoring method is low in monitoring precision of the linear deformation information of the monitoring area is solved.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE HONGTU INFORMATION TECH
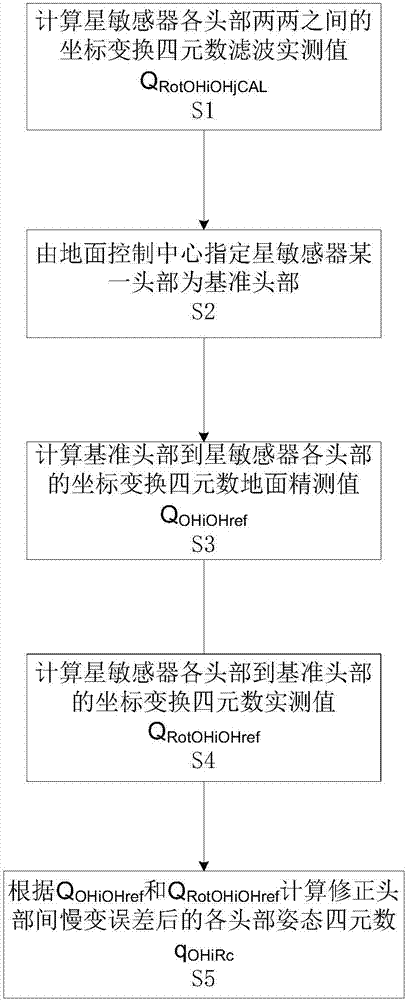
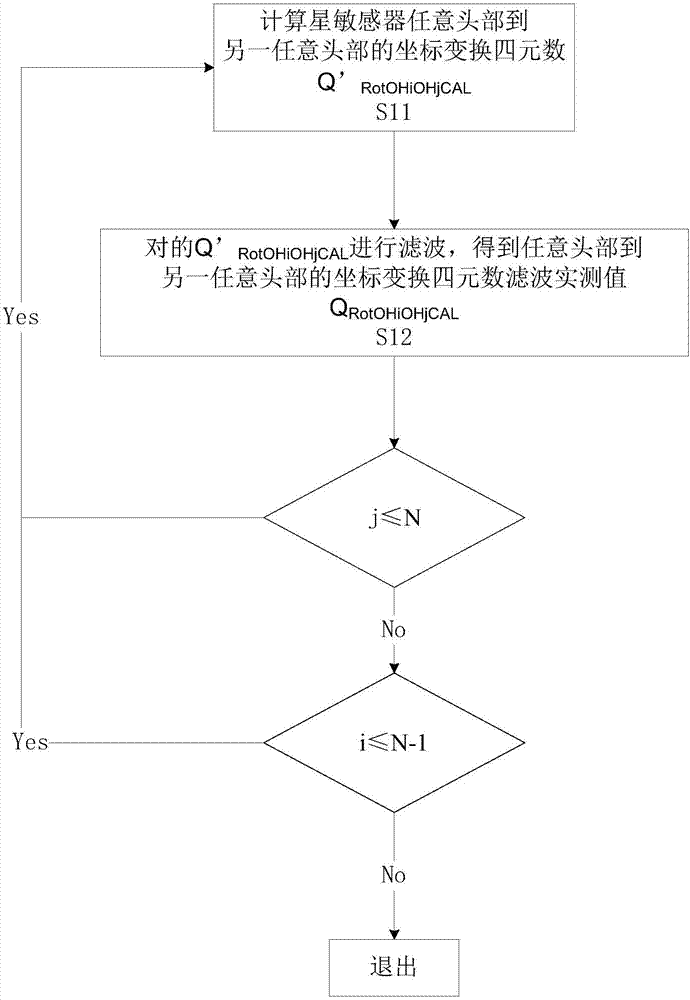
Real-time on-orbit correction method of slow varying errors among plurality of star sensors
ActiveCN107228683AImprove attitude determination accuracyCorrection of slowly varying errorsNavigational calculation instrumentsQuaternionOrbit correction
The invention provides a real-time on-orbit correction method of slow varying errors among a plurality of star sensors. The slow varying errors between every two head parts of the star sensors are corrected. The method comprises the following steps of S1, calculating the coordinate conversion quaternion filtering practical measuring value Q[RotOHiOHjCAL] between every two head parts of the star sensors; S2, specifying a certain head part on the star sensor as a reference head part OHref by a ground control center; S3, calculating the coordinate conversion quaternion ground precise measuring value Q[OHiOHref] from the reference head part OHref to each head part OHi of the star sensors; S4, calculating the coordinate conversion quaternion practical measuring value Q[RotOHiOHref] from each head part OHi of the star sensors to the reference head part OHref; S5, calculating each head part posture quaternion q[OHiRc] after the correction of the slow varying errors between the head parts according to the Q[OHiOHref] and the Q[RotOHiOHref] obtained in the S3 and S4. The method can realize the on-orbit real-time estimation and correction; by using a simple calculation mode, the posture determination precision of the combined fixed posture of the plurality of star sensors is improved; the slow varying errors between the non-reference head parts and the reference head parts is simply and effectively corrected; the head part posture quaternion after the correction of the slow varying errors between the head parts is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
SmallSat Hybrid Propulsion System
A hybrid propulsion system for a small satellite package consisting of a main rocket motor containing a solid propellant with multiple oxidizer tanks positioned to direct oxidizer into the rocker motor, thereby producing a desired thrust necessary for orbit insertion and / or orbit correction. Additionally, oxidizers can serve a dual function in controlling cold fuel thrusters for attitude adjustment.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
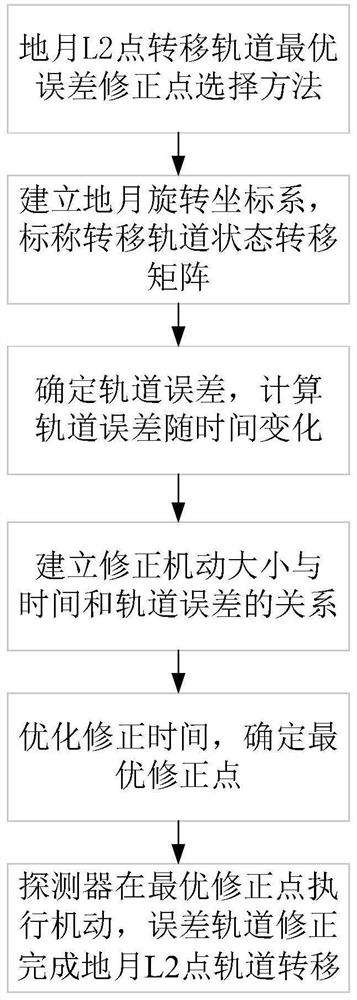
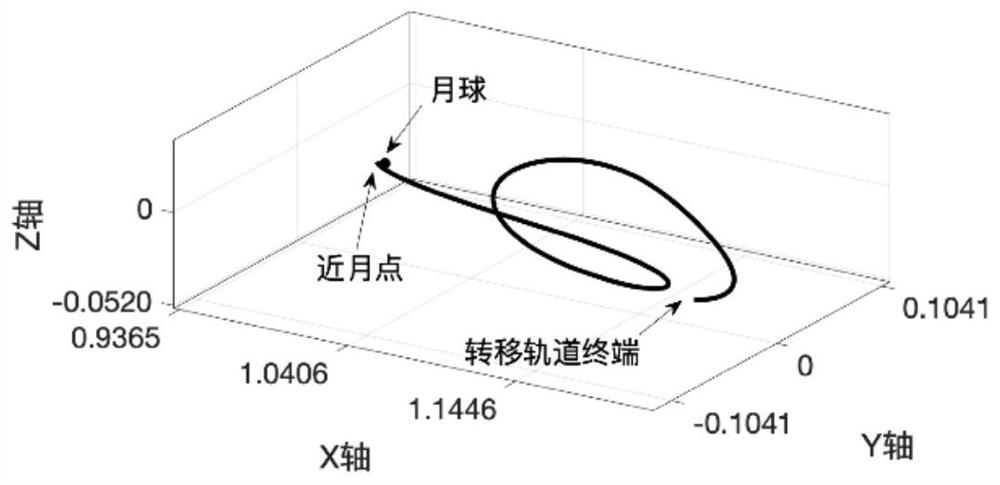
Method for selecting optimal error correction point of earth-moon L2 point transfer orbit
ActiveCN111605736ASmall amount of calculationImprove computing efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesNavigational calculation instrumentsComputational physicsOrbit correction
The invention discloses a method for selecting an optimal error correction point of an earth-moon L2 point transfer orbit, which belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The implementation methodcomprises the following steps of establishing an earth-moon rotating coordinate system, and calculating an earth-moon L2 point nominal transfer orbit state transfer matrix, calculating the change condition of the error along with time according to the state transfer matrix, according to the state transfer matrix, establishing a function relationship between correction maneuver and correction timeand an orbit error, optimizing the correction time of the detector, and determining the optimal error correction point and correction speed increment of the correction speed increment and the terminalspeed increment by utilizing the function relationship, and enabling the detector to apply a speed increment at the optimal correction point to complete orbit correction of the earth-moon L2 point transfer orbit and complete earth-moon L2 point orbit transfer. According to the method, the speed increment required by correction can be minimized, and the method has the advantages of high correctionefficiency and reduction of correction fuel consumption. According to the method, the orbit transfer precision is improved by considering the influence of lunar attraction on the transfer orbit error.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Flexible satellite-borne antenna on-orbit vibration measurement method based on sequence image
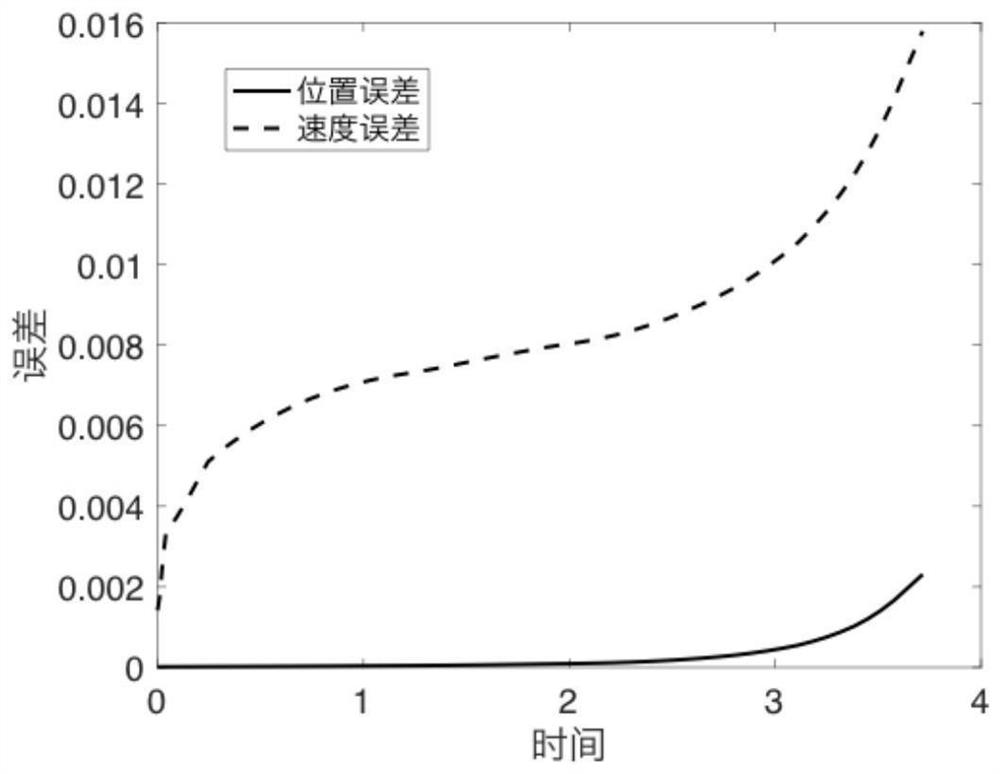
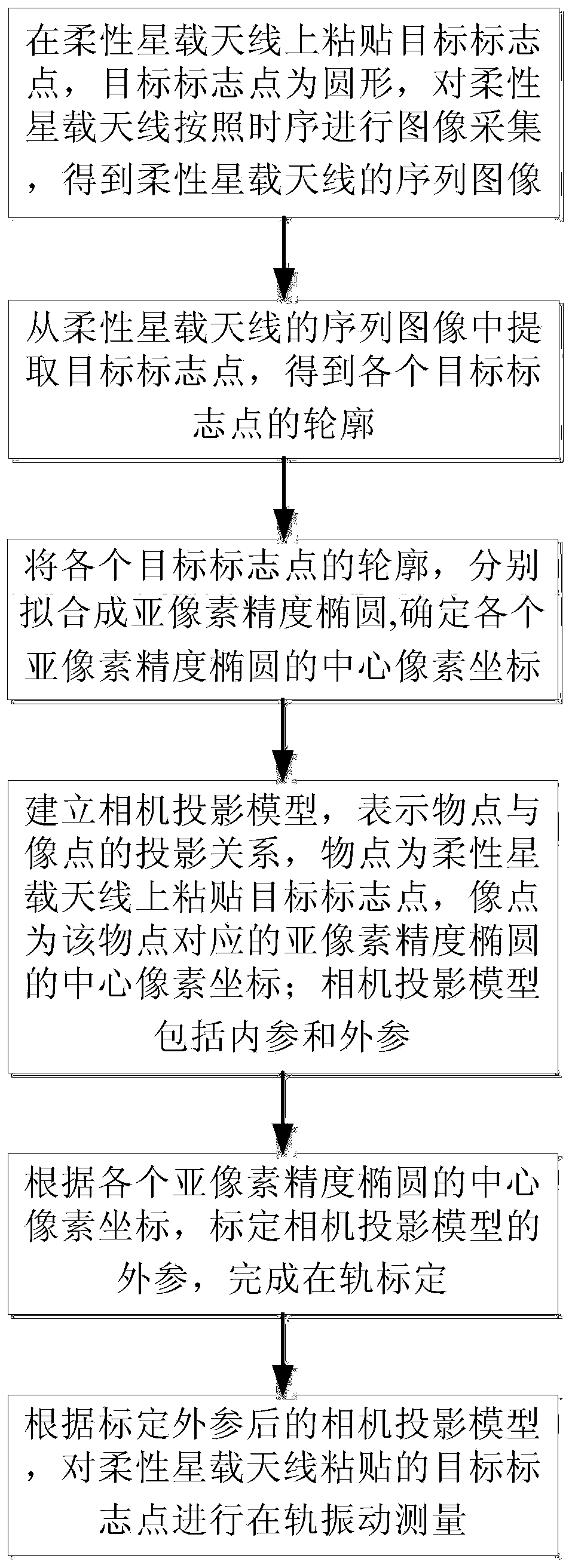
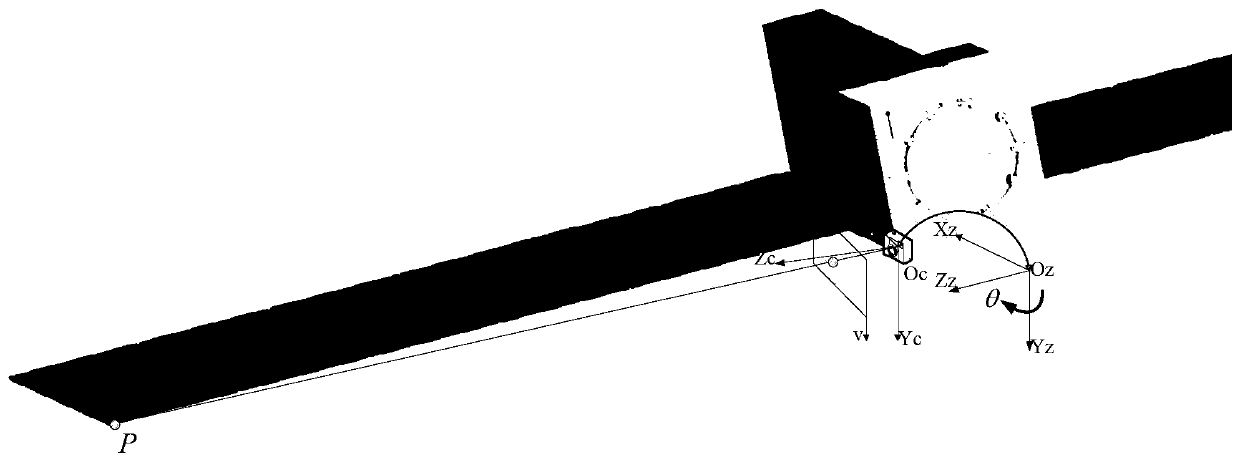
ActiveCN110047110AHas a non-destructive structure under testDoes not interfere with functional featuresImage enhancementImage analysisVibration measurementDynamic models
The invention discloses a flexible satellite-borne antenna on-orbit vibration measurement method based on a sequence image, and the method comprises the steps: pasting a target mark point on a flexible satellite-borne antenna, carrying out the image collection according to the time sequence, and obtaining the sequence image of the flexible satellite-borne antenna; extracting target mark points from the sequence image of the flexible satellite-borne antenna to obtain the contour of each target mark point; fitting the contour of each target mark point into a sub-pixel precision ellipse, and determining the central pixel coordinate of each sub-pixel precision ellipse; establishing a camera projection model; according to the central pixel coordinates of each sub-pixel precision ellipse, calibrating the external parameters of the camera projection model to complete on-orbit calibration; and carrying out on-orbit vibration measurement on the target mark point pasted by the flexible satellite-borne antenna according to the camera projection model after the external parameters are calibrated. The measurement result provides input for antenna surface type fine tuning, vibration suppression,dynamic model on-orbit correction and load-to-ground imaging compensation, and meanwhile provides measurement and image information for satellite on-orbit fault diagnosis and on-orbit health monitoring.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
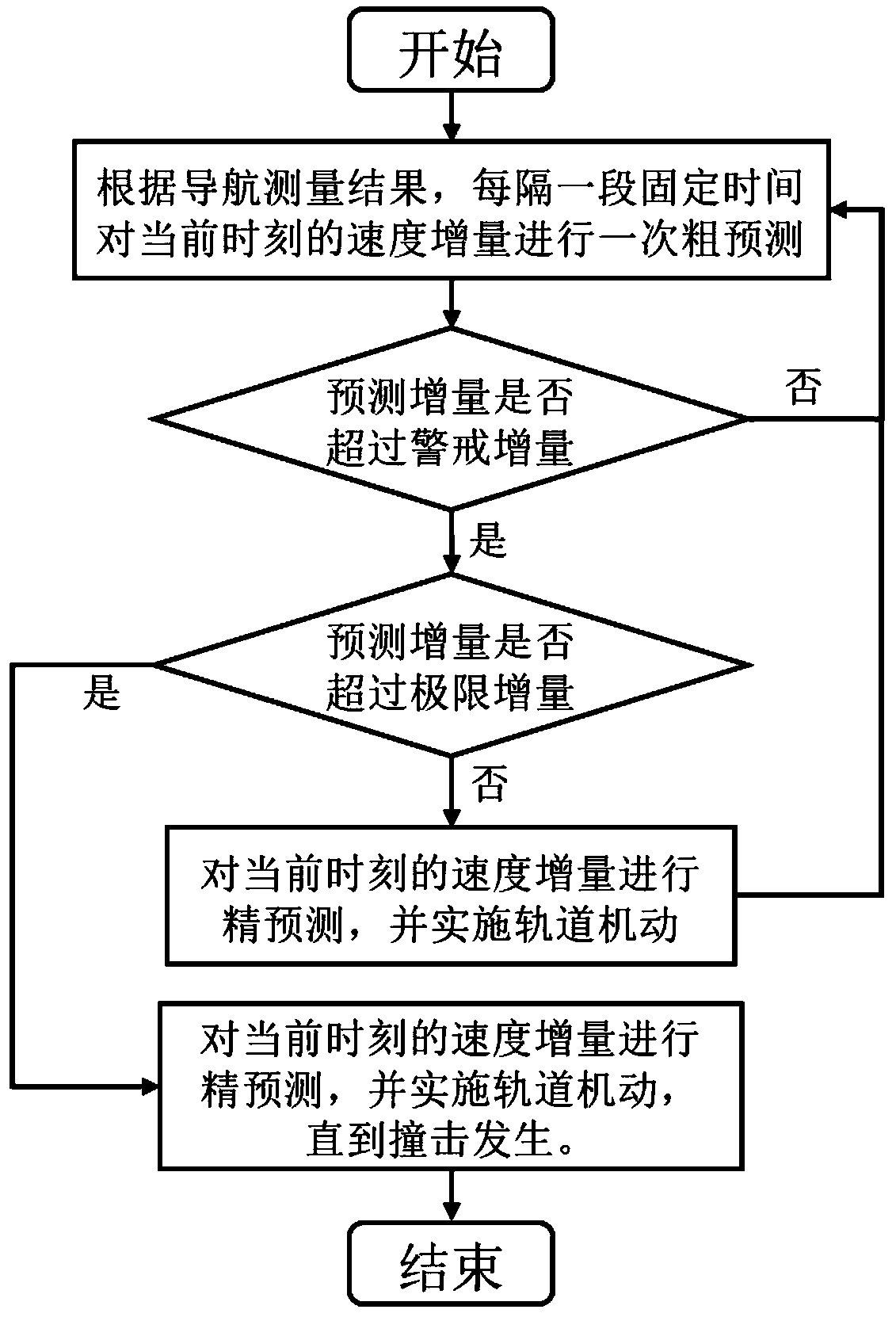
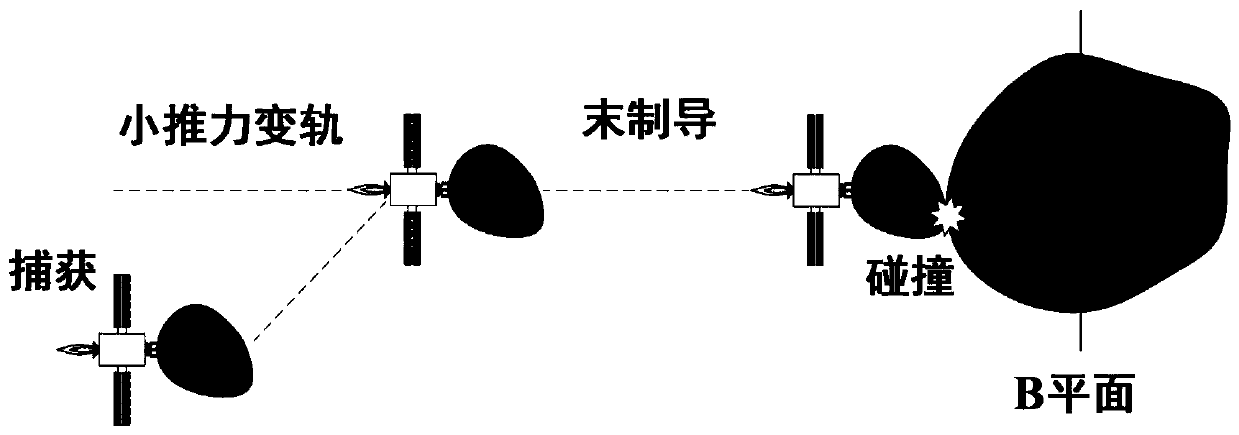
Small celestial body high-speed impact terminal guidance method based on speed increment corridor
ActiveCN110329547AImprove Guidance AccuracyHigh impact accuracyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOn boardCelestial body
The invention discloses a small celestial body high-speed impact terminal guidance method based on a speed increment corridor, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The methodaims at the problem of low high-speed impact terminal guidance accuracy of a big-quality impactor, and a terminal guidance process is designed into multiple times of orbit correction maneuvering of aprediction-correction form. The implementation method of the method comprises the following steps that: an on-board computer carries out coarse prediction for one time on the speed increment of a current moment in every one fixed time interval according to a navigation measurement result, and determines the position of the prediction increment in the speed increment corridor; according to a coarseprediction result, an orbit maneuvering starting moment and starting frequency can be adaptively determined; and accurate prediction is carried out on the speed increment of the current moment, orbitmaneuvering is implemented, circular judgment is carried out until impact is finished, and the small celestial body high-speed impact terminal guidance based on the speed increment corridor is realized. The method has the following advantages that the method is high in impact accuracy (1); the method is low in sensitivity of impact accuracy for system noise (2); and the method exhibits universality for a high-speed impact task under different conditions (3).
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
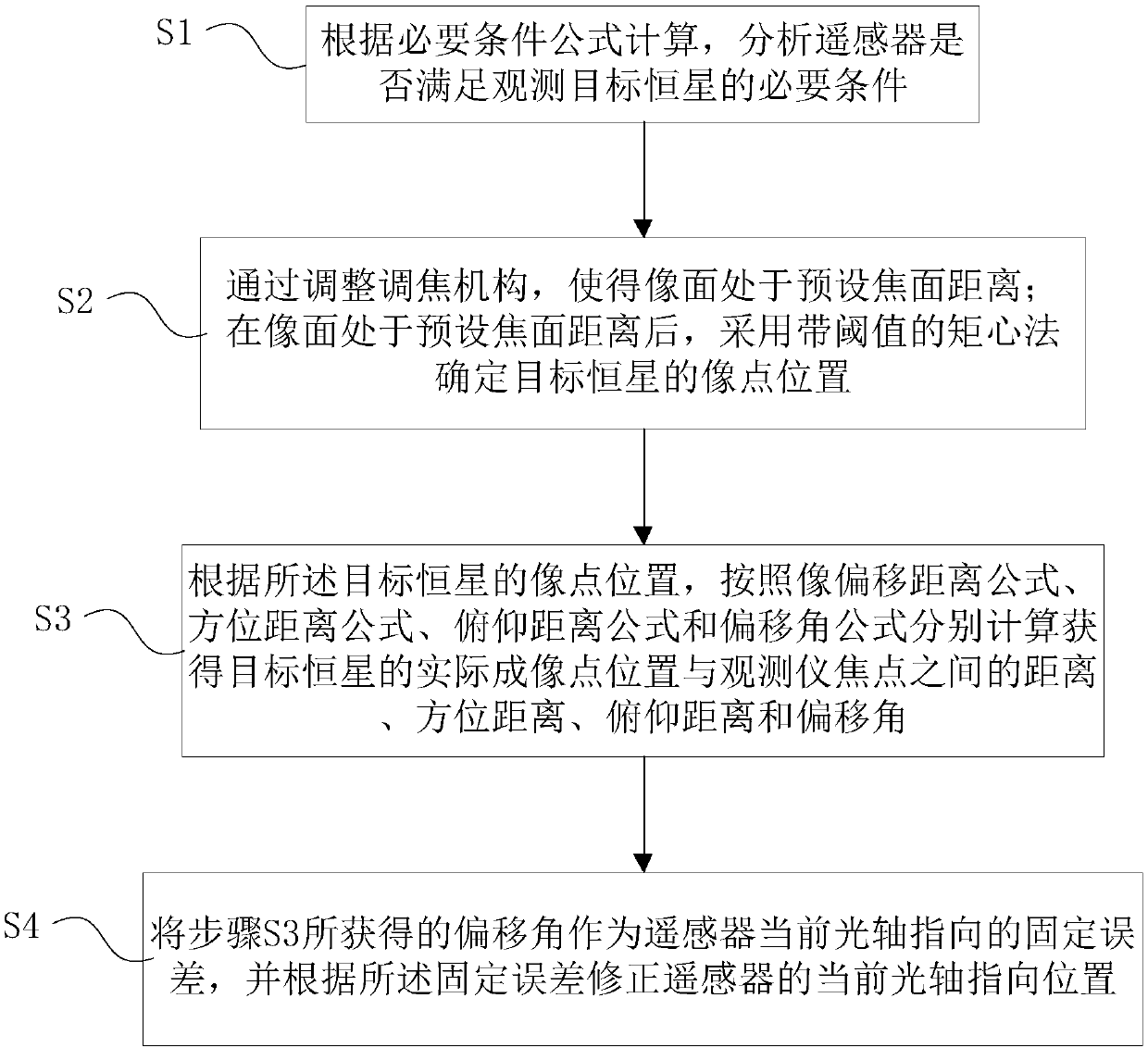
On-orbit correction method for optical axis pointing accuracy of remote sensor
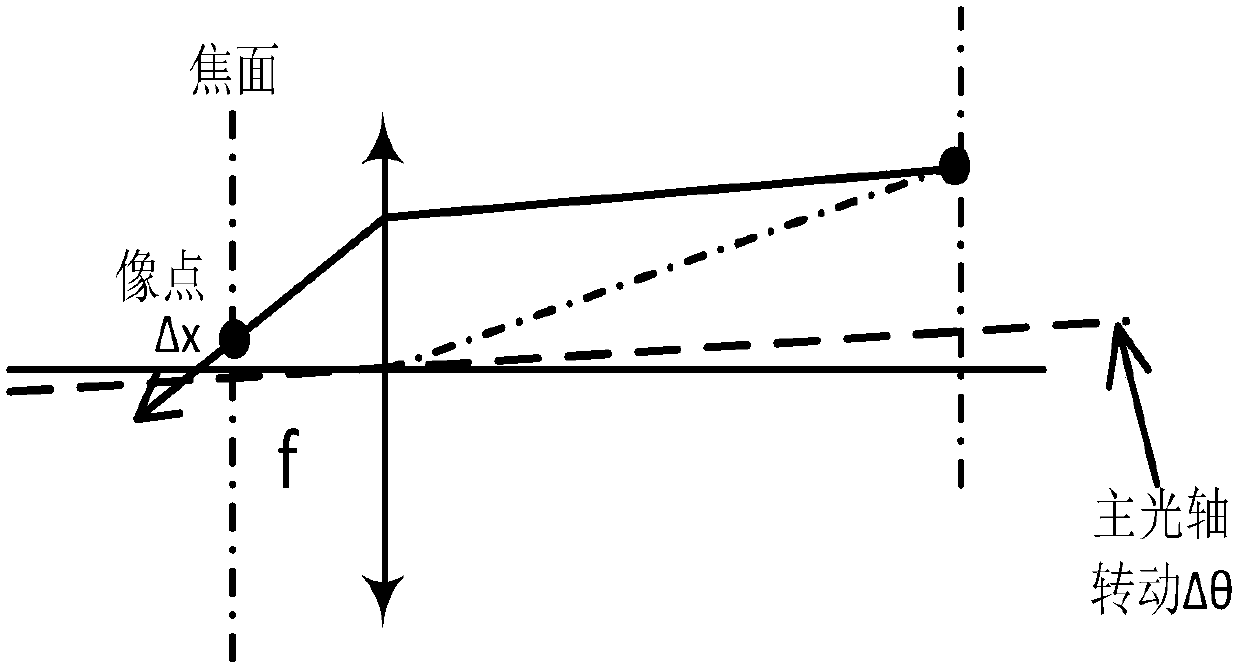
ActiveCN111220178AImproved optical axis pointing accuracySatisfy the accuracy requirements of inversionMeasurement devicesOptical axisOrbit correction
The embodiment of the invention discloses an on-orbit correction method for the optical axis pointing accuracy of a remote sensor. The method comprises the following steps: calculating and analyzing whether a remote sensor meets a necessary condition for observing a target fixed star according to a necessary condition formula; arranging an image plane at a preset focal plane distance by adjustinga focusing mechanism; after the image plane is located at the preset focal plane distance, determining the image point position of the target fixed star by adopting a moment center method with a threshold value; according to the image point position of the target fixed star, calculating a distance, an azimuth distance, a pitch distance and an offset angle between the actual imaging point positionof the target fixed star and the focus of the observer respectively based on an image offset distance formula, an azimuth distance formula, a pitch distance formula and an offset angle formula; withthe obtained deviation angle as a fixed error of the current optical axis pointing of the remote sensor, correcting the current optical axis pointing position of the remote sensor according to the fixed error. The method can correct the optical axis pointing in orbit, thereby effectively improving the optical axis pointing precision of the remote sensor.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
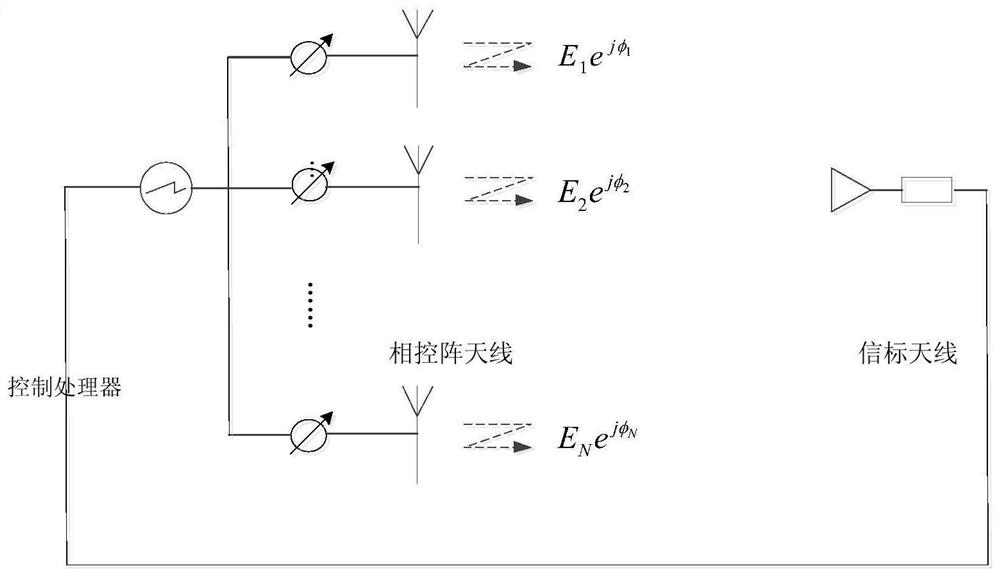
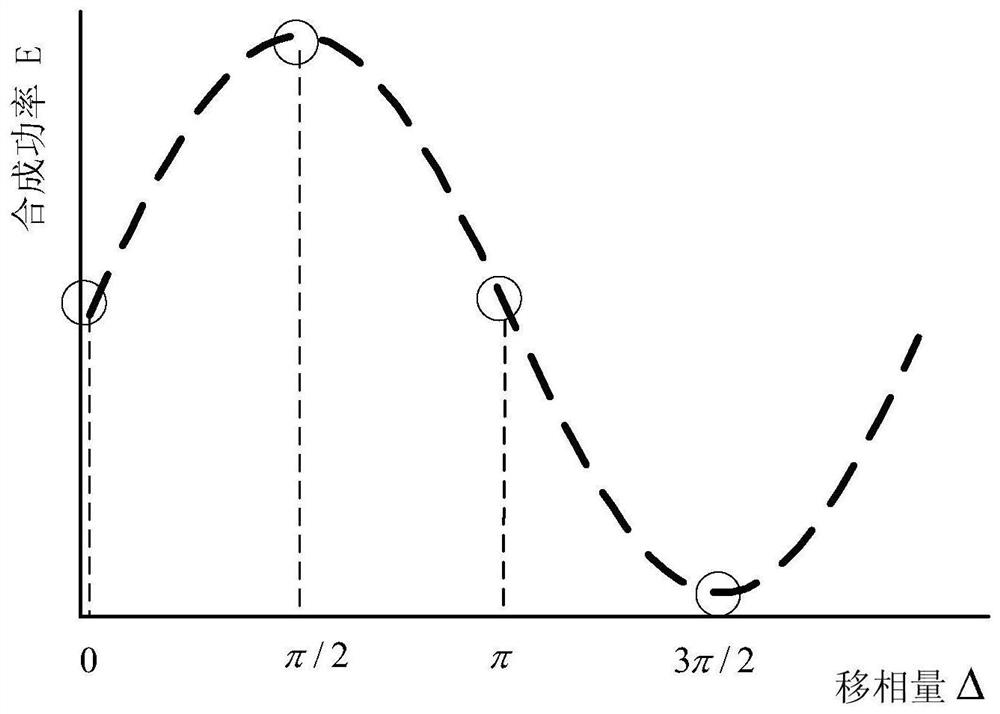
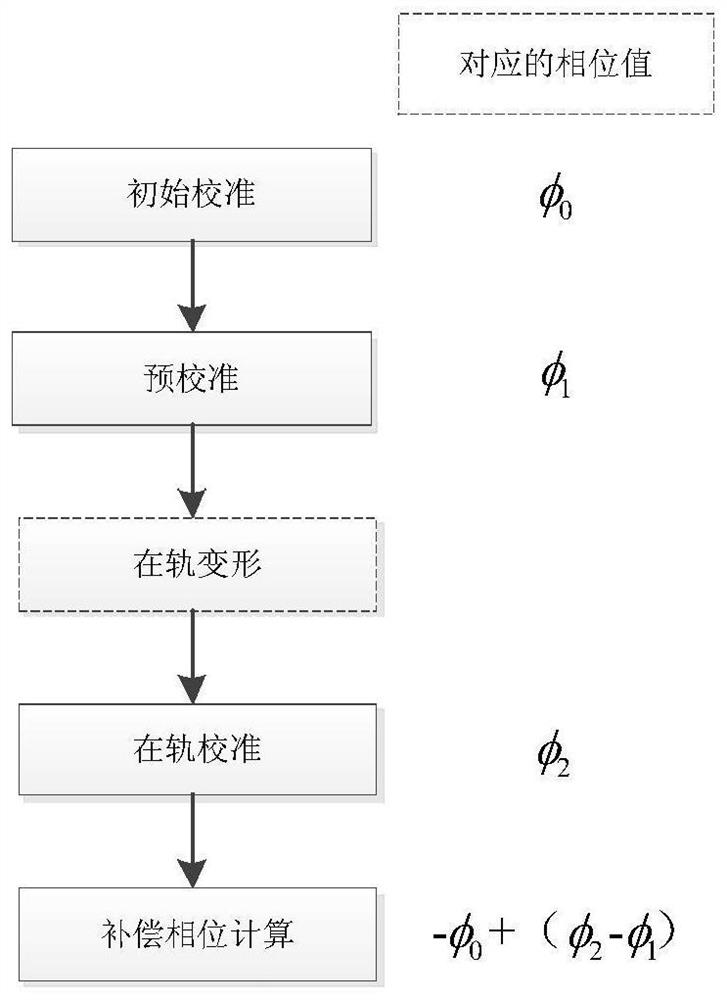
On-orbit correction and deformation evaluation method for phased-array antenna
PendingCN113934965ALoad cost reductionRealize antenna electrical performance correctionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringComputational physics
The invention relates to an on-orbit correction and deformation evaluation method for a phased-array antenna. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out ground structure and amplitude-phase measurement on an integrated link of a beacon, an array plane and a channel of the active phased-array antenna; then obtaining on-orbit compensation phases of all channels through calculation on the basis of ground amplitude-phase measurement data, and on-orbit correction of the electrical performance of the phased-array antenna is completed; secondly, according to the phase change value of each channel, obtaining the physical deformation length from the array antenna beacon to the position of each array plane unit; comparing and calculating with the measured data of the ground structure of the array antenna, and predicting the possible position coordinates of each unit of the array plane after in-orbit deformation; and finally, attributing the array surface deformation on-orbit evaluation to the optimization problem of the array surface unit position, constructing a deformation optimization model and optimization constraint conditions to update the array element position, solving the final array element position coordinate on the basis of multiple iterative optimization, and realizing the on-orbit profile change evaluation.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Medication maneuvering time selecting method for deep space detector approaching orbit
InactiveCN101462597BMeet the requirements of brake implementationGuaranteed normal consumptionArtificial satellitesNavigation by astronomical meansAviationSpace probe
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
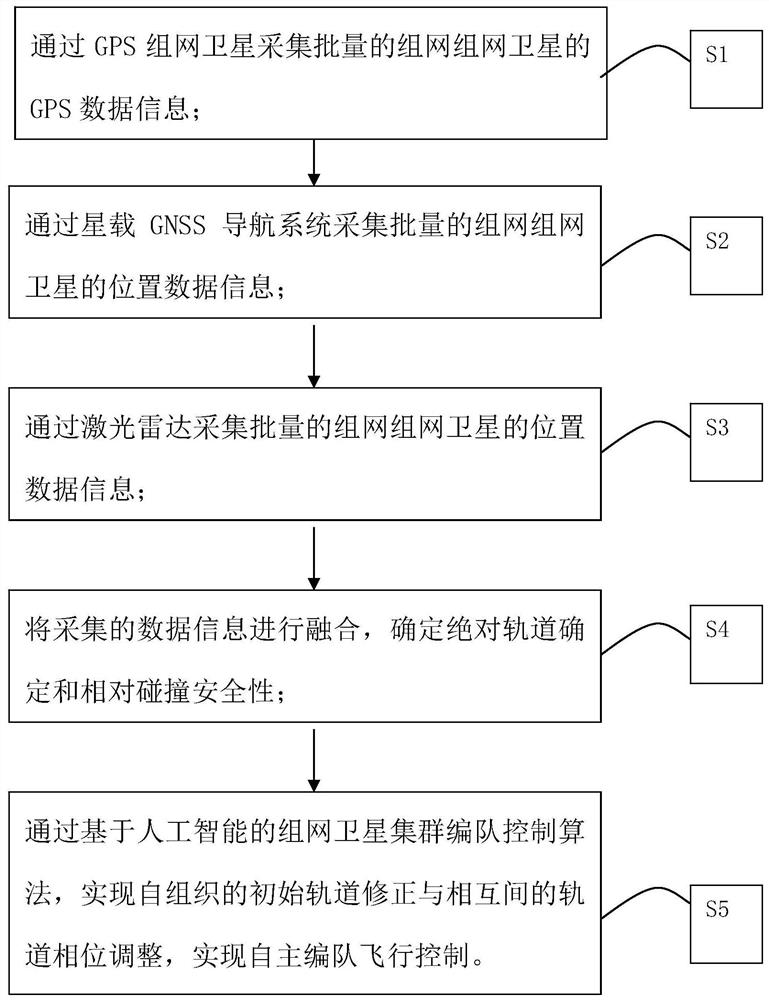
Autonomous formation flight control method for networking satellites in batch at initial orbit injection stage
InactiveCN112484735ARealize flight controlNo risk of collisionInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by terrestrial meansOrbit correctionOrbit phasing
The invention relates to an autonomous formation flight control method for networking satellites, in particular to an autonomous formation flight control method for networking satellites in batch at the initial orbit injection stage, which is suitable for formation flight of networking satellites in batch at the initial orbit injection stage. According to the method, a GPS+GNSS+laser radar fusionpositioning scheme is adopted, and absolute orbit determination and relative collision safety determination are achieved; and a decentralized regional self-organized communication network is adopted for information exchange, and self-organized initial orbit correction and mutual orbit phase adjustment are achieved through a networking satellite cluster formation control algorithm based on artificial intelligence. Due to the adoption of the technical scheme, the control method disclosed by the invention can ensure that the dense satellite groups are not collided at the initial stage of orbit injection. The star group automatically corrects the initial orbit deviation and gets close to the standard orbit. Self-organized orbit phase adjustment is carried out to change into a sequential and ordered flight queue, so that ground measurement and control tracking control is facilitated.
Owner:苏州泰富晶宇科技有限公司
Satellite star sensor pointing on-orbit thermal deformation correction system
InactiveCN111380567AImprove pointing accuracyEasy to implementMeasurement devicesPlanar antennasThermal deformation
The invention provides an on-orbit correction system for pointing thermal deformation of a satellite star sensor. The on-orbit correction system comprises a symmetrically designed large planar antennaload, a temperature sensor, the star sensor and ground high-precision angle measurement equipment; the star sensor is installed in the center of the symmetrically-designed large planar antenna load,and the temperature sensor is installed in the middle of the symmetrically-designed large planar antenna load. During the power-up test of the ground large-scale planar antenna load, the real-time deformation data pointed by the star sensor and measured by the ground high-precision angle measuring equipment is collected; and the temperature sensor collects temperature change data of the ground large planar antenna in a load power-up period, and corrects the on-orbit star sensor pointing direction according to the relationship between the real-time deformation data of the star sensor pointing direction and the temperature change data of the temperature sensor. The system has the advantages of being simple in implementation system and capable of achieving on-orbit real-time correction.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Scroll compressor with improved rotation prevention mechanism
ActiveUS8308461B2Reduce noiseImprove compression performanceEngine of arcuate-engagement typeOscillating piston enginesEngineeringOrbit correction
To provide a scroll compressor capable of reducing a noise occurring in a pin-and-ring type self rotation preventing mechanism and improving compression performance. In a scroll compressor comprising: a fixed scroll member and a revolving scroll member; a driven crank mechanism for driving the revolving scroll member to revolutionary turn; and a pin-and-ring type self rotation preventing mechanism provided in plural places for preventing self rotation of a revolving scroll member, at least one of the self rotation preventing pin, the self rotation preventing ring and the self rotation preventing ring hole, which form the pin-and-ring type self rotation preventing mechanism, is provided with an orbit correction part for reducing a maximum displacement R in a direction of self rotation of the revolving scroll member to smooth a change of an orbit of the revolving scroll member in changing a pin and a ring in a section of prevention of self rotation by means of a corresponding pin and ring part.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
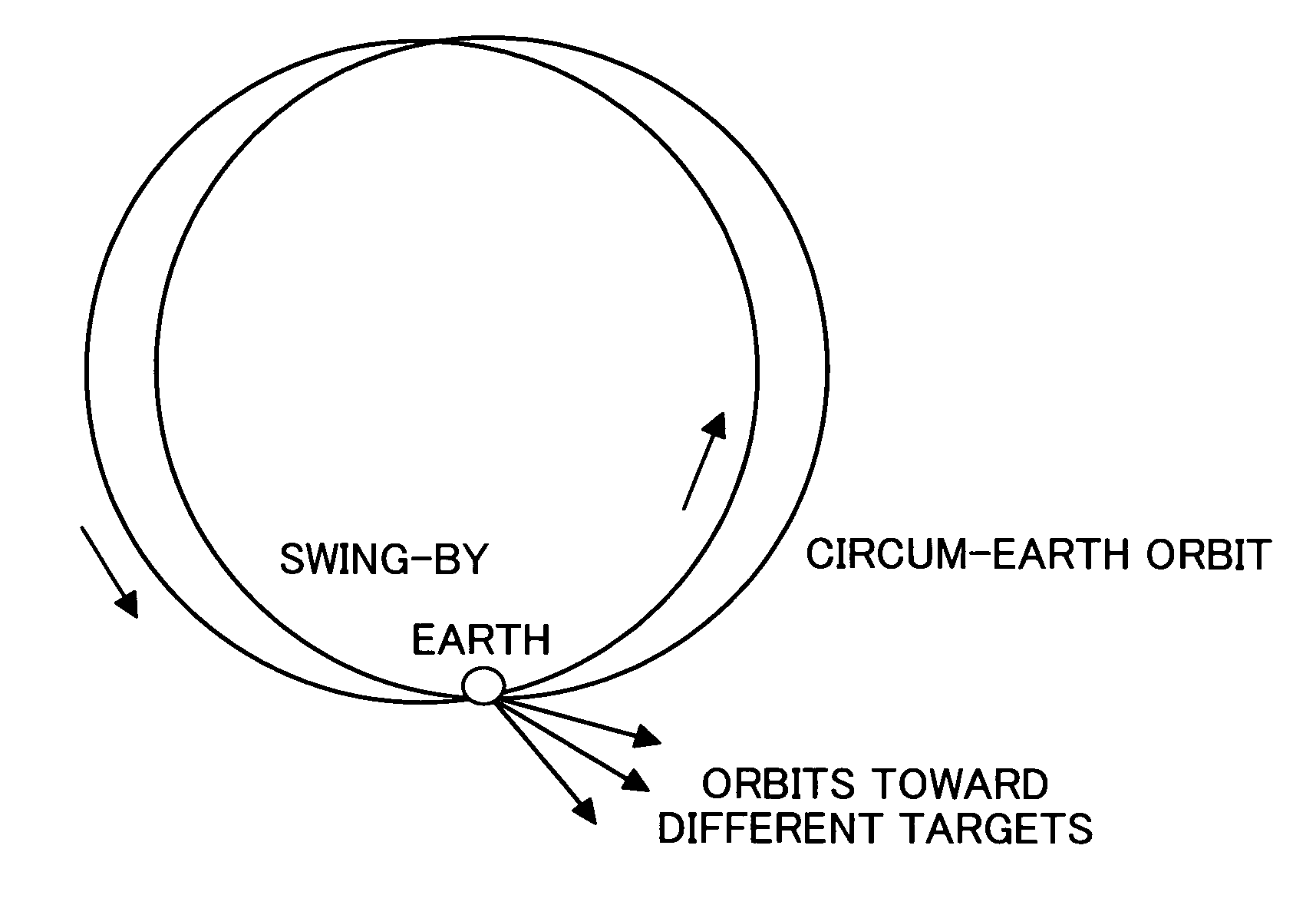
Method of injecting plurality of spacecraft into different orbits individually
InactiveUS7747361B2Wide applicationLaunch systemsDigital data processing detailsAccelerometerSufficient time
In a method for injecting a plurality of spacecraft into different circum-earth or interplanetary orbits individually in a single launch, a plurality of spacecraft coupled to an assist module are injected into an interplanetary orbit having a periodicity synchronous with the earth's revolution period. Then, in a maneuver allowing the assist module to re-counter with and pass near to the earth (Earth swing-by), the assist module appropriately performs an orbital change maneuver and a separation maneuver for each of the spacecraft in a sequential order. Through these maneuvers, a closest-approach point to the earth is changed for each of the spacecraft so as to drastically change a subsequent orbital element for each of the spacecraft. The assist module takes a sufficient time to determine a target orbit for each of the spacecraft with a high degree of accuracy until a half month to several days before a closest-approach time in the Earth swing-by. Based on the determined orbit, the assist module makes an orbit correction of about several m / sec in a sequential order, and then separates the spacecraft therefrom in a sequential order. In this process, an inertia navigation is performed based on an accelerometer mounted in the assist module and information about attitude.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Method and system for on-orbit correction of orbit control strategy based on thruster bias estimation
ActiveCN109649692BExtended life on orbitReduce consumptionCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention discloses an orbit control strategy on-orbit correction method and system based on thruster deviation estimation. The method includes: separately obtaining the positions of the center of mass of the entire satellite, the first orbital thruster and the second orbital thruster relative to the layout system information; and, obtain the thrust vector directions of the first orbital control thruster and the second orbital control thruster; perform on-orbit identification, and determine the generation of the first orbital control thruster and the second orbital control thruster according to the on-orbit identification results The torque; construct the disturbance torque evaluation function; solve the disturbance torque evaluation function, determine the minimum value of the disturbance torque evaluation function, and calculate the jet pulse width; perform orbit control according to the calculated jet pulse width. The invention adopts the energy optimal principle to update the orbit control thrust distribution strategy on the orbit, and realizes the minimization of the orbit control interference.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Low-orbit space target orbit correction method and device and electronic equipment
ActiveCN114132531AHigh precisionCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationOrbit predictionOrbit correction
The invention discloses a low-orbit space target orbit correction method, a low-orbit space target orbit correction device and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a plurality of reference targets which have similar orbits with a main target in a low-orbit space; wherein the similar orbit is determined according to the orbit characteristics of the main target in the low-orbit space; calculating a first track along-track direction error of each reference target; according to the first track along-track direction error of each reference target, calculating a second track along-track direction error of the main target corresponding to the reference target; calculating a final track direction error of the main target according to the second track direction error of the main target corresponding to each reference target; and track correction is carried out on the main target according to the final track along-track direction error of the main target. According to the method, the orbit correction of the main target is realized by utilizing the plurality of reference targets with the similar orbits to the main target, the orbit prediction precision is improved, and the method can be applied to the aspects of spacecraft high-confidence collision early warning, reentry target guide correction and the like.
Owner:中国人民解放军32035部队
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com