Application of algal toxin-degrading enzymes in inhibiting cyanobacteria and degrading algal toxins
A technology for degrading algal toxins and algal toxins, applied in the directions of enzymes, enzymes, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of degradation, cumbersome operation, strong killing ability of oxidants, etc., achieve efficient inhibition or killing, and solve the problems of water pollution. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0048] This preparation example is used to illustrate the preparation method of cyanotoxin degrading enzyme I.
[0049] The MlrA coding sequence (Accession Number: AF411068.1) was constructed on the prokaryotic expression vector pMAL-C2X (inserted between the BamHI and HindIII restriction sites) to obtain the expression vector pMAL-C2X-MlrA expressing MlrA. For the specific construction method, see " Chapter 1 and Chapter 15 of Molecular Cloning Laboratory Guide, Third Edition (J. Sambrook et al., Science Press, 2002).
[0050] Take the prepared competent DH5α out of the refrigerator and freeze-thaw on ice, add 10 μL of the ligation product (expression vector pMAL-C2X-MlrA), reset the EP tube in ice for 30 minutes, and then put it in a 42°C Place in a water bath for 90 seconds, then put it in ice and let it stand for 5 minutes. Add 600 μL of LB medium to each tube, incubate in a shaker at 37°C and 180 rpm for 70 min; then centrifuge at 4000 rpm, take 600 μL of supernatant, mi...
preparation example 2
[0058] This preparation example is used to illustrate the preparation method of algae toxin degrading enzyme II.
[0059] The MlrA coding sequence (Accession Number: AB468058.1) was constructed on the prokaryotic expression vector pET22b (inserted between the BamHI and HindIII restriction sites) to obtain the expression vector pET22b-MlrA expressing MlrA. For the specific construction method, see "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" "Third Edition (J. Sambrook et al., Science Press, 2002) Chapters 1 and 15.
[0060] Take the prepared competent DH5α out of the refrigerator and put it on ice to freeze-thaw, add 10 μL of the ligation product (expression vector pET22b-MlrA), reset the EP tube in ice for 30 minutes, and then put it in a water bath at 42°C , placed for 90s, then placed in ice, and allowed to stand for 5min. Add 600 μL of LB medium to each tube, incubate in a shaker at 37°C and 180 rpm for 70 min; then centrifuge at 4000 rpm, take 600 μL of supernatant, mix the prec...
Embodiment 1
[0069] Experiments on Inhibition of Growth of Cyanobacteria and Degradation of Algal Toxin by Algal Toxin Degrading Enzyme
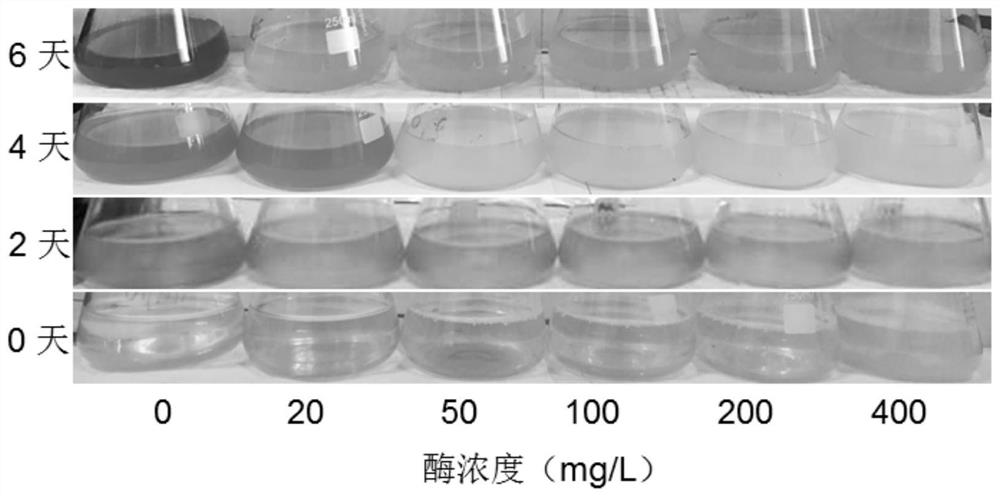
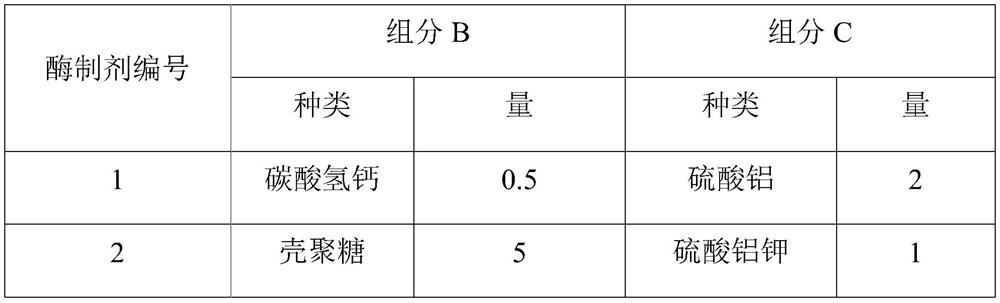
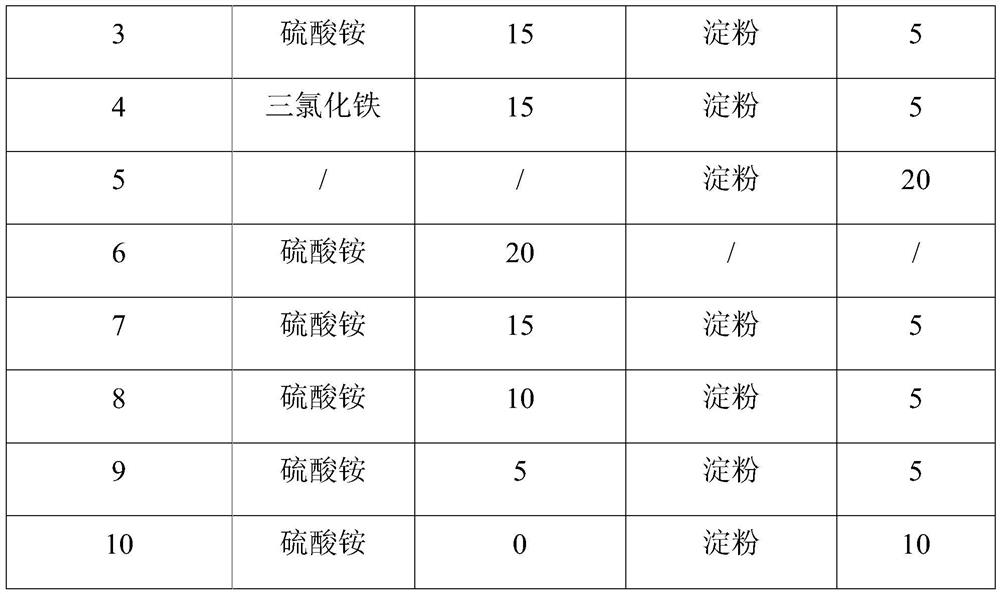
[0070] (1) Add the enzyme preparation to 100mL containing the lower initial algae cell concentration (about 1.0×10 5 algae cells / mL), including Synechocystis 6803, Microcystis aeruginosa 905, and Microcystis aeruginosa 912, were treated continuously for 2, 4, and 6 days to observe and detect the inhibition of different algae. Among them, the inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa 905 by enzyme preparation 3 with different concentrations is shown in figure 1 And table 3, from which it can be seen that the enzyme preparation has a good inhibitory effect on cyanobacteria when it contains 50-400mg in 1L algae liquid. In addition, measure the OD of the algae liquor (enzyme dosage is 200mg) after continuous treatment 6 days 730 value, and start with "(initial OD 730 Value - OD after treatment 730 value) / initial OD 730 The calculation result of "value × 100%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com