Robust adaptive beamforming method based on spatial smoothing
An adaptive beam, spatial smoothing technology, applied in the direction of spatial transmit diversity, diversity/multi-antenna systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of beamformer performance degradation, expected signal cancellation, covariance matrix rank loss, etc. Optimum performance, the effect of reducing coherence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
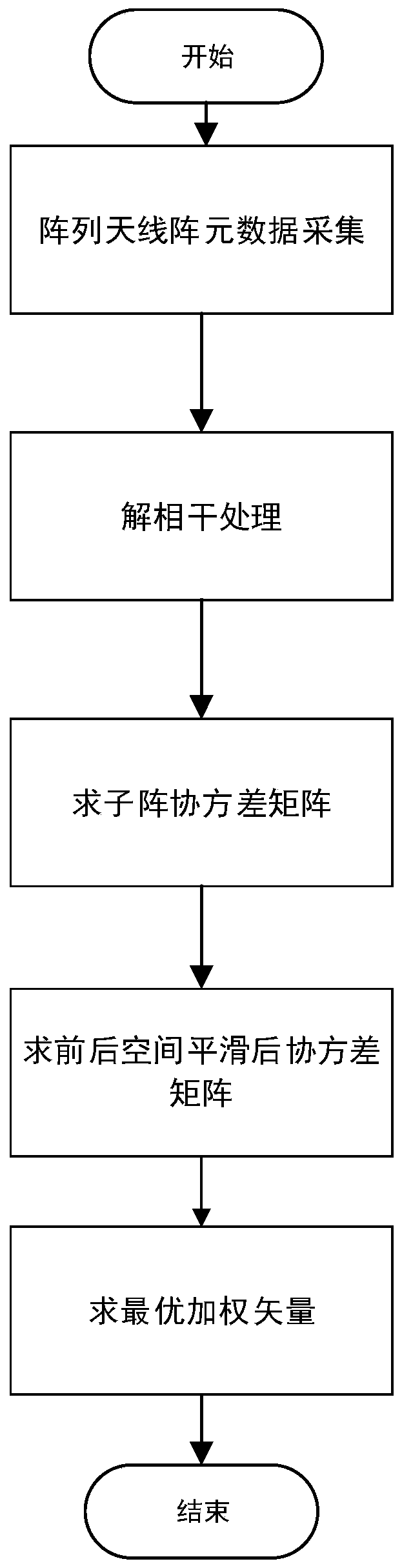
[0040] Specific implementation mode one: a robust adaptive beamforming method based on spatial smoothing, characterized in that the implementation process of the method is:
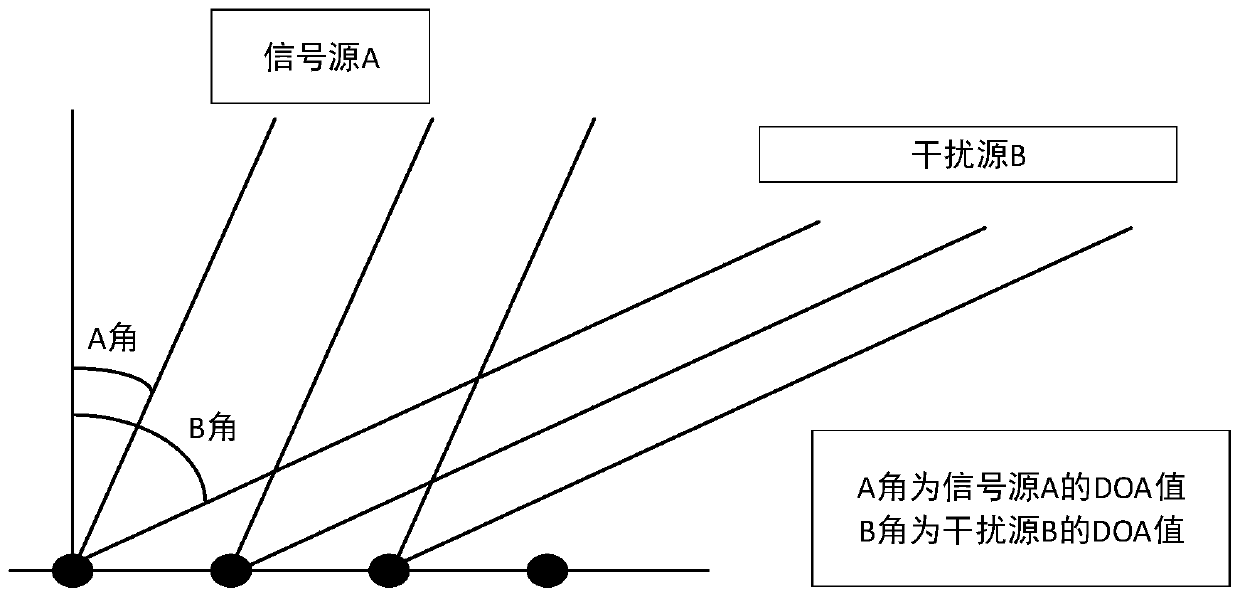
[0041] Step 1. Data collection: collect the array antenna element signal, which contains the target signal (expected signal) s in the signal x(n) 0 (n), coherent interference signal s k (n) and uncorrelated interfering signal s P (n),
[0042]
[0043] Among them, a(θ k ) and a(θ p ) are respectively the complex envelope of the kth coherent interference signal and the pth uncorrelated interference signal;
[0044] n in brackets is the snapshot number of the signal, a(θ 0 ) is the steering vector of the array element signal, n(n) represents noise, and n outside the brackets represents noise;
[0045] Step 2, decoherence processing:
[0046] At present, the array covariance matrix is used to perform decoherence processing,
[0047]
[0048] A c and A u is an array flow matrix.
[0049]Sin...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0063] Embodiment 2: After step 4 is executed, if the data of the sub-arrays are arranged from the back to the front, this is the backward spatial smoothing algorithm, and the combination of the two is the forward and backward spatial smoothing algorithm. After smoothing, the data covariance matrix will be restored to full rank, so the weight vector can be obtained, and then processed by Capon beamforming algorithm. Others are the same as step 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0064] Specific implementation mode three: in step five, the process of seeking the optimal weight vector:
[0065] The adaptive beamforming constraints are expressed as:
[0066]
[0067] The optimal weight vector for beamforming obtained by the forward spatial smoothing algorithm:
[0068] Others are the same as step 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com