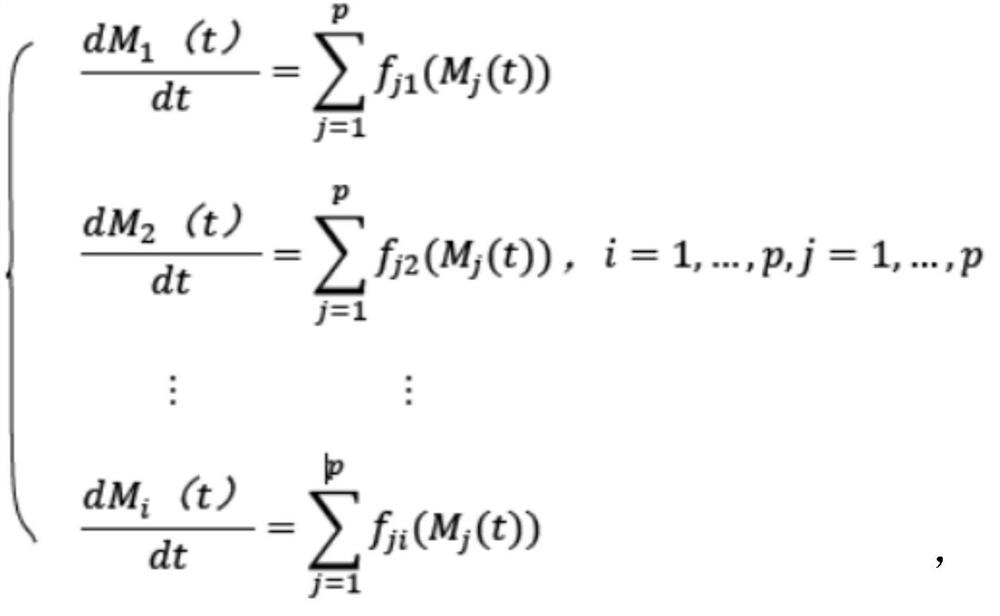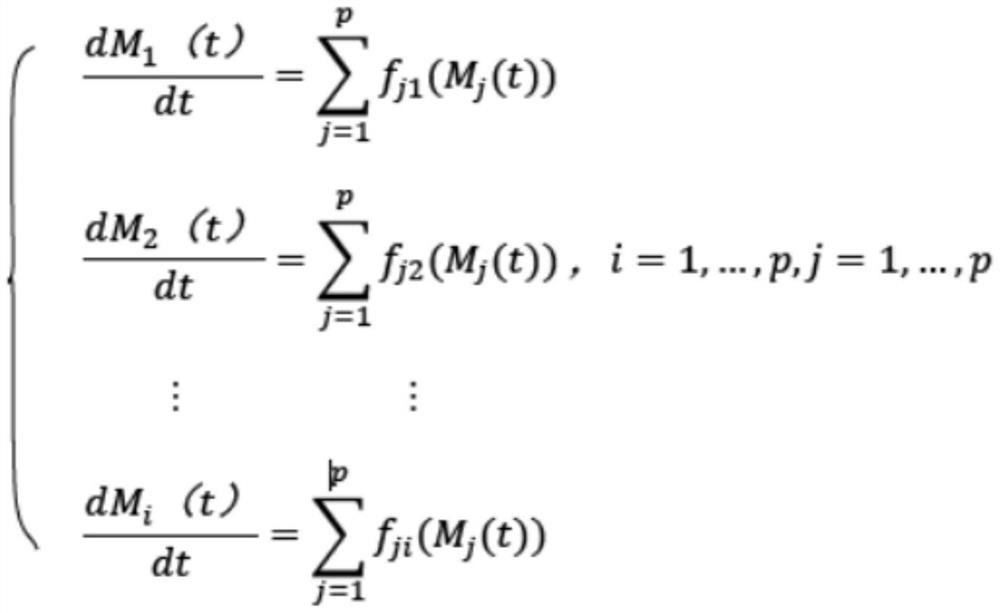The excavation method of the dry willow -resistant salt hub gene
A salt-tolerance and pivot technology, which is applied in the field of excavation of salt-tolerance pivot genes of Salix chinensis, can solve the problem of inability to accurately find salt-tolerance genes, and achieve the effect of good breeding and improving breeding efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] Embodiments of the present invention are described below through specific examples, and those skilled in the art can easily understand other advantages and effects of the present invention from the content disclosed in this specification. The present invention can also be implemented or applied through other different specific implementation modes, and various modifications or changes can be made to the details in this specification based on different viewpoints and applications without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
[0046] The invention provides a method for excavating the salt-tolerant pivotal gene of willow, comprising:
[0047] S1: The offspring F is obtained by crossing the salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive Salix willow 1 group.
[0048] In this example, salt-sensitive dry willow is a dry willow that can only grow normally in an environment with a salt content below 2‰. Salt-tolerant dry willow is a dry willow that can grow in an environment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com