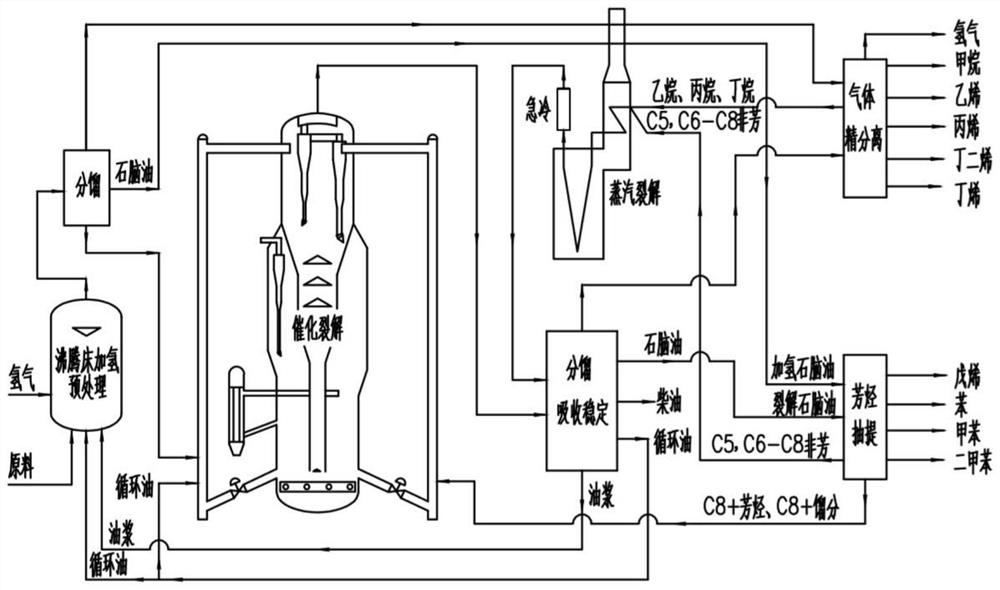
A processing technology for producing olefins and aromatics from inferior heavy oil
A low-quality heavy oil and processing technology technology is applied in the processing technology of aromatic hydrocarbons and the field of producing olefins from low-quality heavy oil. , the effect of improving the reaction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
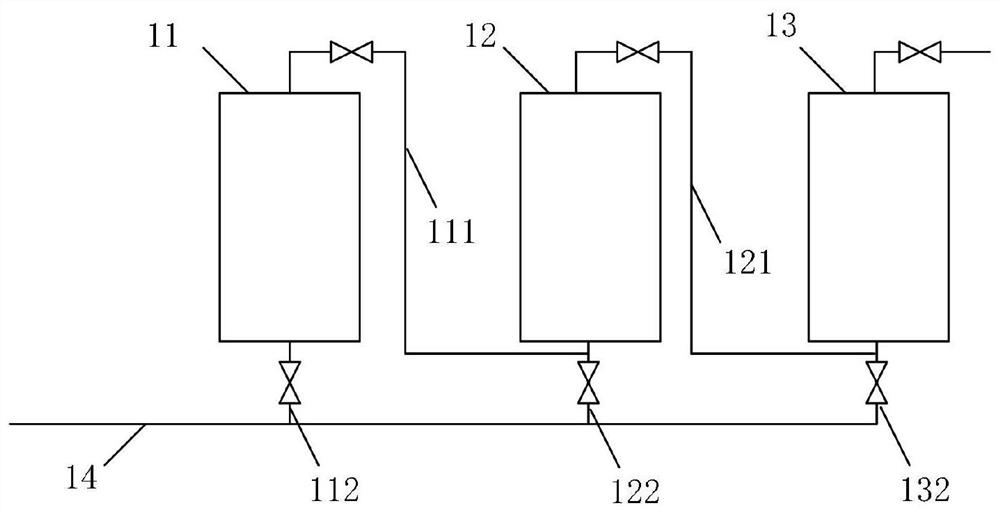
[0074] When the content of metal impurities in inferior heavy oil is ≥400ppm and the content of Kang’s residual carbon is >20%, the combined hydrogenation technology of 3 ebullating beds connected in series is used for raw material pretreatment, see the attached figure 2 , the whole process is described as follows:
[0075] S1: Pump low-quality heavy oil into the hydrogenation reaction unit through the main pipeline 14, open the first feed pipe 112, the first series pipe 111, and the second series pipe 121 in sequence, and simultaneously close the second feed pipe 122 and the third feed pipe. The pipe 132 is pumped into the third ebullating bed 11, the first ebullating bed 12, and the second ebullating bed 13 in sequence, and is respectively mixed with hydrogen to carry out reaction hydrogenation; the catalyst is a Ni-Mo-based microsphere catalyst, and the reaction conditions are: Pressure 16MPa, inlet temperature 250℃, volume space velocity 0.9h -1 , Reaction temperature 39...
Embodiment 2
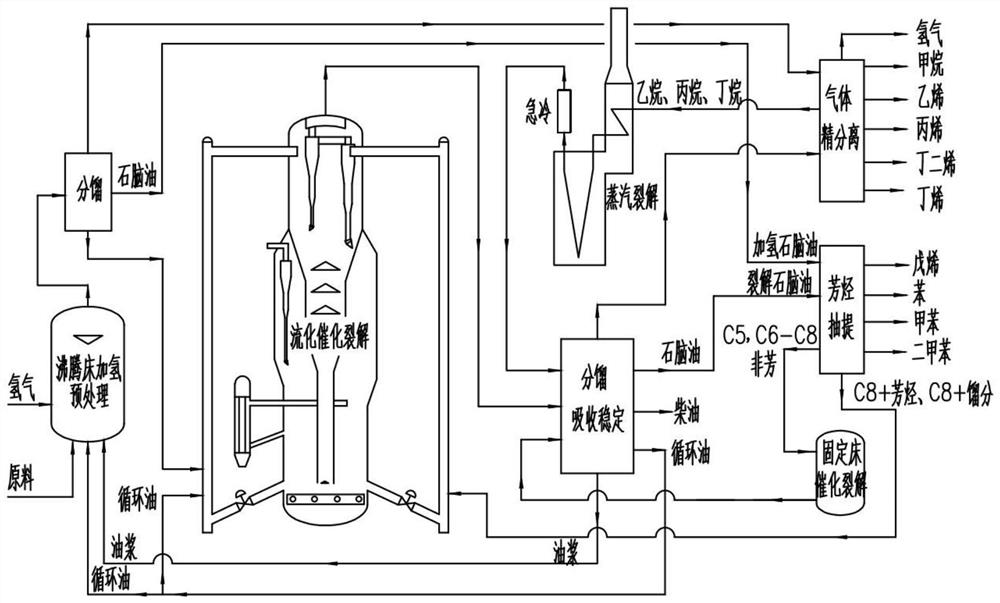
[0084] Such as image 3 As shown, in this example, on the basis of Example 1, the non-aromatic components of naphtha extracted from aromatics are subjected to catalytic cracking in a fixed-bed reactor to produce olefins.
[0085] When 15% of the inferior heavy oil is less than the content of Kang’s residual carbon and less than 20%, and the content of metal impurities is less than 150ppm, the combined hydrogenation technology of two ebullating beds in series is used for raw material pretreatment. The whole process is described as follows:
[0086] S1: Pump the inferior heavy oil into the hydrogenation reaction unit through the main pipeline 14, close the first feed pipe 112, the first series pipe 111, and the third feed pipe 132, and the inferior heavy oil passes through the second feed pipe 122, the second series pipe Pipe 121 is then pumped into the first ebullating bed 12 and the second ebullating bed 13 in sequence, and then mixed with hydrogen for reaction and hydrogenati...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Such as Figure 4 As shown, on the basis of Example 1, this example is combined with a butene aromatization reactor. This process belongs to a local process optimization under the conditions that both the processing capacity of butene and the market of aromatics are applicable. Does not affect the scope of protection of this patent.
[0097] When the content of Kang’s residual carbon in inferior heavy oil is less than 15%, and the content of metal impurities is less than 150ppm, a combined hydrogenation technology with a series of fluidized beds is used for raw material pretreatment. The whole process is described as follows:
[0098] S1: The inferior heavy oil is pumped into the second hydrogenation reaction zone 10 of the hydrogenation reaction unit through the main pipeline 14, the first feed pipe 112, the second feed pipe 122, and the second series pipe 121 are closed, and the inferior heavy oil passes through the third feed The pipe 132 enters the second ebullatin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com