Optimized Maltose Promoter Mutants and Their Applications
A promoter and maltose technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low expression of PsacB promoter, increased production cost, toxicity and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] 3. Preparation and transformation of DNA:
[0024] DNA was isolated from E. coli and B. subtilis or from agarose gels using DNA preparation kits from Tiangen or Omega according to the manufacturer's instructions. Standard molecular techniques were used in all examples. E. coli was transformed using plasmid DNA as described by Chung C.T. et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 1989, 21722175. According to a modified "Paris method" (Harwood C.R. Molecular Biological Methods for Bacillus, 1990, John Wiley & Sons Ltd., England), plasmid DNA or DNA fragments were used to transform Bacillus subtilis.
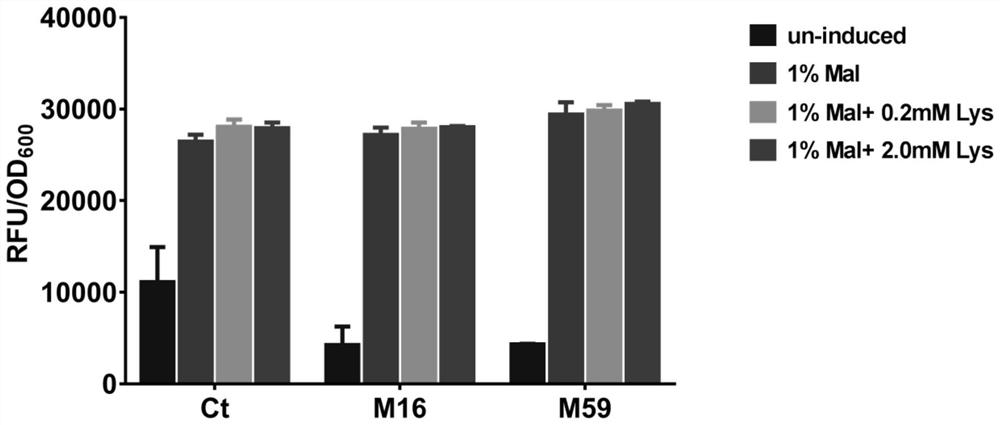
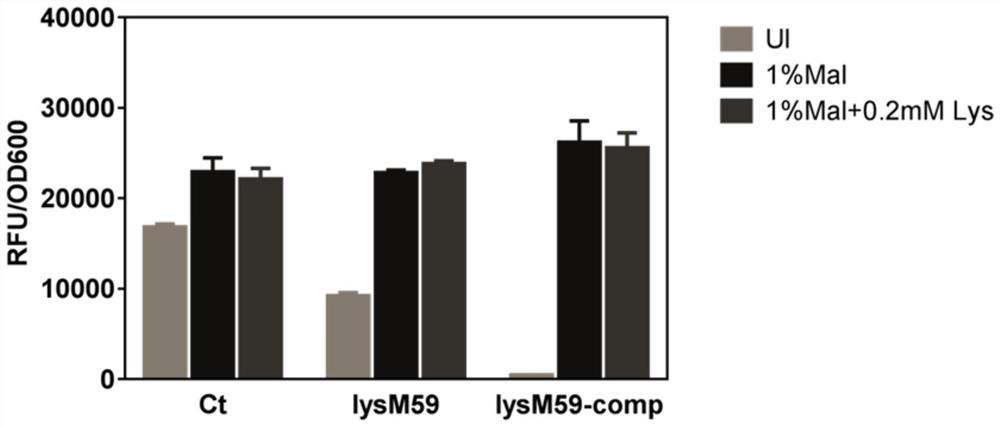
[0025] 4. Determination of green fluorescent protein fluorescence intensity RFU:
[0026] Centrifuge at 4°C and 4000rpm for 10 minutes to collect the bacterial cells cultured to an OD600 of about 0.6-0.8, wash the bacterial cells twice with pre-cooled PBS solution, and transfer 150 μL to a 96-well black-bottomed microtiter plate (Corning , USA), placed in a microplate Spectra...
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Mutant Construction of Carbon Metabolism Responsive Elements in Maltose Promoter
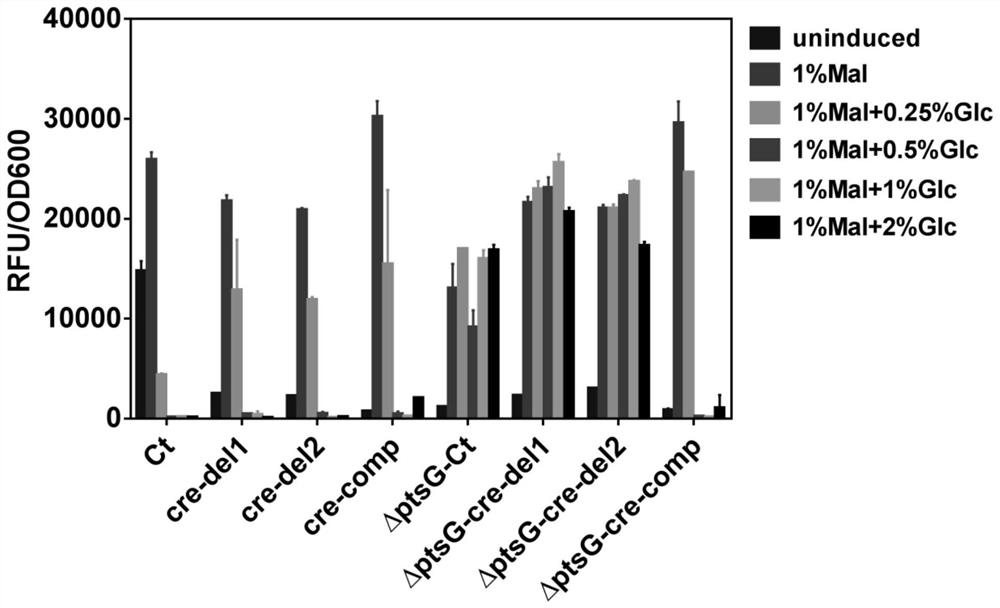
[0036] Due to the existence of the CCR effect in the maltose metabolic pathway of Bacillus subtilis, the application of the expression system based on the maltose promoter PmalA in the fermentation containing glucose carbon source is restricted. In order to relieve the CCR effect, the carbon metabolism response element cre (cataboliteresponse element, cre) in the maltose promoter PmalA responsible for interacting with the carbon metabolism repressor protein ccpA can be mutated to partially relieve the CCR effect. The construction method is as follows. The GFP fluorescent protein gene was inserted into the pMATE vector through the NdeI / BamHI restriction site to construct the pMATE-GFP vector. Furthermore, using the pMATE-GFP vector as a template, cre-del1.for / cre-del1.rev and cre-del2.for / cre-del2.rev as primers, the 13bp cre element sequence in the Bacillus subtilis maltose prom...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 Construction of Bacillus subtilis ptsG knockout strain
[0039] In addition, by knocking out the glucose transporter gene ptsG in Bacillus subtilis, the intracellular transport of glucose can be weakened to relieve the effect of CCR. The ptsG gene in the Bacillus subtilis 1A751 expression host strain was knocked out by using the AraR-based Bacillus subtilis traceless knockout technology, and the 1A751△ptsG genetically engineered strain was constructed. The wild-type maltose promoter expression vector pMATE-GFP and the carbon metabolism response element deletion mutants pMATE-cre-del1-GFP, pMATE-cre-del2-GFP and pMATE-cre-comp-GFP constructed above were transformed into 1A751△ptsG In the genetically engineered strains, induce culture at 37°C, 220rpm, 1% maltose and add glucose with gradient concentration (0.25-2%), then use a microplate reader to measure the fluorescence intensity of GFP, and evaluate the ability of knocking out the glucose transporter gene pts...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com