Method for separating microplastics in environmental soil or sediment based on combination of flotation and centrifugation
A technology for microplastics and sediments, applied in chemical instruments and methods, centrifuges, wet separation, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome and time-consuming extraction of microplastics, poor reliability, low efficiency, etc., to improve the enrichment and concentration capacity, The effect of low cost and little environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The present invention provides a method for separating microplastics in environmental soil or sediment based on the combination of flotation and centrifugation, comprising the following steps:
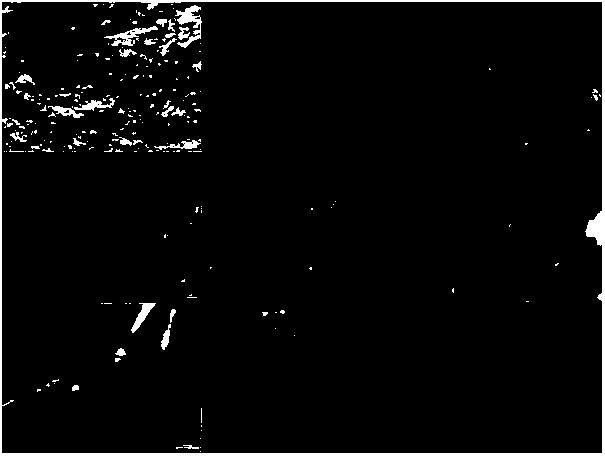
[0038] Step A Sampling: Naturally dry the soil or sediment samples collected in the field to constant weight; then slightly crush them with a mortar, crush the large particles, and filter them with 1mm and 5mm pore diameter stainless steel screens respectively. Microplastic particles of 1mm to 5mm and above 5mm are sorted out and stored, and the soil passed through a 1mm sieve is put into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask for subsequent operations.
[0039] Digestion before step B: add digestion solution in the 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, the digestion solution is 30% H 2 o 2 solution, the mass ratio of the digestion solution to the sample is 10:2 to 3, stirred with a glass rod until there is no hard lump of soil, left to stand at room temperature for digestion for 3 to 12 hours, and the di...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Soil samples collected from a farmland in Kaifeng City, Henan Province were selected to dry naturally; filtered through a stainless steel screen with a pore size of 1mm, 100g of the treated soil sample was mixed with 30 PE microplastic particles with a particle size of 0.2-1mm, and artificially The agitation method makes PE fully coated into the soil particles.
[0052] Add the treated soil sample into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, add the digestion solution, stir with a glass rod until there are no hard lumps of soil, and let it stand at room temperature for 12 hours for digestion.
[0053] Add the flotation solution to the sample that has been digested, stop adding the flotation solution when the flotation solution reaches two-thirds of the 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, and place the sample solution on the stirrer to stir for 10min and let it stand 5min.
[0054] When the sample solution can be clearly stratified, put the 250ml Erlenmeyer flask into a 1L beaker, and continue t...
Embodiment 3
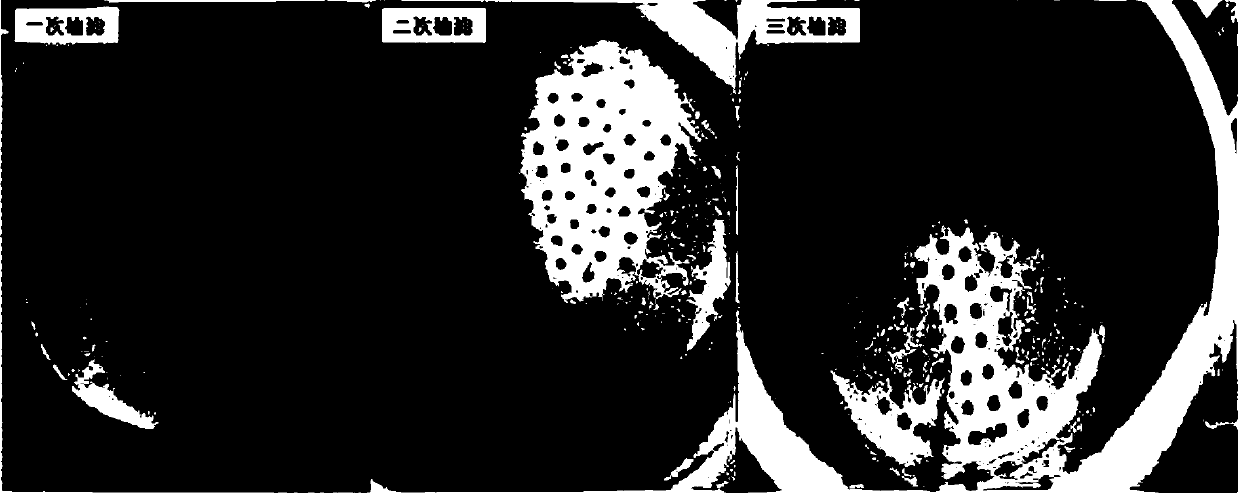
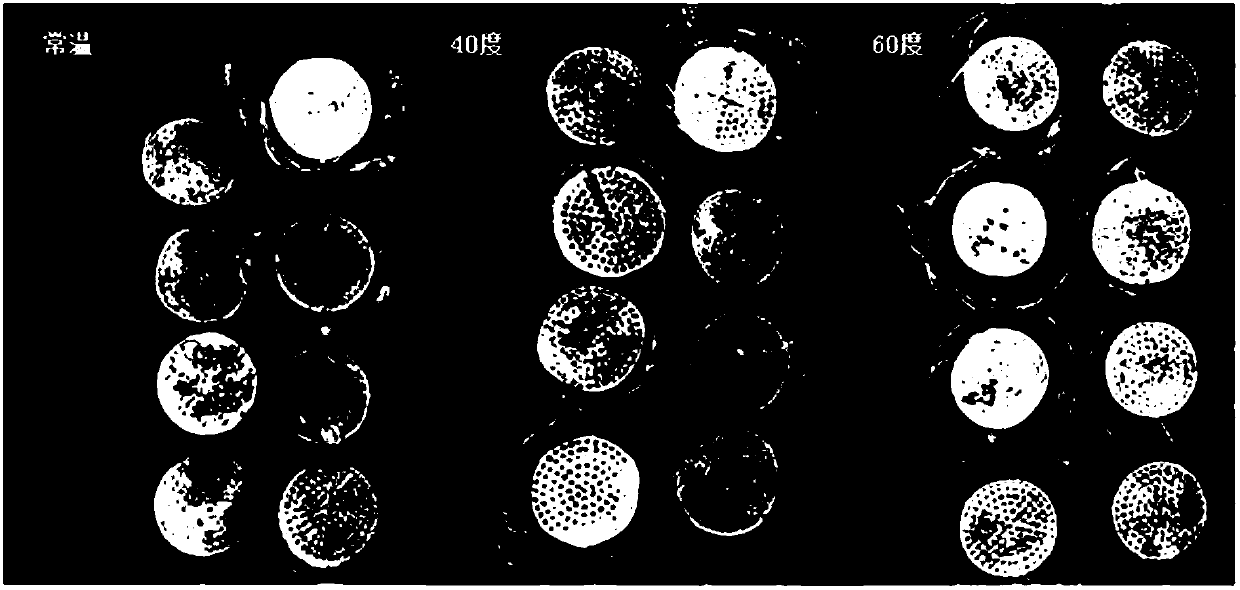
[0064] This embodiment is for the selection of the optimum digestion temperature for the sample soil. The basic steps are the same as in Example 2, except that three temperature control groups are set during the digestion step, which are respectively normal temperature, 40°C and 60°C, and are set at three temperatures respectively. Add the same volume of digestion solution to a beaker containing 25g soil samples at different temperatures, and compare the digestion effects of organic matter at different temperatures. The effect of the filter membrane after three flotation suction filtrations is shown image 3 shown, from image 3 It can be seen that after repeating the flotation and suction filtration three times, under the conditions of normal temperature and 60°C digestion temperature, the content of organic matter on the filter membrane is less, and the recovery rates under the three temperatures are all 100%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com