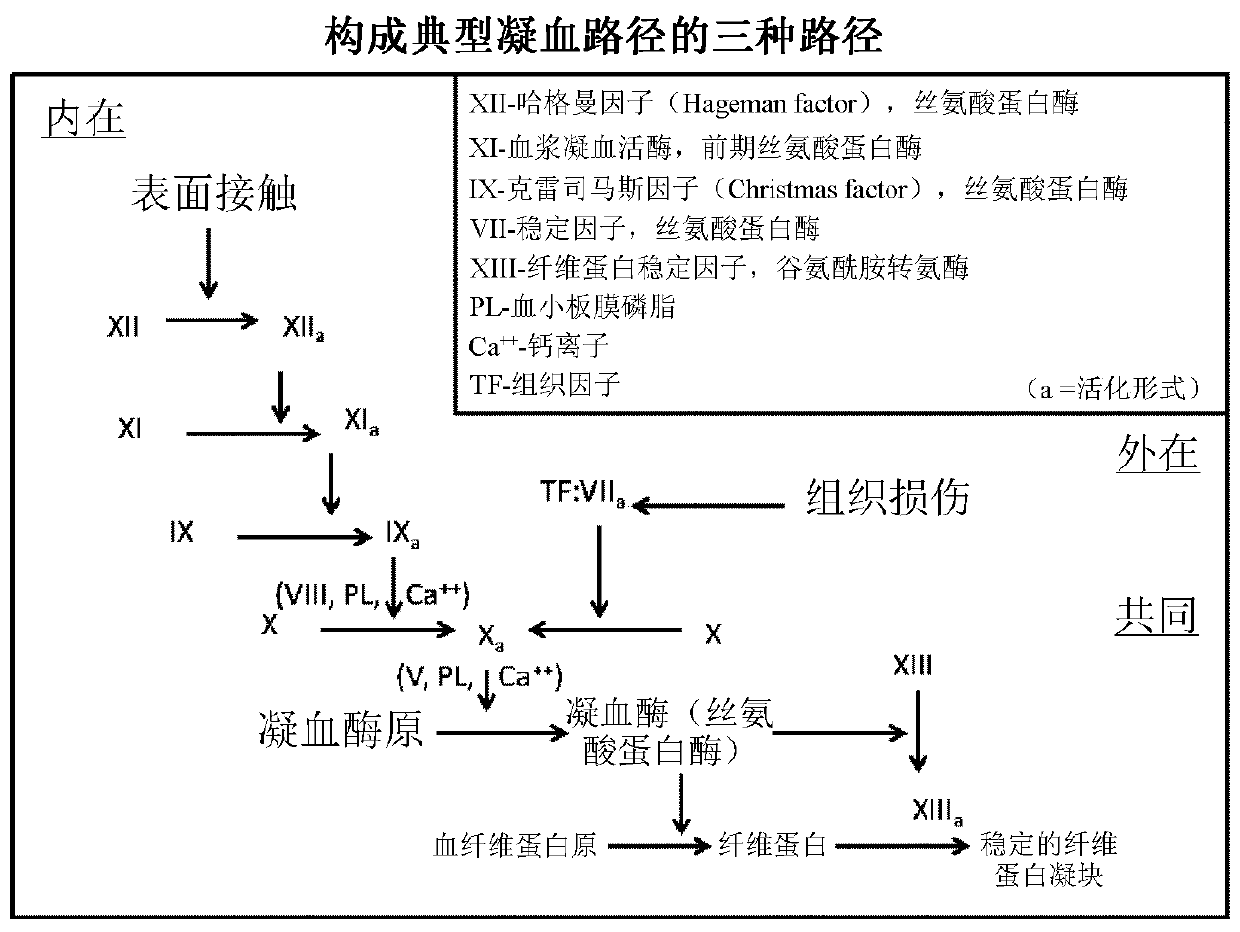
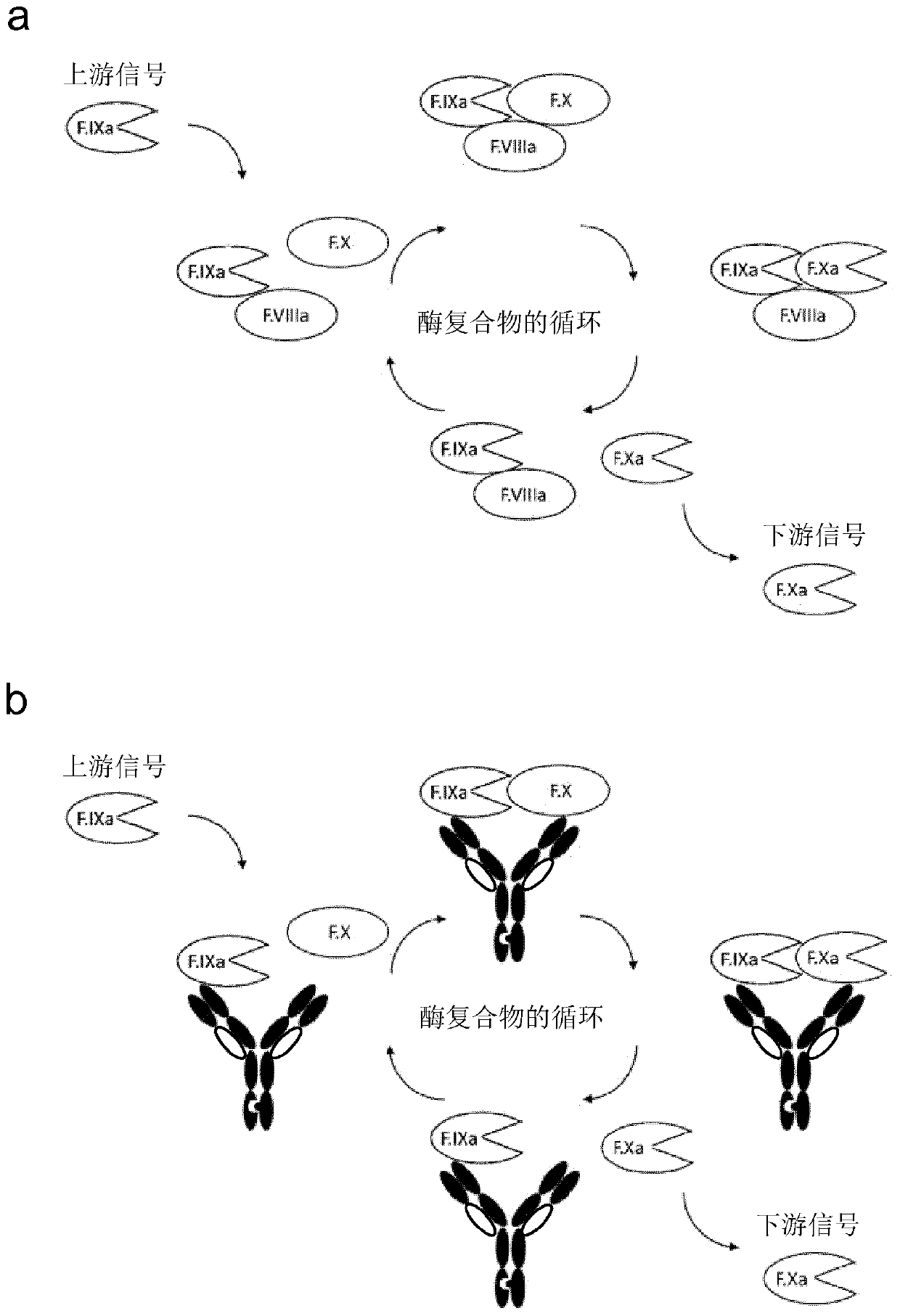
Bispecific antibodies for factor ix and factor x
A bispecific, antibody technology, applied in the field of bispecific antigen binding molecules, can solve problems such as increased patient deaths and safety issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0561] The following examples describe the generation, characterization and performance of anti-FIXa antibodies, anti-FX antibodies and bispecific antibodies generated from combinations of the FIXa-binding and FX-binding polypeptide arms of anti-FIXa and anti-FX antibodies, respectively. Using Kymouse TM (a transgenic mouse platform capable of producing antibodies with human variable domains) to produce antibodies. Antibodies from Kymouse have human variable domains and mouse constant domains generated from human v(d) and j fragments. Endogenous mouse variable genes have been silenced and represent only a small fraction of the antibody repertoire (less than 0.5% of all heavy chain variable regions are of mouse origin). The Kymouse system was described in Lee et al. 2014 [ 11 ], described in WO2011 / 004192, WO2011 / 158009 and WO2013 / 061098. This project employed the Kymouse HK strain in which the heavy chain locus and the light chain kappa locus were humanized, and the Kymouse...
example 1
[0562] Example 1. Production of Antibodies Against Factor IXa (FIXa)
[0563] Four Kymouse HK mice (male, 4 months old at the start of immunization) and four Kymouse HL mice (male, 3 months old at the start of immunization) were directed against human Factor IXa (Enzyme Research Laboratories , Inc.)) immunity.
[0564] Spleen tissue was collected from immunized mice, and splenocytes were suspended and sorted by FACS to isolate antigen-specific B cells. A total of 2,460 Factor IXa-specific B cells were sorted from 8 immunized animals. Coupled antibody heavy and light chain variable domain sequences are recovered from B cells by reverse transcription of RNA and PCR amplification of the variable regions.
[0565] Nucleic acid encoding the antibody was transfected into the human cell line Expi293F for expression, and the supernatant collected.
example 2
[0566] Example 2. Production of Factor IXa Antibodies (Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence) Screening
[0567] The HTRF assay was used to screen for anti-FIXa antibodies that bind to FIXa. FIXa and antibody were labeled with two different fluorophores (donor and acceptor). When the two entities are close enough to each other, excitation of the donor by the energy source triggers energy transfer towards the acceptor, which in turn emits a specific fluorescence at a given wavelength. Therefore, the binding of FIXa to its specific antibody can be detected by detection at the emission wavelength of the receptor.
[0568] Serial dilutions of the anti-human Factor IX reference antibody AbN and the CM7 isotype control antibody were prepared using Expi293 expression medium (Invitrogen). 5 μL of supernatant from each of the 2,460 antibody-secreting human cells generated in Example 1 was transferred to the assay plate. Transfer 5 μL of AbN and CM7 isotype control antibodies to e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com