Agaricus bisporus grading judgment method
A technology of Agaricus bisporus and mushroom, applied in image analysis, image data processing, instrument and other directions, can solve the problems of low efficiency and large error of Agaricus bisporus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
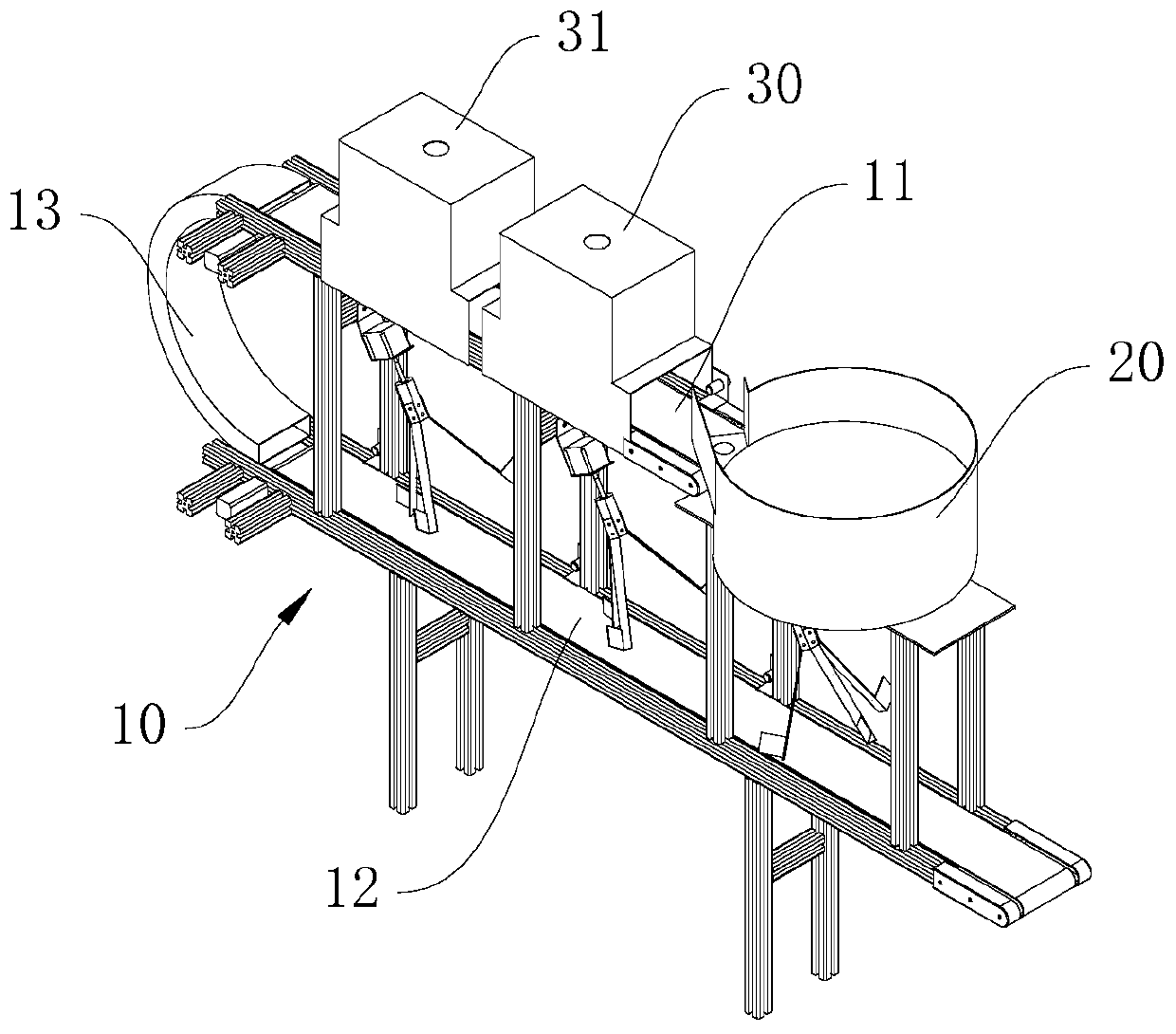
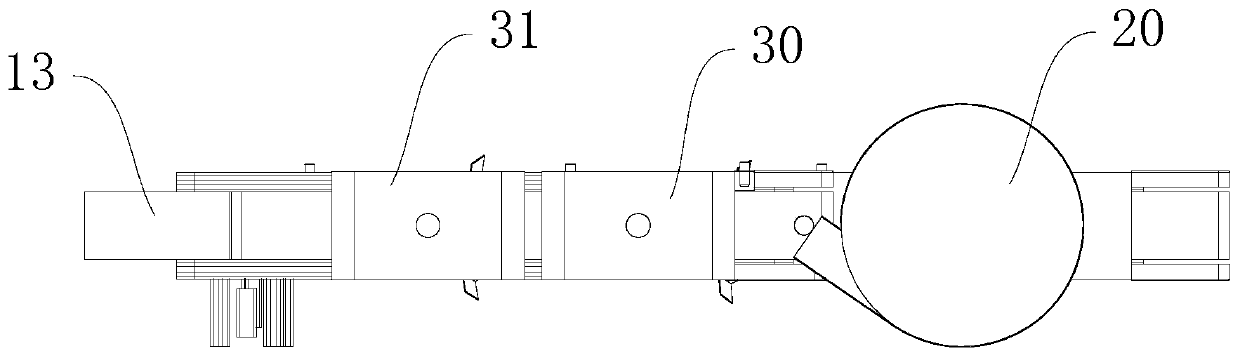
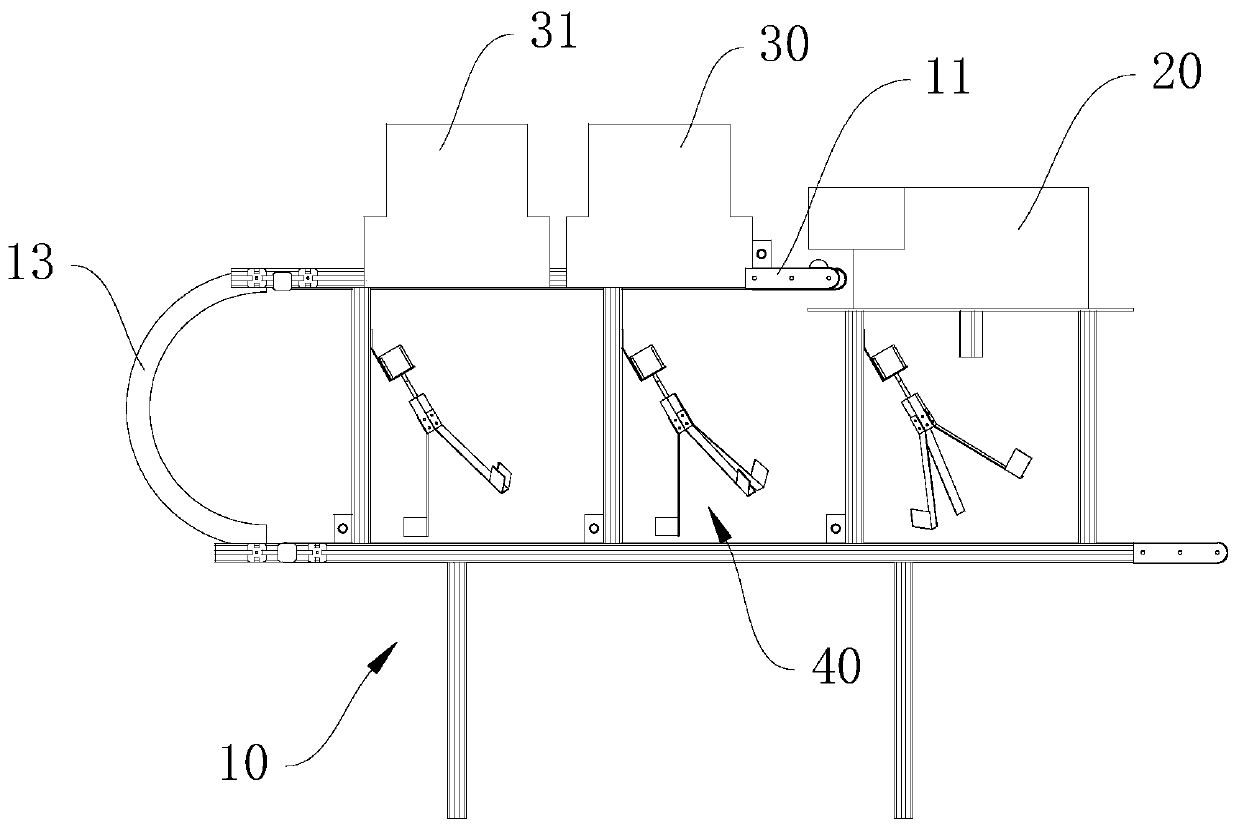
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] When making a specific judgment, the system uses the size of Agaricus bisporus as a characteristic parameter, and divides it into four grades: A grade, B grade, C grade and D grade.
[0070] Grading judgments include the following steps:
[0071] S1, acquiring mushroom image information through a camera;
[0072] S2, extract the region of interest: according to the shooting environment of the mushroom image, set the parameters and intercept the mushroom image with a single background color to obtain the image to be extracted; calculate the coordinate value of the upper left point of the minimum circumscribing rectangle of the mushroom outline, and the minimum circumscribing The width W and height H of the rectangle.
[0073] Specifically, in this embodiment, the camera resolution is 96 as an example. The mushroom image acquired by the system includes the conveyor belt and its edge. In order to accurately obtain the characteristic parameters of Agaricus bisporus, it is ...
Embodiment 2
[0089] The SURF (Speeded-up Robust Features) algorithm is an improved algorithm based on the SIFT (Scale-invariant feature transform) algorithm. It was proposed by Herbert Bay at the European International Conference on Computer Vision in 2006. The algorithm does not depend on pixel values and is occluded, angled etc. The shooting effect is less affected, and it has the characteristics of fast calculation speed and high stability. The SURF algorithm mainly includes two parts: feature point extraction and feature point description.
[0090] On the basis of Example 1, as Figure 14 with Figure 15 As shown, this embodiment also includes S41, which includes:
[0091] S411, extracting feature points: constructing a Hessian matrix, the Hessian matrix H(X, σ) of any pixel point X=(x, y) in the image to be extracted is as follows:
[0092]
[0093] Among them, σ is the scale, Lxx(X,σ), Lxy(X,σ), and Lyy(X,σ) are the second derivatives of the image to be extracted in each dire...
Embodiment 3
[0106] On the basis of embodiment one or two, the step of screening according to browning is also included. Such as Figure 16 As shown, the L value in the Lab format image can better reflect the brightness of the mushroom, thereby reflecting the degree of mushroom browning, so the RGB format image acquired by the camera is converted into a Lab format image. L=0 means black, L=100 means white, large L value means white, small L value means black; L value 86 and above is good quality mushroom, L value between 80-85 is better Mushrooms, L value between 70-79 are poor mushrooms, and mushrooms with L value lower than 69 have no edible value, corresponding to four grades of 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. Traverse each pixel of the cap, count the number of pixels corresponding to each level, and calculate the number of pixels corresponding to the four levels of 1, 2, 3, and 4 according to the number of pixels of the cap obtained by the watershed algorithm The ratio of the number to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com