Lower digestive tract endoscope image recognition method and system
An image recognition and digestive tract technology, which is applied in the field of digestive tract endoscope image recognition, can solve the problems of affecting the quality of lower digestive tract endoscopy, the inability to accurately judge the lesion site, and the inability to accurately determine, so as to facilitate treatment and follow-up, The effect of improving recognition accuracy and improving precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
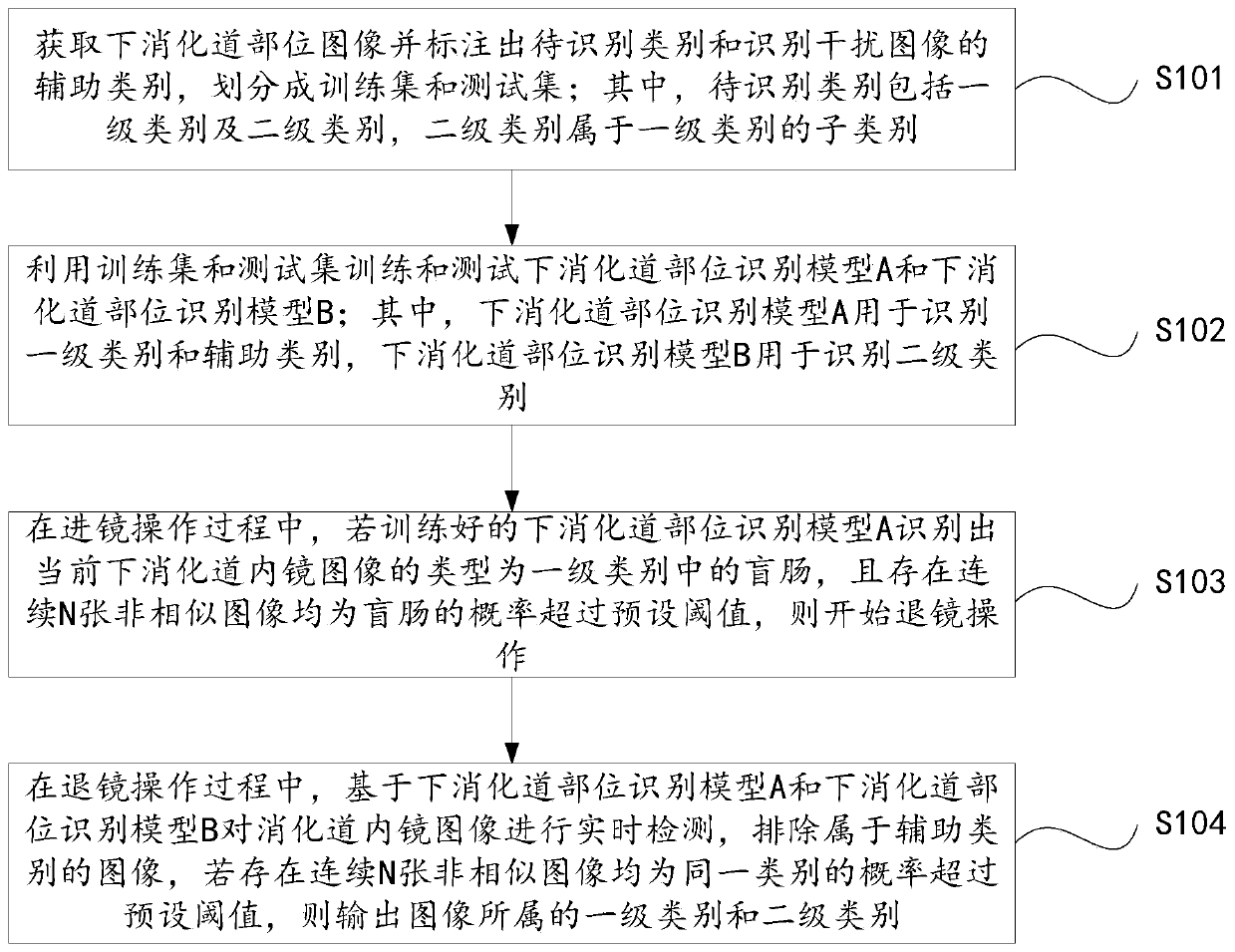
[0030] figure 1 A flow chart of a lower gastrointestinal endoscope image recognition method in this embodiment is given.
[0031] Combine below figure 1 To describe in detail the specific implementation process of the lower gastrointestinal endoscope image recognition method of this embodiment:
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, a kind of lower gastrointestinal endoscope image recognition method of the present embodiment at least includes:
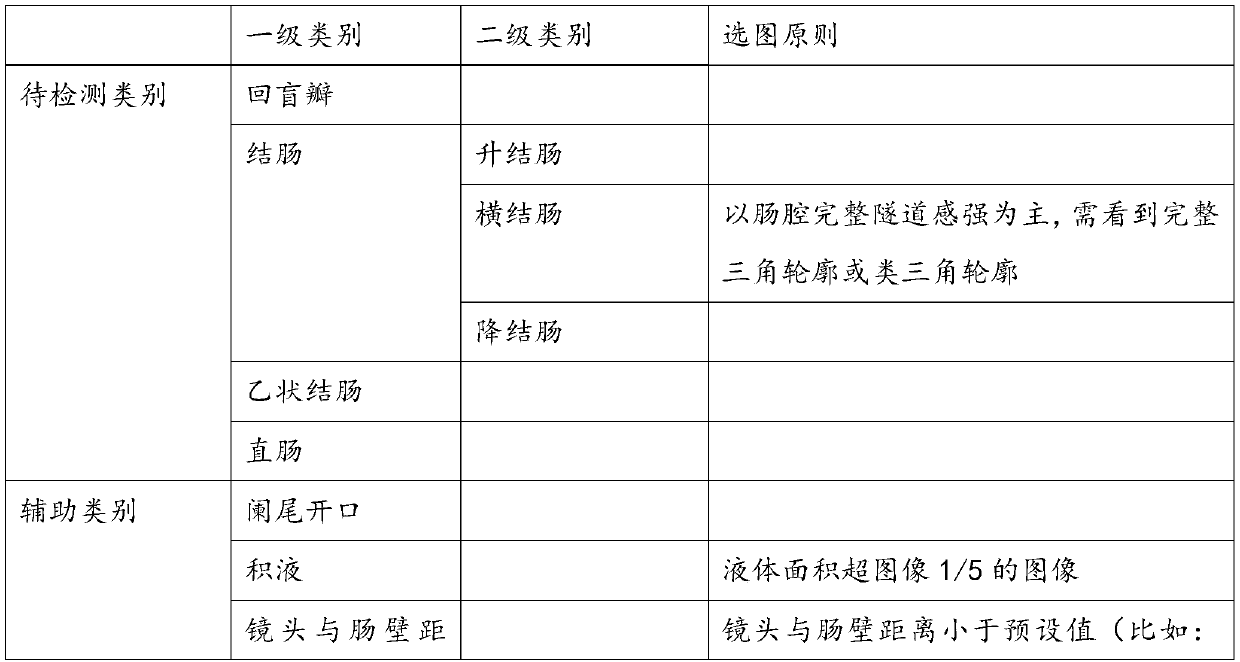
[0033] Step S101: Obtain the image of the lower gastrointestinal tract, mark the category to be recognized and the auxiliary category of the recognition interference image, and divide it into a training set and a test set; wherein, the category to be recognized includes a first-level category and a second-level category, and the second-level category belongs to the first-level category. subcategory of the level category.
[0034] In the specific implementation, the primary category includes the ileocecal valve, colon, sigmoid colon, a...
Embodiment 2
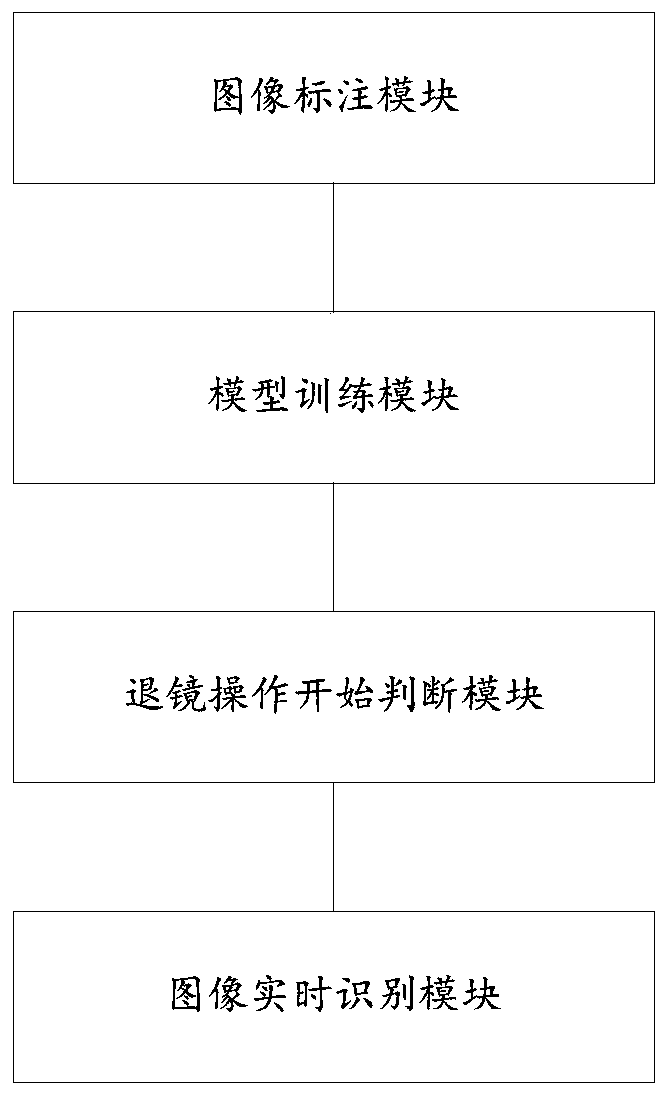
[0070] figure 2 A schematic structural diagram of a lower gastrointestinal endoscope image recognition system of this embodiment is given.
[0071] Combine below figure 2 To describe in detail the structural composition of the lower gastrointestinal endoscope image recognition system of this embodiment:
[0072] Such as figure 2 As shown, a kind of lower gastrointestinal endoscope image recognition system of the present embodiment at least includes:
[0073] (1) Image labeling module, which is used to obtain the image of the lower digestive tract and mark the auxiliary category of the category to be identified and the recognition interference image, and is divided into a training set and a test set; wherein, the category to be identified includes a first-level category and a second-level category Category, the secondary category is a subcategory of the primary category.
[0074] In the specific implementation, the primary category includes the ileocecal valve, colon, si...
Embodiment 3
[0110] This embodiment provides a computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored, and it is characterized in that, when the program is executed by a processor, the following figure 1 The steps in the image recognition method for lower gastrointestinal endoscopy are shown.
[0111] In this embodiment, the image of the lower digestive tract is obtained and the category to be identified and the auxiliary category for identifying the interference image are marked; wherein, the category to be identified includes a first-level category and a second-level category, and the second-level category belongs to a subcategory of the first-level category; The lower gastrointestinal part images of the auxiliary category and the lower gastrointestinal part images of the first-level category are used to train the lower gastrointestinal part recognition model A, which reduces the impact of blurred images, out-of-focus images, reflection artifacts, residual debris, and effu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com