Method for driving Methanosarcina to produce methane
A methanosarcina and methanogenic technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems that have not been discovered, and achieve the effects of reducing process costs, easy optimization, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Inoculate Methanosarcina barkeri and Rhodopseudomonas palustris with 20% (v / v) and 2% (v / v) respectively into acetic acid medium with pH 7.0, and culture at 37°C; China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center), the preservation number is CGMCC-1.2180, Methanosarcina barkeri was purchased from the German Microbiological Culture Collection Center (Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen), the preservation number is DSM-800.
[0026] (2) When Methanosarcina barkeri and Rhodopseudomonas palustris grow to late logarithmic phase in step 1, centrifuge at 7500r / min for 10min to collect the bacterial solution, wash the bacteria with normal saline for 3 times, and finally dilute the OD of the bacterial solution with normal saline 600 value to 0.3.
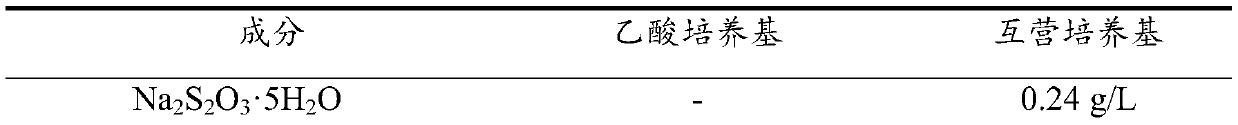
[0027] (3) Take 2% (v / v) Methanosarcina barkeri and Rhodopseudomonas palustris bacterium solution in step 2 and inoculate it into the interoperabili...
Embodiment 2
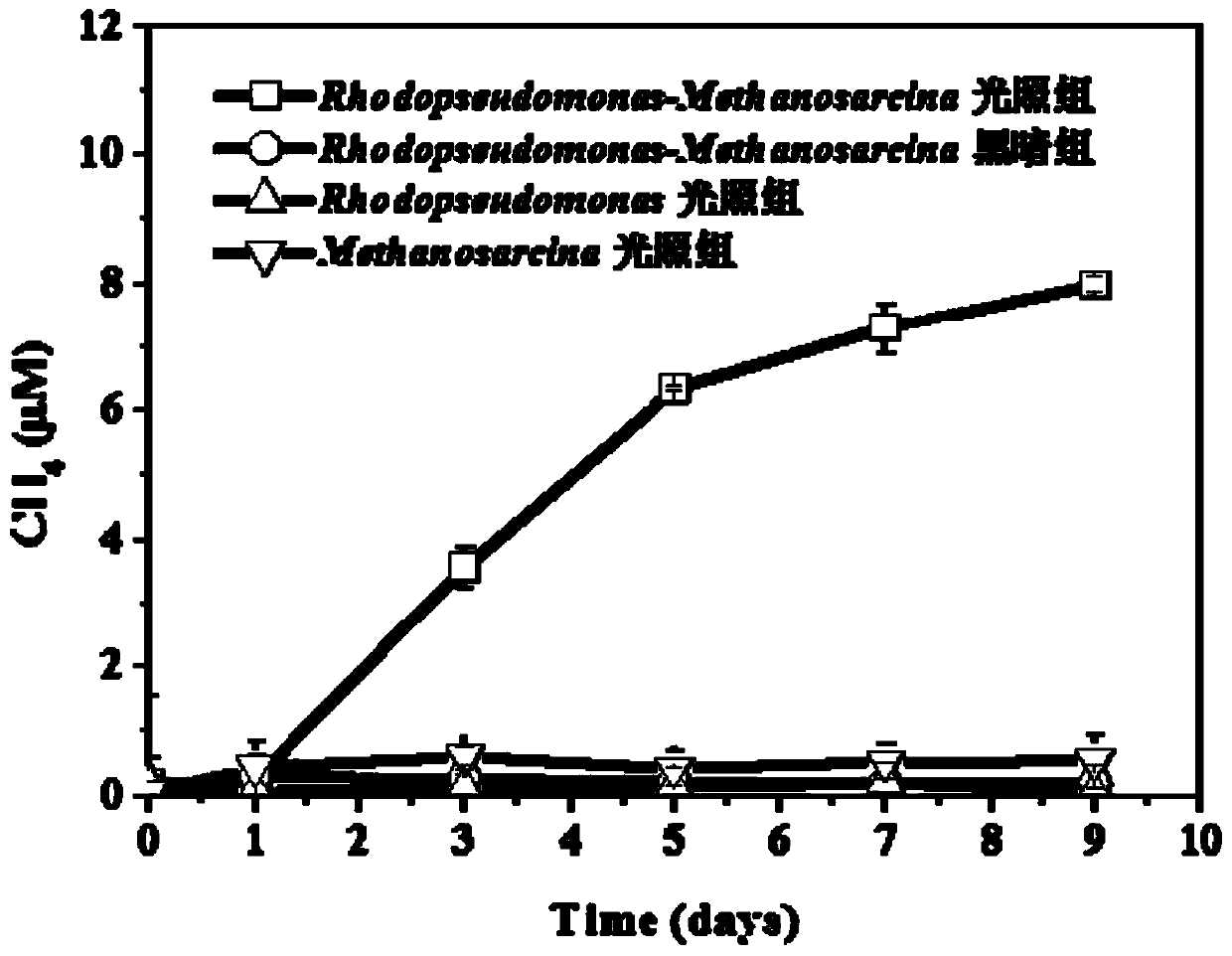
[0039] To analyze the inorganic photosynthesis of Rhodopseudomonas palustris the fixation of CO in Methanosarcinabarkeri 2 In order to reduce the effect of methanogenesis, a control group experiment was also carried out, including: Methanosarcina barkeri light group, that is, without adding Rhodopseudomonas palustris bacteria, and other operations are the same as in Example 1; Rhodopseudomonas palustris light group, that is, without adding Methanosarcina barkeri bacteria, other operations All the same as in Example 1; Methanosarcinabarkeri-Rhodopseudomonas palustris dark group, that is, cultivated under no light conditions, and other operations are all the same as in Example 1. The test results showed that there was no obvious methane production in the above three control groups.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com