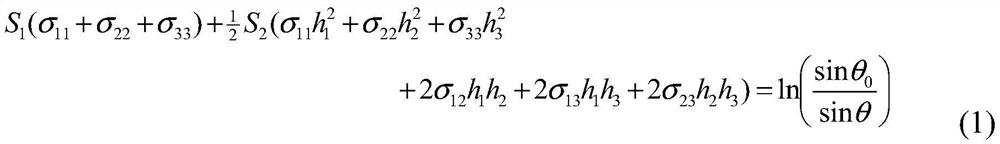A method for rapid detection of residual principal stress of polymer material products
A technology of polymer materials and principal stress, applied in the analysis of materials, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, material analysis using radiation diffraction, etc., can solve problems such as sample center offset and calculation result errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] The polymer material article employed in this embodiment is polyethylene (a grade TR480M). The polyethylene pellets were injected on the sea day MA900 injection into a diaphragm and a size of 60 mm × 60 mm × 2 mm. The screw is 5 segments, and the temperature is 180 ° C, 180 ° C, 170 ° C, 160 ° C, 150 ° C, and the mold temperature is 40 ° C. The injection time is 3s, the holding time is 60s, and the cooling time is 10s. The injection pressure is 5 MPa, the screw speed is 45 rpm, and the back pressure is 0.2 MPa.
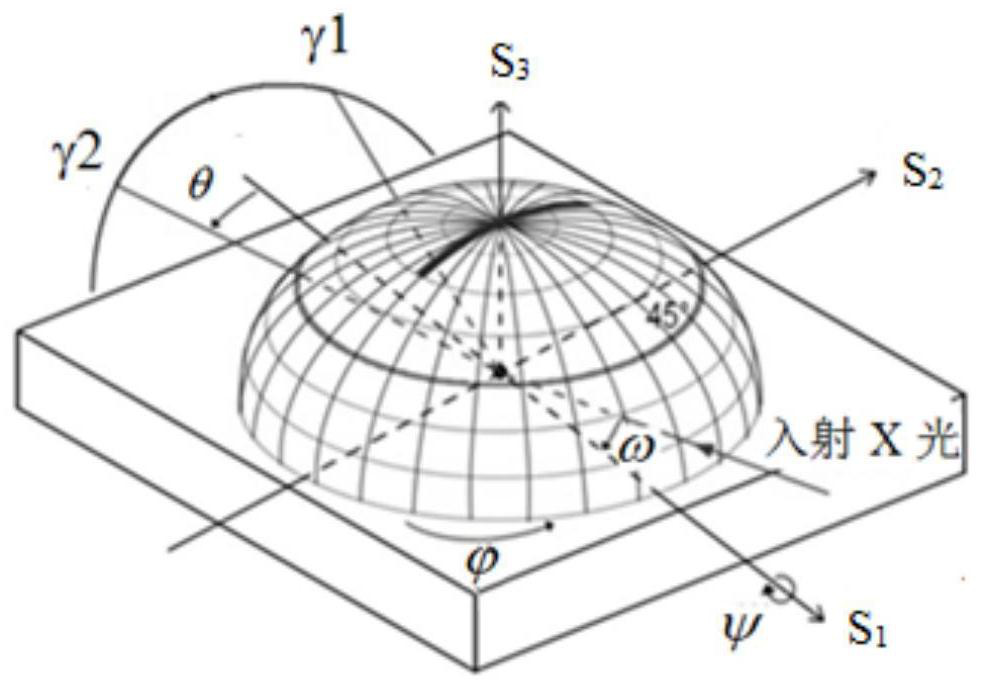
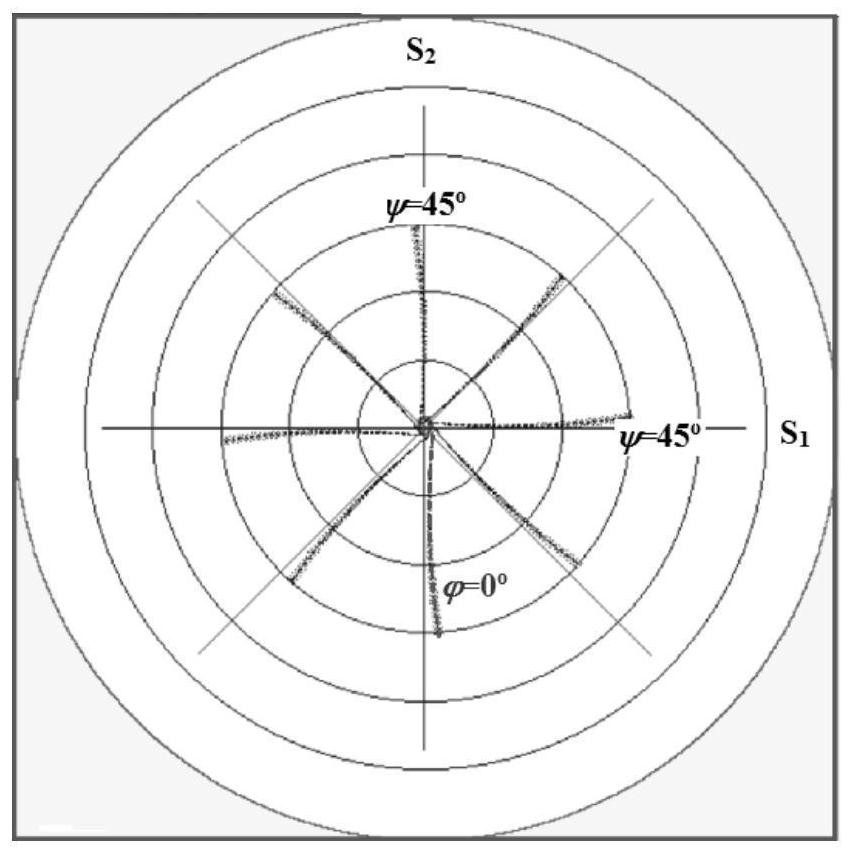
[0065]The residual main stress of the injection diaphragm was quantitatively detected by a two-dimensional X-ray diffraction method. During the detection process, the injection film sheet was first placed in a sample stage of the X-ray diffraction, and the X-ray incident position is adjusted to the surface of the injection film. To be tested, adjust the detector angle to a sample diffraction arc to the intermediate position of the detector (at this time, the X-ray ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] The polymer material articles employed in this example are polypropylene (grades NS06). The polypropylene pellets were injected into a diaphragm on the sea day MA900 injection, and the size was 60 mm × 60 mm × 2 mm. The screw is 5 segments, and the temperature is 190 ° C, 180 ° C, 170 ° C, 160 ° C, 150 ° C, and the mold temperature is 40 ° C. The injection time is 3s, the holding time is 60s, and the cooling time is 10s. The injection pressure is 5 MPa, the screw speed is 45 rpm, and the back pressure is 0.2 MPa.
[0072] The residual main stress of the film was quantitatively detected by a two-dimensional X-ray diffraction method. During the detection process, the injection film sheet was first placed in a sample stage of the X-ray diffraction instrument, and the X-ray incident position to the surface of the injection film surface. Location, adjustment detector angle to a sample diffraction arc to reach the intermediate position of the detector (at this time, the X-ray inc...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The polymer material articles employed in this example are polypropylene (grades MM20S). The polypropylene pellets were injected into a diaphragm on the sea day MA900 injection, and the size was 60 mm × 60 mm × 2 mm. The screw is 5 segments, and the temperature is 190 ° C, 180 ° C, 170 ° C, 160 ° C, 150 ° C, and the mold temperature is 40 ° C. The injection time is 3s, the holding time is 60s, and the cooling time is 10s. The injection pressure is 5 MPa, the screw speed is 45 rpm, and the back pressure is 0.2 MPa.
[0078] The residual main stress of the film was quantitatively detected by a two-dimensional X-ray diffraction method. During the detection process, the injection film sheet was first placed in a sample stage of the X-ray diffraction instrument, and the X-ray incident position to the surface of the injection film surface. Location, adjustment detector angle to a sample diffraction arc to reach the intermediate position of the detector (at this time, the X-ray in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Poisson's ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com