A method for in-situ observation of liquid nitrogen frozen rock microstructure
A microstructure and liquid nitrogen freezing technology, applied in measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of water-sensitive water lock reaction, high crack initiation pressure, low rock breaking efficiency of hot dry rock reservoirs, etc., and achieve image High resolution, simple sample preparation, and adjustable magnification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
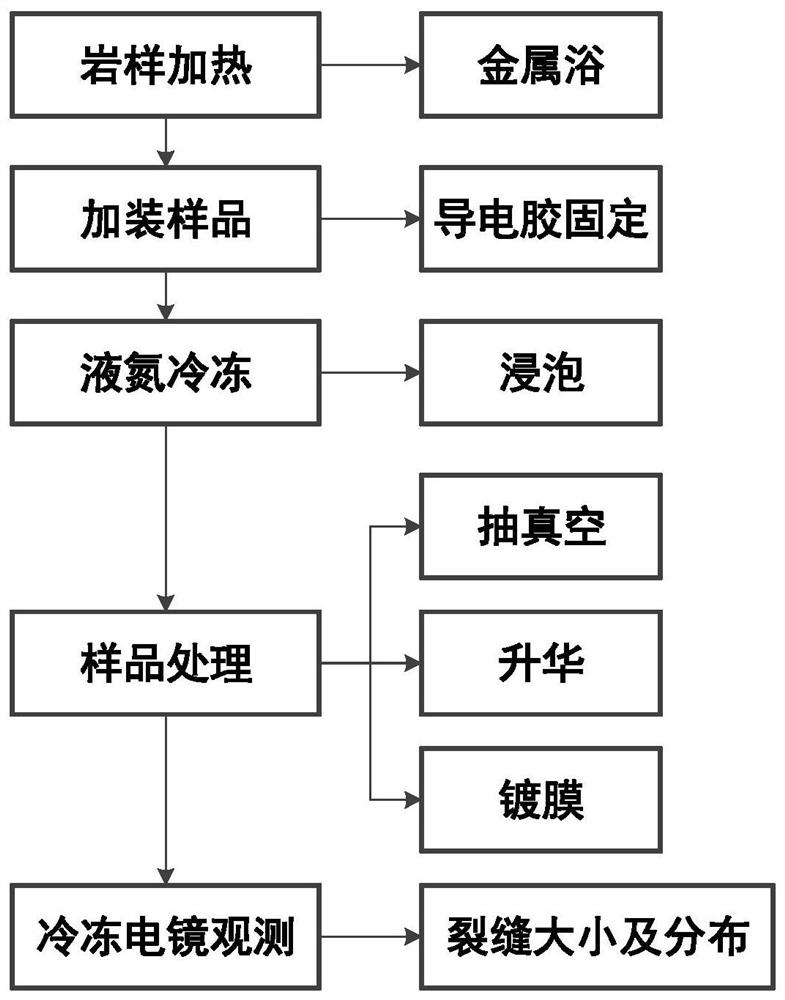
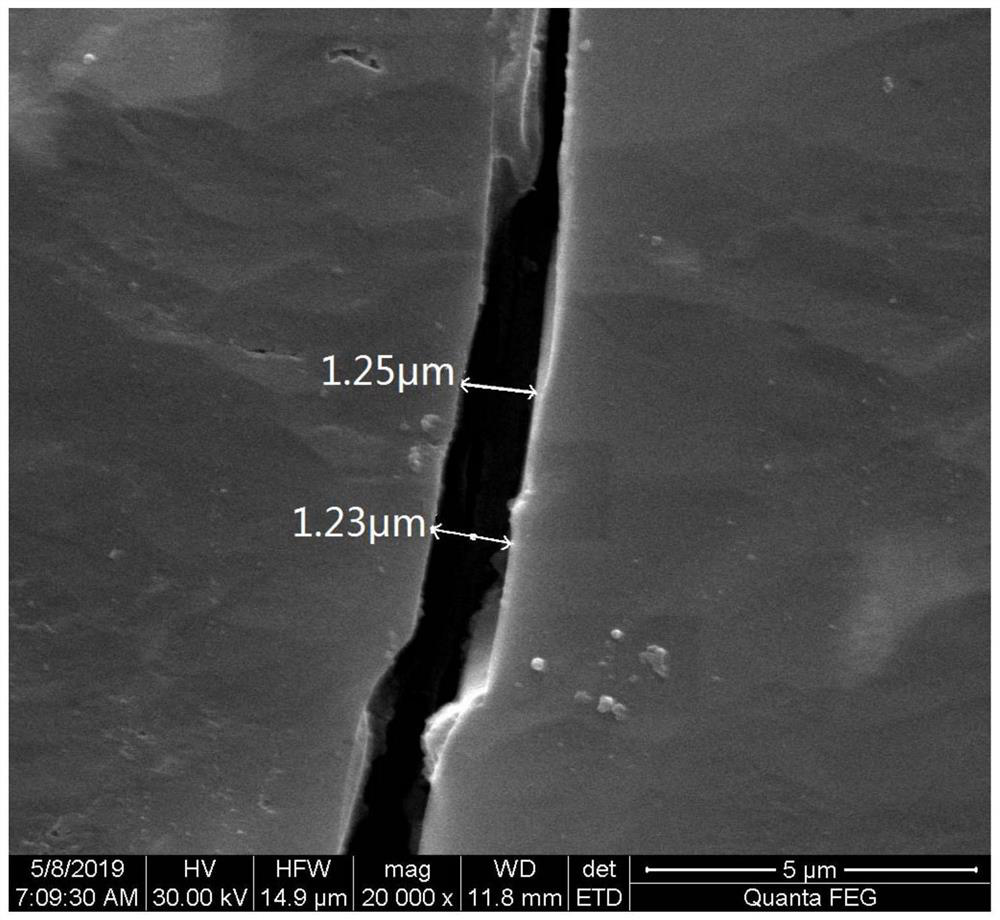
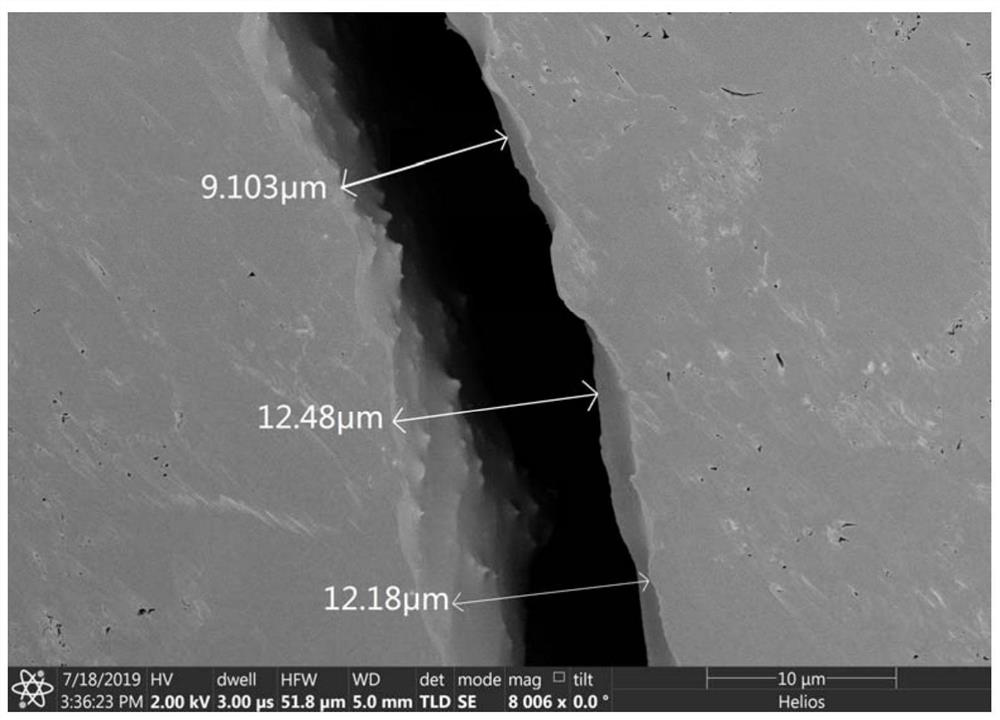
[0047] The liquid nitrogen frozen rock microstructure in-situ observation method of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the following steps are included: (1) put the sliced polished coal into the digital display heating mantle, and heat it to 50°C; (2) take it out after the rock sample is heated evenly, soak it in liquid nitrogen until the internal temperature field Reach stability; (3) Take the rock sample out of liquid nitrogen and fix it on the loading disk with conductive glue; (4) Carry out vacuum treatment, sublimation treatment and coating treatment in sequence; (5) Send the sample into the cryo-electron microscope observe.
[0048] The size of the sliced and polished rock sample is 6mm×6mm×1.5mm. Four rock samples of this size can be placed on the cryo-electron microscope loading disk for observation at a time. After one sample is observed, the next one can be observed by moving the lens position, which can save sample preparation. time.
[0049] Ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com