Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) primer, kit and detection method for detecting ditylenchus destructor thorne
A detection method, stem nematode technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of false positives easily, and achieve high sensitivity, accurate detection, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1, D. destructor D. destructor RPA amplification primer design and establishment of detection method
[0028] 1.1 Design and screening of D. destructor RPA primers
[0029] According to the comparative analysis of ITS and ribosomal RNA 28s nucleotide sequences of D. destructor and other D. nematodes, three pairs of primers suitable for RPA reactions were designed (Table 1).
[0030] Table 1: Primers used for detection and screening of D. destructor RPA in sweet potato
[0031]
[0032] 1.2 Preparation of D. destructor DNA template
[0033] Collect D. destructor of sweet potato into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 5000rpm for 10 minutes, use a pipette to absorb the water in the tube as much as possible, put the centrifuge tube into liquid nitrogen for 30 seconds, and grind it with a grinding pestle. Nematode DNA was extracted from the homogenate after grinding using Animal Genome DNA Rapid Extraction Kit (Shanghai Sangong).
[0034] 1.3 RPA reaction...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2, sweet potato D. destructor RPA specific amplification accuracy and reliability test
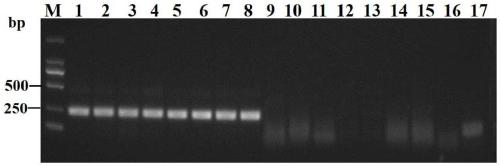
[0041] A total of 15 populations of D. destructor, Meloidogyne incognita, Meloidogyne javanica, Root-knot nematode Elephant ear, soybean cyst nematode, cereal cyst nematode, S. bessiei, and Brachypodia coffeee were collected (Table 1) 2) According to Example 1.2, extract DNA from different populations of nematodes as templates, and use ddH 2 O is a negative control, and RPA reaction is carried out and detected according to examples 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5. figure 1 The results showed that only the D. destructor population obtained a 230bp specific amplification product, and no other nematode populations produced bands here.
[0042] Table 2 Nematode populations used in the experiment
[0043]
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3, sweet potato D. destructor RPA reaction sensitivity detection
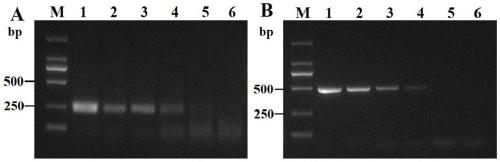
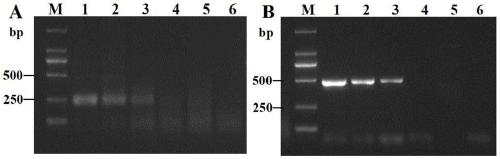
[0045] 3.1 Genomic DNA RPA reaction sensitivity detection of D. destructor population
[0046] Using the extraction method in Example 1.2, extract the DNA of D. destructor D. destructor, use Nanodrop2000 to measure its genomic DNA concentration, and use water to dilute it to 10 ng / μL, 1ng / μL, 10 -1 ng / μL, 10 -2 ng / μL, 10 -3 ng / μL.
[0047] RPA detection: Using the DNA of these five different concentrations of D. destructor D. destructor as templates (1 μL) and water as the control, perform RPA reactions and detection according to 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5.
[0048] PCR detection: DNA template diluted in the above gradient, amplification system 25 μL, DNA template 1 μL, primer pair DdF1 / DdR1 (20 μM) 1 μL, EmeraldAmp® MAX PCR Master Mix (TaKaRa, Dalian) 12.5 μL, ddH 2 O to make up to 25 μL. Negative worm DNA template was used as negative control. Amplification was performed on an Eppendorf PCR cyc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com