The kasp primer set associated with resistance to scab in wheat and its application
A technology related to wheat head blight and resistance, applied in the field of crop breeding and molecular biology, can solve problems such as difficulty in using disease-resistant sites, poor agronomic traits, large genetic and physical distances, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
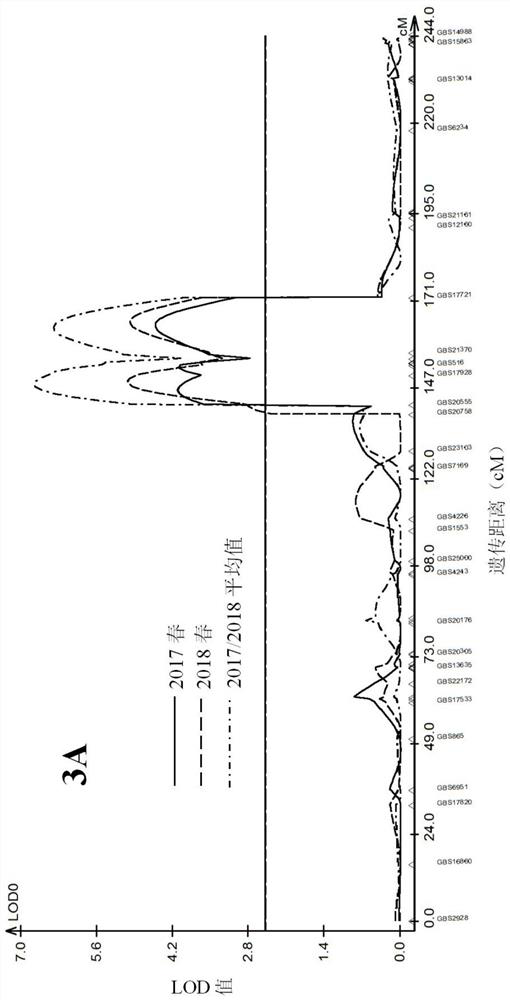
[0033] Example 1, Qfhb.3AL17928 molecular marker development:
[0034] In this example, Yangmai 158 and Zhengmai 9023 were used as the female parent and male parent (reserved seeds in the laboratory of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences), and a total of 231 recombinant inbred lines F were obtained by single-grain transmission. 5:7 As material, it was planted in greenhouses for two consecutive years in 2016–2017 and 2017–2018.
[0035] Wheat seeds were first sown in 96-hole plug trays. After the seeds absorbed water, the plug trays were placed in a vernalization room (6°C) for vernalization for 28 days, and then transferred to the greenhouse and planted in flower pots. Each pot was planted with 8 plants, and each line was planted. 2 pots, arranged randomly. In the first month after planting, set the daytime temperature to 17±2°C and the night temperature to 13±2°C, then set the daytime temperature to 22±5°C and the night temperature to 19±2°C until maturity. During the ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2, Qfhb.3AL17928 is verified in the recombinant inbred line:
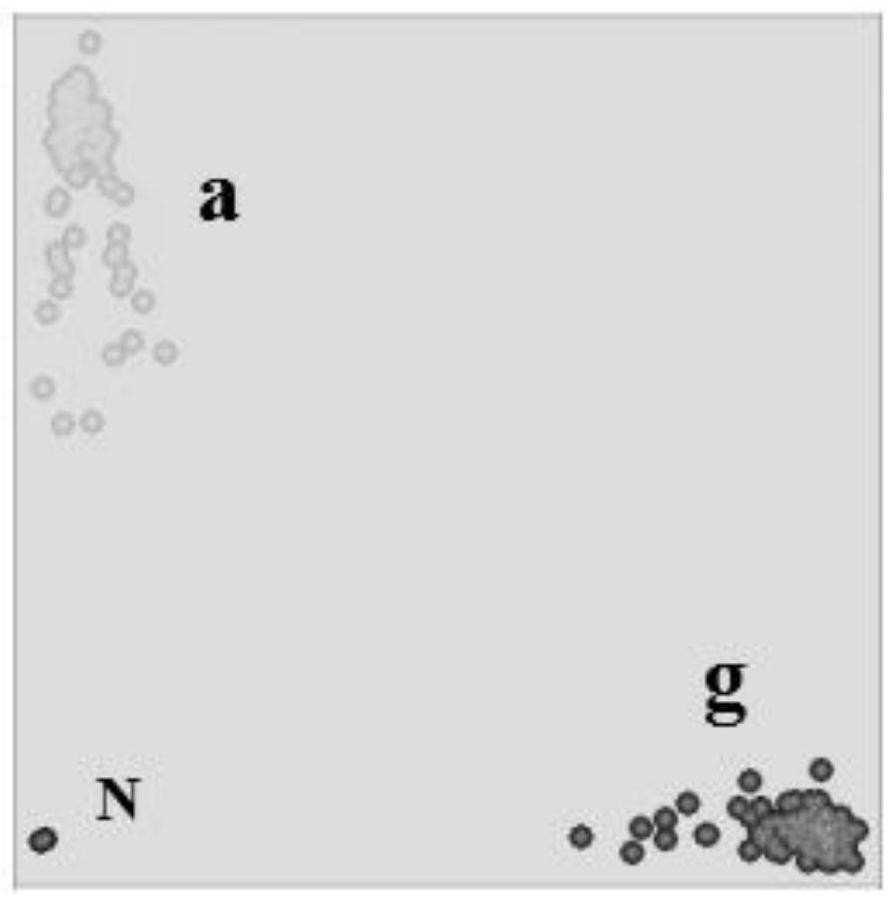
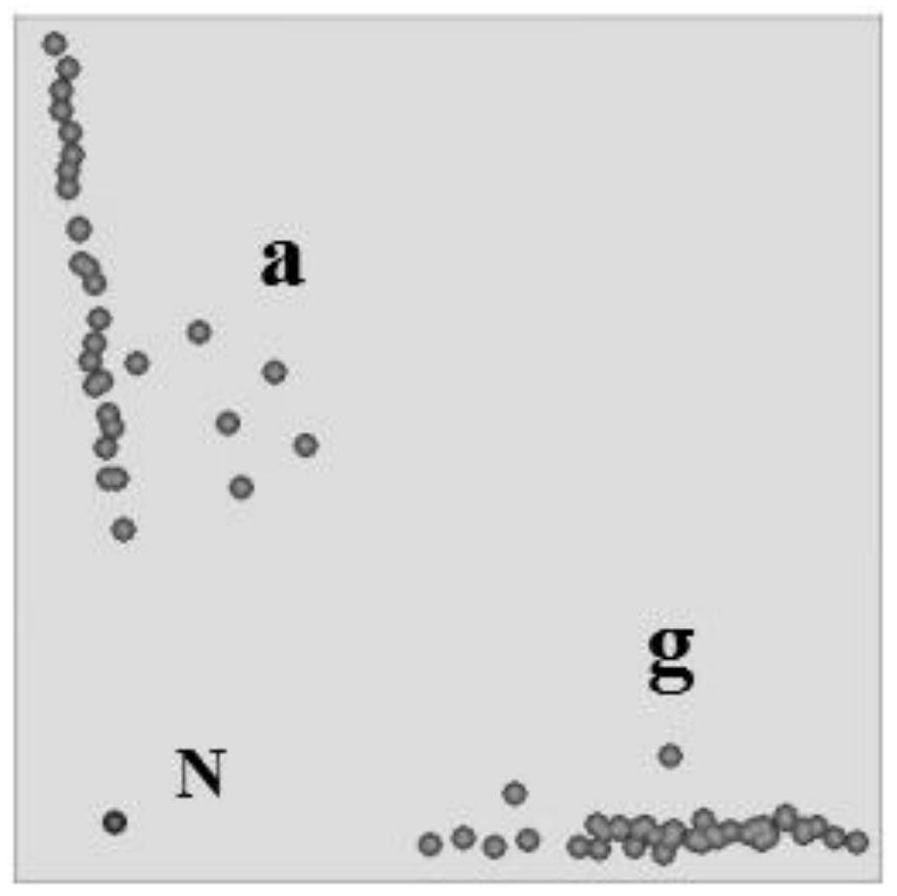
[0045] 231 recombinant inbred lines F for the recombinant inbred line population in Example 1 5:7 The wheat samples were detected by KASP marker amplification using Qfhb.3AL17928 according to the method of Example 1, and the detection results were as follows: figure 2 shown. figure 2 Among them, the blank control N, the disease-resistant SNP allelic variation g, and the susceptible SNP allelic variation a were well-typed, and the coincidence rate with the GBS sequencing SNP allelic variation in Example 1 was 100%. It indicated that the KASP marker was successfully developed, and Qfhb.3AL17928 could be further applied to prediction of resistance to Fusarium head blight in wheat samples.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3, Qfhb.3AL17928 is verified in natural population:
[0047] In order to verify the effectiveness of Qfhb.3AL17928, 74 cultivars or high-generation lines were selected from the wheat areas in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and were inoculated and identified by 3 points for 2 consecutive years. The inoculation method is similar to Example 1, selects 10 wheat ears with the F0609 conidia suspension of F. graminearum strong pathogenicity race, is bagged and moisturizing 72h after the inoculation, and investigates the diseased smallness of each wheat ear 14 days after the inoculation. The number of spikes, the number of diseased spikelets of each variety (line) was calculated as the average of 10 wheat spikes, as shown in Table 1.
[0048] Table 1 Qfhb.3AL17928 SNP allelic variation and number of diseased spikelets in 74 wheat varieties (lines)
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] Genomic DNA extraction was the same as in Example 1. Using the KAS...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com