Carbon fiber woven fabric for fuel cell gas diffusion layer and fuel cell
A gas diffusion layer, carbon fiber fabric technology, applied in electrical components, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of uneven absorption thickness, low buffering, and many processes that consume energy, and achieve the effect of high power generation capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
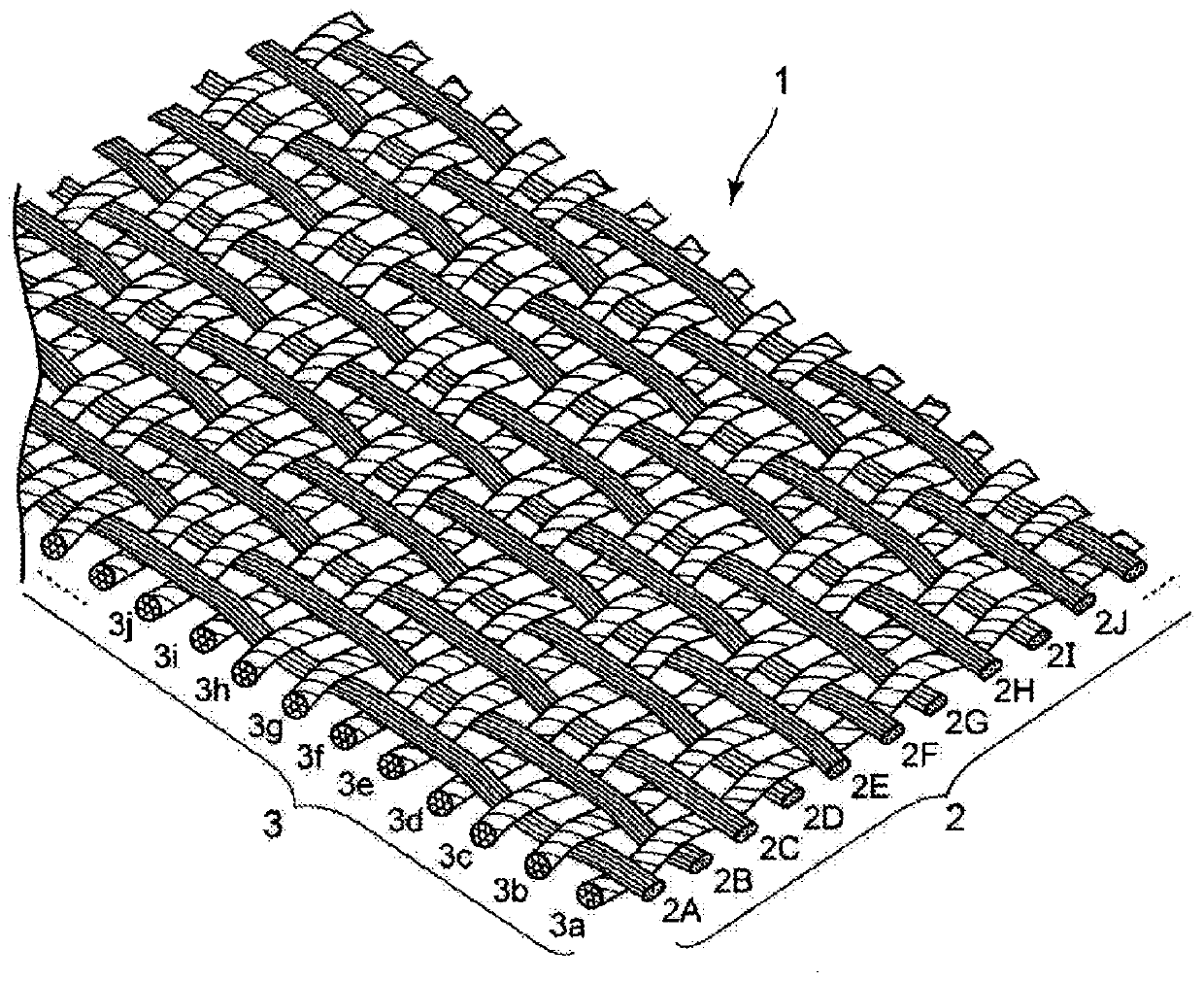
[0082] A fuel cell cell (hereinafter referred to as "cell") was produced using the GDL of each carbon fiber fabric using the material of the present invention and the comparative material, and the power generation performance of the cell was measured, so the measurement results will be described. The GDL used in this measurement was made into the GDL of each carbon fiber fabric which used 2 types of this invention materials (this invention material 1 and 2) and 2 types of comparison materials (comparative materials 1 and 2). Material 1 of the present invention is figure 1 as well as figure 2 In the GDL of the twill weave shown (a weaving method in which one warp passes over three wefts and then passes under two wefts), only the warp is substantially untwisted. In addition, the present invention material 2 is the same as the invention material 1 figure 1 as well as figure 2 In the shown twill-woven GDL, both the warp and the weft are substantially untwisted.
[0083] In c...
Embodiment 2
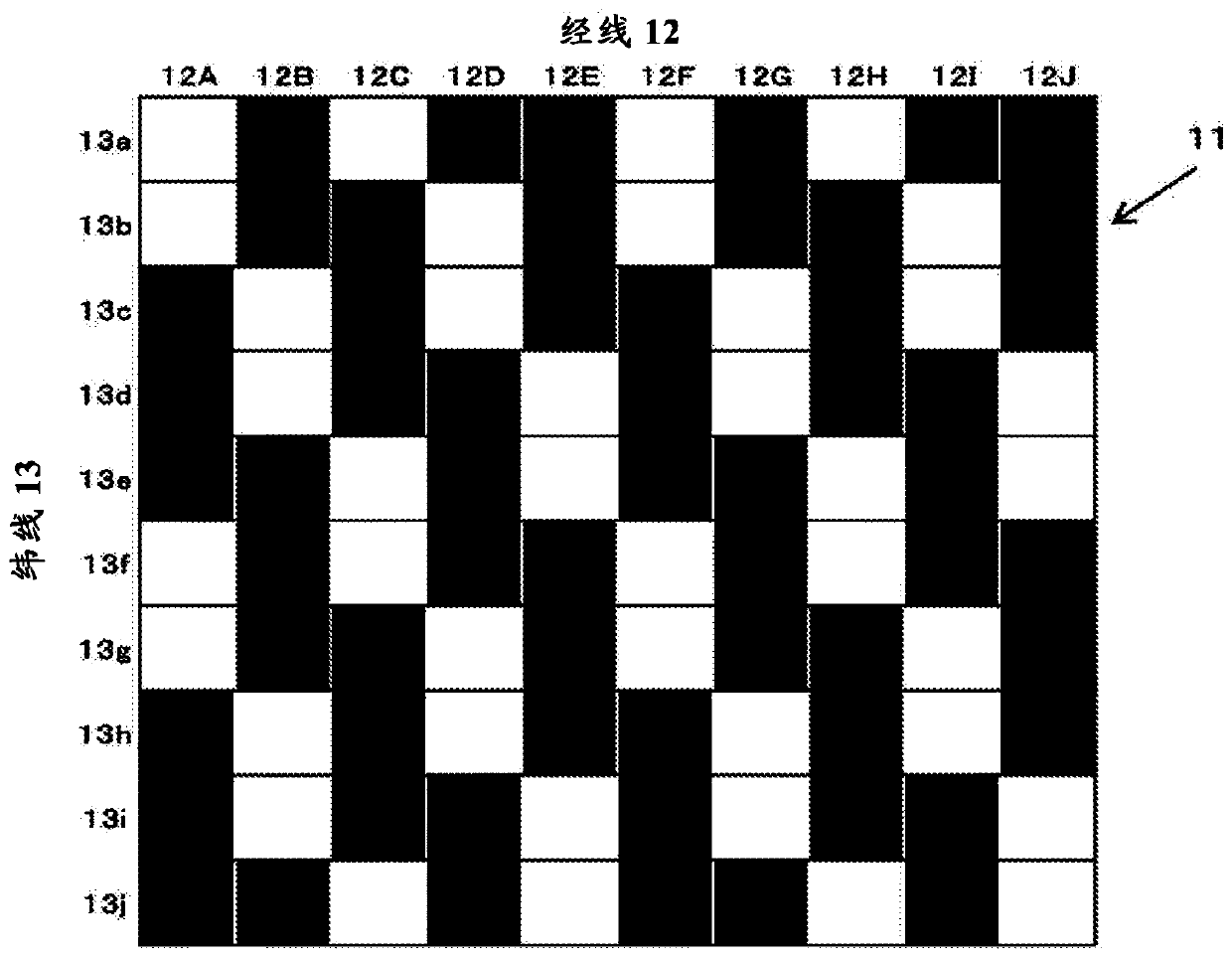
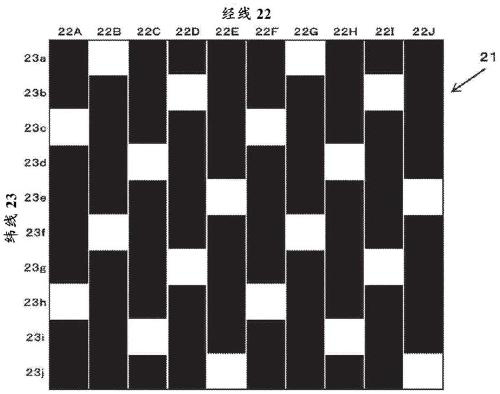
[0098] Next, in order to compare the ease of fluidity of the fluid (water) in each GDL of the material of the present invention and the comparative material, a water passage test was performed. The GDL used in this test was the present invention material 2 and comparative material 2 (hereinafter referred to as present invention material 3 and comparative material 3) used in Example 1. Figure 12 A schematic plan view of the test setup used in this test is shown in , Figure 13 shown in Figure 12 The X-X profile.
[0099] Regarding this test device, such as Figure 12 as well as Figure 13 As shown, a GDL with a thickness of 0.1 mm x width 50 mm x length 100 mm is set on a steel base and gaskets are placed around it, and the GDL is pressed from above with a transparent resin plate and a steel pressing plate. Airtight. With regard to the hermetic GDL, it is possible to pass such as Figure 13 Check the water flow of the GDL by using the pressing plate with the opening in th...
Embodiment 3
[0102] The difference in the bending amount under predetermined pressing was measured using the inventive material and the comparative material, and the measurement results will be described. In addition, the same invention material and comparative material were also used to measure the same power generation performance as in Example 1, so the measurement results will also be described together.
[0103] The GDL used in the measurement of the amount of bending of the GDL and the measurement of the power generation performance in this example is a material obtained by curing both sides of the material 1 of the present invention used in Example 1 (hereinafter referred to as the present invention). Material 4) and a comparative material obtained by curing both surfaces of Comparative Material 1 used in Example 1 with a thermosetting resin (hereinafter referred to as Comparative Material 4).
[0104] Regarding the curing treatment carried out on both sides of the inventive materia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com