Thermal characteristic analysis method, thermal error modeling method and thermal error compensation system of shaft system based on analytical method
An analysis method and technology of thermal characteristics, applied in complex mathematical operations, geometric CAD, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to obtain the thermal characteristics of the shaft system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
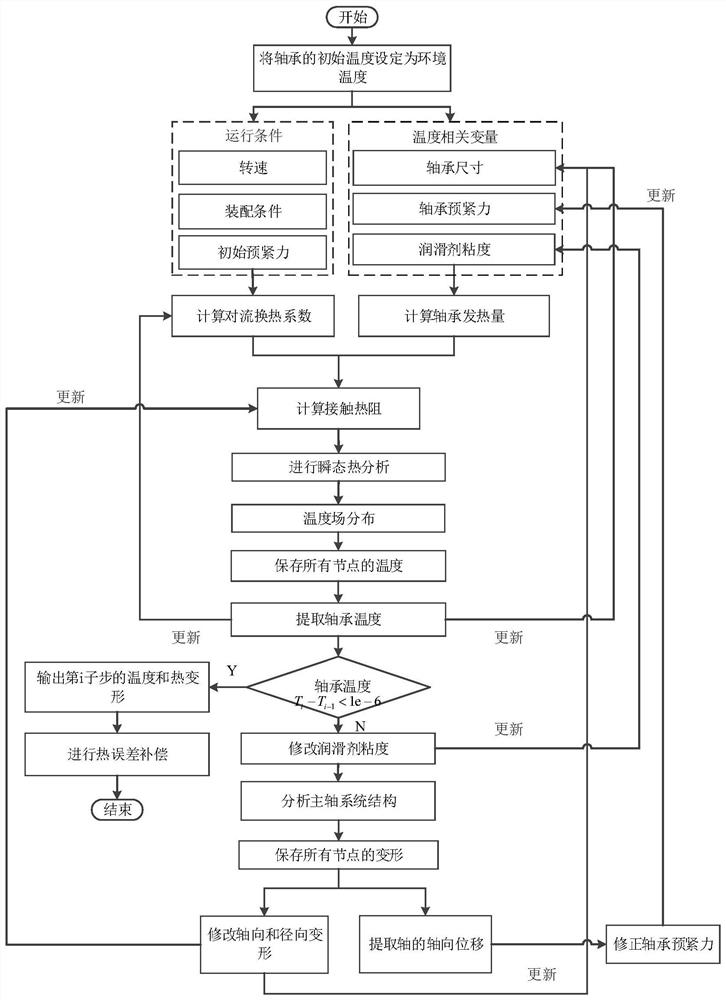
[0128] In this embodiment, the method for analyzing the thermal characteristics of the shaft system based on the analytical method includes the following steps:
[0129] 1) According to the heat balance principle, the heat balance equation of the rolling element of the shaft system is established, and the transient thermal characteristic model of the shaft system is created from the heat balance equation. The rolling elements of the shaft system of this embodiment include balls, inner rings and outer rings of the bearing.
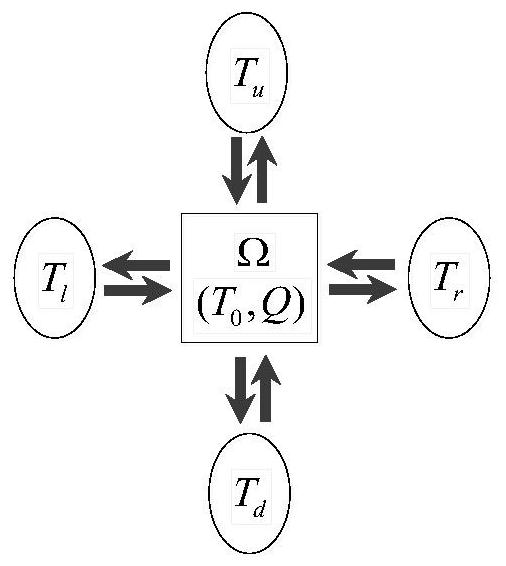
[0130] Specifically, the heat balance principle is: according to the temperature transfer principle of the shaft system, the heat balance equation for controlling the volume Ω is constructed:
[0131]
[0132] Among them, T Ω Indicates the temperature of the control volume; C indicates the specific heat capacity of the control volume; T l , T u , T r and T d Respectively represent the temperature of the object in contact with the control volume; R ...
Embodiment 2
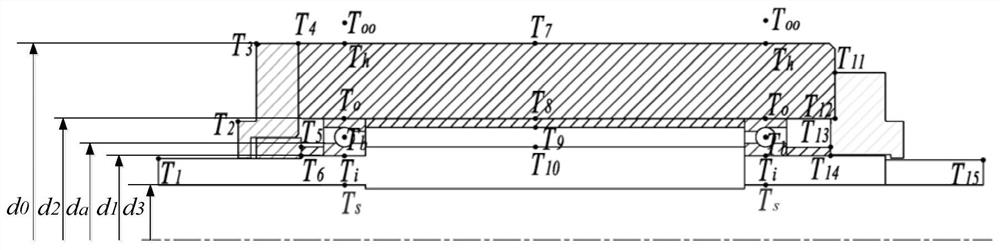
[0275] The shaft in the shaft system is heated by the thermal load of the front and rear bearings, and the shaft temperature can be expressed as
[0276]
[0277] Among them, T(x,t) represents the heat load at the position x on the axis at time t; T fb (x,t) and T rb (x, t) represent the thermal load applied to the shaft by the front and rear bearings respectively; C 1 、C 2 、C 3 and C 4 Both are coefficients; h is the convection coefficient; λ shaft core expansion coefficient; d is the diameter of the shaft; ρ is the density of the shaft; c is the specific heat capacity of the shaft core;
[0278] For a shaft system with free ends, that is, at least one end of the shaft has only radial constraints and no axial constraints, the thermal expansion is:
[0279]
[0280] In the formula, α represents the axial thermal elongation coefficient; L represents the length of the shaft; T ∞ Indicates the ambient temperature.
[0281] Since the coefficient C cannot be determined...
Embodiment 3
[0351] like Figure 19 As shown, the thermal error compensation system of the shaft system based on the analytical method in this embodiment includes:
[0352] CNC machining center, including PLC controller and temperature sensor;
[0353] The data acquisition system is connected with the CNC machining center, and is used to collect the running speed information and running time information of the shaft system, and process the running speed information and running time information through filters, amplifiers and A / D converters to obtain the shaft The actual running time and speed of the system;
[0354] The thermal error compensation system is connected to the data acquisition system, and the thermal error modeling method based on the analytical method of the shaft system described in Embodiment 2 is used to calculate the thermal error to obtain the compensation components of the shaft in all directions;
[0355] The PLC controller is connected to the thermal error compensat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com