A method and application of regulating unsaturated fatty acid synthesis in Synechocystis
A technology for unsaturated fatty acids and Synechocystis, which is applied in the field of regulating the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids in Synechocystis, and can solve problems such as the content of unsaturated fatty acids cannot be further increased.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] spkD gene cloning and insertion into quick connection vector and spkG gene cloning and insertion into quick connection vector:
[0074] Using the primer pair to carry out electrophoresis after PCR amplification of the Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 genomic DNA, the length of the spkD gene fragment is 1.9kb. The spkD gene sequence is SEQ ID NO.17, which is verified to be correct and recovered by cutting the gel; the primer pair is as follows:
[0075] spkD-F: 5'-ACTTACCCGTTCTGATTGA-3' SEQ ID NO.1
[0076] spkD-R: 5'-TAACCATTGATAA GCAGAT-3'SEQ ID NO.2;
[0077] Synechocystis PCC6803 genomic DNA was subjected to electrophoresis after PCR amplification with a primer pair, and the spkG gene fragment length was 1.9kb. The spkG gene sequence was SEQ ID NO.18, which was verified to be correct, and the gel was cut and recovered; the primer pair was as follows:
[0078] spkG-F: 5'-AGACTTTTCTCTATTGCCTC-3' SEQ ID NO.3
[0079] spkG-R: 5'-GGACCCAAATCCAGAAGAC-3' SEQ ID NO.4.
[0080] T...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Construction of spkD gene knockout (insertion inactivation) and spkG gene knockout (insertion inactivation) plasmids:
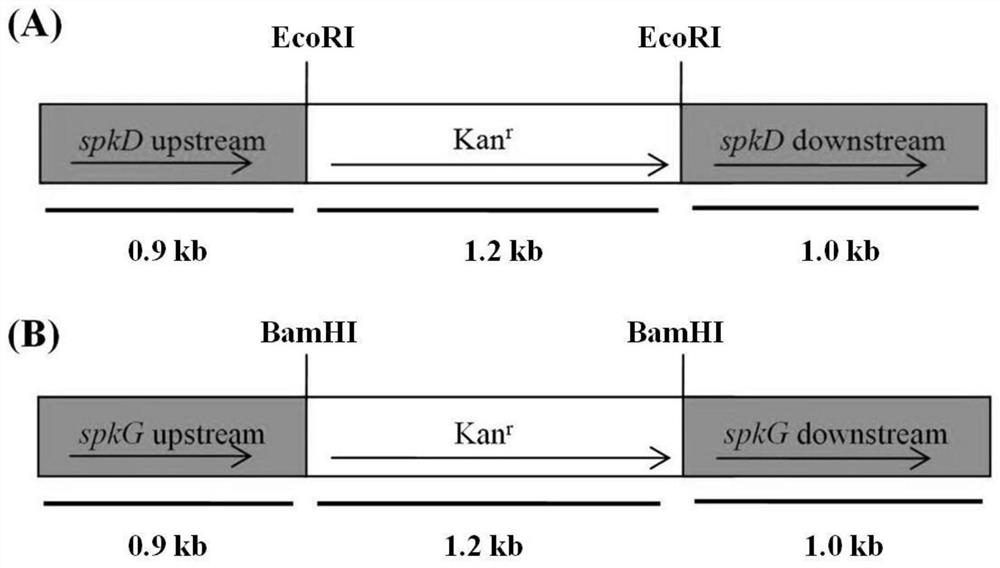
[0088] The 007-spkD plasmid was digested with EcoR I to obtain 007-spkD-EcoR I. The restriction site of EcoR I is at 0.9kb of the spkD gene fragment, the first 0.9kb is used as the upstream arm of homologous recombination, and the latter 1.0kb (the length of the spkD gene fragment is 1.9kb) is used as the downstream arm of homologous recombination. The 007-spkG plasmid was digested with BamHI to obtain 007-spkG-BamHI. The restriction site of BamHI is at the first 0.9kb of spkG gene. The first 0.9 kb was used as the upstream arm of homologous recombination, and the last 1.0 kb (the length of the spkG gene fragment was 1.9 kb) was used as the downstream arm of homologous recombination.
[0089] Digest the plasmid pBluescript-Kan (providing a kanamycin resistance fragment) with EcoR I endonuclease, and recover the kanamycin fragment (1.2kb) by electroph...
Embodiment 3
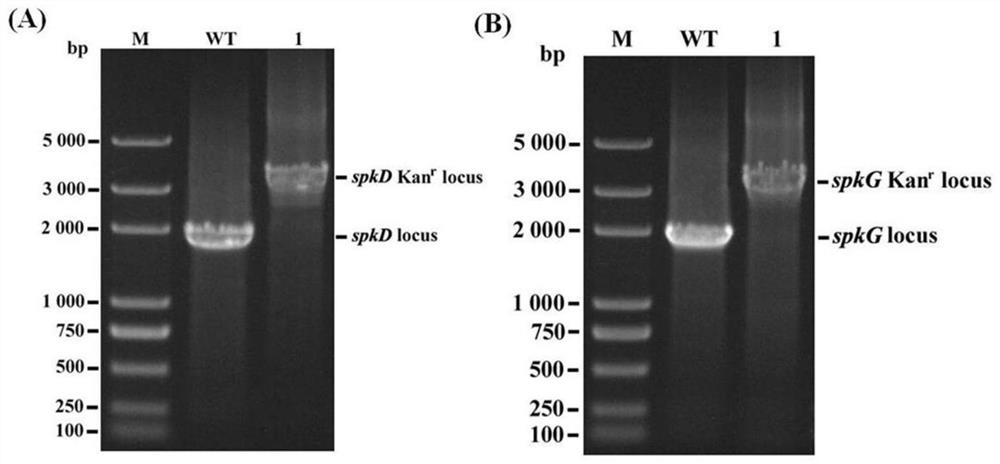
[0092] The acquisition of spkD gene knockout (insertion inactivation) mutant strain and spkG gene knockout (insertion inactivation) mutant strain:
[0093] Take the logarithmic culture period (OD 730 =0.6) (Culture condition: BG-11 liquid medium, 30°C, light condition 40μmol·m -2 ·s -1 ) Synechocystis PCC6803 culture solution 30ml, at room temperature, centrifuge at 4500g for 8min, discard the supernatant; add fresh BG-11 liquid medium to wash once, centrifuge, remove the culture medium, add fresh BG-11 liquid medium to final concentration OD 730 =4.8, and immediately used for transformation, the specific transformation process; the algae liquid collected is divided into 1.5ml EP tubes (400 μl per tube), and each tube adds 5 μg of plasmid (respectively for the plasmid 007-spkD- prepared in Example 2) kan and 007-spkG-kan), and incubated for 6 hours under low light conditions (light conditions: 10 μmol·m -2 ·s -1 , the temperature is 30°C), during which the mixture was sli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com