SVC optimization control method and device for suppressing DC continuous commutation failure
A technology for optimizing control and commutation failure. It is applied in circuit devices, AC network circuits, flexible AC transmission systems, etc. It can solve the coordination and cooperation of DC system recovery that cannot be considered for dynamic reactive power compensation equipment, and the continuous commutation failure of DC system, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of coordinated recovery and risk reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A SVC optimization control method for suppressing DC continuous commutation failure, comprising steps:
[0046] Step 1, when it is detected that the DC control and protection system outputs the first DC commutation failure signal, the control signal CA is optimized through electrical quantity calculation;
[0047] Electrical quantities include: DC system commutation voltage, DC arc extinguishing angle, SVC control voltage reference value;
[0048] The calculation process of the optimized control signal CA is:
[0049] If the formulas (1)~(3) are satisfied at the same time, the optimization control signal CA is 0:
[0050] γ(t)>γ ref (1)
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] Among them, t is the moment, γ(t) is the real-time value of the DC arc extinguishing angle at the moment t, γ ref is the reference value of DC arc extinguishing angle, u ac (t) is the effective value of the DC system commutation voltage detected at time t;
[0054] 2) If the formulas (4) and (5) ar...
Embodiment 2
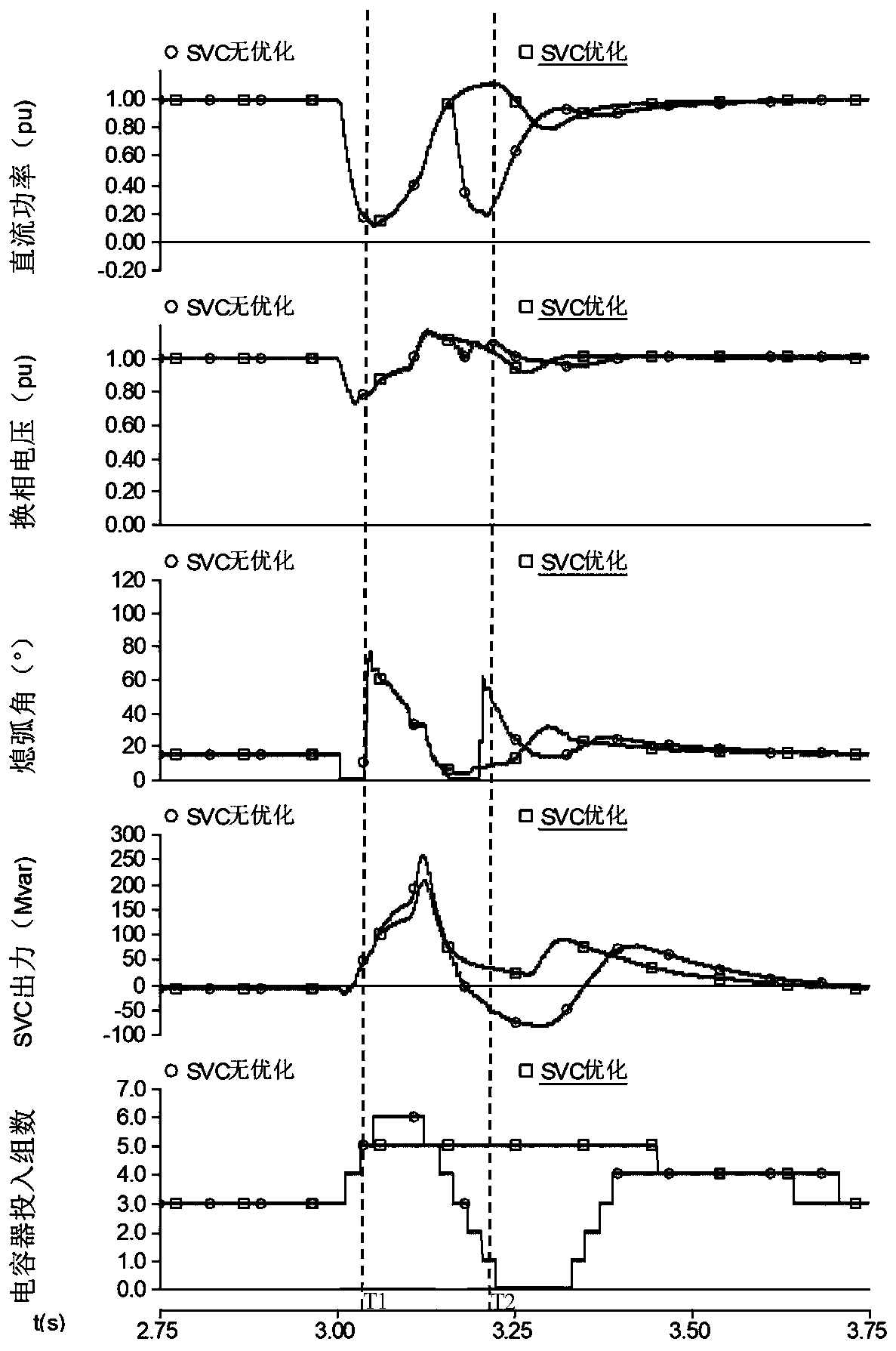
[0064] Such as figure 1 As shown, taking the CIGRE (International Conference on Large Power Grids) DC system as an example, the simulation is carried out in the electromagnetic transient simulation software PSCAD. A TCR-TSC type SVC is installed at the DC receiving end. The SVC adopts constant voltage control (the voltage reference value is 1.0p.u.). The fault occurs at 3s, and the fault lasts for 0.1s (five cycles).
[0065] Judging that the arc extinguishing angle rises above the reference value at T1, the rate of change of the arc extinguishing angle is greater than 0, the rate of change of the commutation voltage is greater than 0, and the formulas (1) to (3) are satisfied at the same time, the control signal CA is set to 0, which is consistent with the original control The phase sum of the signal KB is 0, and the capacitor is no longer switched; at T2, the commutation voltage drops below the SVC control reference voltage, and the change rate of the commutation voltage is ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] An SVC optimization control device for suppressing DC continuous commutation failure, comprising:
[0069] The optimization control signal CA calculation module is used to optimize the control signal CA through electrical quantity calculation when the DC control and protection system is detected to output the DC first commutation failure signal;
[0070] Electrical quantities include: DC system commutation voltage, DC arc extinguishing angle, SVC control voltage reference value;
[0071] The calculation process of the optimized control signal CA is:
[0072] If the formulas (1)~(3) are satisfied at the same time, the optimization control signal CA is 0:
[0073] γ(t)>γ ref (1)
[0074]
[0075]
[0076] Among them, t is the moment, γ(t) is the real-time value of the DC arc extinguishing angle at the moment t, γ ref is the reference value of DC arc extinguishing angle, u ac (t) is the effective value of the DC system commutation voltage detected at time t;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com