Hydrophilic polyamide reverse osmosis membrane with compact surface as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of reverse osmosis membrane and polyamide, used in reverse osmosis, semi-permeable membrane separation, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as membrane water flux decline
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
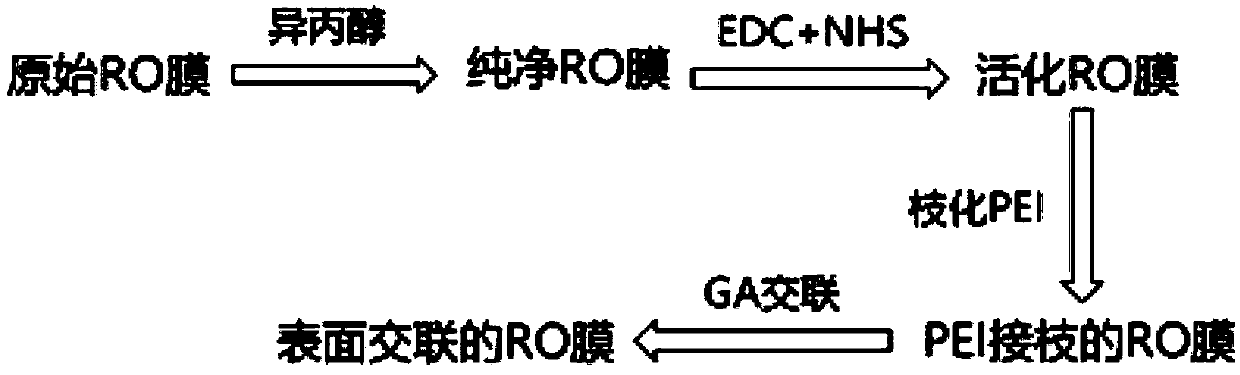
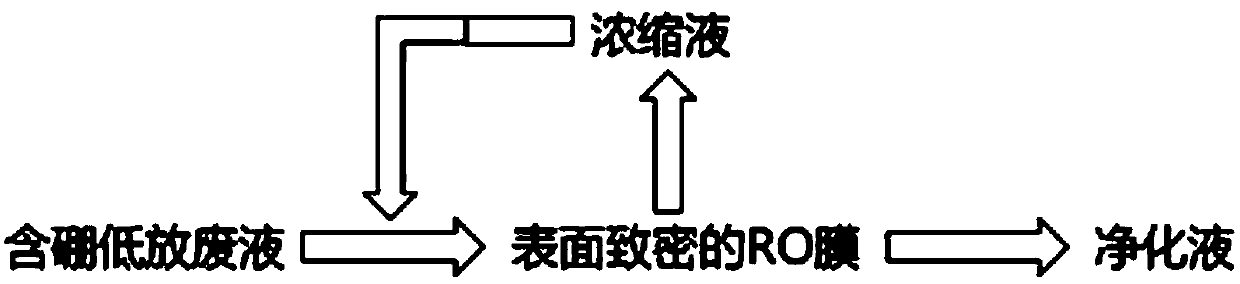
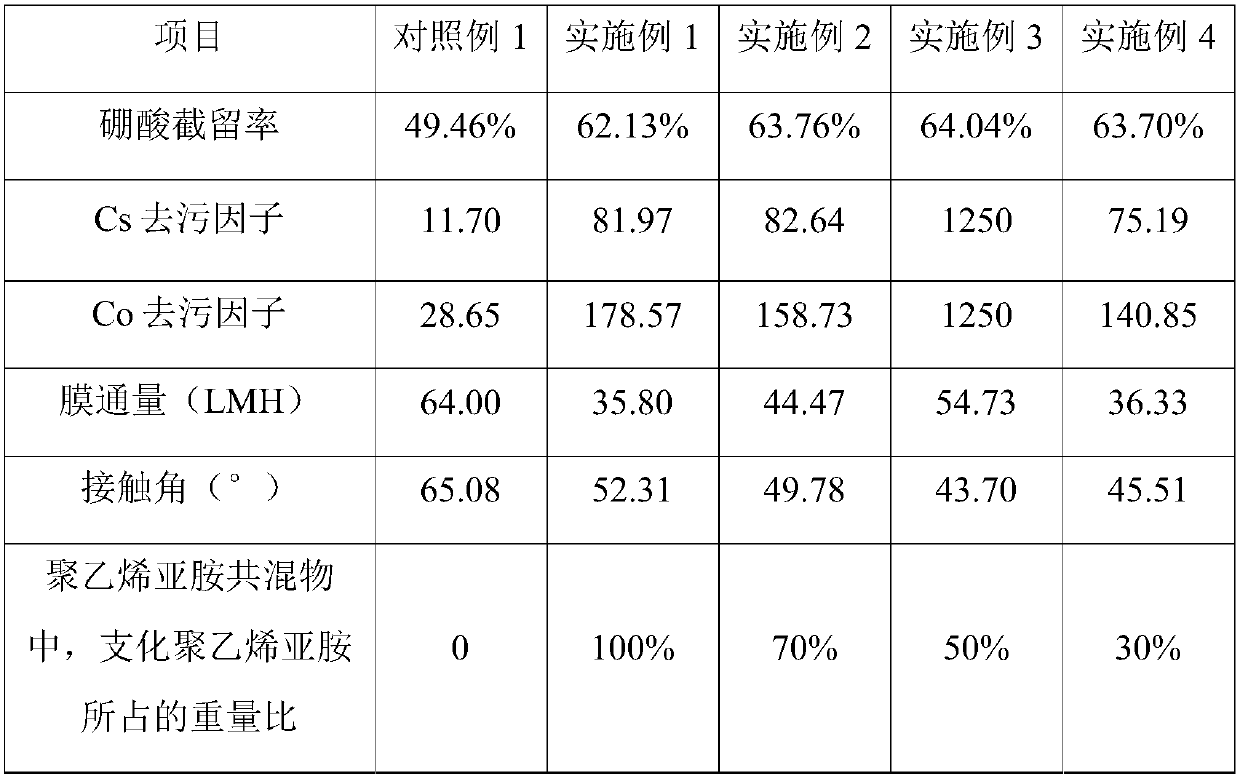
[0039] A method for intercepting boric acid in nuclear power plant liquid effluents, comprising the steps of: placing a reverse osmosis membrane (polyamide commercial reverse osmosis membrane LE) in 25% isopropanol solution to soak for 20 minutes, and then cleaning with deionized water 6 times, 30 minutes each time, store in deionized water at 4°C; then place the reverse osmosis membrane in the modification pool, cover with carbodiimide solution for 10 minutes, then add N-hydroxysuccinimide solution , poured out the waste liquid after covering for 50 minutes, and cleaned the reverse osmosis membrane with deionized water for 2 times; then the concentration of the reverse osmosis membrane was 5%, and the proportion of branched polyethyleneimine (branching degree was 60%) was 100%. The solution was covered for 12 hours, and light-shielding treatment was carried out during the process. Afterwards, the waste liquid was poured out, and the membrane was washed twice with deionized wat...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A method for intercepting boric acid in nuclear power plant liquid effluents, comprising the steps of: placing a reverse osmosis membrane (polyamide commercial reverse osmosis membrane LE) in 25% isopropanol solution to soak for 20 minutes, and then cleaning with deionized water 6 times, 30 minutes each time, store in deionized water at 4°C; then place the reverse osmosis membrane in the modification pool, cover with carbodiimide solution for 10 minutes, then add N-hydroxysuccinimide solution , poured out the waste liquid after covering for 50 minutes, and cleaned the reverse osmosis membrane 2 times with deionized water; then the concentration of the reverse osmosis membrane was 5%, and the proportion of branched polyethyleneimine (branching degree was 60%) was 70%. The solution was covered for 12 hours, and light-shielding treatment was carried out during the process. Afterwards, the waste liquid was poured out, and the membrane was washed twice with deionized water to...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A method for intercepting boric acid in nuclear power plant liquid effluents, comprising the steps of: placing a reverse osmosis membrane (polyamide commercial reverse osmosis membrane LE) in 25% isopropanol solution to soak for 20 minutes, and then cleaning with deionized water 6 times, 30 minutes each time, store in deionized water at 4°C; then place the reverse osmosis membrane in the modification pool, cover with carbodiimide solution for 10 minutes, then add N-hydroxysuccinimide solution , poured out the waste liquid after covering for 50 minutes, and cleaned the reverse osmosis membrane 2 times with deionized water; then the concentration of the reverse osmosis membrane was 5%, and the proportion of branched polyethyleneimine (branching degree was 60%) was 50%. The solution was covered for 12 hours, and light-shielding treatment was carried out during the process. Afterwards, the waste liquid was poured out, and the membrane was washed twice with deionized water to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com