Manufacturing process of metal seated ball valve nickel-based tungsten carbide wear-proof coating
A technology of nickel-based tungsten carbide and wear-resistant coating, which is applied in the direction of metal material coating process, coating, fusion spraying, etc., and can solve the problems of easy peeling off of wear-resistant material coating, fast heating speed, and slow heating process , to achieve the effect of solving poor wear resistance, improving wear resistance, and uniform heating temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
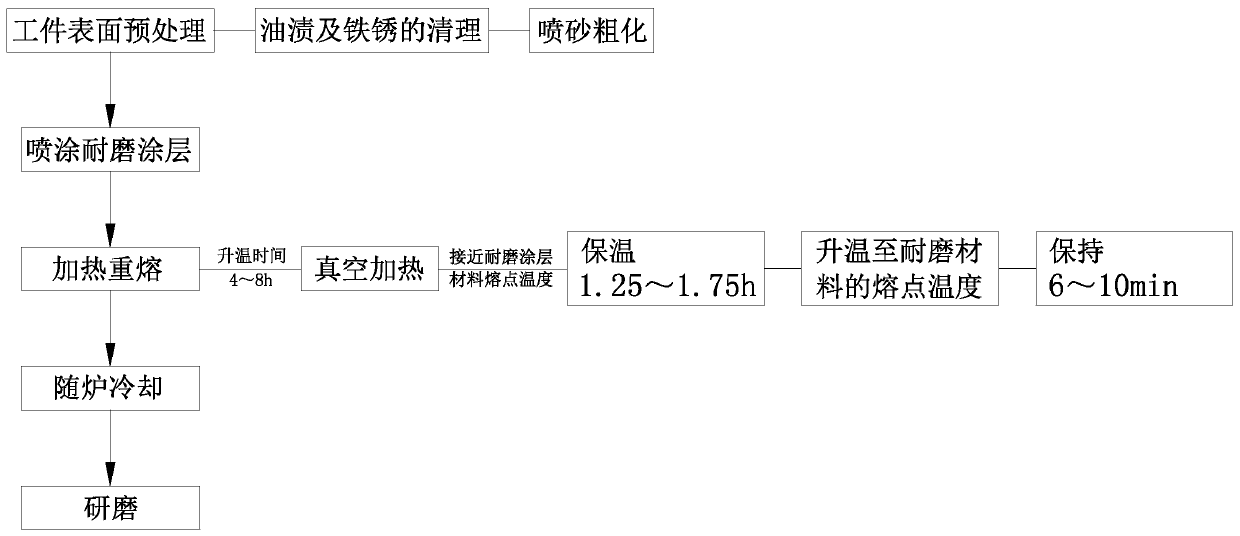
[0032] Example: A manufacturing process of nickel-based tungsten carbide wear-resistant coating for metal hard-sealed ball valves, the process is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0033] S1. Surface pretreatment of the workpiece: surface cleaning and roughening of the machined ball and valve seat;
[0034] S2. Spray wear-resistant coating: use supersonic flame spraying process to evenly spray wear-resistant coating powder material to the surface of the ball and valve seat;
[0035] S3. Heating and remelting: put the sprayed ball and valve seat into a vacuum furnace in batches for heating and remelting, so that both the ball and the valve seat are metallurgically bonded with the wear-resistant material;
[0036] S4. Cooling: After the ball and the valve seat are remelted, they are slowly cooled together with the vacuum furnace. The whole part is cooled evenly, and it is not easy to produce cracks and other defects;
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com