Method and system for extracting stray capacitance of igbt dynamic parameter test circuit
A technology for testing circuits and dynamic parameters. It is applied in the direction of measuring resistance/reactance/impedance, measuring electricity, and capacitance measurement. It can solve problems such as current distortion, inability to obtain stray capacitance in the IGBT test circuit, and affecting device parameter test results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
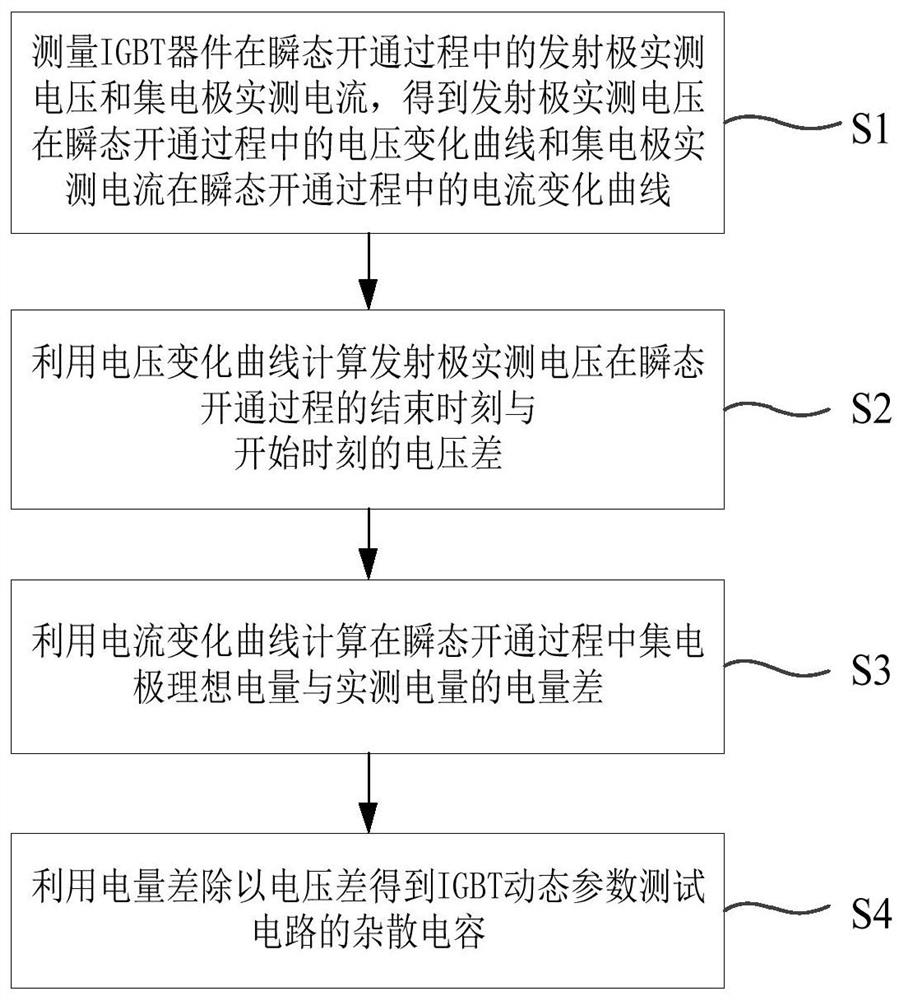
[0044] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for extracting stray capacitance of an IGBT dynamic parameter test circuit, wherein the IGBT dynamic parameter test circuit is used to connect an IGBT device to test the IGBT device, such as figure 1 As shown, the method for extracting the stray capacitance of the IGBT dynamic parameter test circuit according to the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
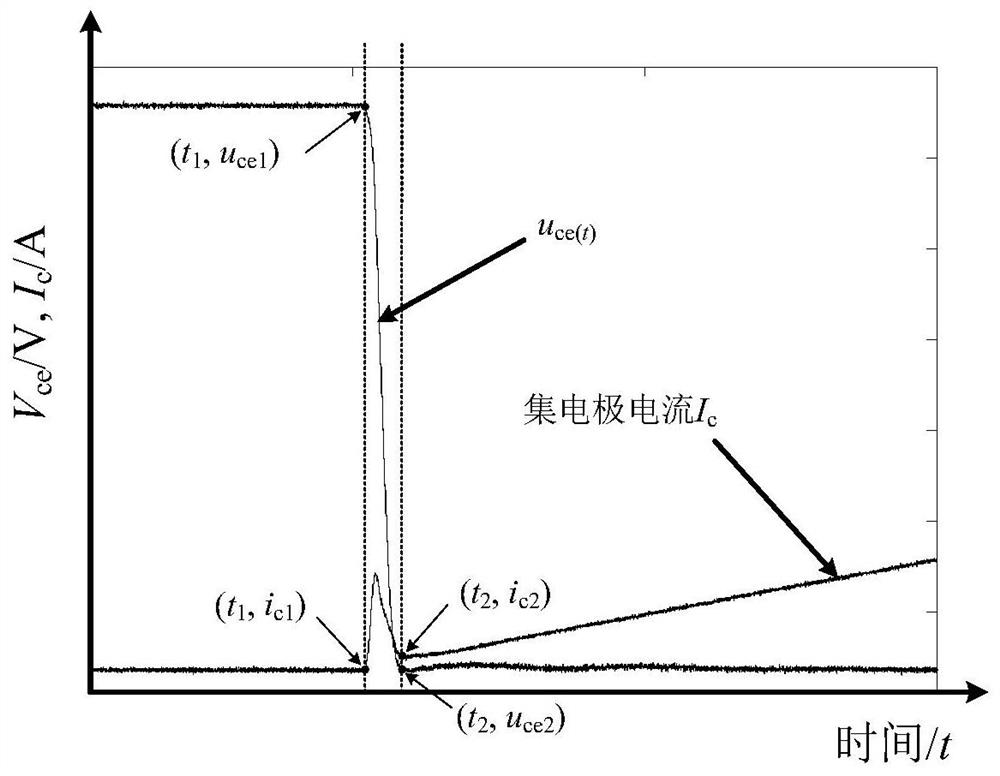
[0045] Step S1: Measure the measured voltage of the emitter and the measured current of the collector during the transient turn-on process of the IGBT device, and obtain the voltage change curve of the measured voltage of the emitter during the transient turn-on process and the measured current of the collector during the transient turn-on process. Current variation curve.
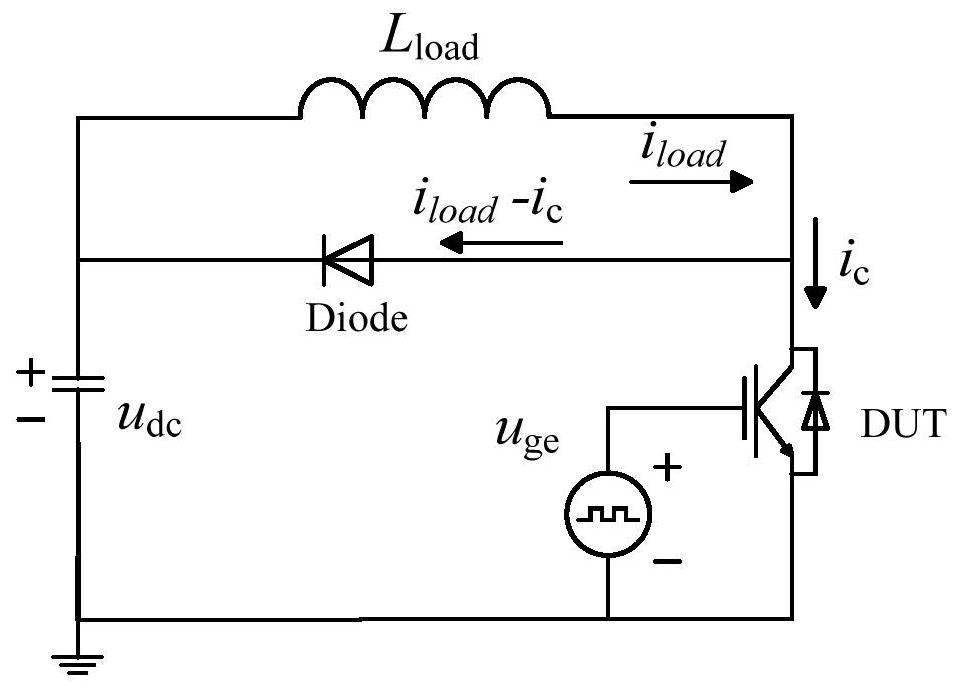
[0046] In the embodiment of the present invention, an IGBT dynamic parameter test platform is built based on the double-pulse test method, and the test circuit sc...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The embodiment of the present invention provides an IGBT dynamic parameter test circuit stray capacitance extraction system, such as Figure 5 shown, including:
[0092] The acquisition module 1 is used to measure the measured voltage of the emitter and the measured current of the collector during the transient turn-on process of the IGBT device, and obtain the voltage change curve of the measured voltage of the emitter during the transient turn-on process and the measured current of the collector during the transient turn-on. The current change curve in the process; this module executes the method described in step S1 in Embodiment 1, and details are not repeated here.
[0093] The first calculation module 2 is used to calculate the voltage difference between the actual measured voltage of the emitter at the end moment of the transient turn-on process and the start moment by using the voltage change curve; this module executes the method described in step S2 in Embodim...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Embodiments of the present invention provide an electronic device, such as Image 6 As shown, it includes: at least one processor 401 , such as a CPU (Central Processing Unit, central processing unit), at least one communication interface 403 , memory 404 , and at least one communication bus 402 . Among them, the communication bus 402 is used to realize the connection and communication between these components. The communication interface 403 may include a display screen (Display) and a keyboard (Keyboard), and the optional communication interface 403 may also include a standard wired interface and a wireless interface. The memory 404 may be a high-speed RAM memory (Ramdom Access Memory, volatile random access memory), or may be a non-volatile memory (non-volatile memory), such as at least one disk memory. The memory 404 can optionally also be at least one storage device located away from the aforementioned processor 401 . The processor 401 may execute the method for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com