High-light-transmittance simplified cultivation method for hybrid japonica rice
A technology for hybrid japonica rice and a cultivation method, which is applied in the field of hybrid japonica rice with high light transmittance and light simplification, can solve the problems of insignificant yield advantage and low efficiency of hybrid japonica rice, and achieve the effects of improving the tillering ability of a single plant, avoiding premature aging and developing a root system.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: the present invention provides a kind of hybrid japonica rice high light transmittance light simplified cultivation method, comprises the following steps:
[0025] Step 1: Soil preparation. Before transplanting, sprinkle the base fertilizer on the original stubble of the paddy field and soak the field with water. After 24 hours or a little longer, the depth of the water layer in the field reaches the level of 3cm-4cm in the field. Use a rotary tiller for rotary tillage. Break up the soil clods and rice stubble, then use a walking tractor to harrow the ground, and pull the board to level it.
[0026] Step 2: Variety selection. In this example, the variety selection makes full use of the variety characteristics, and selects a combination of hybrid japonica rice that can be safely matured locally and has a strong edge row advantage, so as to improve the yield advantage of hybrid japonica rice.
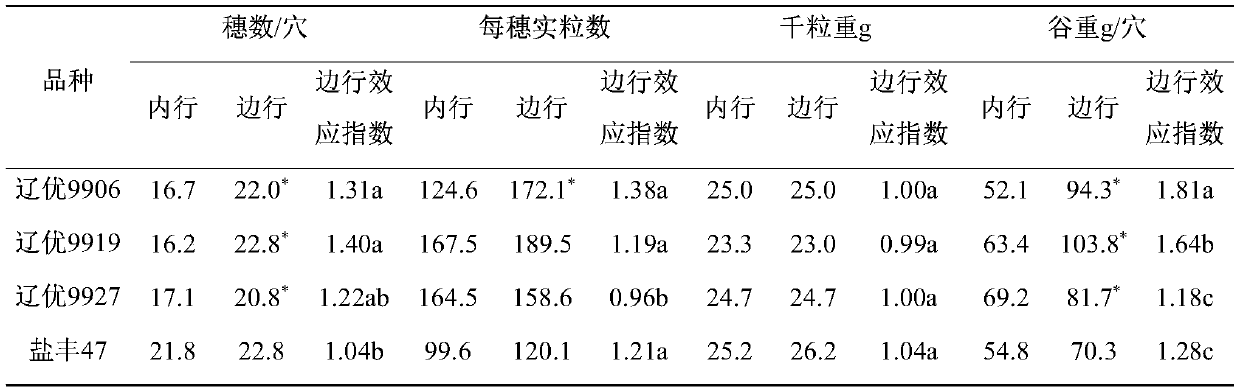
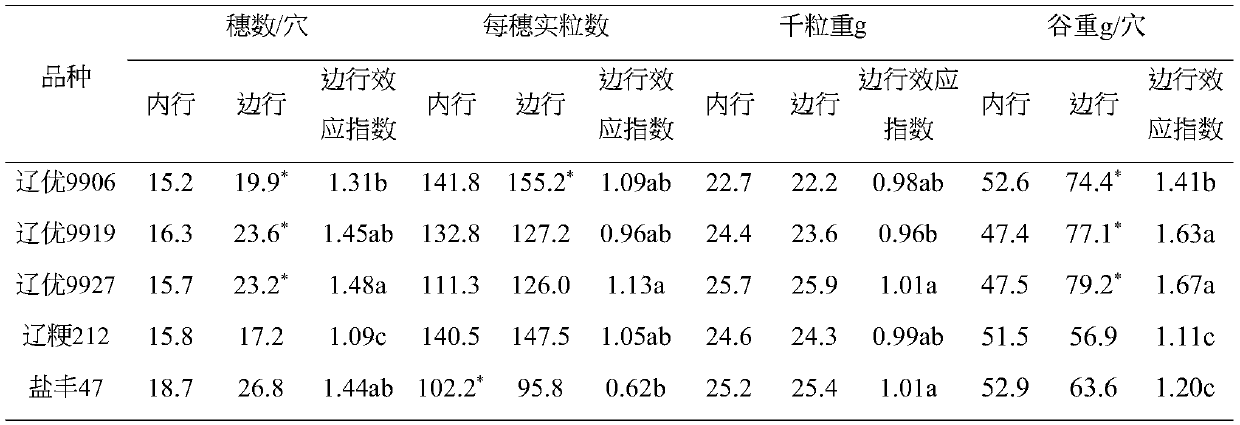
[0027] In 2019, research on the marginal effects of different va...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: what this example is different from embodiment 1 is: in this example cultivation method:
[0045] For sowing, choose the variety with a thousand-grain weight less than 24g, sow about 100g of dry seeds; for varieties greater than 26g, sow 110-120g of dry seeds;
[0046] Seedling transplanting adopts a six-row rice transplanter with a row spacing of 30 cm, and every six rows are empty, and the plant spacing is adjusted to 16 cm. Compared with the commonly used cultivation density of farmers 30cm×18cm, 0.05 million holes per mu are reduced, and the basic seedlings are reduced by 4.0%. Since one row has a significant side row effect, two out of every six rows have a side row effect. The edge row effect index should be above 1.6, such as: Liaoyou 9919, Liaoyou 9906, etc., which can make up for the yield loss caused by the reduction of basic seedlings in theory.
[0047] In this example, 60% of the base fertilizer was applied during soil preparation, 30% of th...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: The difference between this example and Example 1 is that in this example cultivation method: the described rice transplanting adopts a four-row rice transplanter, the four rows of rice transplanting are vacated and one row is not transplanted, and the plant spacing is adjusted to 14-16cm. Compared with the commonly used cultivation density of farmers, which is 30cm×18cm, the number of holes per mu is reduced by 0.05-0.13 million holes, which is 4.0%-8.1%. Variety edge row effect index should be 1.6-1.7.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com