Relative position self-adaptive control method for spacecraft approaching space rolling target
A technology of self-adaptive control and relative position, applied in attitude control and other directions, which can solve the problems of not strictly guaranteeing mission safety, complex parameter selection process, and limited processing capacity of spacecraft on-board computing equipment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
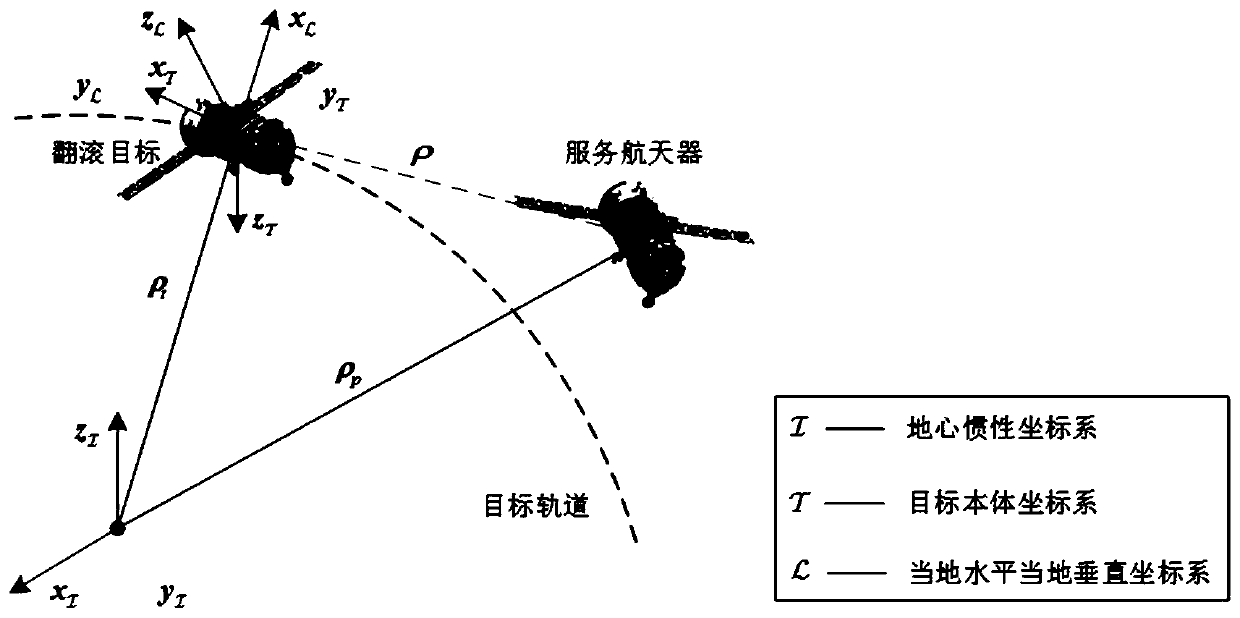
[0070] In the first step, based on the transport theorem, a relative positional dynamics model is established.
[0071] Such as figure 2 As shown, with the center of the earth as the origin, the earth-centered inertial coordinate system is established With the center of mass of the space tumbling target as the origin, establish a local horizontal local vertical coordinate system and target system Different from the traditional relative position dynamics modeling method (the relative position dynamics model is established in the local horizontal and local vertical coordinate systems), the present invention is based on the transmission theorem, and establishes a new relative position dynamics model in the target system as follows:
[0072]
[0073]
[0074] Among them, ρ represents the position vector of the spacecraft in the target system relative to the space tumbling target; v represents the velocity vector of the spacecraft in the target system relative to the sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com