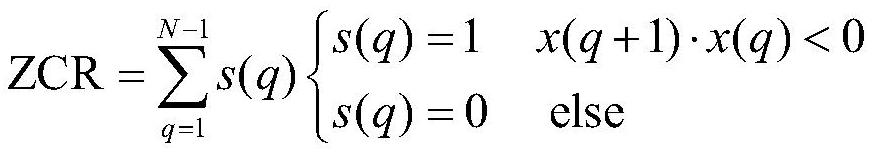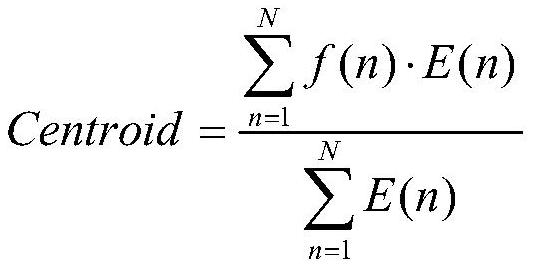Underwater acoustic target ranging method based on feature extraction and neural network
A neural network and feature extraction technology, applied in neural learning methods, biological neural network models, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as inability to achieve positioning without depth sensors, inability to use positioning targets for real-time positioning, large measurement errors, etc., to achieve cost Low, low average relative error, and the effect of avoiding manual intervention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
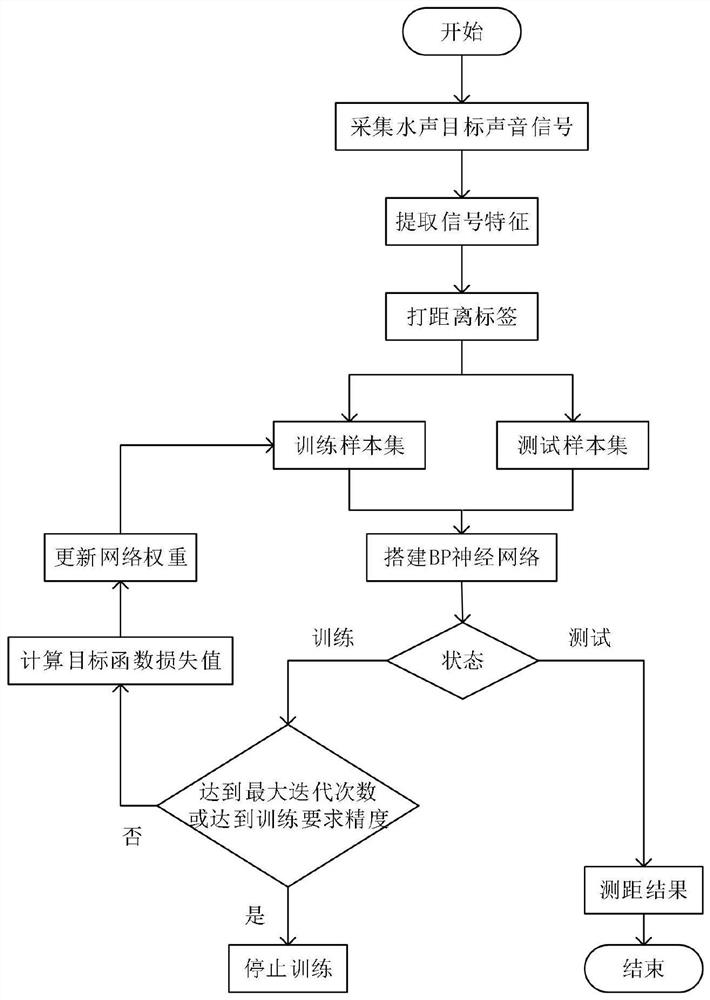
[0044] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the present invention and implement it, but the examples given are not intended to limit the present invention.
[0045] 1. Collect the underwater acoustic signals sent by the underwater acoustic target at different distances, and split the data by second, and the data of one second is taken as a sample;
[0046] 2. Divide each sample into frames, set the frame length to 20ms, and set the frame shift to 10ms;
[0047] 3. Calculate the zero-crossing rate of the time-domain waveform, the 2nd, 5th, and 8th coefficients of MFCC, spectral centroid, spectral skewness, spectral entropy, and spectral sharpness for each frame of data of each sample;
[0048] The zero-crossing rate (ZCR) is defined as:
[0049]
[0050] Among them, N is the number of sampling points per frame, and x(q) is the ampli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com