Method for solving too low low-temperature ballistic work after tempering of high alloy structure steel
A technology of alloy structural steel and low-temperature impact, which is applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of low low-temperature impact energy, and achieve the effects of preventing low-temperature impact energy from being low, preventing internal loss, and avoiding temper brittleness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] The chemical composition of the high-alloy structural steel in this embodiment includes by weight percentage: C 0.45-0.50%, Si 0.40-0.50%, Mn 0.45-0.60%, P≤0.010%, S≤0.005%, Cr 2.00-2.50 %, Ni 4.00-4.50%, Mo 1.55-1.60%, V 0.15-0.20%, W 0.50-0.60%, Cu≤0.060%, Al≤0.030%, and the rest are Fe and unavoidable impurities.
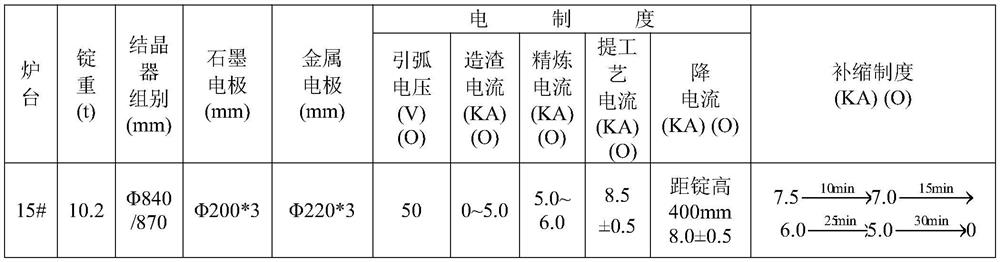
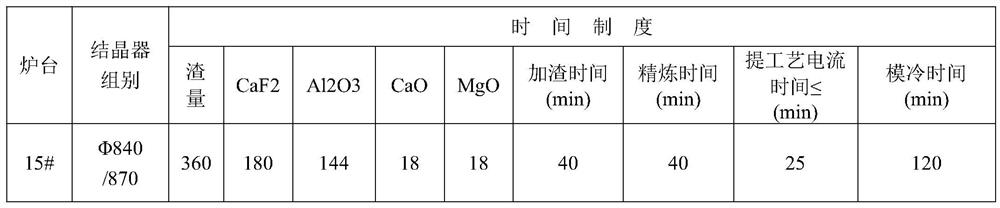
[0019] The production process of high-alloy structural steel in this example is: electric furnace smelting + LF refining + VD vacuum refining → pouring steel ingot → rolling electrode blank 220*220mm → hot annealing → grinding → electroslag remelting → electroslag ingot hot delivery Annealing→heating, forging→annealing→primary roughing→flaw detection→drilling→secondary roughing→flaw detection→quenching and tempering→straightening→inspection, inspection→flaw detection→hand in.
[0020] High-alloy structural steel electric furnace smelting:
[0021] 1. In order to reduce the content of harmful elements as much as possible, the ingredients require pig iron ≥...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The chemical composition of the high-alloy structural steel in this embodiment includes by weight percentage: C 0.45-0.50%, Si 0.40-0.50%, Mn 0.45-0.60%, P≤0.010%, S≤0.005%, Cr 2.00-2.50 %, Ni 4.00-4.50%, Mo 1.55-1.60%, V 0.15-0.20%, W 0.50-0.60%, Cu≤0.060%, Al≤0.030%, and the rest are Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0067] The production process of high-alloy structural steel in this example is: electric furnace smelting + LF refining + VD vacuum refining → pouring steel ingot → rolling electrode blank 220*220mm → hot annealing → grinding → electroslag remelting → electroslag ingot hot delivery Annealing→heating, forging→annealing→primary roughing→flaw detection→drilling→secondary roughing→flaw detection→quenching and tempering→straightening, rectification→inspection, inspection→flaw detection→hand in.
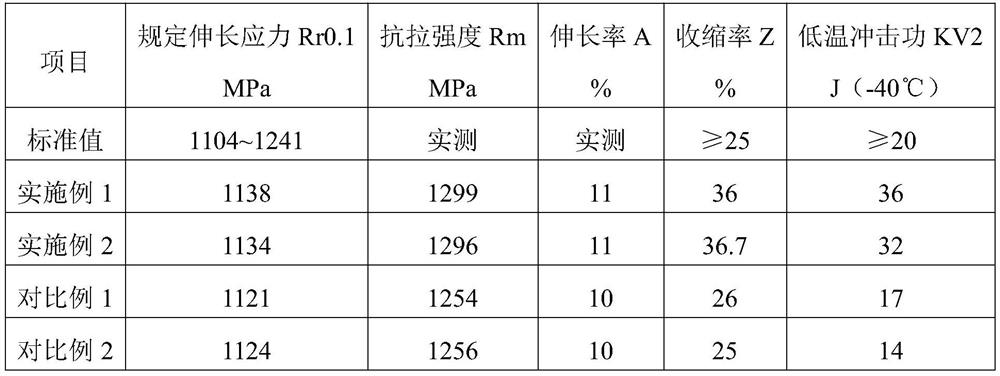
[0068] Among them, the method provided in this embodiment to solve the low-temperature impact energy of high-alloy structural steel after quenching and tempering incl...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The chemical composition of the high-alloy structural steel in this embodiment includes by weight percentage: C 0.45-0.50%, Si 0.40-0.50%, Mn 0.45-0.60%, P≤0.010%, S≤0.005%, Cr 2.00-2.50 %, Ni 4.00-4.50%, Mo 1.55-1.60%, V 0.15-0.20%, W 0.50-0.60%, Cu≤0.060%, Al≤0.030%, and the rest are Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0073] The production process of high-alloy structural steel in this example is: electric furnace smelting + LF refining + VD vacuum refining → pouring steel ingot → rolling electrode blank 220*220mm → hot annealing → grinding → electroslag remelting → electroslag ingot hot delivery Annealing→heating, forging→annealing→primary roughing→flaw detection→drilling→secondary roughing→flaw detection→quenching and tempering→straightening, rectification→inspection, inspection→flaw detection→hand in.
[0074] Among them, the method provided in this embodiment to solve the low-temperature impact energy of high-alloy structural steel after quenching and tempering incl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com