Structure for improving return loss and application
A return loss, integrated technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problem of mutual restriction of return loss, and achieve the effect of improving return loss, avoiding reliability risks, and improving mass production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
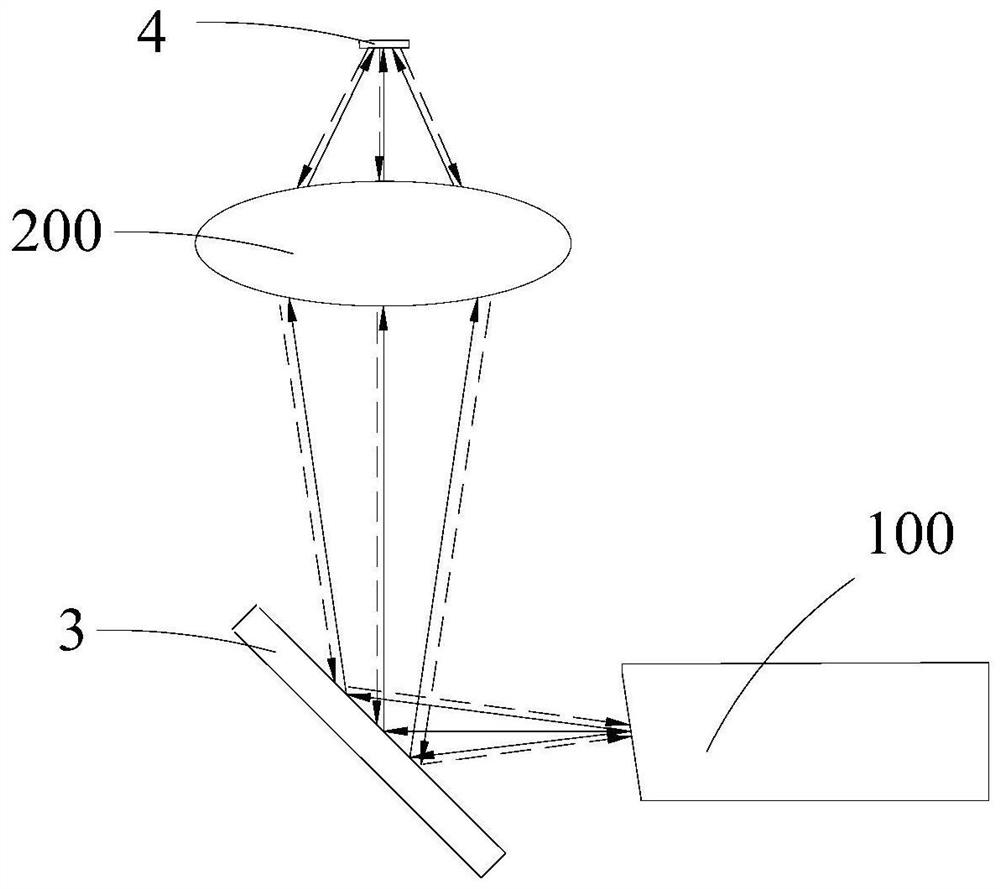
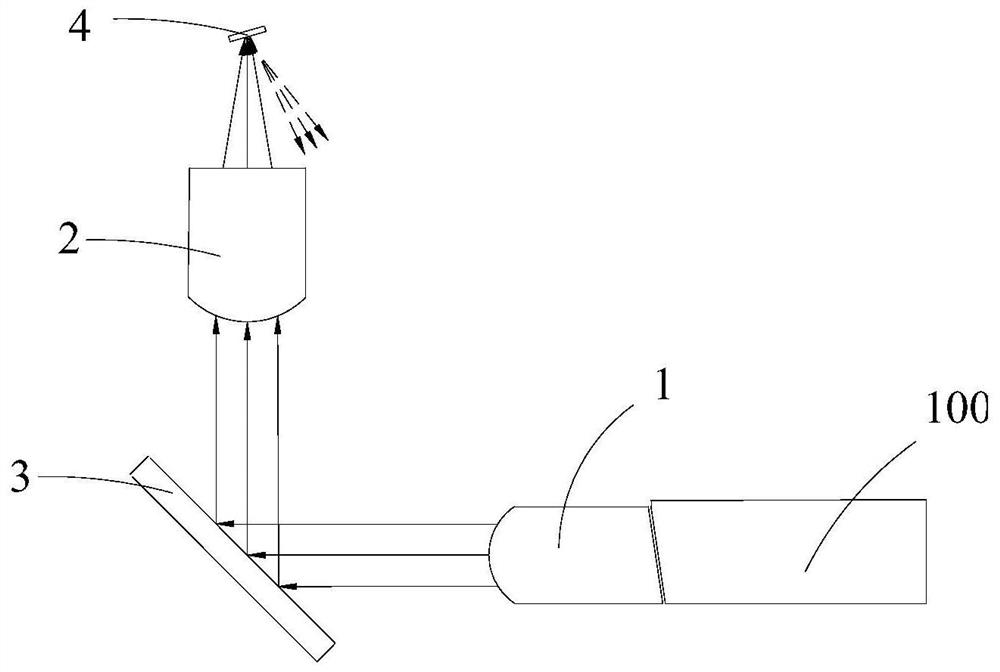
[0047] A structure to improve return loss, such as Figure 4 As shown, it includes a first collimating lens 1, a filter glass 3, a second collimating lens 2 and a PD chip 4;
[0048] The first collimating lens 1 is used to convert incident light into collimated light;
[0049] The axis of the second collimating lens 2 is perpendicular to the axis of the first collimating lens 1;
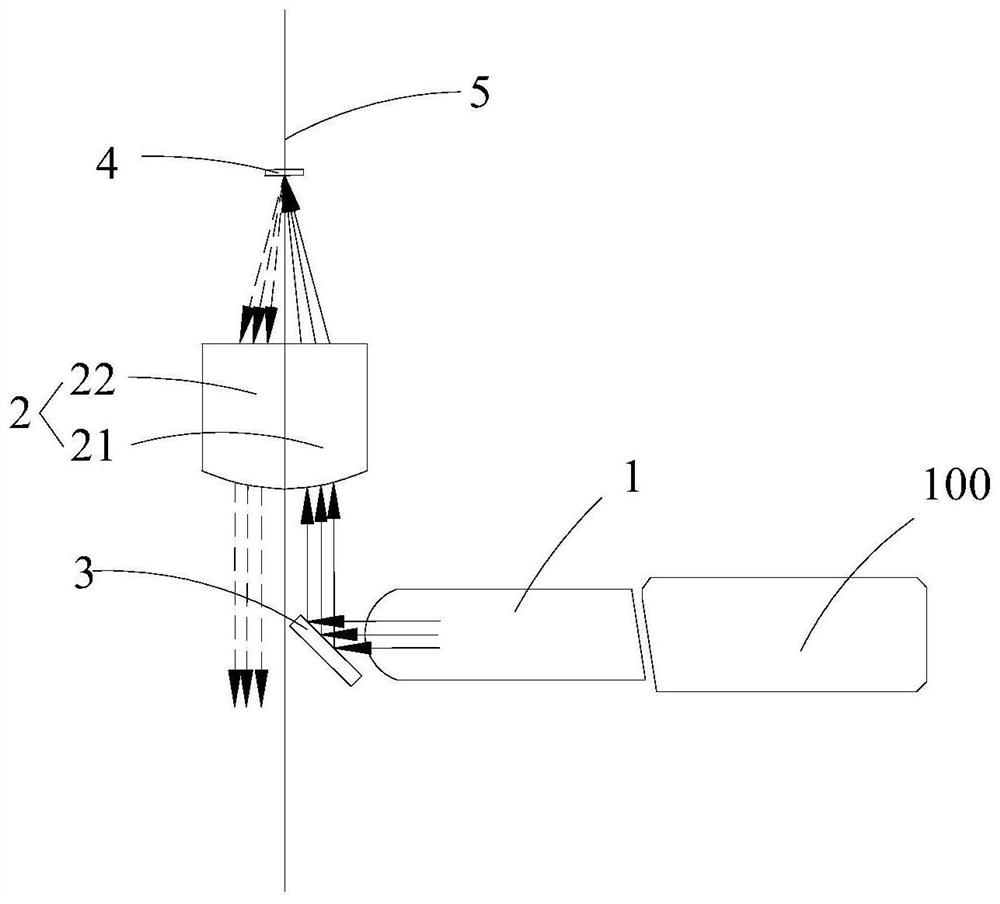
[0050] The second collimating lens 2 is provided with a virtual plane 5, the axis of the first collimating lens 1 is perpendicular to the virtual plane 5, and the axis of the second collimating lens 2 is located in the virtual plane 5;
[0051] The virtual plane 5 divides the second collimating lens 2 into a first partial lens 21 close to the first collimating lens 1 and a second partial lens 22 far from the first collimating lens 1;
[0052] The filter glass 3 is located on the side of the virtual plane 5 close to the first collimating lens 1, and is used to reflect the collimated light to the first partial l...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the filter glass 3 is located on the side of the virtual plane 5 away from the first collimating lens 1 and is used to reflect the collimated light to the second partial lens 22. Its structure and light path are as Figure 4 As shown, this structure is used for single-fiber bidirectional optical components.
Embodiment 3
[0062] This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that the filter glass 3 includes a first filter glass 31 and a second filter glass 32. The first filter glass 31 is a 13° filter glass, and the second filter glass 32 is a +32° filter glass.
[0063] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the first filter glass 31 is located outside the optical path of the second collimating lens 2, that is, the first filter glass is not on the optical path of incident light and reflected light. The second filter glass 32 is located on the side of the virtual plane 5 close to the first collimating lens 1; the light of the optical fiber is converted into collimated light through the first collimating lens 1, and then reflected to the second through the first filter glass 31 The filter glass 32 is then reflected to the first partial lens 21 and reaches the photosensitive surface 4. The reflected light from the photosensitive surface 4 passes through the second partial lens 22 of the second collimating l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com