Antibacterial drug based on antimicrobial peptide C-terminal connection
A technology of antibacterial drugs and antibacterial peptides, applied in the field of antibacterial drugs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Design of polypeptide machinery by PEG modification
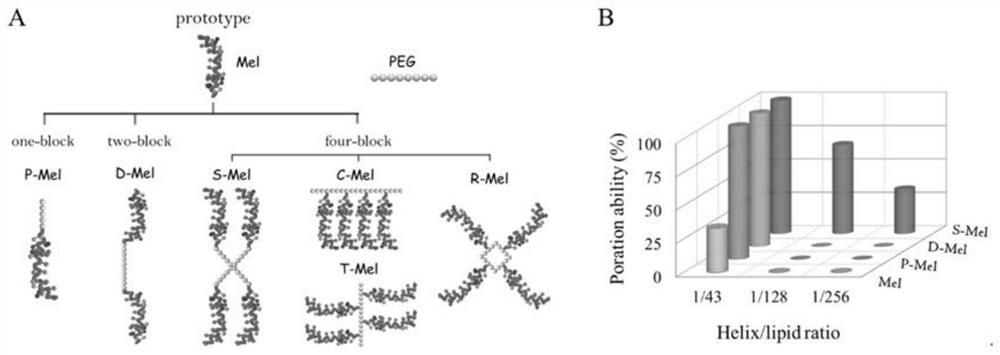
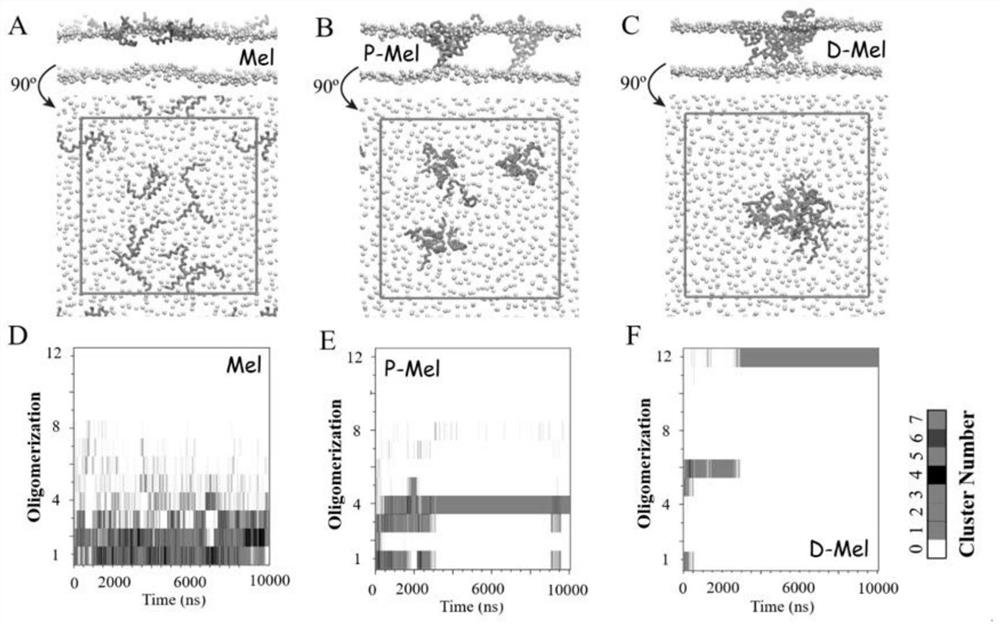
[0033]First of all, this embodiment designs Mel with single arm (a PEG short chain is connected to the C-terminus of one Mel, P-Mel) and double arms (a PEG chain twice as long is connected to the C-terminus of two Mel, D-Mel). Connectors, and simulate the situation of two kinds of connectors and native Mel forming pores on the membrane. Compared with the original type Mel at the concentration of H / L=1 / 43 to form pores (the probability of forming pores is 33%, figure 1 B), both P-Mel and D-Mel can form pores at this concentration (the probability of forming pores is 100%). In addition, native Mel forms transient pores in the membrane, while P-Mel and D-Mel form very stable pores in the membrane (the polypeptide forms a transmembrane state in the membrane). These results indicated that the pore-forming ability of Mel was significantly improved after PEGylation. And compared with the polypeptide modified a...
Embodiment 2
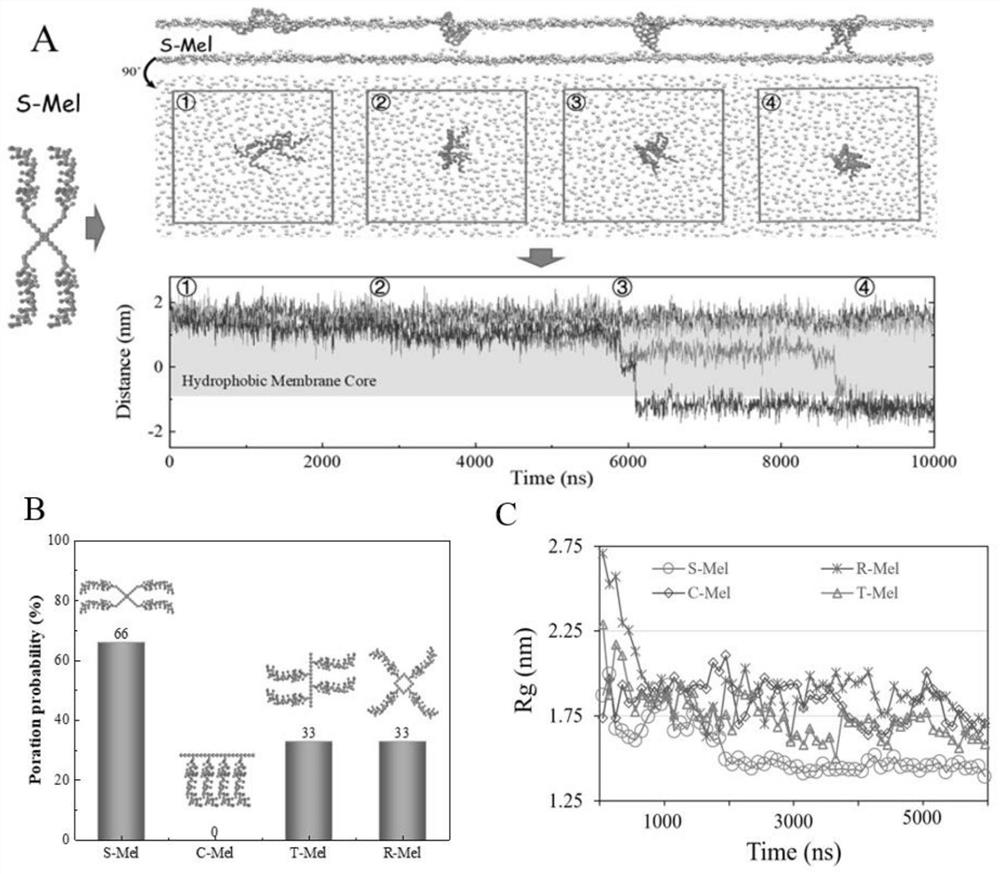
[0037] This embodiment designs a series of tetrameric polypeptide machines, including star shape (S-Mel), comb shape (C-Mel), tree shape (T-Mel) and ring shape (R-Mel), such as figure 1 a. Among them, S-Mel exhibits the strongest pore-forming ability, and it can form pores at an extremely low concentration (1 / 256).
[0038] In order to understand the specific process of S-Mel pore formation, calculate the Z component of the distance between the N end of each Mel and the membrane centroid (such as image 3 ). At the beginning, all four Mels in S-Mel were adsorbed on the membrane surface, and two Mels were slightly embedded between the head and tail of the leaf phospholipids on the membrane. The two Mels then rapidly insert into the lower leaflet of the membrane to form a transmembrane channel. By analyzing the radius of gyration of S-Mel molecules, we found that S-Mel shrinks rapidly with time, and all the Mel helices gather together before forming holes. Results at lower c...
Embodiment 3
[0042] In addition to geometry and length, other properties of PEG chains can also affect the pore-forming efficiency of S-Mel, such as stiffness, which is most likely to be regulated by external stimuli (such as light, changes in solvents, or changes in salt concentration, etc.) of. A S-Mel with enhanced chain rigidity (referred to as S*-Mel) was designed, and its pore-forming efficiency was simulated at the same concentration (1 / 128). Such as Figure 4 , the results show that when the PEG chain is very rigid, the linker has been adsorbed on the membrane surface and presents a spread state, however, when the PEG chain becomes flexible again, the helix inside the linker quickly gathers and forms a transmembrane hole . The response of S-Mel to the rigidity and flexibility of PEG chains endows it with the potential for application in different cellular environments. By adjusting the stiffness of the PEG chains, the pore-forming efficiency of the complex can be effectively adj...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com