Nuclear radiation resistant mobile cable for crown block
A nuclear radiation-resistant and mobile cable technology, which is applied in the field of cables, can solve the problems that easily affect the erection of construction supports, the large footprint of flat cables, and affect the safety of use, so as to achieve a small footprint, reduce the impact of erection, and alleviate wear effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
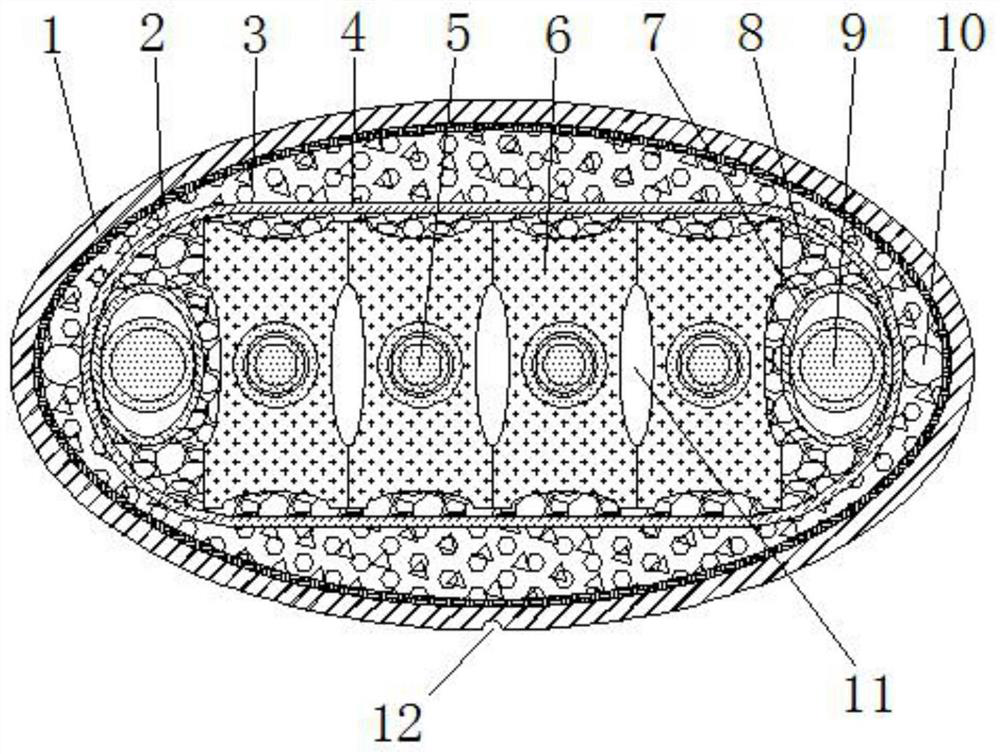
[0028] like figure 1 A nuclear radiation-resistant mobile cable for cranes shown includes a cable core, an insulating layer 4 wrapped outside the cable core, an armor layer 2 arranged outside the insulating layer 4, and an armor layer wrapped outside the armor layer 2. Sheath layer 1, the cable core includes a main core 5 and a ground core 9;
[0029] The cross-sections of the armor layer 2 and the sheath layer 1 are both oval, the sheath layer 1 is made of irradiated cross-linked polyethylene material, and the outer surface of the sheath layer 1 is provided with a A wear-resistant groove 12 extending in the length direction, and the groove surface in the wear-resistant groove 12 is sprayed with wear-resistant paint; the armor layer 2 is a sleeve-like structure formed by braiding copper tape;
[0030] The cross-section of the insulating layer 4 is flat, and its two sides are in a convex arc shape. The insulating layer 4 is an insulating layer of irradiated cross-linked polyet...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
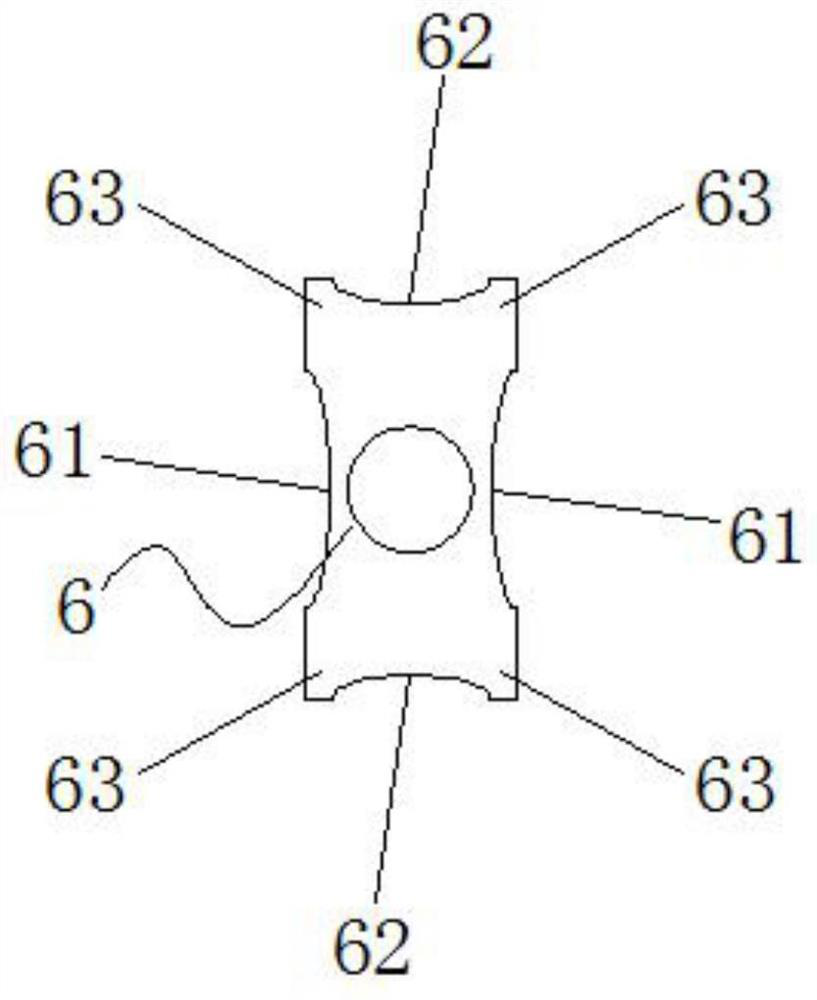
[0036] In this example, if image 3 As shown, the cable core is provided with a row of first protective sheaths 6 attached one by one, and each first protective sheath 6 is provided with two main cores 5 on the inner side, and each adjacent two first protective sheaths 6 face each other. The first arc-shaped grooves 61 on the side are pieced together to form an oval cavity 11 . The arrangement of more main wire cores 5 can be realized.
[0037] In this example, if image 3 As shown, the outer surface of the sheath layer 1 is provided with two wear-resistant grooves 12 extending along its length direction, and the two wear-resistant grooves 12 are symmetrical with respect to the cross-sectional center of the cable.
[0038] Others are the same as embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0040] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
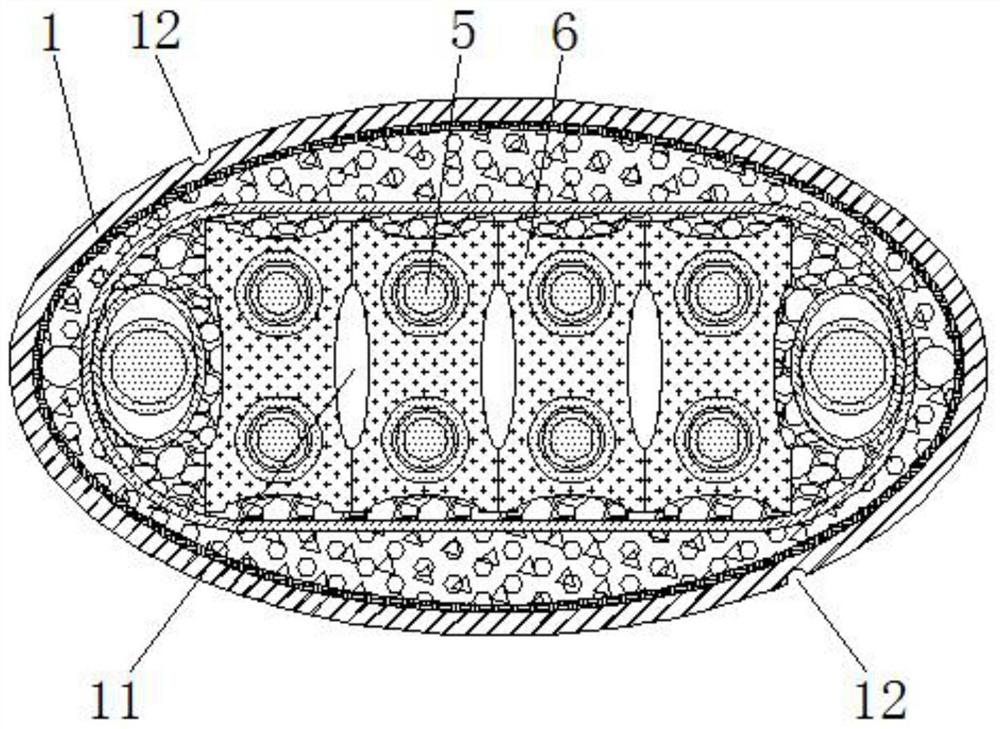
[0041] In this example, if Figure 4 and Figure 5 As shown, the cable core is provided with two rows of first protective sheaths 6 attached one by one, and the bottom of the first protective sheath 6 of the last row is attached to the top of the first protective sheath 6 of the next row, The inner side of each first protective cover 6 is provided with a main wire core 5, and the first arc-shaped grooves 61 on the opposite sides of each adjacent two first protective covers 6 are pieced together to form an oval cavity 11, and each adjacent two The second arc-shaped grooves 62 on opposite sides of the first protective sleeve 6 form an oval cavity 11. The arrangement of more main cores 5 can be realized, and the number of cavities 11 can be increased, thereby improving the flexibility of the cable.
[0042] In this example, if Figure 4 As shown, the outer surface of the sheath layer 1 is provided with four ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com