Wireless charging receiving end, wireless charging transmitting end, wireless charging system, wireless charging control method and electric vehicle
A technology of wireless charging and receiving end, which is applied in the field of transmitting end, control method, electric vehicle, system, and wireless charging receiving end, and can solve the problem of inaccurate position information obtained, inability to align power transmitting coils and power receiving coils, and interference And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
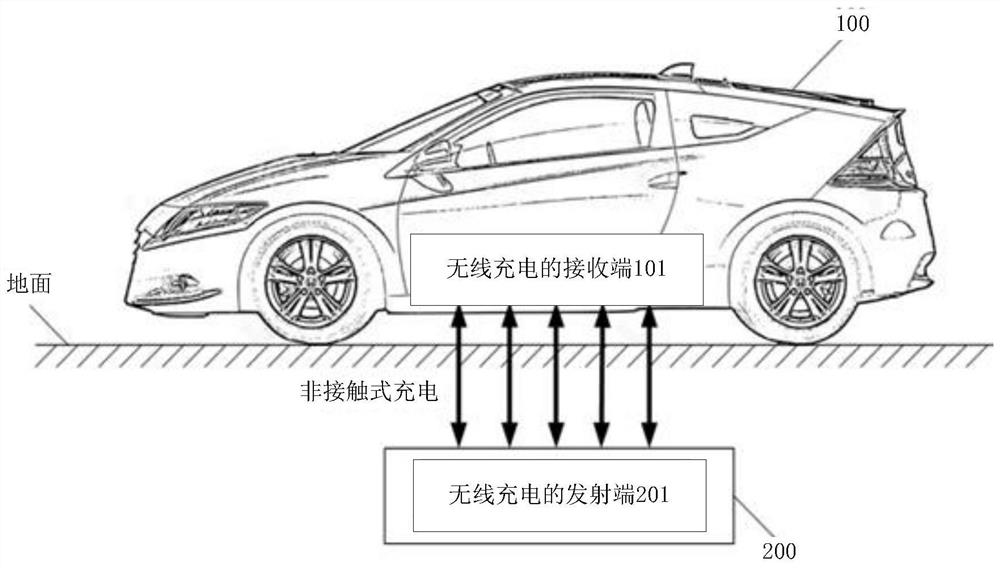
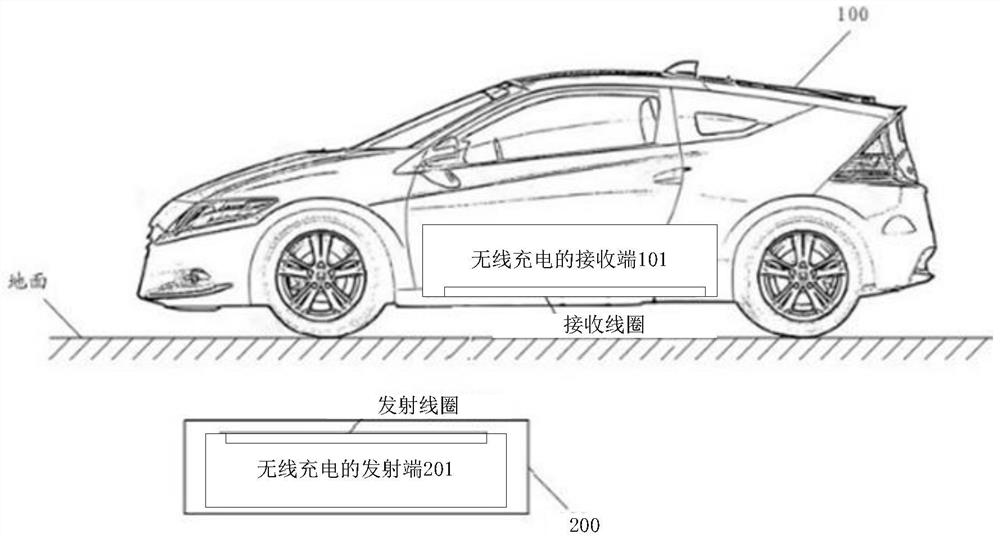
[0119] see Figure 6 , which is a schematic diagram of a wireless charging system corresponding to a wireless charging receiving end provided in an embodiment of the present application.
[0120] The wireless charging system includes a wireless charging receiving end 101 and a wireless charging transmitting end 201 .
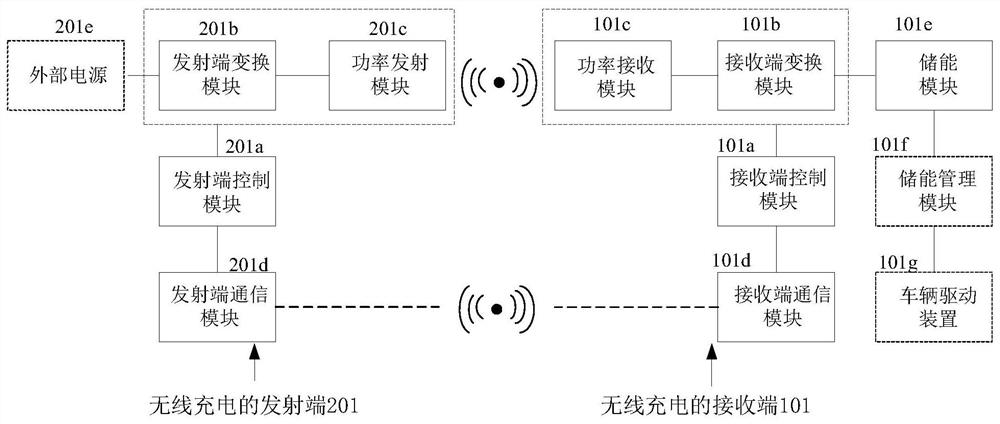
[0121] Wherein, the receiving end of wireless charging (hereinafter referred to as the receiving end) 101 includes: a receiving end controller 401 , a low frequency magnetic field receiving coil 403 and a power receiving coil (not shown in the figure).
[0122] The transmitting end 201 of wireless charging (hereinafter referred to as the transmitting end) includes: a transmitting end controller 301 , a low frequency magnetic field transmitting coil 302 and a power transmitting coil (not shown in the figure).
[0123] The power transmitting coil transmits the alternating current in the form of an alternating magnetic field.
[0124] The power receiving coil con...
Embodiment 2
[0144] The working principle of the receiving end and the transmitting end when the signal characteristic is the signal pulse width is firstly described below, and the signal pulse width is the time width of the signal pulse.
[0145] see Figure 7 , which is a schematic diagram of a wireless charging system provided in an embodiment of the present application.
[0146] Wherein, the wireless charging transmitting end includes: low frequency magnetic field transmitting coils Ltx1 and Ltx2 , transmitting end controller 301 , inverter circuit 302 and low frequency magnetic field transmitting end communication module 304 .
[0147] The receiving end of wireless charging includes: low frequency magnetic field receiving coils Lrx1-Lrx4, receiving end controller 401, detection circuit 402 and low frequency magnetic field receiving end communication module 404.
[0148] In the embodiment of the present application, the inverter circuit 302 is specifically two half-bridge inverter cir...
Embodiment 3
[0179] continue to see Figure 7 , the embodiment of the present application can be implemented based on the same hardware device as the second embodiment. For the description of the hardware device, please refer to the second embodiment. , as explained below.
[0180] The signal characteristic of the embodiments of the present application is signal encoding, and the magnetic field signal emitted by the low-frequency magnetic field transmitting coil is controlled so that the magnetic field signal can represent the encoding. The following description takes binary coding as an example to explain the signal coding method used. In practical applications, other signal coding methods can also be used, such as 4-ary coding, octal coding, etc. The principles are similar, and the embodiments of this application are no longer repeat.
[0181] When the signal coding mode is binary coding, different binary numbers can be used to represent the magnetic field signal sent by a low-frequenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com