A method for cultivating fruiting bodies by a strain of A. chinensis and its liquid strain
A technology of variegated mushrooms and liquid seeds, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of small planting scale, large-scale cultivation without market demand, and fruiting bodies obtained without cultivation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1. Isolation, Identification and Preservation of Lepista sordida DCH618CGMCC No.16980
[0083] 1. Isolation of the fungus DCH618
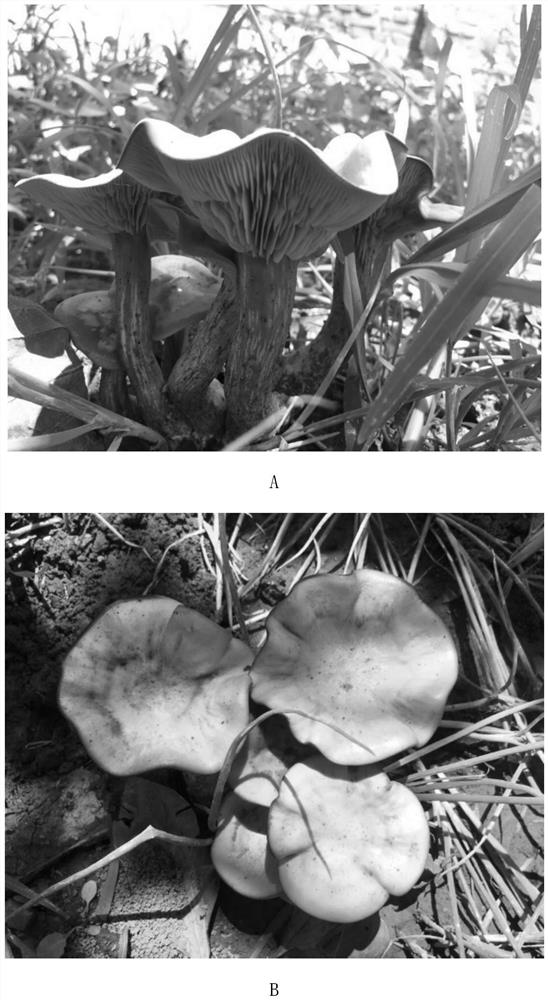
[0084] The inventor of the present invention collects wild fungus fruiting bodies from Dashiwo Town, Fangshan District, Beijing (see figure 1 , A is a side view, B is a top view). The tissue at the junction of the cap and the stipe was picked, placed on PDA medium, and cultured in the dark at 25° C. for 2 weeks to obtain mycelium. The hyphae were picked out and purified twice to obtain the fungus DCH618. The steps of each purification are as follows: the mycelium is placed on the PDA medium, and cultured in the dark at 25° C. for 2 weeks.
[0085] 2. Identification of the fungus DCH618
[0086] 1. Morphological identification
[0087] (1) Inoculate the mycelia of the fungus DCH618 on PDA medium (slant), culture in dark at 25° C. for 2 weeks, and observe the growth state of the mycelium.
[0088] See the experimental results f...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Embodiment 2, the cultivation of the fruiting bodies of DCH618
[0100] 1. Cultivation process
[0101] The cultivation process of DCH618 fruiting body is as follows: preparation of mother seed → preparation of first-level liquid seed → preparation of second-level liquid seed (that is, cultivation liquid seed) → inoculation, film covering and germination → soil covering → fruiting management → Fruiting → Harvesting.
[0102] 1. Preparation of mother species
[0103] Inoculate the mycelium of DCH618 on the PDA medium (test tube slope), and cultivate in the dark at 25°C until the mycelia cover the medium, and the mycelium on the medium is the mother species.
[0104] 2. Preparation of primary liquid species
[0105] After completing step 1, transfer the mother species to the first-level liquid medium (the inoculum size is 8-10 mother species strains (about 1.0cm in diameter) per 200mL first-level liquid medium), at 25°C , 150rpm dark culture for 7-10d, to obtain a fir...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Example 3, High Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis of DCH618 Fruiting Body
[0144] In this embodiment, the mobile phase for HPLC analysis is composed of 17 parts by volume of pH 6.5, 10 mM phosphate buffer and 3 parts by volume of methanol, the flow rate is 1.0 mL / min, and the column temperature is room temperature. The detection wavelength is 260nm.
[0145] 1. According to the cultivation process of step 1 in embodiment 2, obtain the flush mushroom, i.e. the fruiting body.
[0146] 2. After step 1 is completed, the fruiting bodies are taken, dried, and then ground to obtain fruiting body powder.
[0147] 3. After completing step 2, take a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, add 0.5 g of fruiting body powder and 10 mL of 90% (v / v) methanol aqueous solution, seal it tightly, shake well, and heat to reflux for 30 min.
[0148] 4. After completing step 3, cool naturally, filter, and collect the filtrate.
[0149] 5. After completing step 4, take the test tube, add the f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com