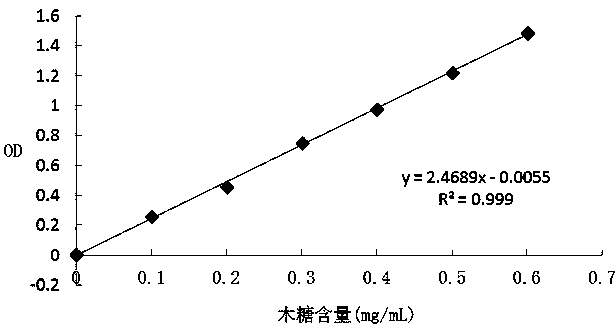
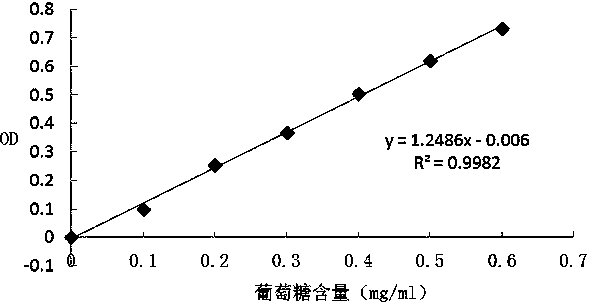
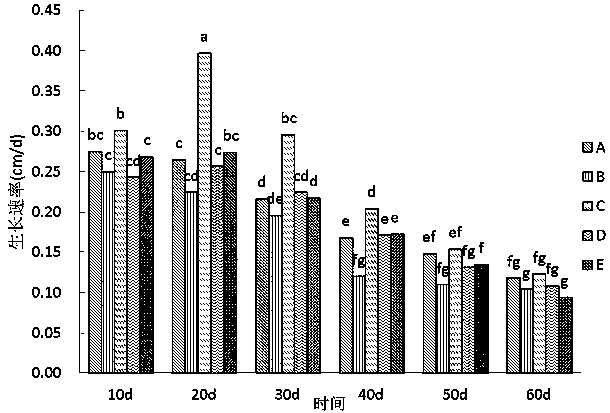
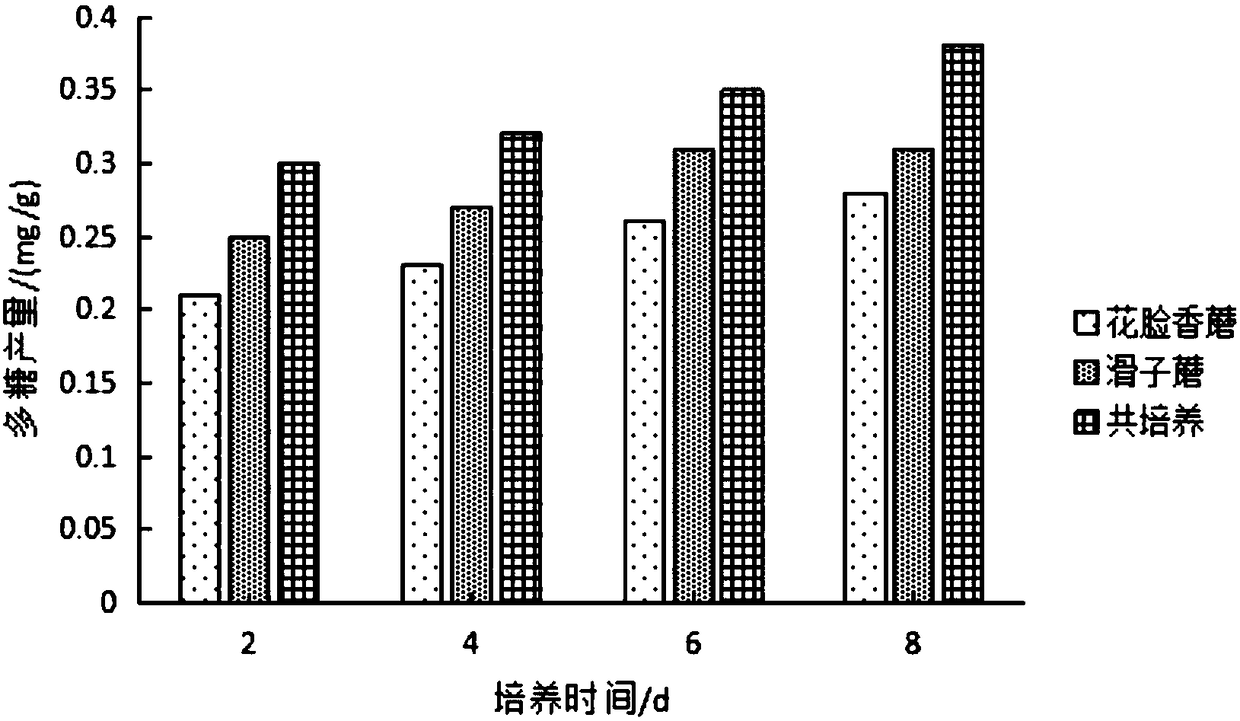
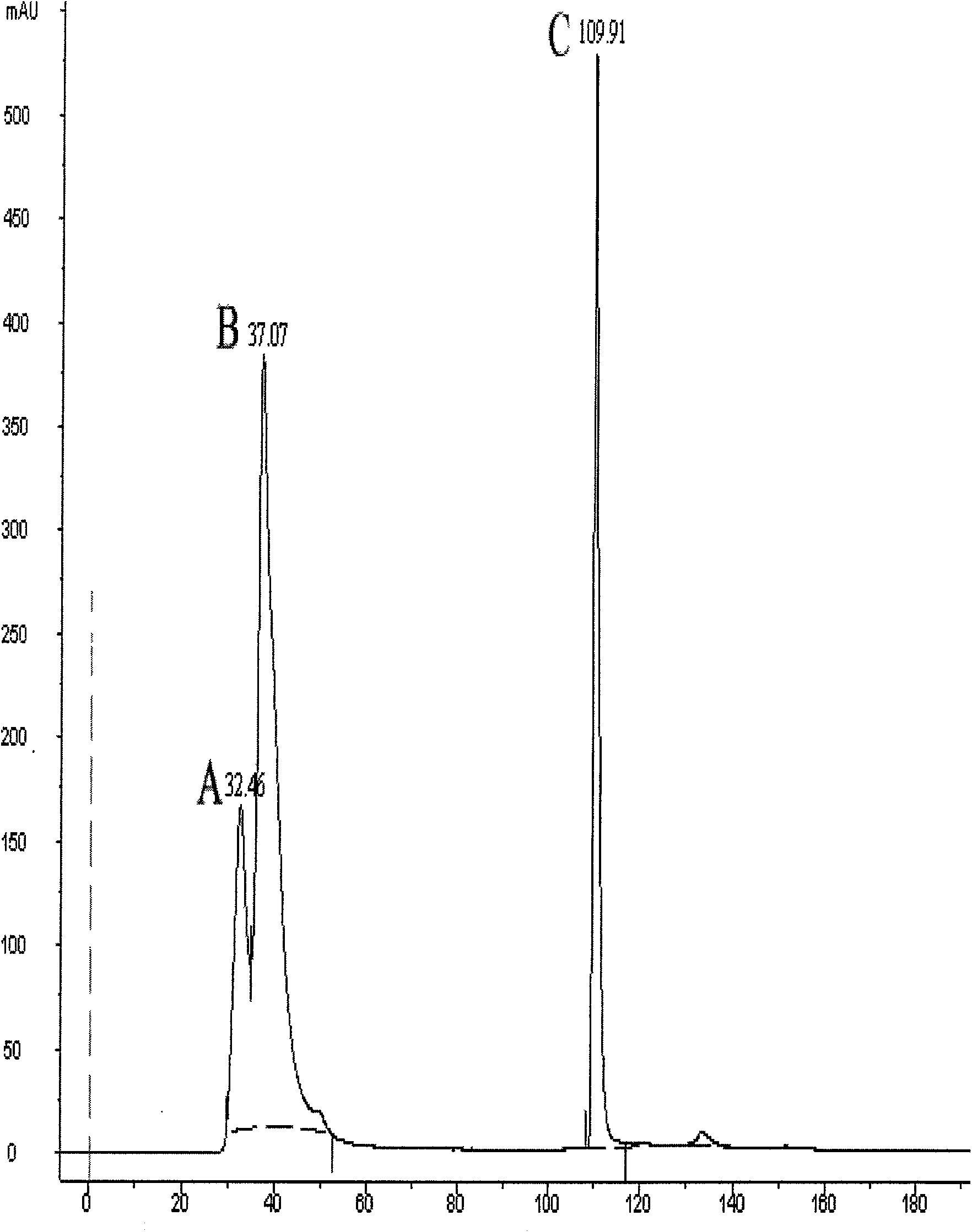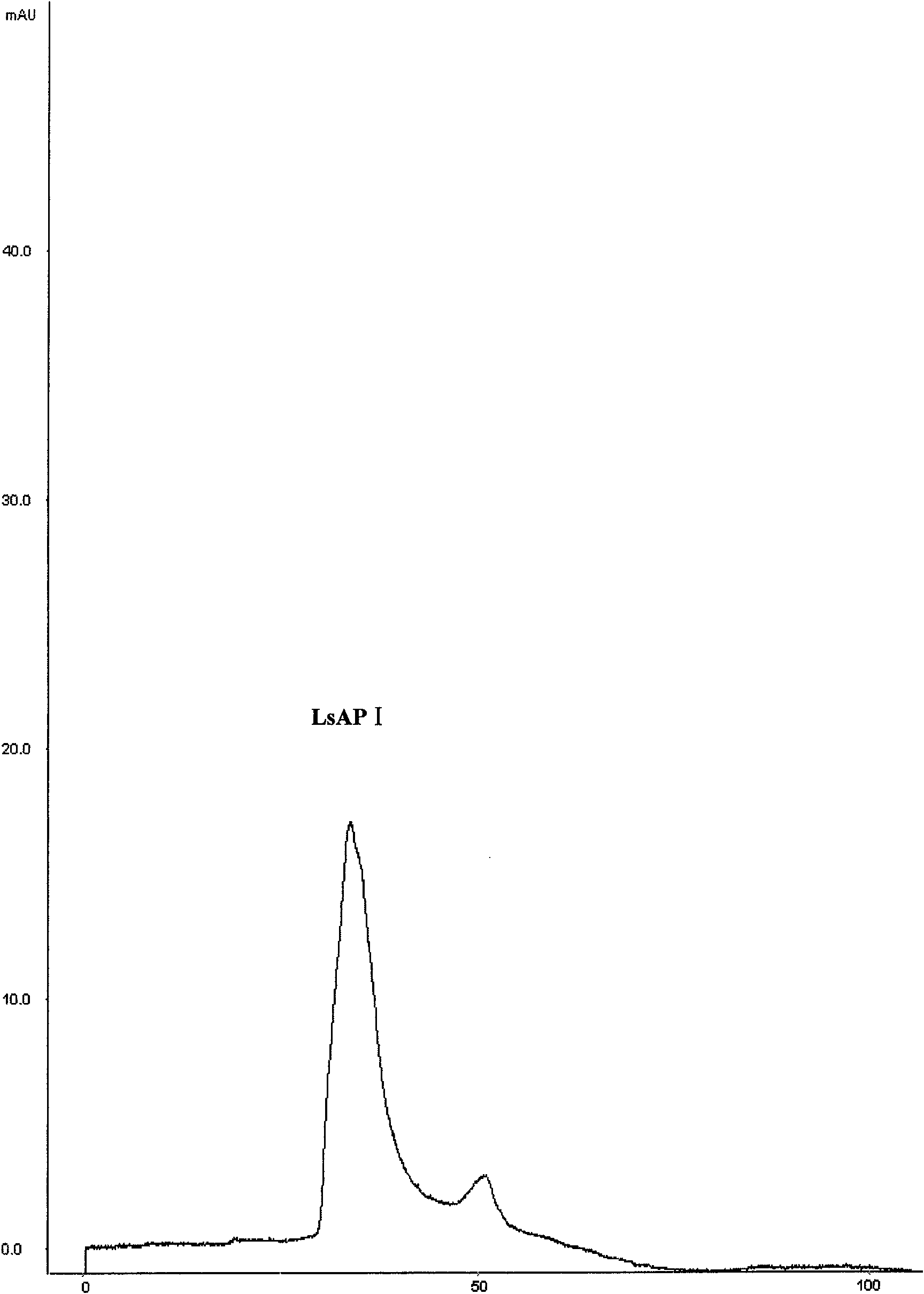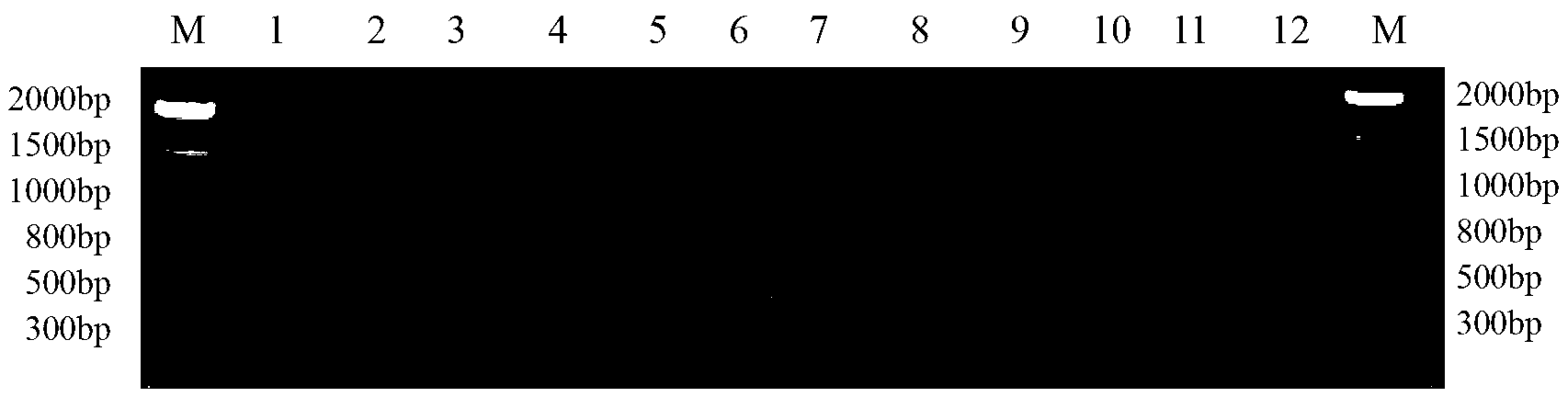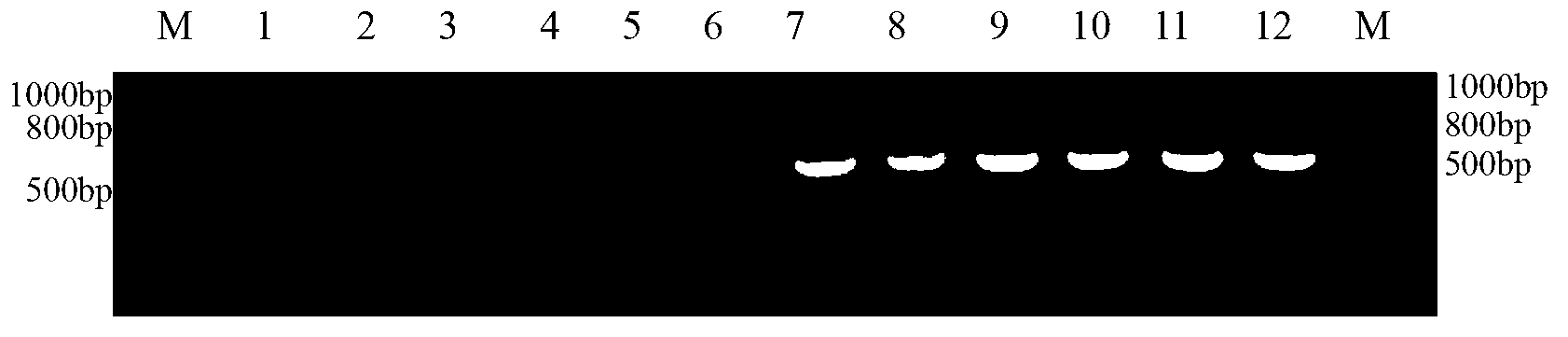Patents
Literature
48 results about "Lepista sordida" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
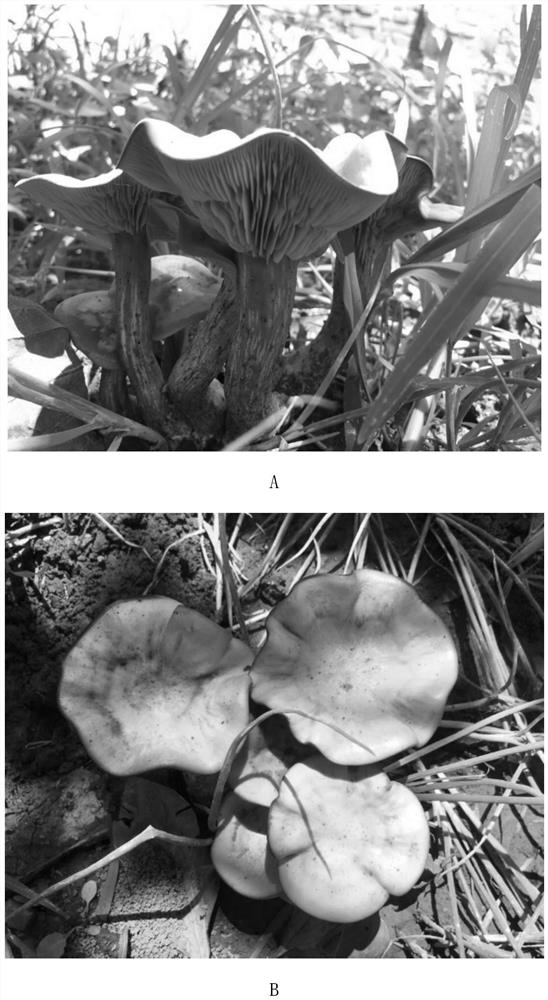
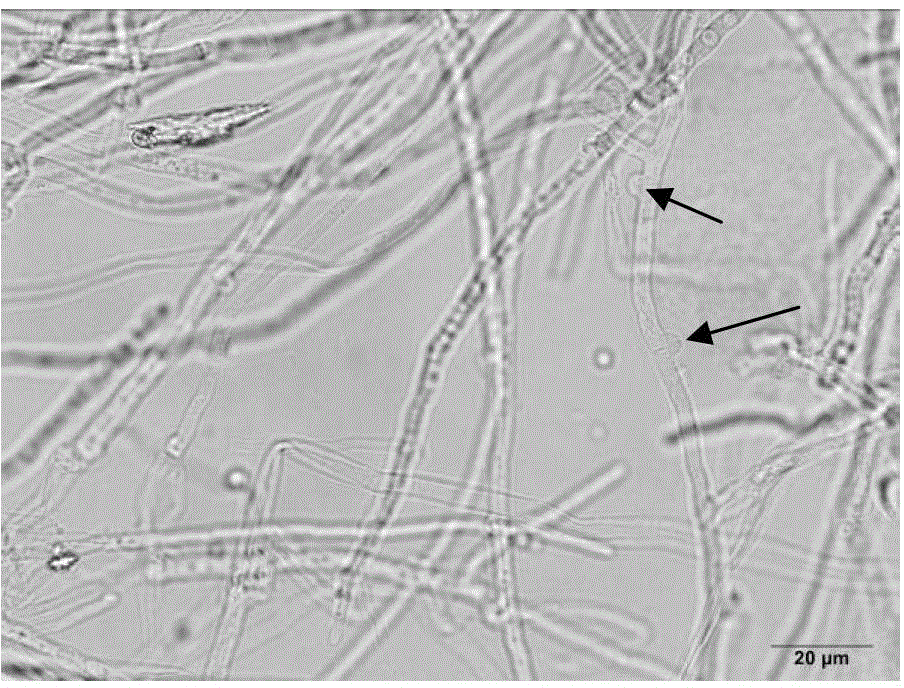
Lepista sordida is a species of mushroom found across the Northern Hemisphere. It is known to form fairy rings.
Preparation method for edible fungus flavor food
The invention discloses a preparation method for an edible fungus flavor food. The edible fungus can be any one from edible agaricus bisporus, straw mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, shii-take, needle mushrooms, pleurotus nebrodensis, pleurotus eryngii, agrocybe aegerita, hypsizigus marmoreus, agaricus pratensis schaeff, spring mushrooms, stropharia rugoso-annulata, sparassis crispa, macrolepiota procera, tremellodon gelatinosum, black trumpet mushrooms, hericium erinaceus, pholiota nameko, lepista personata, mitake mushrooms, lactarius hatsudake, golden oyster mushrooms, pholiota adiposa, cantharellus cibarius, termitomyces albuminosus, tricholoma giganteum, pleurotus citrinopileatus, calocybe gambosa, truffle, amillariella mellea, fungus suillus, beef-steak fungus, lactarius deliciosus, tricholoma matsutake, agaricus bitorquis, pleurotus pulmonarius, toadstool and russula vinosa, and after treatment, the edible fungus is steeped into a steeping liquor prepared from red wine vinasse, high quality dry red wine and a flavouring agent in a vacuum and normal temperature and normal pressure combined condition, so as to obtain the flavor food; the edible fungus flavor food for leisure is prepared through oil-bath dewatering; a flavor food flavor puffed food is obtained through a swelling process, so as to meet consumers' hobbies and requirements.
Owner:徐州绿之野生物食品有限公司
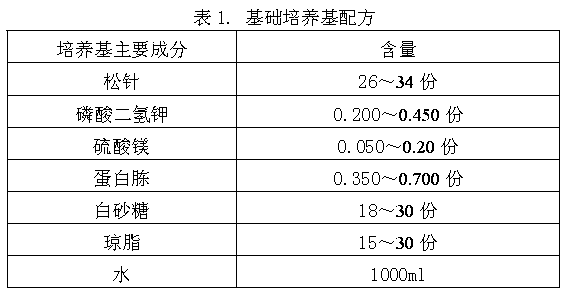
Lepista sordida first-class strain solid culture medium and strain rapid cultivating method
InactiveCN103708968APromote growthKeep activeHorticultureFertilizer mixturesMonopotassium phosphateMaterial resources
The invention discloses a lepista sordida first-class strain solid culture medium and a strain rapid cultivating method. A preparation method of the culture medium comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing flour, pine needle, monopotassium phosphate, magnesium sulfate, peptone, white granulated sugar, agar and water, heating to boil, sterilizing a conical flask filled with the culture medium for 25-40 minutes at the temperature of 120-125 DEG C and under the pressure of 0.15Mpa, and pouring the culture medium obtained after the sterilization into a flat plate in a super clean bench to obtain the lepista sordida first-class strain solid culture medium. By adopting the technical scheme, the lepista sordida first-class strain is vigorous in growth, dense, thick and strong in mycelium, many in aerial mycelium and short in growth cycle; the activity of the strain is effectively guaranteed; lots of manpower and material resources are saved for industrial artificial cultivation and breeding of lepista sordida.
Owner:贵州尚恩生物科技有限公司
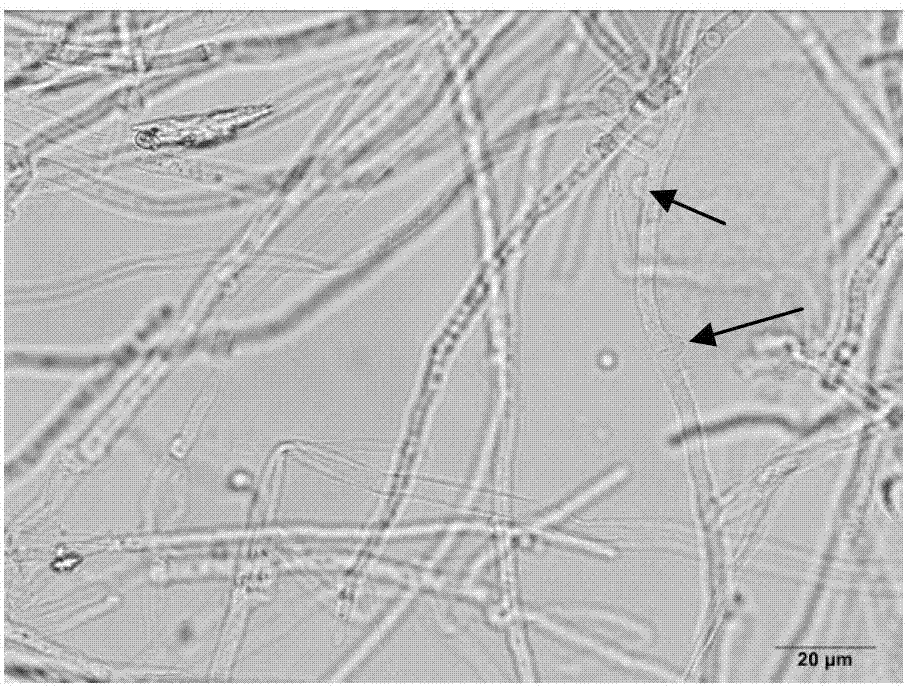
Artificial culturing method of lepista sordida mycelium and culturing medium thereof
The invention discloses an artificial culturing method of a lepista sordida mycelium and a culturing medium thereof, wherein the culturing medium comprise the following components according to parts by weight: 30-50 parts of pine needle, 5-12 parts of peptone, 6-12 parts of yeast extract powder, 2.5-10 parts of glucose, and 15-20 parts of agar; the artificial culturing method comprises cleaning and boiling the pine needle in water for 20-30 minutes, filtering to extract the juice, metering 1000ml of pine needle juice, then sequentially adding the peptone, the yeast extract powder, the glucose and the agar, boiling and mixing uniformly, subpackaging the prepared culturing medium into a test tube, covering a rubber plug, sterilizing under the temperature of 120-130 DEG C for 20-30 minutes, then taking out the culturing medium, naturally cooling to 20-30 DEG C, making an inclined plane culturing medium, inoculating a purified lepista sordida strain under the aseptic condition, putting the inoculated culturing medium in a constant temperature incubator, culturing for 5-10 days at the temperature of 20-30 DEG C until the mycelium grows fully in the test tube, and then refrigerating the mycelium. According to the artificial culturing method and the culturing medium, the operation is simple, the culturing period is shortened, no pollutants or wastes are produced, and the yield of the mycelium is high.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
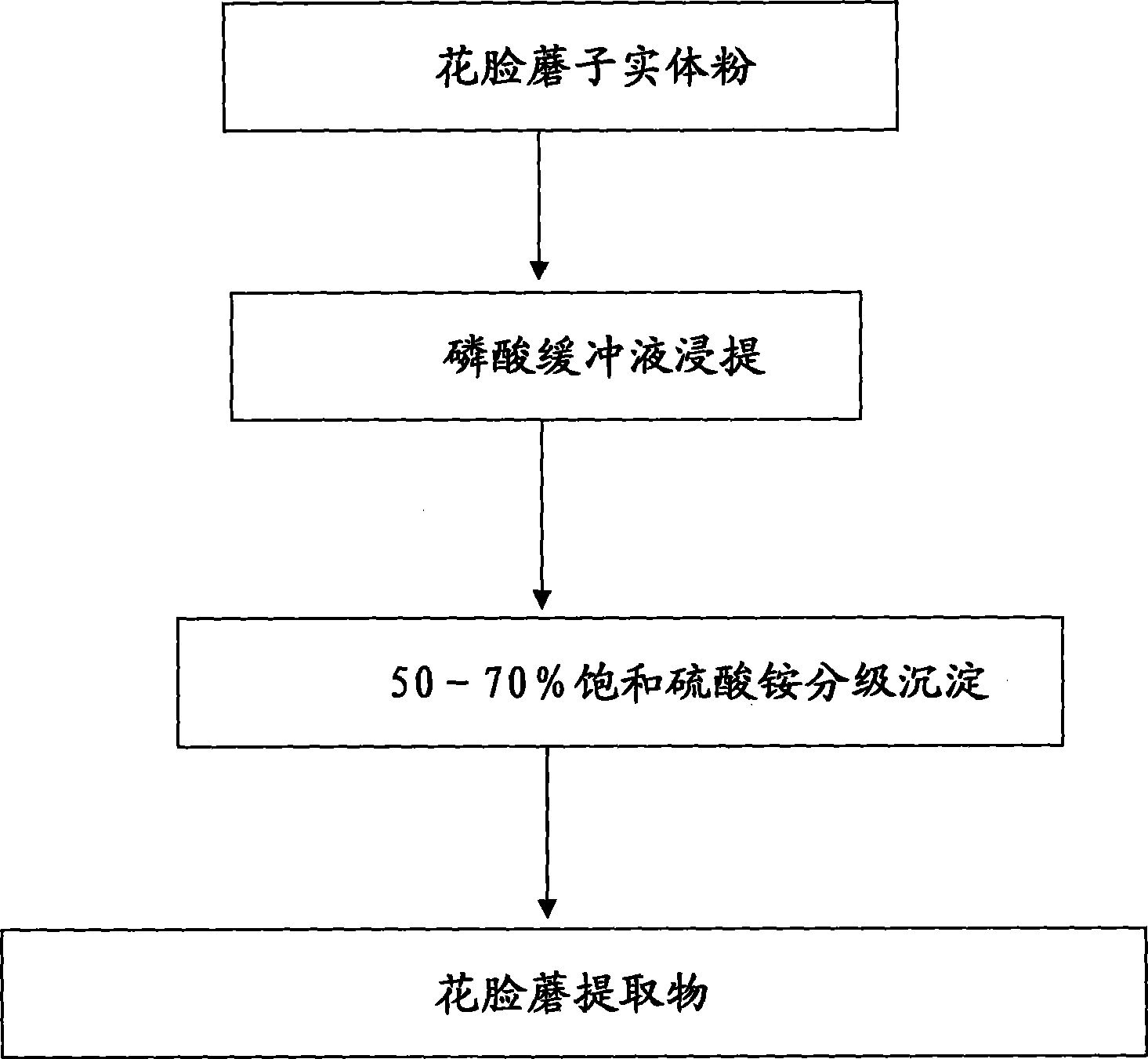
Lepista sordida extract as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101375691AEnhanced inhibitory effectEasy to prepareBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyDistilled water
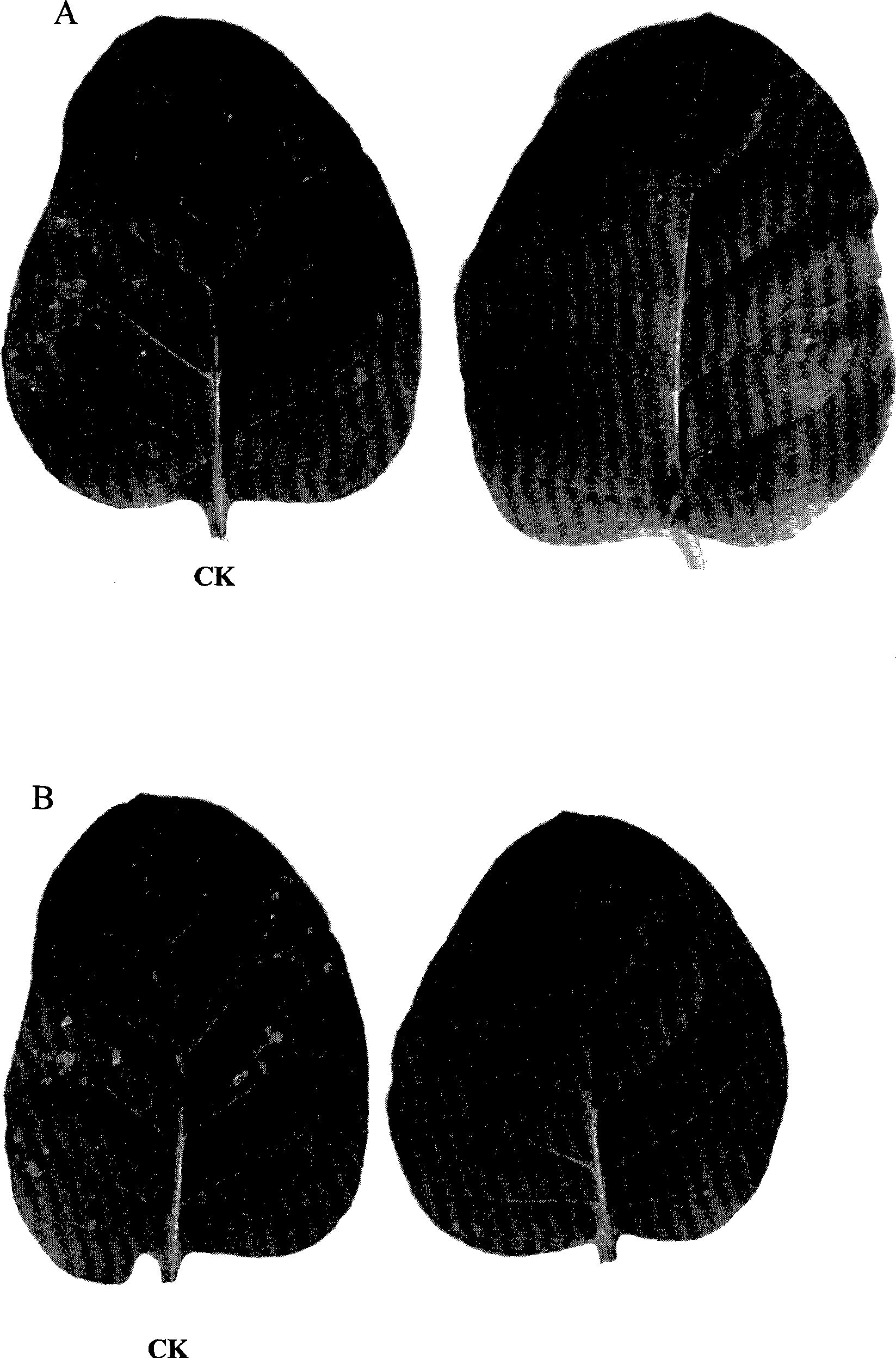
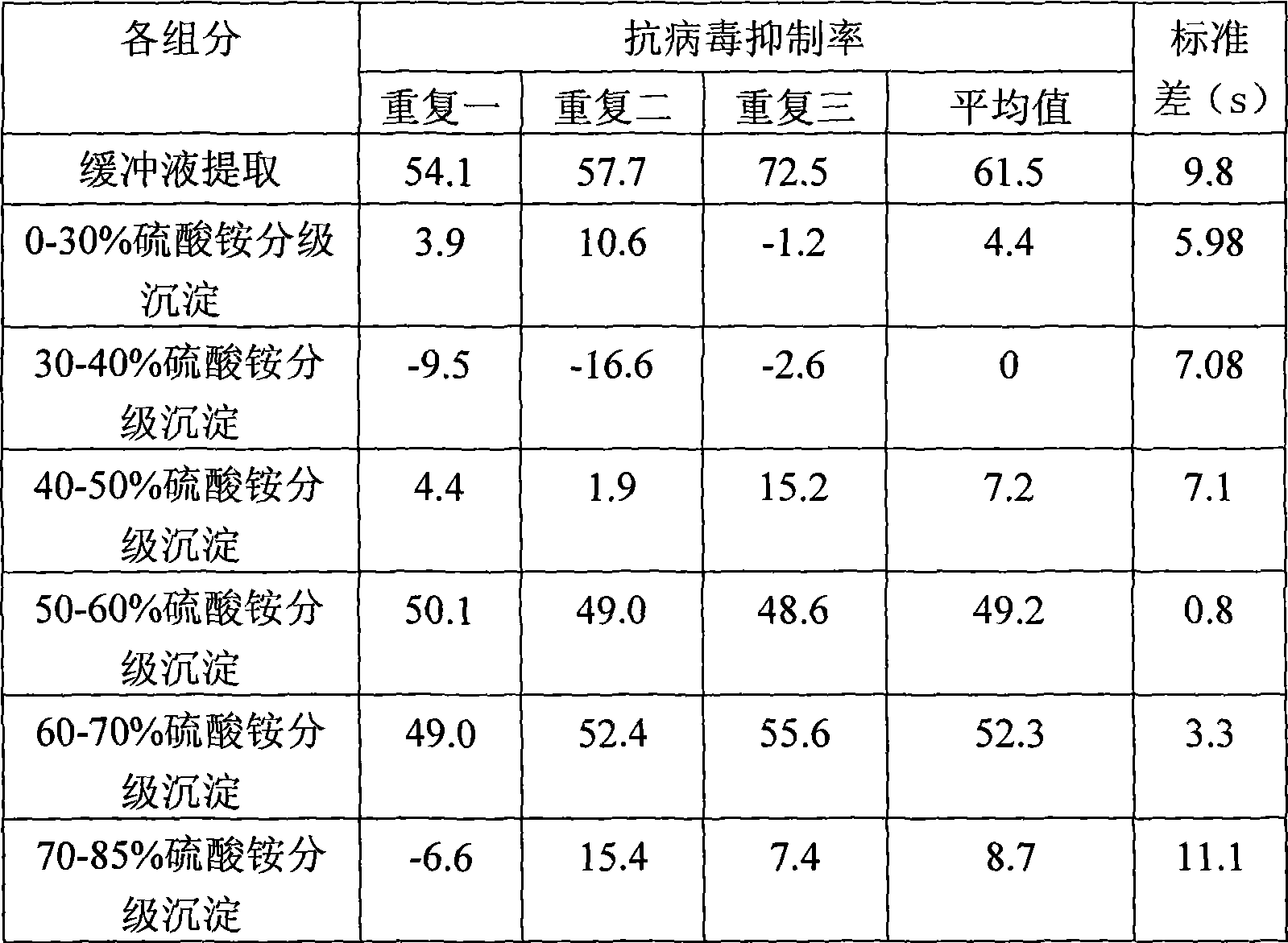
The invention provides an extract of a Lepista sordida, a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the Lepista sordida entity powder with a phosphate buffer, the PH value of which is 6-9; leaching at the temperature ranging from 0 to 4 DEG C; centrifuging to extract a supernatant fluid to acquire a crude extract from the Lepista sordida; (2) adding ammonium sulphate in the supernatant fluid to achieve 50 percent of saturation and centrifuging the supernatant fluid after the supernatant fluid stands for 8-16 hours at the temperature ranging from 0 to 4 DEG C; (3) adding ammonium sulphate in the supernatant fluid to achieve 70 percent of saturation, and centrifuging the supernatant fluid after the supernatant fluid stands for 8-16 hours at the temperature ranging from 0 to 4 DEG C; (4) dissolving with distilled water and precipitating, so as to acquire the protein of the Lepista sordida which resists TMV. The extract of the Lepista sordida belongs to the natural extract, is not harmful to the human beings, and is environment-friendly. Furthermore, the purifying method of the extract of the Lepista sordida is very simple, detailed in steps, and easy to operate.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Lepista sordida and separation and propagation method and soil covering cultivation method thereof
ActiveCN108293599AMaster the multiplication methodConservation of Germplasm ResourcesFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismGermplasm
The invention discloses lepista sordida and a separation and propagation method and soil covering cultivation method thereof. N006# strains are obtained by tissue separation of wild lepista sordida fruiting bodies, and the lepista sordida N006# strains are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC); the preservation date is June 1st, 2016; the preservation registration number is CGMCC NO. 12507. The lepista sordida N006# strains are obtained through tissue separation, a propagation method of the strains is mastered, and strain guarantees are provided for artificial cultivation of lepista sordida. The lepista sordida fruiting bodies are obtained through artificial soil covering cultivation, germplasm resources of this specie are protected, and a novel edible fungus variety is developed.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI CHINA NAT SUPPLY & MARKETING GENERAL COOP
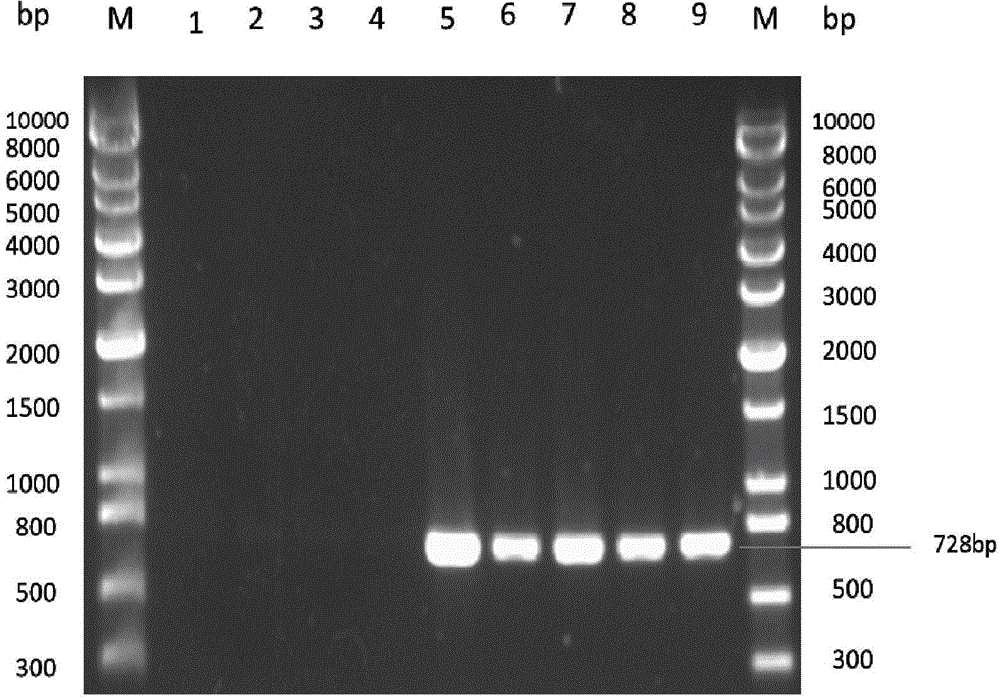
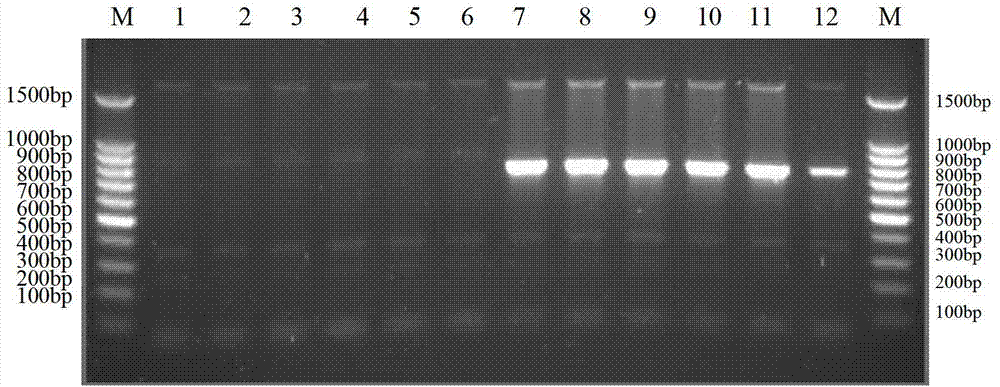
Method for identifying mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and special primer pair IS-879b thereof
InactiveCN103276070AShorten identification timeSimplify the identification stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationSingle strand dna
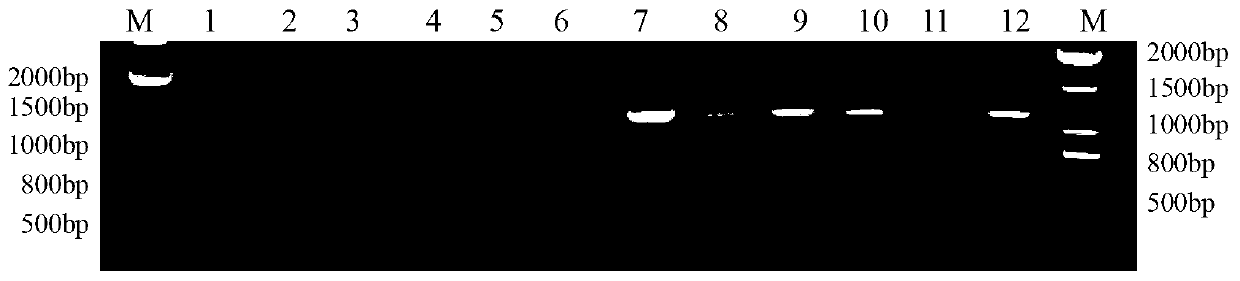
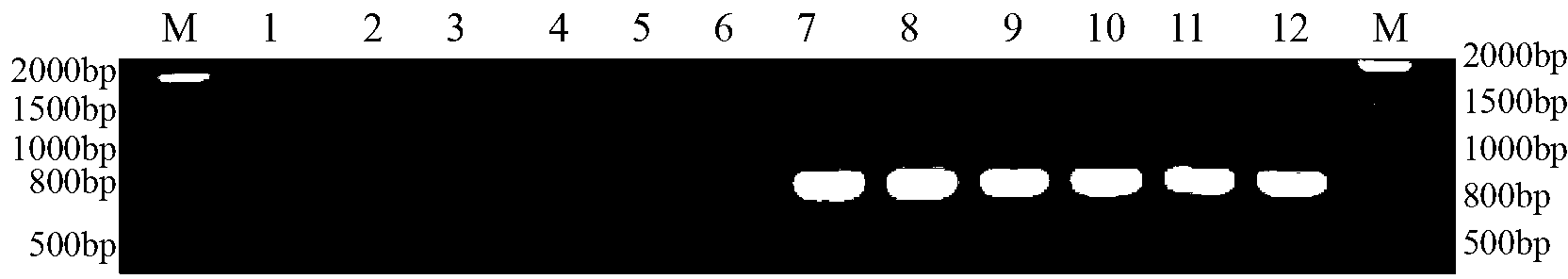
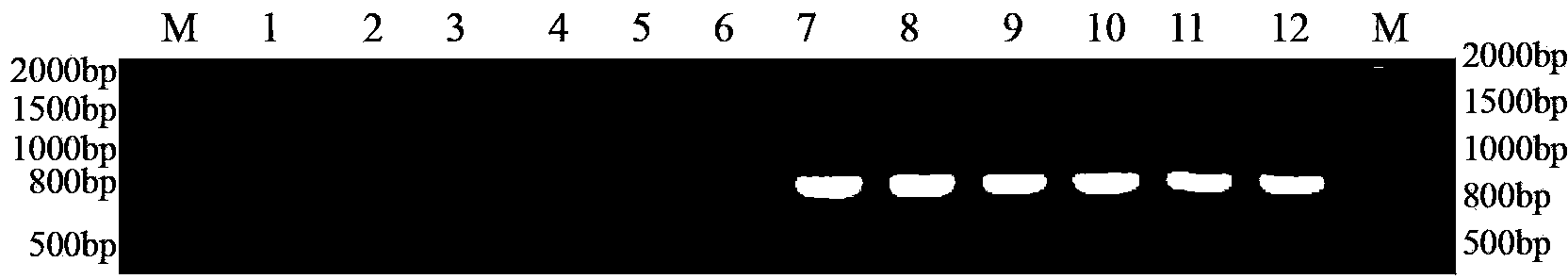
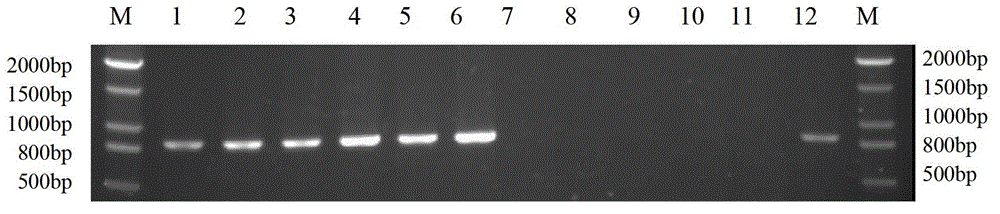
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and a special primer pair IS-879b thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking genomes DNA of two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified as templates respectively, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using a PCR primer pair consisting of two single chains DNA shown as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2, and detecting the magnitude of the obtained PCR products, wherein if the PCR products of both the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified contain or do not contain DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are identical; and if the PCR product of one protoplasted monokaryon contains the DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp and the PCR product of the other one does not contain the DNA fragments of 1000bp-1500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for cultivating lepista sordida (Schum.: Fr.) Sing.with miscanthus sacchariflorus and culture medium of method
ActiveCN105766368AReduce in quantityIncrease the number ofCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingPunchingMiscanthus sacchariflorus
The invention discloses a method for cultivating lepista sordida (Schum.: Fr.) Sing.with miscanthus sacchariflorus and a culture medium of the method.The culture medium is composed of, by weight, 75-80% of the miscanthus sacchariflorus, 17-20% of wheat bran, 1-2% of urea and 2-3% of gypsum, the water content of the culture medium is controlled to be 65-70%, and pH is 7.5-8.5; the cultivation method includes the steps that a small segment of the miscanthus sacchariflorus is placed into lime water for soaking, and after the miscanthus sacchariflorus is dried, the wheat bran, the urea and the gypsum are added, mixed and stirred; then heap building is conducted, air holes are formed in a punching mode, membrane covering is conducted, heap turning is conducted when the material temperature is raised to 70 DEG C or above, heap turning is conducted once every day, and water is added for preserving moisture when the water content is lower than 65%; fermentation is conducted for 13-17 days; bed building is conducted, inoculation is conducted when the material temperature reaches 20-30 DEG C, and the weight ratio of the material to seeds is 5: 1, compression is conducted, and the heap is covered with turfy soil which is 1.8-2.2 cm in thickness; culture is conducted for 30 days at the temperature of 20-25 DEG C.According to the method, planting raw materials are sufficient, low in price and good in quality.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Corncob lepista sordida culture material and method for cultivating lepista sordida
InactiveCN107082698AFull of nutritionNutritious and rich sourceCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingAfter treatmentRapeseed
The invention discloses a corncob lepista sordida culture material and a method for cultivating lepista sordida. The corncob lepista sordida culture material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 77 to 80 parts of corncobs, 10 to 15 parts of rapeseed cakes, 5 to 8 parts of vermiculite, 3 to 5 parts of quick lime and 1 to 2 parts of gypsum. The method for cultivating the lepista sordida adopts corncobs as a culture medium, and after treatment, the corncobs is in synerqistic interaction with the rapeseed cakes, the vermiculite and other components, the permeability and water retention of the culture material are improved, the strain resistance is enhanced, mycelia grows quickly, the mycelia is long, dense and robust, compared with a traditional cultivation method entering into a mature period in 35 days, the method for enabling the lepista sordida to enter the mature period can be 5 to 8 days ahead of time, the spawn running time is saved. The method for cultivating the lepista sordida is low in cost, the raw materials sources of the method are wide, and the yield of fruiting is 10% higher than that of cotton seed hull, the cost is lower by 25.3%, and the fruiting is stable, the method is high in quality and high in yield, and the method for cultivating the lepista sordida is easy to promote and popularize.
Owner:达州市农业科学研究院
Lepista sordida artificial planting method
InactiveCN108243832AGrow fastSuitable for growthCalcareous fertilisersExcrement fertilisersFermentationCulture mediums
The invention discloses a lepista sordida artificial planting method which includes the steps: (1) lepista sordida strain preparation: extracting female strains from lepista sordida fruit bodies, propagating the female strains into original strains or cultivation strains in test tubes, and taking rice as grain strain culture media to prepare lepista sordida strains; (2) fermentation material preparation: mixing and fermenting raw materials to prepare fermentation materials; (3) sowing and earthing: ridging on the fermentation materials, performing hole sowing, covering films, and earthing after hyphae overgrows a bed surface; (4) fruiting stage management: performing sun shading, enabling the air temperature to reach 18 DEG C to 28 DEG C, and enabling the soil humidity to reach 65%-70%. The fermentation materials comprise, in weight percent, 50%-60% of crop straws, 31%-45% of cow dung, 1%-2% of lime, 1%-2% of gypsum and 3%-5% of humus. According to the method, wild lepista sordida canbe artificially domesticated, the yield of the lepista sordida is improved, and secondary utilization of a rice nursery greenhouse is facilitated.
Owner:金珠满江农业有限公司
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-6*6 therefor
InactiveCN103233081AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingDNA fragmentation
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
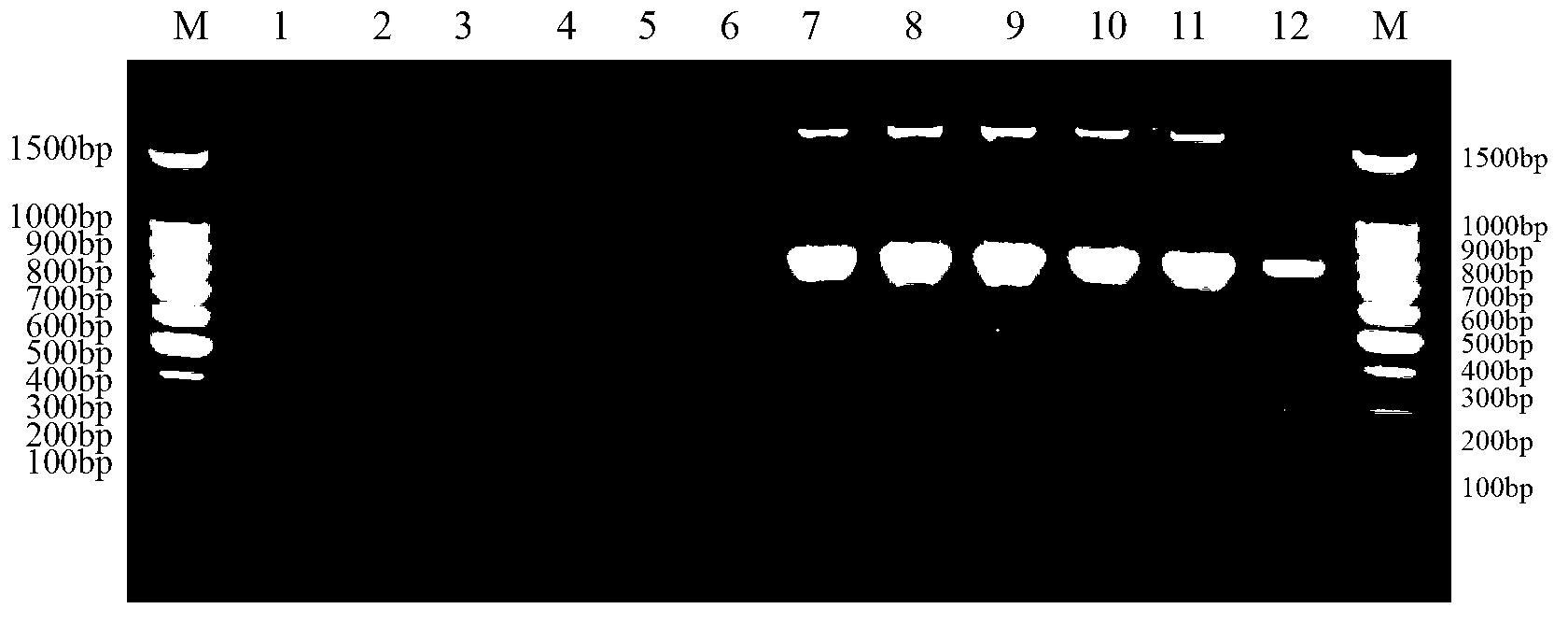
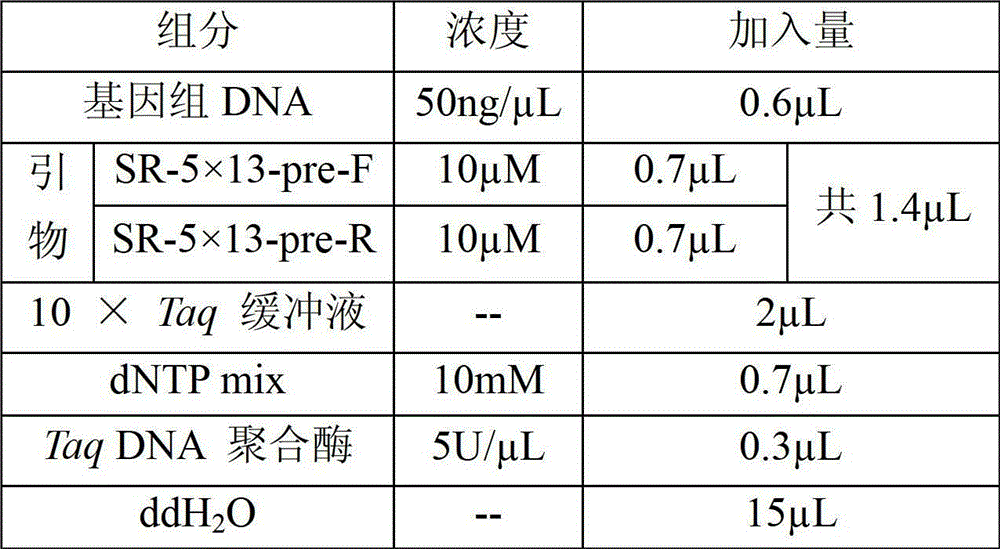
Method and special primer SR-5*13 for differentiating and auxiliarily differentiating mating types of bioplast monokaryons of lepista sordida (Fr) sings
ActiveCN103184282AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationMatingDNA fragmentation
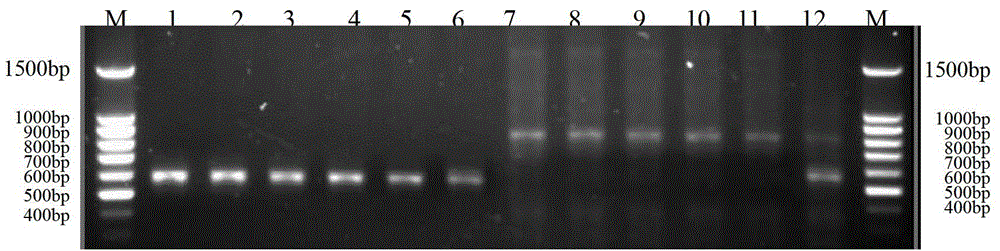
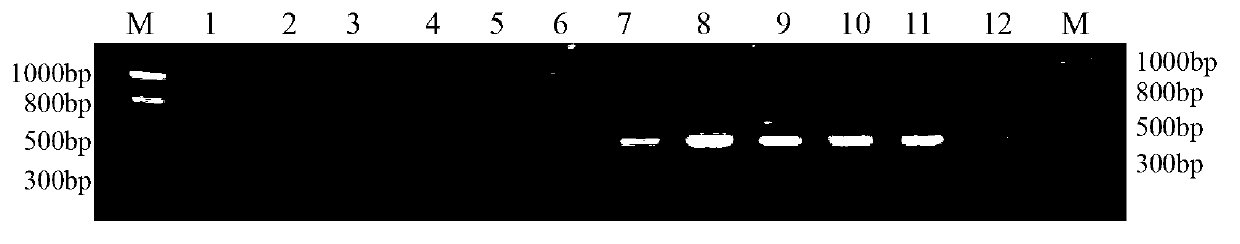
The invention discloses a method and a special primer SR-5*13 for differentiating and auxiliarily differentiating mating types of bioplast monokaryons of lepista sordida (Fr) sings. The method comprises the following steps: genome DNAs of bioplast monokaryons of two lepista sordida (Fr) sings to be differentiated are respectively taken as templates; PCR primers shown by SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2 are used for PCR increase; the sizes of the obtained PCR products are detected; if the PCR products of the bioplast monokaryons of both the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings to be differentiated contain DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp or don't contain the DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp, the mating types of the bioplast monokaryons of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings are same; and if the PCR product of the bioplast monokaryon of one of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings contains DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp, and the PCR product of the bioplast monokaryon of the other of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings dose not contain the DNA fragments of 500bp-800bp, the mating types of the bioplast monkaryones of the two lepista sordida (Fr) sings are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for manufacturing Lepista sordida cultivar by utilizing fungus residues
ActiveCN111066574ASolve the problem of efficient reuseStrong germinationCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention discloses a culture material for a Lepista sordida cultivar. The culture material is composed of the following components in percentages by weight: 38% of chicken manure, 35% of flammulina velutipes waste residue, 25% of wheat straw, 1% of gypsum and 1% of calcium carbonate. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a method for cultivating the Lepista sordida cultivar by using the Lepistasordida culture material. According to the invention, through addition of the flammulina velutipes waste residue into the Lepista sordida cultivar, nutrition of a culture medium is improved; the activity of a strain is reinforced; mycelia are promoted to achieve strong germination force and grow rapidly, densely and strongly; compared with a traditional cultivar, the culture material provided by the invention is rich and stable in raw material sources, and has low cost; and the Cultivated species prepared from the culture material are rich in extracellular enzyme system, rapid in germination,high in feeding capacity and easy to popularize, and the problem of efficient reutilization of flammulina velutipes residues is well solved.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Fresh keeping agent
ActiveCN108157744AGood fresh-keeping effectImprove freshnessFungiFood preservationPholiotaEdible mushroom
The invention relates to a fresh keeping agent. The fresh keeping agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15% of lepista sordida and pholiota nameko co-culture polysaccharide, 3-7% of tea polyphenols and the balance of water. Through compounding of polysaccharide obtained through co-culture of edible mushrooms and tea polyphenols, the fresh keeping agent is used for fresh keeping of foods, and is good in effects of fresh keeping. Under the condition of co-culture of the lepista sordida and pholiota nameko, compared with the number of polysaccharide obtained by single culture, the number of the polysaccharide obtained by co-culture is higher, and the fresh keeping effect of the polysaccharide obtained by co-culture is obviously better than that of the polysaccharide cultured separately.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Lepista sordida mycelium rich in anthocyanidin and culture method for lepista sordida mycelium and application of lepista sordida mycelium
ActiveCN111386970ASolve the problem of low anthocyanin contentPromote generationFood ingredient as colourPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiotechnologyVitamin C
The invention discloses a lepista sordida mycelium rich in anthocyanidin and a culture method for the lepista sordida. mycelium and application of the lepista sordida mycelium. The culture method comprises the following steps: aerated fermentation cultivation is performed on a lepista sordida strain for 4-6 days; a solid culture medium to which additives are added is used during culture, and the additives include yeast copper, tea polyphenol, vitamin C, yeast zinc, ferrous glycinate, riboflavin and L-phenylalanine; and in addition, magnetic field treatment starts to be used in the second day after culture. According to the scheme of the invention, a certain culture method is employed on the lepista sordida mycelium at the later stage of culture to make the mycelium rich in anthocyanidin, and thus, the industrial utilization of the mycelium is facilitated, and the blank of research and utilization of the anthocyanidin in edible fungi at present is remedied; a new way is opened to development and utilization of the anthocyanidin of the edible fungi; and the mycelium has considerable economic benefits and far-reaching social benefits.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI
Method for identifying mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof
InactiveCN103305606AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologySingle strand
The invention discloses a method for identifying a mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: by taking the genome DNAs of the protoplasted monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida as templates, respectively, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-stranded DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2; detecting the sizes of the PCR products obtained; if the PCR products of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp or not, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are the same; if one plant contains the DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp while the other plant contains no DNA segment of 500 bp-800 bp, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
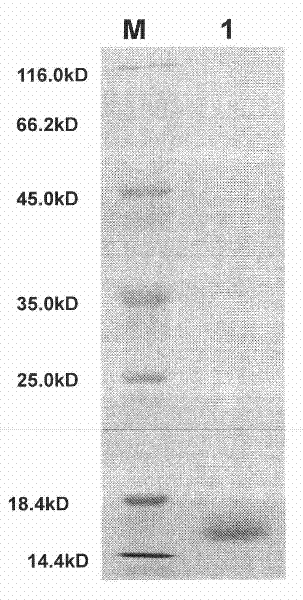
Lepista sordida protein LsAPI, preparation method and application thereof
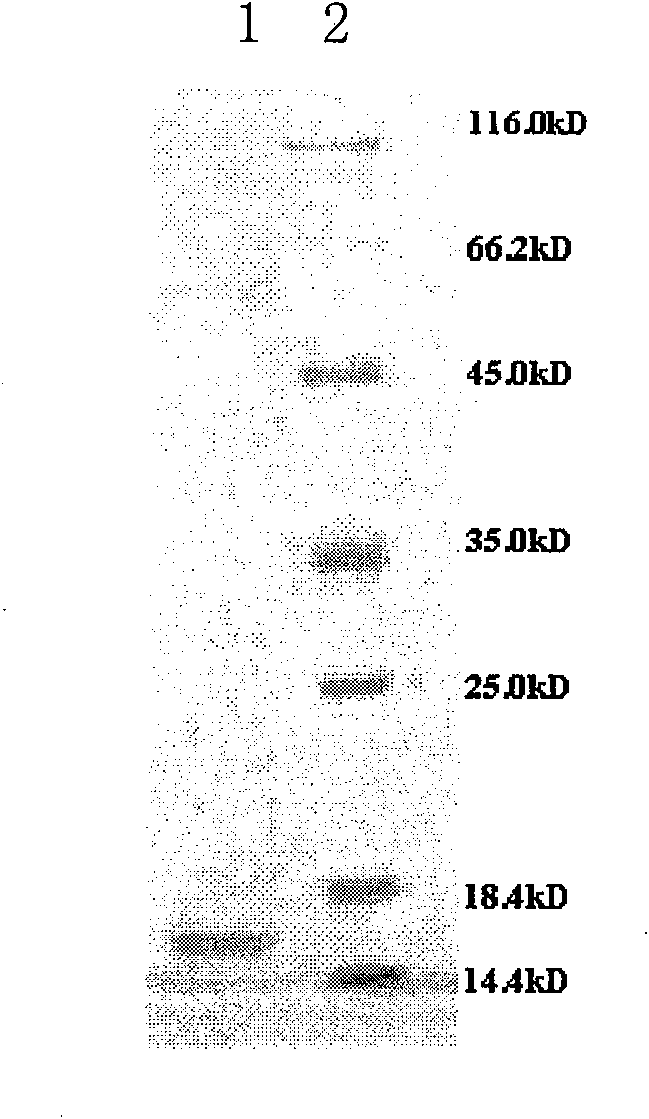
InactiveCN101671386AEasy to prepareRaw materials are easy to getBiocidePeptide preparation methodsProtein solutionTobacco mosaic virus
The invention discloses a lepista sordida protein LsAPI and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the LsAPI comprises the steps: adding lepista sordida entity powder into phosphate buffer solution to be soaked and centrifuged; adding ammonium sulfate into supernate until degree of saturation being 50%-70%, placing for 6-16h at the temperature of 0-6 DEG C, and centrifuging; dissolving precipitation by the phosphate buffer solution, dialyzing by re-distilled water, and carrying out ultra-filtration by an ultra-filtration tube to obtain protein solution; and separating by an anion exchange column, eluting by 0.02mol / L of Tris-HCl with the pH value of 8.0, and obtaining the LsAPI which is the substance contained in the eluent. The LsAPI is a single protein and provides the foundation for genetic engineering application thereof; secondly, the LsAPI has good virus inhibition for tobacco mosaic virus, and is a natural extract so as to be harmless to both the human being andthe environment; and furthermore, the preparation method of the LsAPI is easy, the raw materials are easily obtained, and the cost is lower.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof
InactiveCN103290117AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingGenome
The invention discloses a method for identifying the protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: with genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) of the protoplast monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida to be identified as templates, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain or do not obtain 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are the same; and if one plant contains 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, while the other plant contains no 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof
InactiveCN103290117BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method for identifying the protoplast monokaryon mating types of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-4*2 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: with genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) of the protoplast monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida to be identified as templates, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if the PCR products of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain or do not obtain 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are the same; and if one plant contains 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, while the other plant contains no 500 bp-800 bp of DNA segments, indicating that the mating types of the protoplast monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof
InactiveCN103305606BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologySingle strand
The invention discloses a method for identifying a mating type of protoplasted monokaryon of lepista sordida and a special primer pair SR-6*4 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: by taking the genome DNAs of the protoplasted monokaryons of two plants of lepista sordida as templates, respectively, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-stranded DNAs as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2; detecting the sizes of the PCR products obtained; if the PCR products of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified both contain DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp or not, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are the same; if one plant contains the DNA segments of 500 bp-800 bp while the other plant contains no DNA segment of 500 bp-800 bp, indicating that the mating types of the protoplasted monokaryons of the two plants of lepista sordida to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
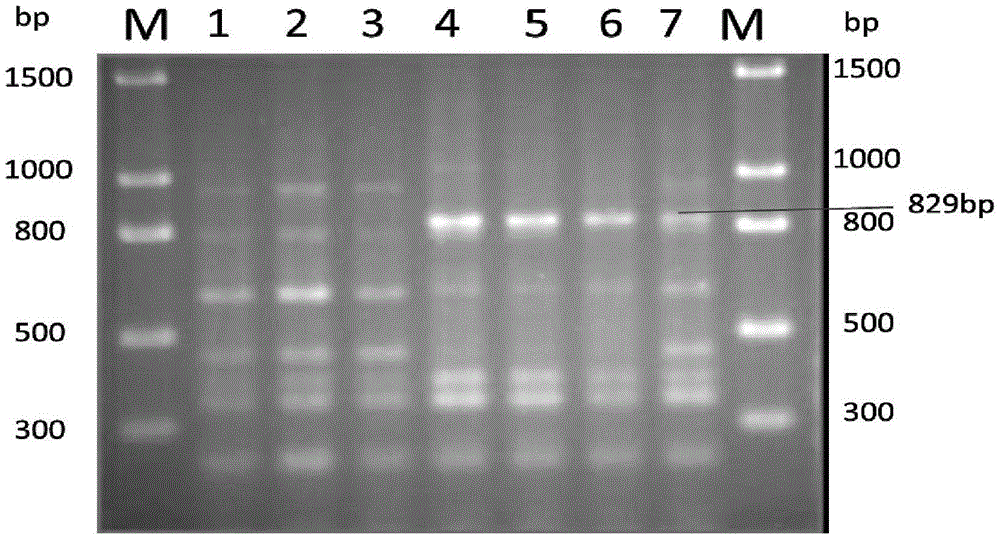
Method for identifying mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and special primer pair SR-2x8 thereof
InactiveCN103276072AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingDNA fragmentation
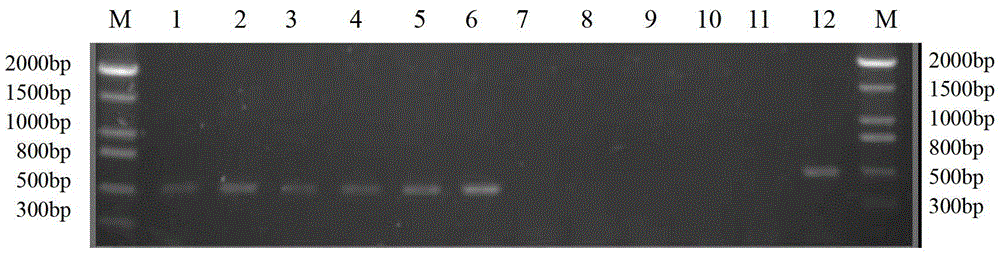
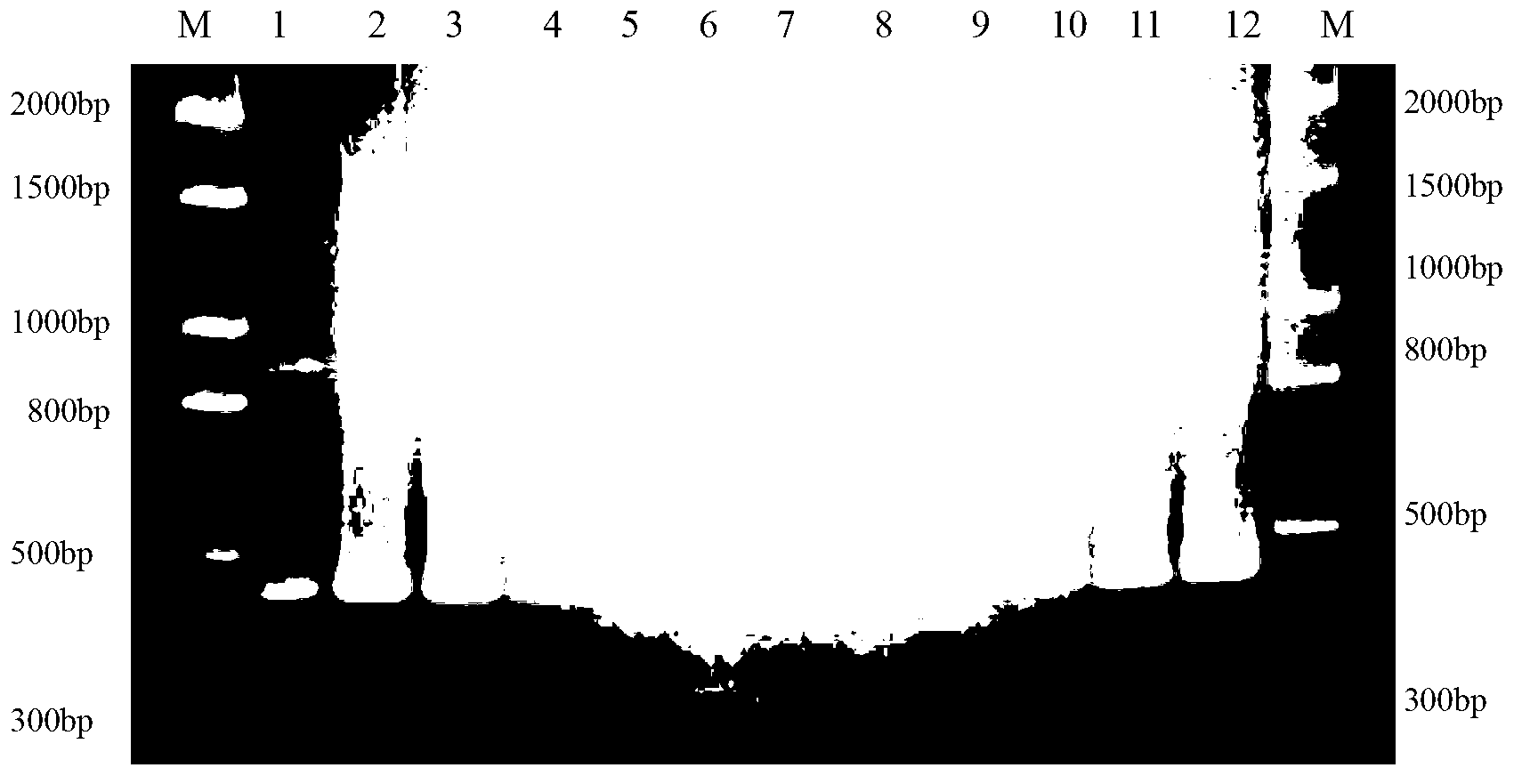
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-2x8 thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking genomes DNA of two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified as templates respectively, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using a PCR primer pair consisting of two single chains DNA shown as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2, and detecting the magnitude of the obtained PCR products, wherein if the PCR products of both the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified contain or do not contain DNA fragments of 300bp-500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are identical; and if the PCR product of one protoplasted monokaryon contains the DNA fragments of 300bp-500bp and the PCR product of the other one does not contain the DNA fragments of 300bp-500bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplasted monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor
InactiveCN103224992BSimplify the identification stepsShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingA-DNA
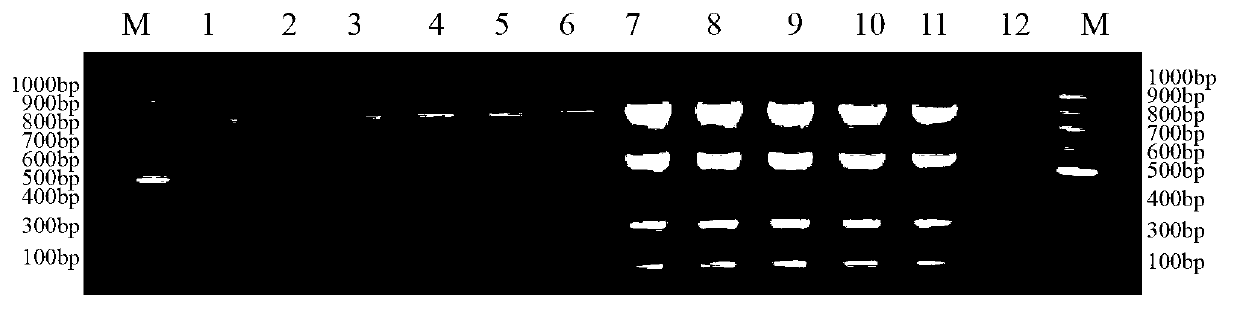
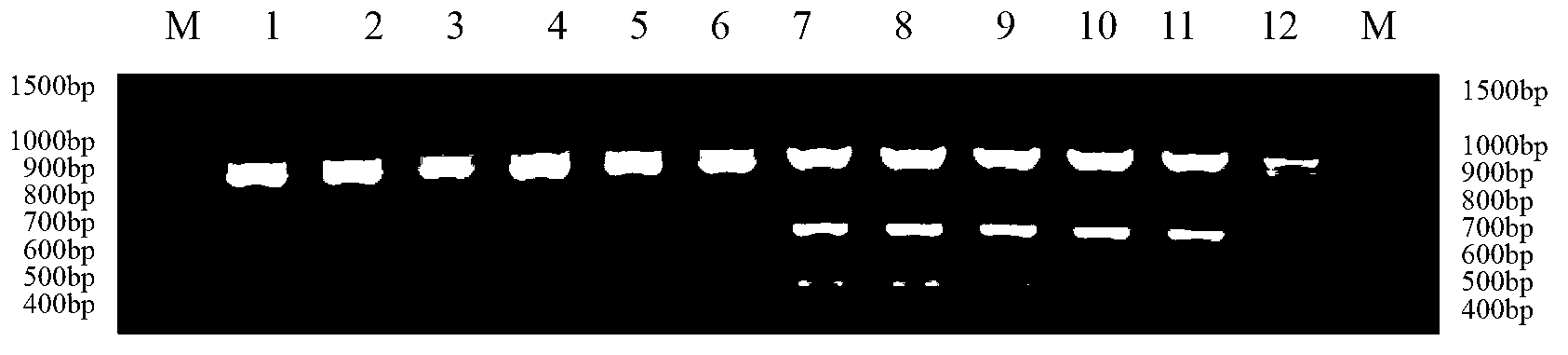
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor. The method comprises the following steps: respectively taking genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acid) of two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if both or neither of the PCR products of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are the same; and if one of the two contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp and the other does not contain a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor
InactiveCN103224992ASimplify the identification stepsShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-1*10 therefor. The method comprises the following steps: respectively taking genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acid) of two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if both or neither of the PCR products of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are the same; and if one of the two contains a DNA segment of 800-1000bp and the other does not contain a DNA segment of 800-1000bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Lepista sordida mycelium fermented tea and processing method thereof
The invention discloses lepista sordida mycelium fermented tea. Tea is taken as a raw material and inoculated with original species of lepista sordida or cultivated species of lepista sordida, sterilization, cultivation, inactivation and drying are performed, and the lepista sordida mycelium fermented tea is obtained. The invention further discloses a processing method of the lepista sordida mycelium fermented tea. On the premise that no cultivation auxiliary materials are added, the tea is taken as a culture medium for growth of lepista sordida mycelia, no external pollutants exist in the whole process, and the safety of the product is guaranteed. In the culture process of the lepista sordida mycelia, a large quantity of amino acid substances and polysaccharide substances are synthesized and the freshness of taste of the product and the richness of inclusions are improved. Through natural oxidation of tea polyphenol substances, the bitterness is reduced, and the quality of the tea serving as the culture medium is improved. The lepista sordida strains are edible mushrooms and have good safety. A large amount of lepista sordida mycelia exist in the tea in the fermentation process. The lepista sordida mycelium fermented tea has the efficacy of improving the immunity of a human body, regulating metabolism of the human body and prolonging the life.
Owner:罗倩 +6
Lepista sordida protein LsAPII as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101665531BEasy to prepareRaw materials are easy to getBiocidePeptide preparation methodsPhosphateFiltration
The invention discloses a lepista sordida protein LsAPII, wherein the N-terminal amino acid sequence is DGEYVNDLEGTISVDA. The preparation method comprises the following steps: soaking lepista sordida sporophore powder in phosphate buffer solution, and centrifugating to take supernatant; then adding ammonium sulfate to a saturation of 50 percent and a saturation of 70 percent respectively and standing at a temperature of 0-6 DEG C for 6 to 16 hours; respectively centrifugating to take supernatant or precipitation; reusing phosphate buffer solution to dissolve, dialyze, ultra-filtrate by an ultra-filtration pipe, separate through an anion exchange column, and elute by 0.3 mol / L NaCl, and then obtaining lepista sordida protein LsAPII. The LsAPII has good inhibitory effect on tobacco mosaic virus, and then the LsAPII is identified as single protein, which provides the basis for the genetic engineering applications. As the LsAPII is a natural extract, the invention is harmless to humans and environments. In addition, the preparation method of the LsAPII is simple and has the advantages of easily-obtained raw material and lower production cost.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
A kind of method of adopting Di grass to cultivate Azalea chinensis
ActiveCN105766368BReduce in quantityIncrease the number ofCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingMiscanthus sacchariflorusMushroom
The invention discloses a method for cultivating lepista sordida (Schum.: Fr.) Sing.with miscanthus sacchariflorus and a culture medium of the method.The culture medium is composed of, by weight, 75-80% of the miscanthus sacchariflorus, 17-20% of wheat bran, 1-2% of urea and 2-3% of gypsum, the water content of the culture medium is controlled to be 65-70%, and pH is 7.5-8.5; the cultivation method includes the steps that a small segment of the miscanthus sacchariflorus is placed into lime water for soaking, and after the miscanthus sacchariflorus is dried, the wheat bran, the urea and the gypsum are added, mixed and stirred; then heap building is conducted, air holes are formed in a punching mode, membrane covering is conducted, heap turning is conducted when the material temperature is raised to 70 DEG C or above, heap turning is conducted once every day, and water is added for preserving moisture when the water content is lower than 65%; fermentation is conducted for 13-17 days; bed building is conducted, inoculation is conducted when the material temperature reaches 20-30 DEG C, and the weight ratio of the material to seeds is 5: 1, compression is conducted, and the heap is covered with turfy soil which is 1.8-2.2 cm in thickness; culture is conducted for 30 days at the temperature of 20-25 DEG C.According to the method, planting raw materials are sufficient, low in price and good in quality.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-6*6 therefor
InactiveCN103233081BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingA-DNA
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon mating types and special primer pair SR-6*14 therefor
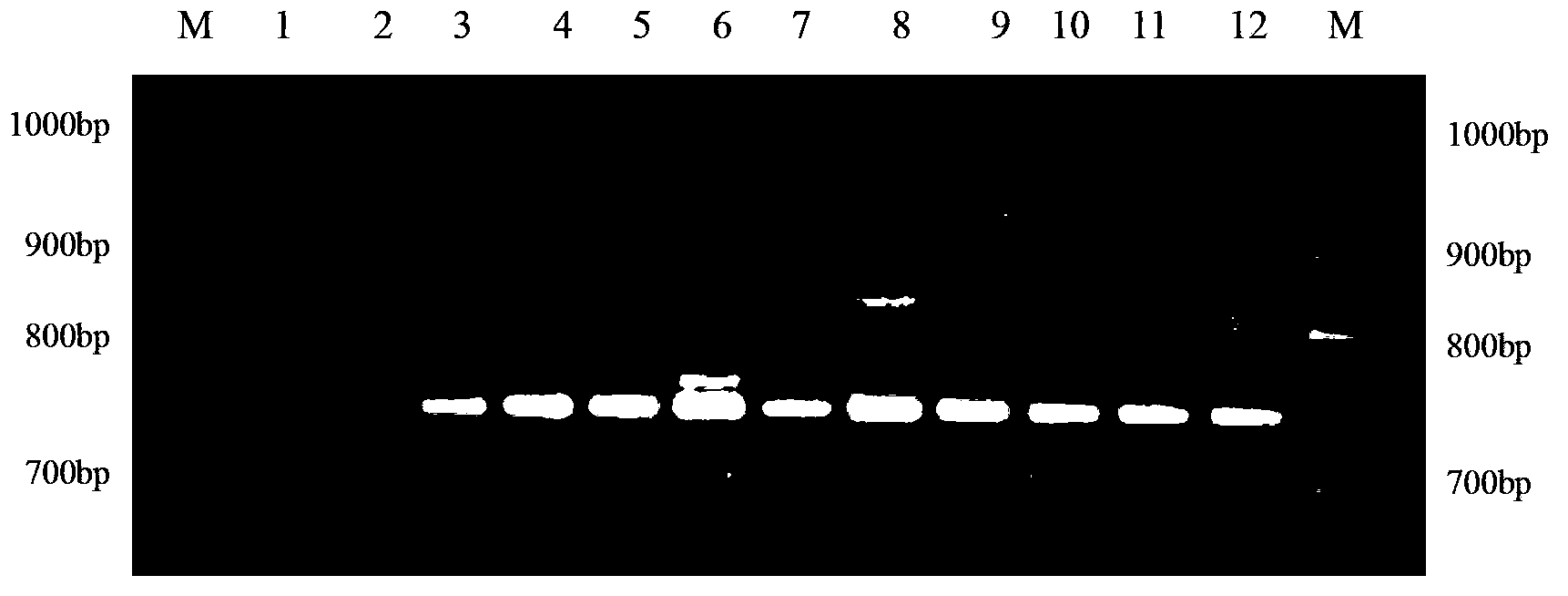
InactiveCN103266173AShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationGenomic DNADNA fragmentation
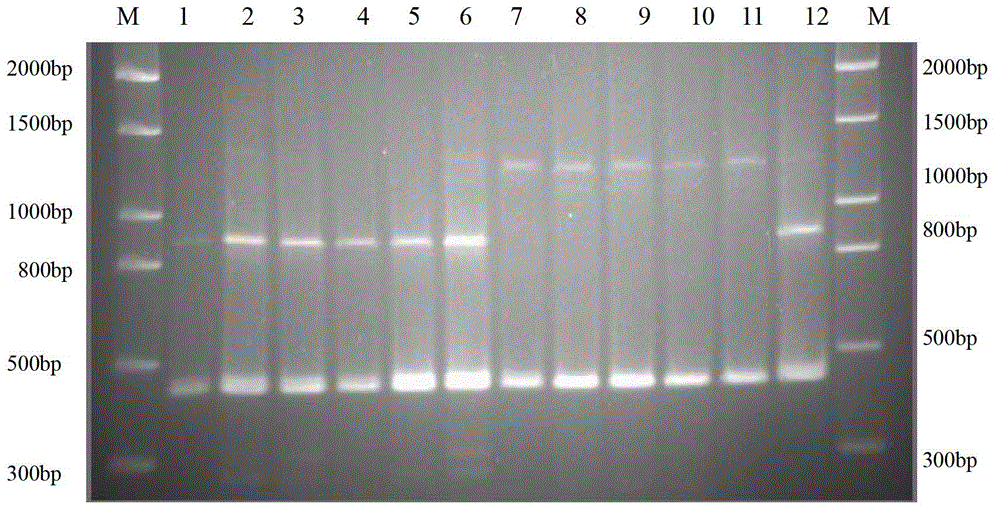
The invention discloses a method for identifying lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon mating types and a special primer pair SR-6*14 therefor. The method comprises the following steps of: with genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of two lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon to be identified as templates, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair consisting of two single-stranded DNA shown by SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID No.2; and detecting the sizes of the obtained PRC products, wherein if the PCR products of the two lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon to be identified contain or do not contain the DNA fragment of 500bp-800bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon to be identified are same, if the PCR product of one of the two lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon to be identified contains the DNA fragment of 500bp-800bp, and the PRC product of the other of the two lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon to be identified does not contain the DNA fragment of 500bp-800bp, the mating types of the two lepista sordida protoplast monokaryon to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-1*3 therefor
InactiveCN103233080BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-1*3 therefor. The method comprises the following steps: respectively taking genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acid) of two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if both or neither of the PCR products of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified contains a DNA segment of 500-800bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are the same; and if one of the two contains a DNA segment of 500-800bp and the other does not contain a DNA segment of 500-800bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Lepista sordida strain and method for cultivating fruiting body by using liquid strain thereof
ActiveCN111742778ARealize large-scale factory cultivationFungiNervous disorderBiotechnologyFood processing
The invention discloses a Lepista sordida strain and a method for cultivating a fruiting body by using a liquid strain thereof. The invention provides Lepista sordida DCH618, and the preservation number of the Lepista sordida DCH618 is CGMCC No. 16980. Experiments prove that the fruiting body rich in nucleoside compounds and / or ergosterol can be cultivated by using the Lepista sordida DCH618 liquid strain, and large-scale industrialized cultivation can be realized. Therefore, the Lepista sordida DCH618 has important application value in food processing, medicine processing or health care product processing. The Lepista sordida strain and the method have important application value.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for identifying mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and special primer pair SR-5*1 therefor
ActiveCN103233079BShorten identification timeSteps to Simplify Mating Type IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMatingA-DNA
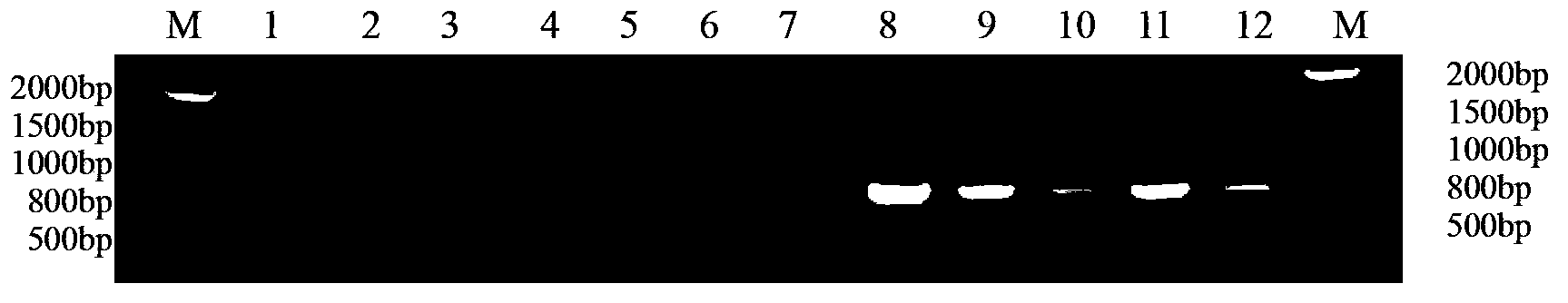
The invention discloses a method for identifying or helping to identify the mating types of Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons and a special primer pair SR-5*1 therefor. The method comprises the following steps: respectively taking genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acid) of two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified as templates, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a PCR primer pair composed of two single-chain DNAs as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and detecting the sizes of the obtained PCR products; if both or neither of the PCR products of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified contains a DNA segment of 1000-1500bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are the same; and if one of the two contains a DNA segment of 1000-1500bp and the other does not contain a DNA segment of 1000-1500bp, indicating that the mating types of the two Lepista sordida protoplast monokaryons to be identified are different.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com