Radiation source individual identification method based on multi-domain feature fusion
A feature fusion and recognition method technology, applied in the field of information detection and recognition, can solve the problems of incomplete feature information, low individual recognition rate of radiation sources, and weak generalization ability of classifiers, so as to improve generalization ability and improve radiation source The effect of the individual identification effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
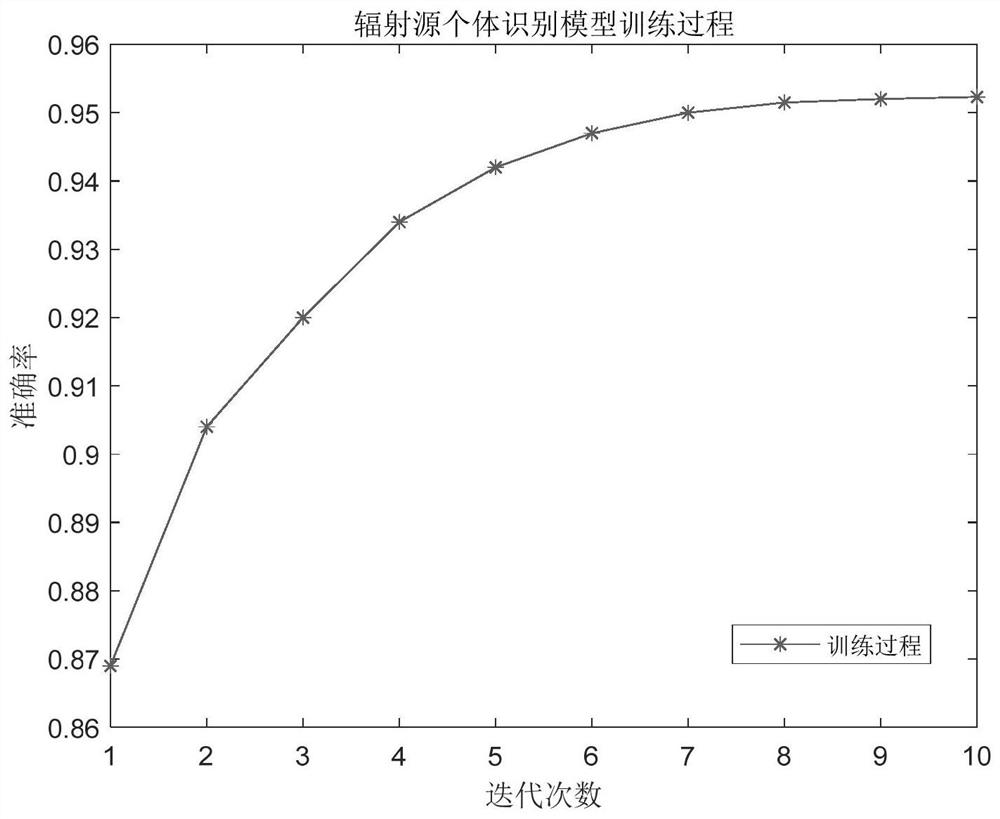
Embodiment 1
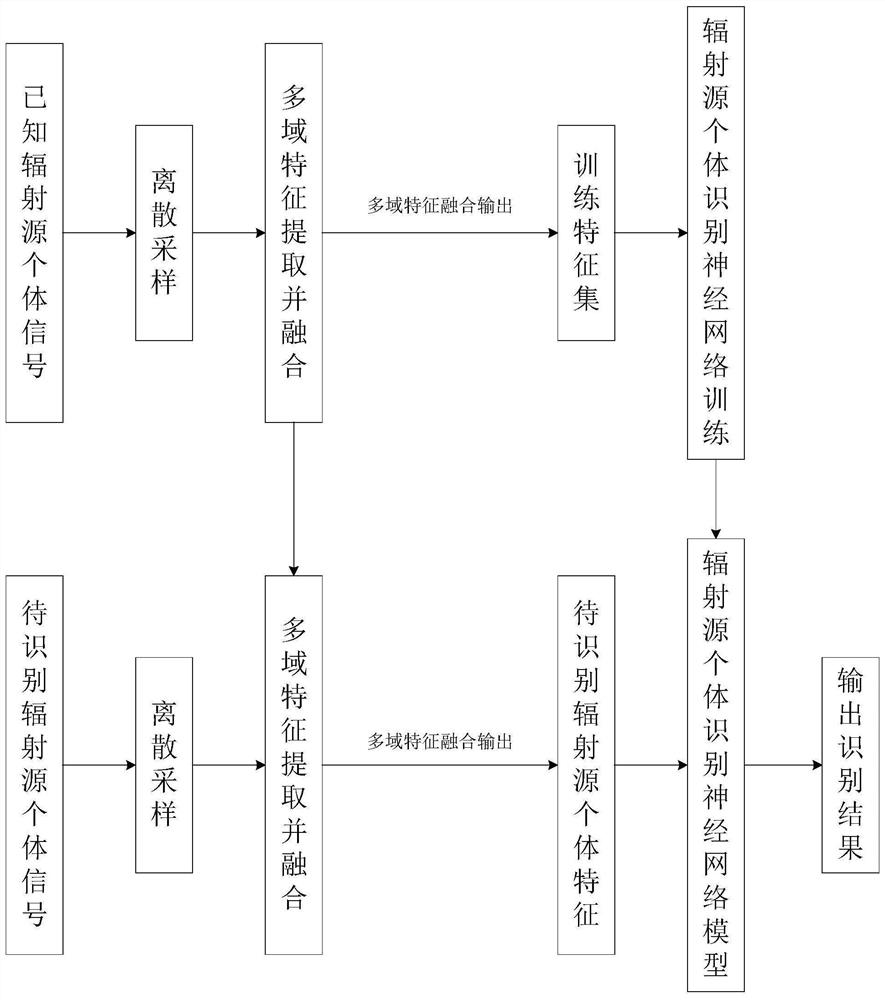
[0048] A radiation source individual identification method based on multi-domain feature fusion, comprising the following steps:
[0049] Step 1: Input a signal set containing multiple different radar radiation source transmitters, and perform discrete processing on each signal in the signal set to obtain the original data set; divide the original data set randomly into cyclic neural network signal data set and A dataset of transmitter signals from known radiation sources;
[0050] Step 2: use the cyclic neural network signal data set to train the cyclic neural network to obtain the cyclic neural network feature extractor;
[0051] Step 3: Select a signal data x from the known radiation source transmitter signal data set i (n), put x i (n) Input to the cyclic neural network feature extractor to obtain the time-domain cyclic feature F i1 ; Wherein, i=1,2,...,R, R is the number of data in the known radiation source transmitter signal data set; n is the signal data x i The nu...
Embodiment 2
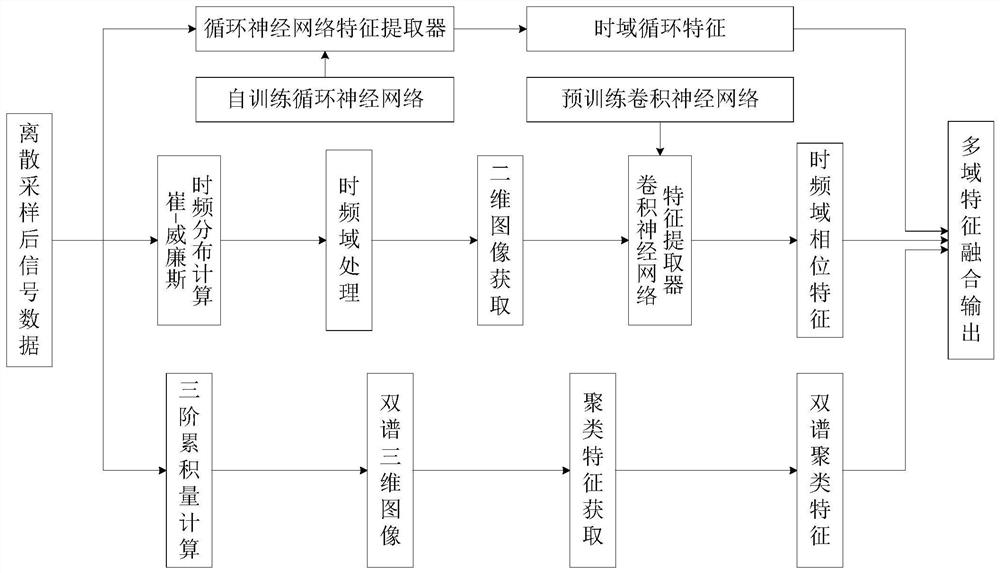
[0076] Obtain signal data x in step 4 i The time-frequency domain phase characteristic F of (n) i2 The specific method is:
[0077] Step 4.1: For signal data x i (n) Perform Cui-Williams time-frequency distribution calculation to obtain CWD(n,ω); perform time-frequency domain processing on CWD(n,ω) to obtain the phase absolute value result Φ(n,ω);
[0078]
[0079]
[0080]
[0081] Among them, * represents the conjugate operation; σ is the scaling factor; ω is the angular frequency; γ is the time shift variable; μ is the time variable; A three-dimensional phase image is obtained. The value of the angular frequency ω in Φ(n,ω) is continuous, take a positive integer and write it as The value of n is already a positive integer, and discrete phase values can be obtained 2D phase image Fig for discrete 3D phase images 1 Obtain. Define a two-dimensional image, the position of any pixel in the image is defined by Indicates that the pixel is located in the nth r...
Embodiment 3
[0086] The pre-trained convolutional neural network model in described step 4.3 is the VGG-16 network model based on ImageNet image data set pre-training; Described VGG-16 network model contains input layer, hidden layer and output layer, wherein hidden layer Containing 13 convolutional layers and 3 fully connected layers, the output layer of the VGG-16 network model is the third fully connected layer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com