Falling-preventing safety belt for hot-line work
A live working and anti-falling technology, applied to safety belts, textiles, fabrics, etc., can solve problems such as inability to work, normal use, and hazards to construction personnel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
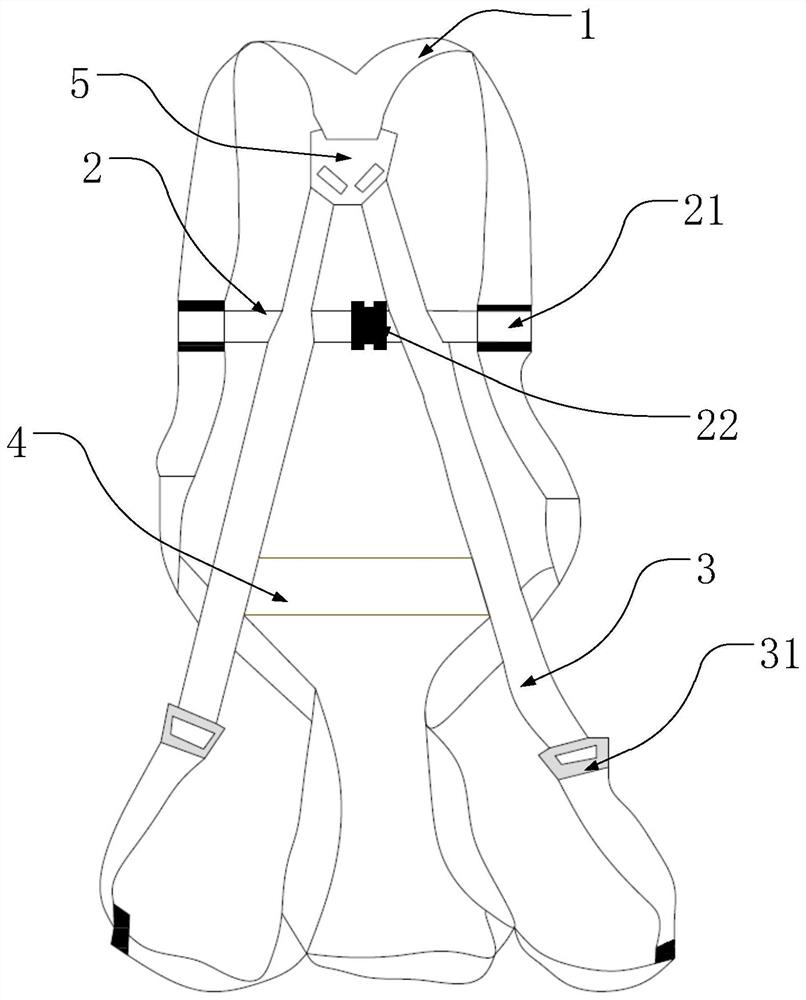
[0062] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the anti-fall safety belt for live work disclosed in Embodiment 1.
[0063] The anti-fall safety belt for live work disclosed in Embodiment 1 includes:
[0064] Two shoulder straps 1, one end of which extends downwards from the front of the wearer's left and right shoulders respectively, and the other end respectively extends downwards from the rear of the wearer's left and right shoulders, and is fixedly connected together by the fixing part 5 at the back position;
[0065] The chest strap 2 is a length-adjustable component, which is arranged horizontally on the chest, and its two ends are respectively movably connected with the two shoulder straps 1 through the first connecting part 21; the chest strap 2 is composed of two parts, and the two parts are connected by a quick release Buckle 22 is detachably connected;
[0066] Two straps 3, one end of which is connected with the fixing part 5, and the other end extends downward from...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specification | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com