Blast-furnace hot metal decarburization method utilizing blast-furnace dust
A technology for blast furnace molten iron and blast furnace ash, which is applied to the processing field of blast furnace molten iron in the process of flipping, and can solve problems such as potential safety hazards, aggravation of carbon-containing dust, molten iron splashing and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
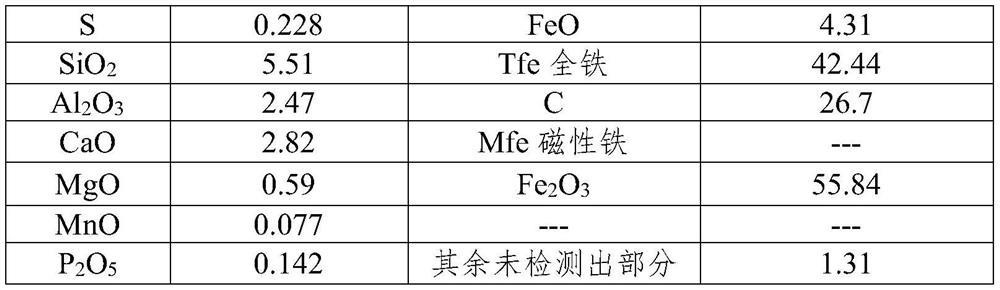
[0056] In this embodiment, blast furnace ash treated with aerobic roasting is used as a decarburizing agent, which is mixed with blast furnace molten iron to realize decarburization. In this embodiment, the composition of the blast furnace ash sample before roasting is shown in Table 1:
[0057] Table 1
[0058]
[0059]
[0060] Take 500g of the above-mentioned blast furnace ash and roast it at 1250°C for 6 hours in the air environment, and measure the composition of the blast furnace ash after roasting, see Table 2.
[0061] Table 2
[0062] Element Mass percentage Element Mass percentage S 0.310 FeO 1.493 SiO 2
7.481 Tfe full iron 57.619 al 2 o 3
3.353 C 0.000 CaO 3.829 Mfe magnetic iron --- MgO 0.801 Fe 2 o 3
80.65 MnO 0.105 --- --- P 2 o 5
0.193 The remaining undetected parts 1.78
[0063] Take the roasted blast furnace ash in Table 2, mix it with bentonite and an a...
Embodiment 2
[0071] In this example, the roasted blast furnace ash (see Table 2 for the composition) was added to bentonite (bentonite accounts for the total amount of the block decarburizer), an appropriate amount of water was mixed evenly to make a slurry, and pelletized by a disc pelletizer. After drying, the diameter The spherical decarburizing agent is 2 cm in size and dried at 110-120° C. for 3-5 hours to obtain the spherical decarburizing agent. Among them, bentonite accounts for 5% of the mass of the block decarburizer. The preparation process of the decarburizer refers to Example 1.
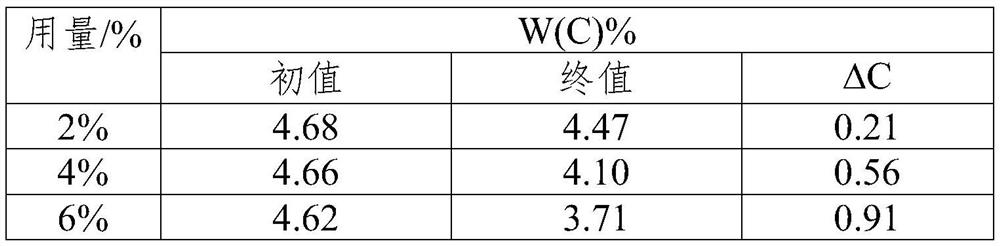
[0072] The amount of the above-mentioned massive decarburizer is 2% of the mass of molten iron (which does not contain bentonite), and the reaction temperatures of the molten iron for the decarburization reaction are kept at 1330°C, 1390°C, and 1450°C respectively, and each group of temperature experiments is paralleled for 3 times, and the calculation Average of 3 times. The experimental results a...
Embodiment 3
[0077] In this embodiment, the roasted blast furnace ash and iron ore powder are mixed in a mass ratio of 70:3 to make a decarburizer. The composition of iron concentrate powder is shown in Table 5.
[0078] table 5
[0079]
[0080] The composition of the mixture is shown in Table 6 after the fully roasted blast furnace ash and iron concentrate powder are mixed according to the mass ratio of 70:30.
[0081] Table 6
[0082] Element Mass percentage Element Mass percentage S 0.217 FeO 1.201 SiO 2
6.334 Tfe full iron 59.902 Al 2 o 3
2.797 C 0.000 CaO 2.680 Mfe magnetic iron --- MgO 0.561 Fe 2 o 3
84.24 MnO 0.280 --- --- P 2 o 5
0.135 The remaining undetected parts 1.55
[0083] Mix the components in Table 6 with bentonite and an appropriate amount of water to uniformly make a slurry, pelletize through a disc pelletizer, and obtain a spherical decarburizer with a diameter of 2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com