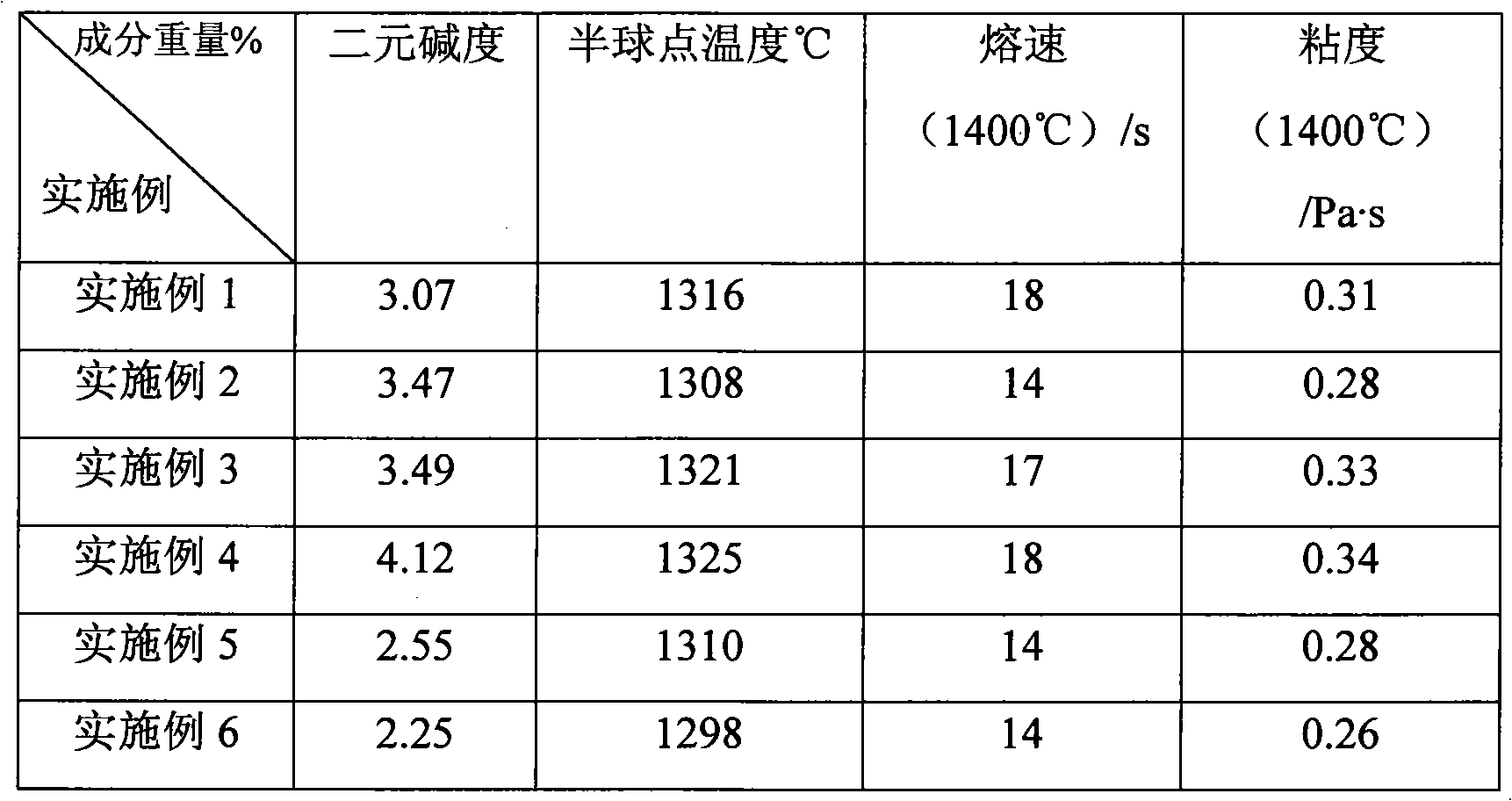
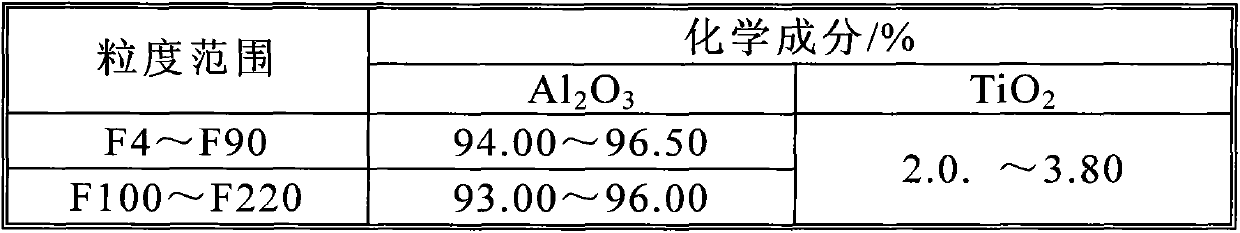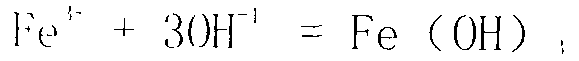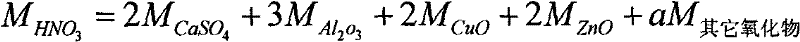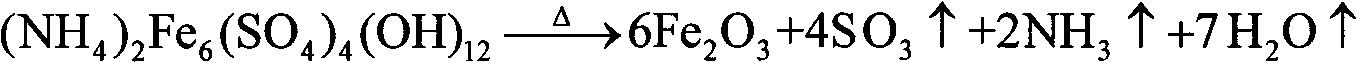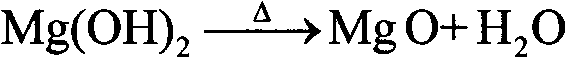Patents
Literature
842 results about "Iron(III) oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe₂O₃. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe₃O₄), which also occurs naturally as the mineral magnetite. As the mineral known as hematite, Fe₂O₃ is the main source of iron for the steel industry. Fe₂O₃ is readily attacked by acids. Iron(III) oxide is often called rust, and to some extent this label is useful, because rust shares several properties and has a similar composition. To a chemist, rust is considered an ill-defined material, described as hydrated ferric oxide.
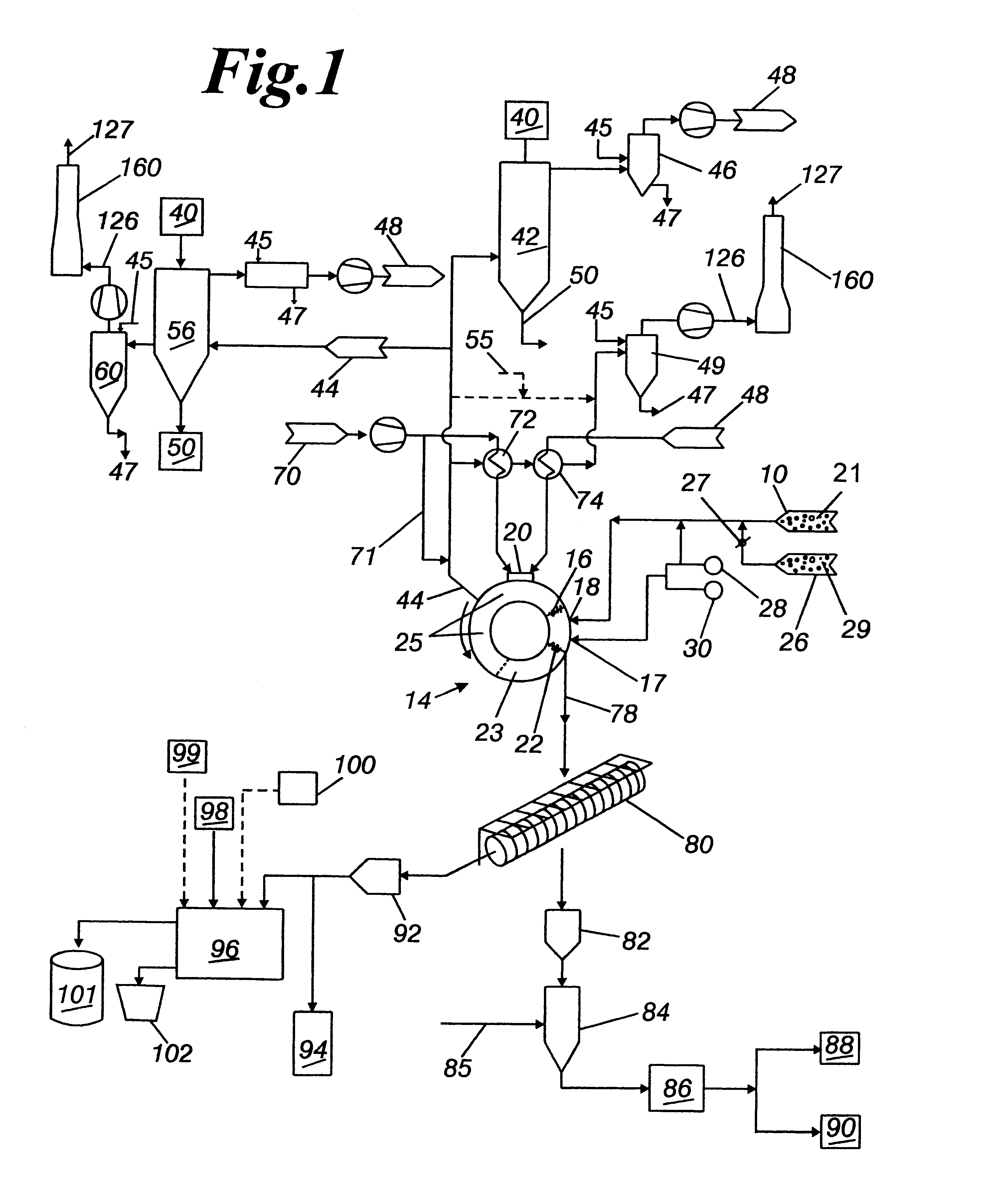
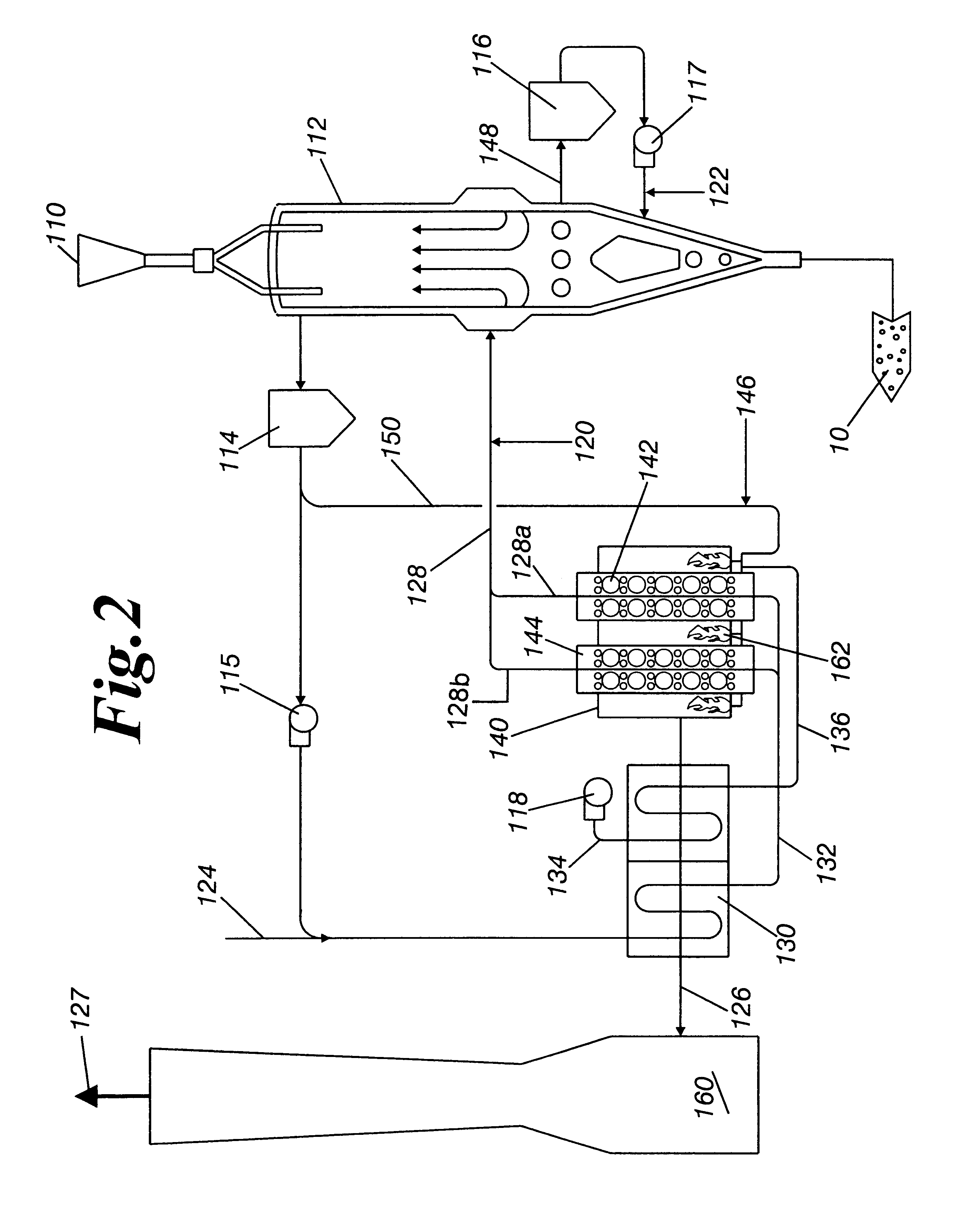
Method of making iron and steel
InactiveUS6149709AEasy to getLess impurity contentProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceHigh energyRefractory
Molten iron is prepared by (1) providing iron oxide and a carbonaceous reducing agent, (2) preparing a shaped product from the carbonaceous reducing agent and the iron oxide, (3) preparing solid reduced iron from the shaped product, wherein the solid reduced iron has a metallization of at least 60%, a specific gravity of at least 1.7, and a carbon content of at least 50% of the theoretical amount required for reducing the iron oxide remaining in the solid reduced iron, and, (4) before substantial cooling occurs, heating the solid reduced iron in an arc heating-type melting furnace at a high temperature. The molten iron can be prepared efficiently from iron ores of relatively low iron content without causing erosion of refractories, at high energy and high reduction efficiencies, and by a simple operation in a simple facility.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
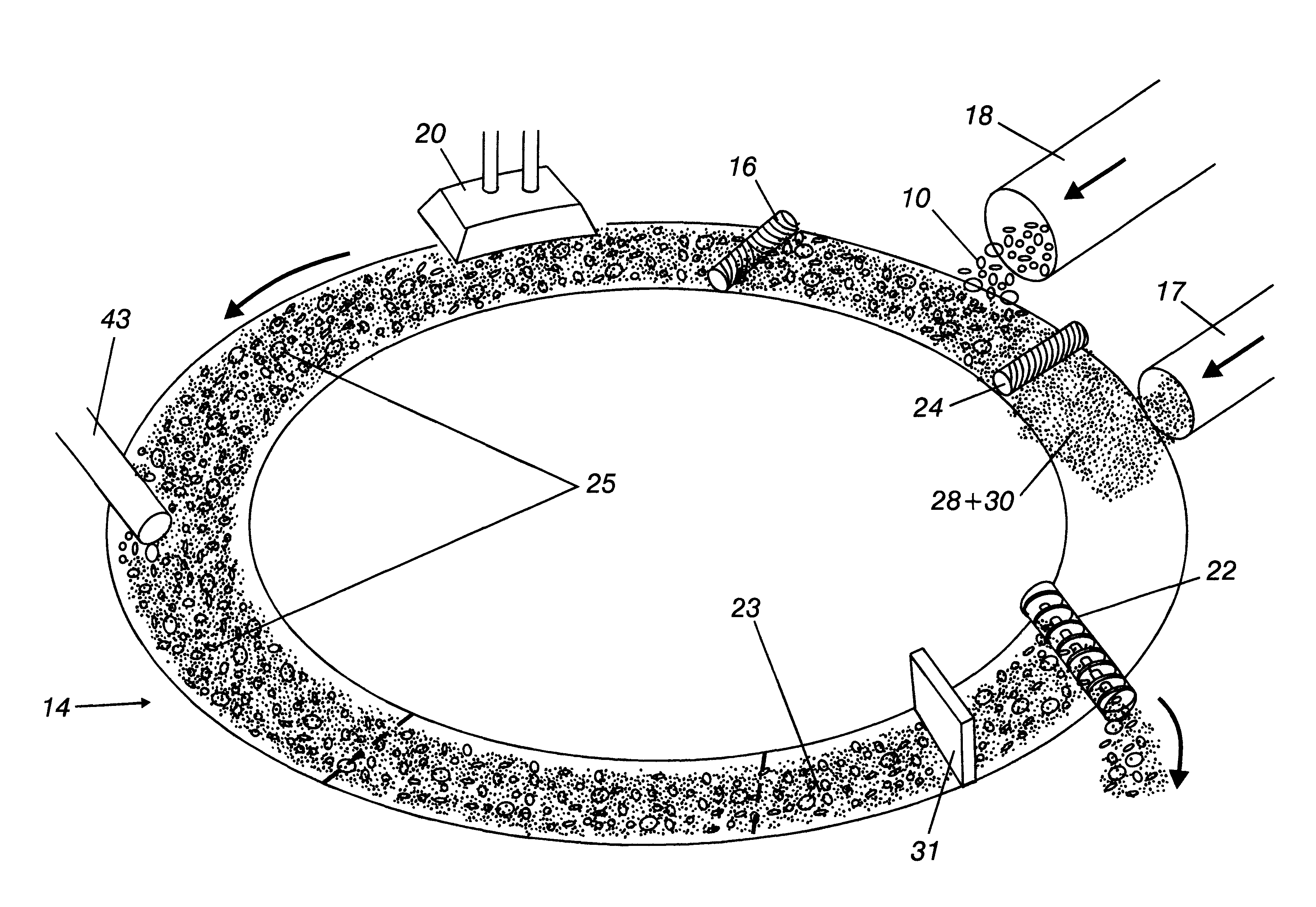
Method of direct iron-making / steel-making via gas or coal-based direct reduction and apparatus
The invention is a method and apparatus for iron-making / steel-making using a modified rotary hearth furnace, that is a finisher-hearth-melter (FHM) furnace. In the method the refractory surface of the hearth is coated with carbonaceous hearth conditioners and refractory compounds, where onto said hearth is charged with pre-reduced metallized iron. The pre-reduced metallized iron is leveled, then heated until molten, and then reacted with the carbon and reducing gas burner gases until any residual iron oxide is converted to iron having a low sulfur content. Nascent slag separates from the molted iron forming carburized iron nuggets. The nuggets are cooled, and then the iron nuggets and the hearth conditioners, including the refractory compounds, are discharged onto a screen, which separate the iron nuggets from the hearth conditioner. The hearth conditioner is recycled, and the iron nuggets are either prepared for sale or for additional treatment, such as alloying, in a final melter, where the final melter is preferably an electric furnace. Exhaust gases from the FHM furnace are recovered for calcining coal into fuel gases and coke.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
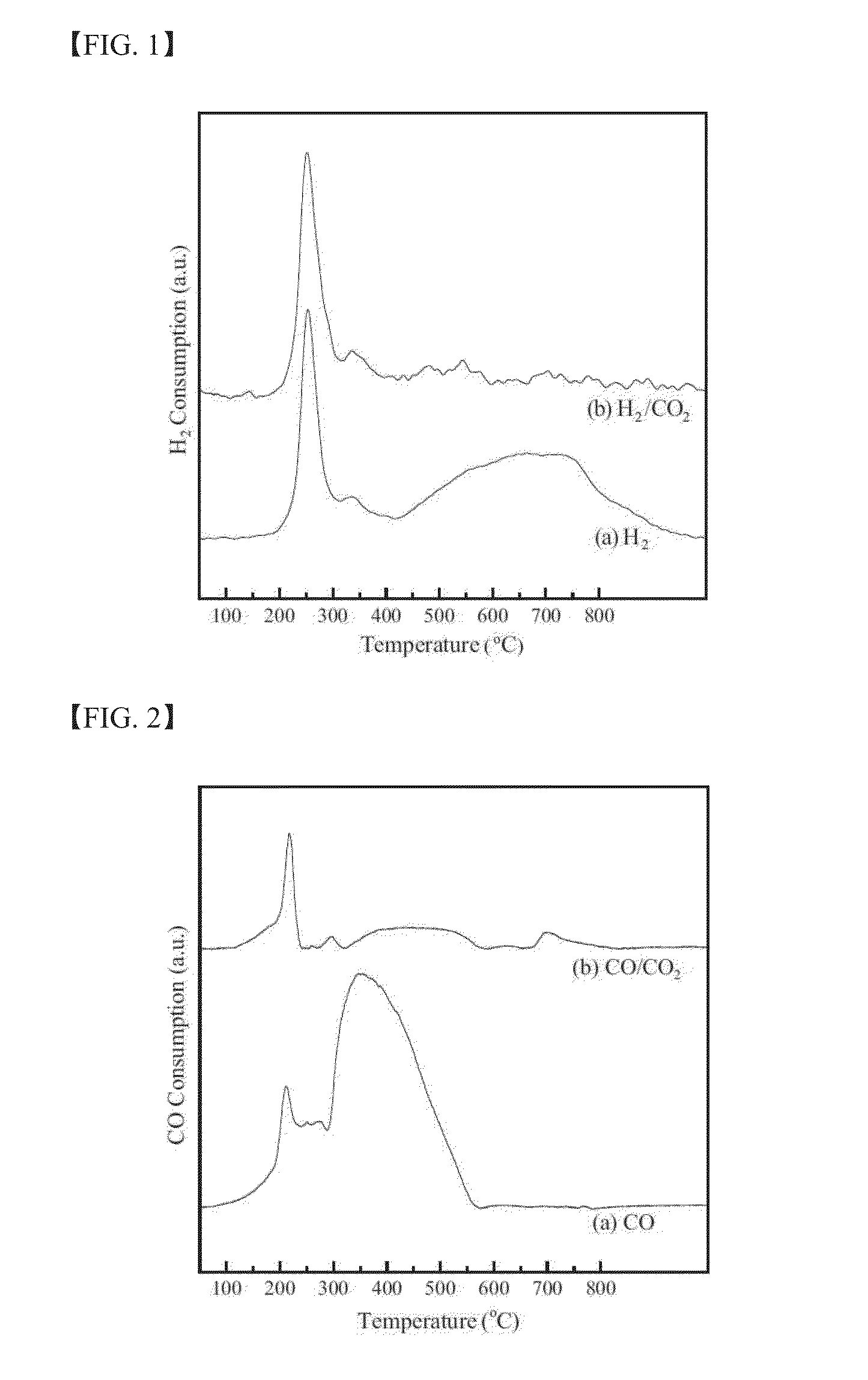
Iron-based catalyst and method for preparing the same and use thereof
ActiveUS20160045901A1Superior productivity and selectivityGood effectOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionProduction rateSyngas
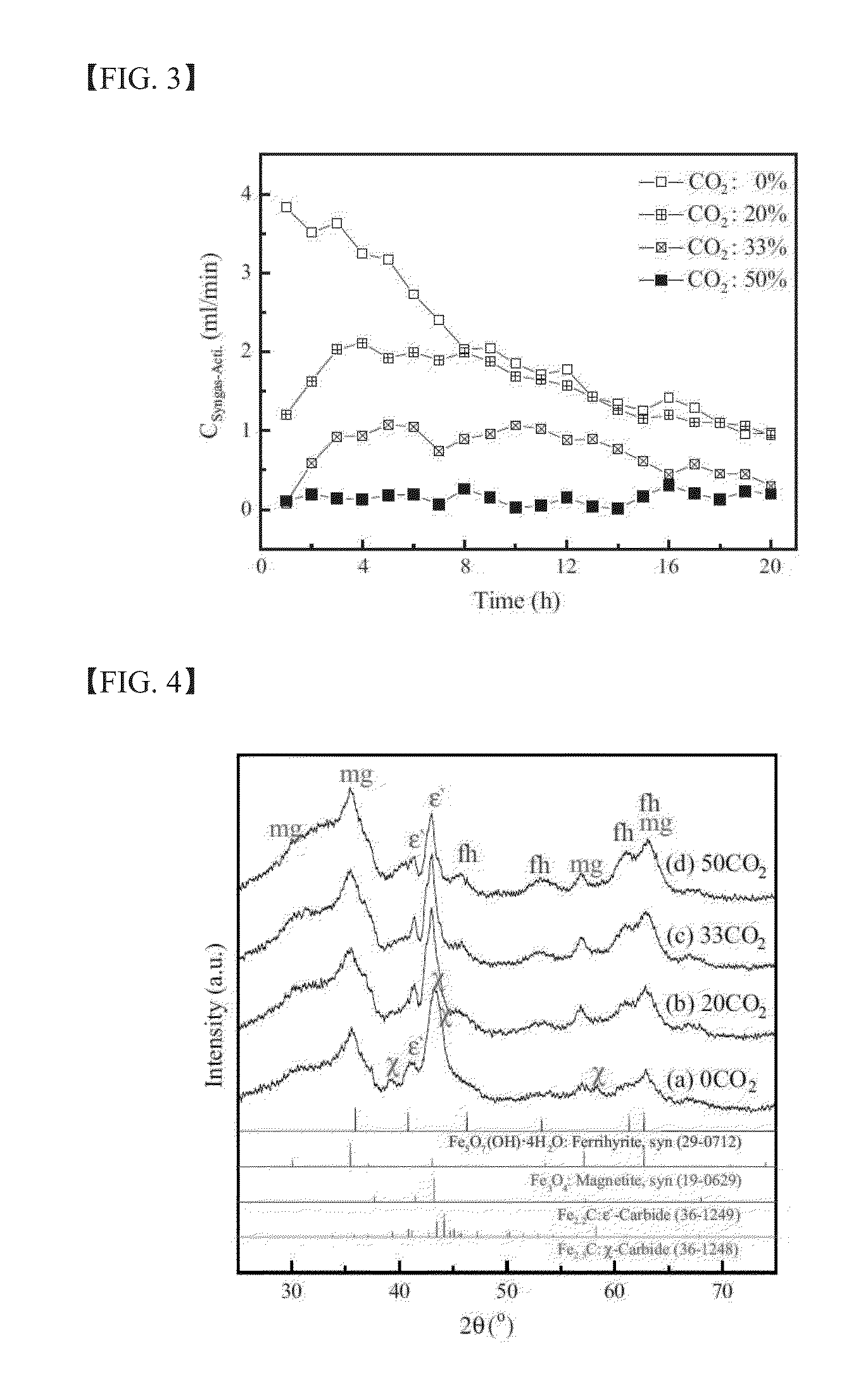
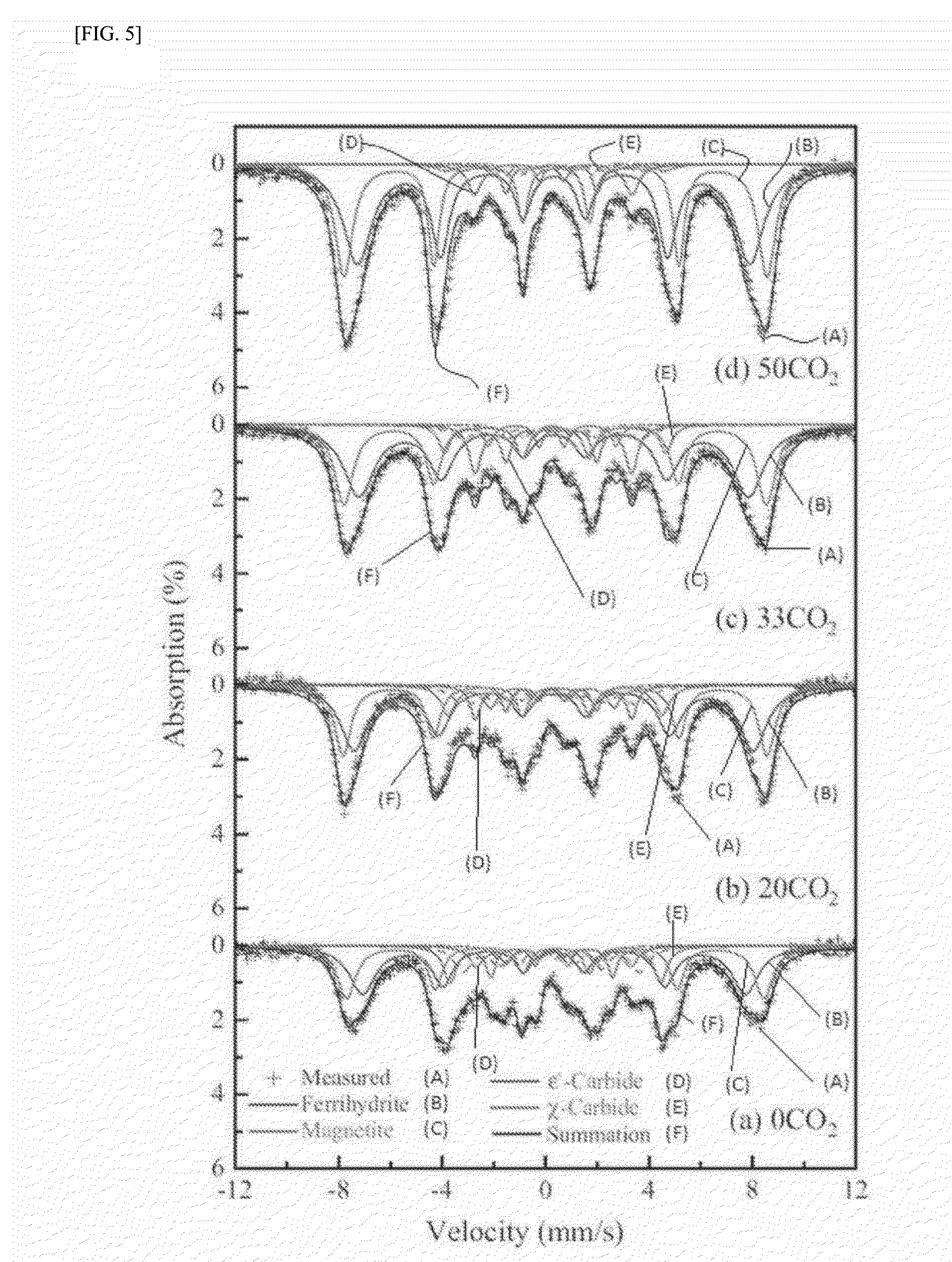
The present invention relates to a method for preparing liquid or solid hydrocarbons from syngas via the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in the presence of iron-based catalysts, the iron-based catalysts for the use thereof, and a method for preparing the iron-based catalysts; more specifically, in the Fischer-Tropsch reaction, liquid or solid hydrocarbons may be prepared specifically with superior productivity and selectivity for C5+ hydrocarbons using the iron-based catalysts comprising iron hydroxide, iron oxide, and iron carbide wherein the number of iron atoms contained in the iron hydroxide is 30% or higher, and the number of iron atoms contained in the iron carbide is 50% or lower, relative to 100% of the number of iron atoms contained in the iron-based catalysts.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Multiple element composite metal oxidate arsenic removal settling agent and use method thereof
The invention belongs to the material field for removing the arsenic in water by settlement, more particularly relates to polyelement composite metal oxide arsenic removal settlement agent and an application method thereof based on iron oxide, manganese oxide, and aluminum oxide. The invention uses an ectopic preparation method or situ preparation method for preparing and obtaining polyelement composite metal oxide arsenic removal settlement agent which comprises hydrated iron oxide, hydroxyl-hydrated ferric hydroxide, hydrated aluminum oxide, hydroxyl-hydrated alumina, hydrated manganese oxide and the like. The polyelement composite metal oxide arsenic removal settlement agent can be used for removing the arsenic pollutants in water bodies such as lakes, reservoirs, rivers, groundwater, drinking water, industrial waste water, and the like; in addition, the settlement agent can also be used for removing the heavy metals such as copper, chromium, cadmium, lead, and the like, and the pollutants such as iron, manganese, phosphates, and the like in water by settlement.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting copper from printed circuit board acidic spent etching solution and preparing poly ferric chloride
InactiveCN101353795ASolve the rare problem of recyclingPromote resource recyclingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementAcid etchingElectrolysis
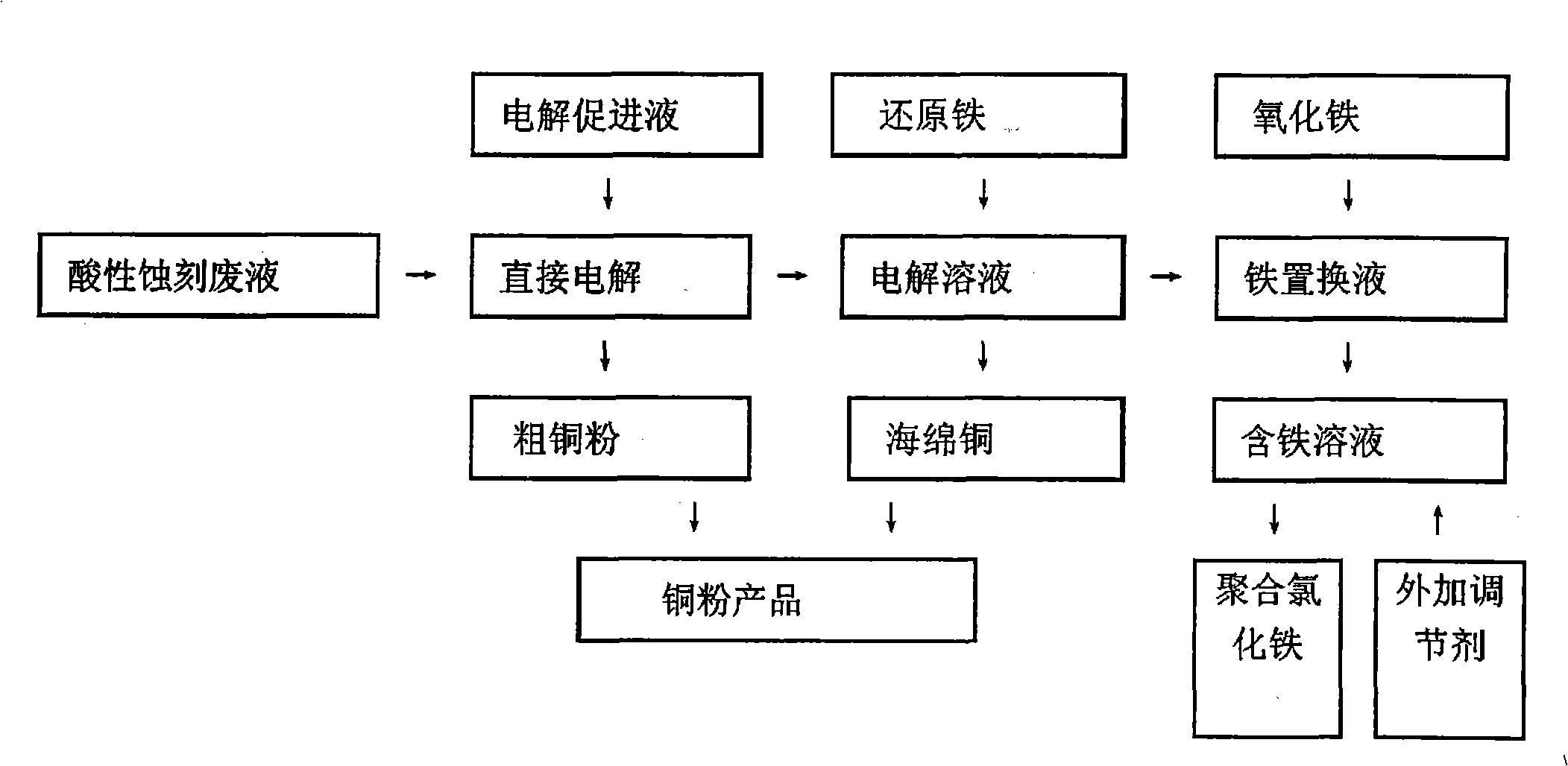
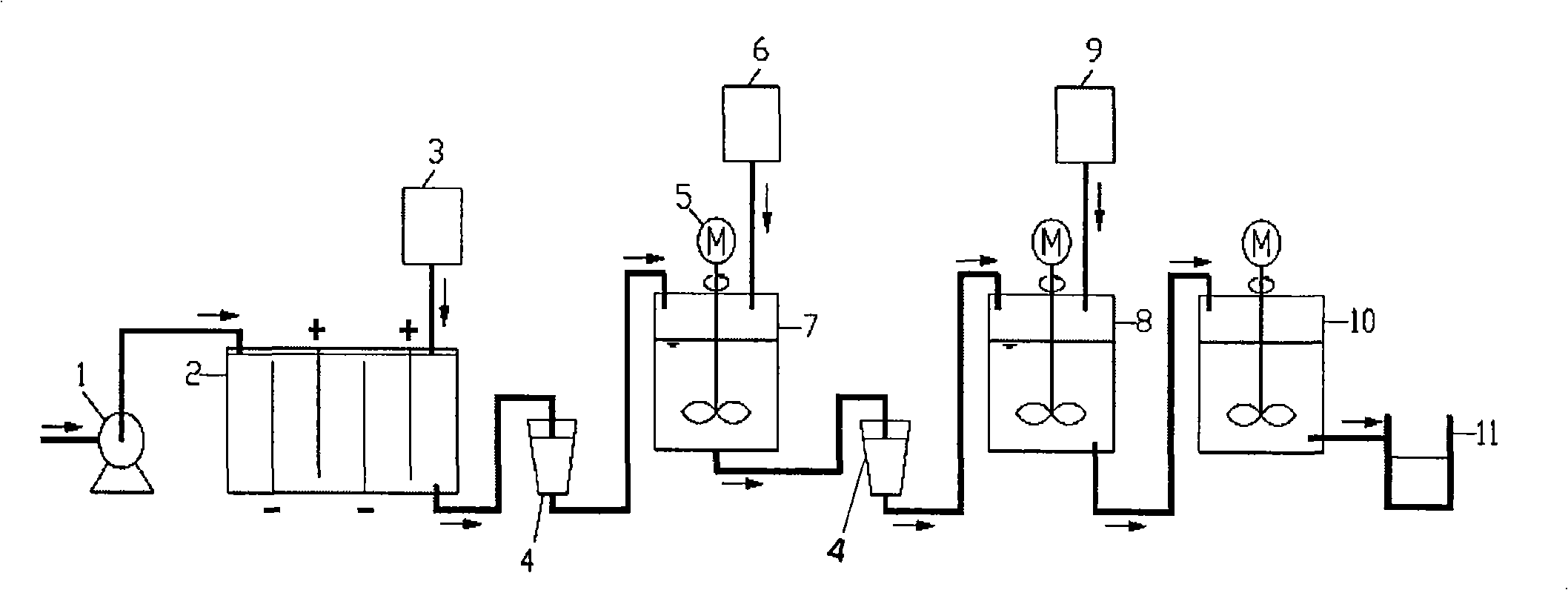
The invention relates to a method for extracting copper of a PCB acid etching waste liquid and preparing polyferric chloride, which comprises the following steps: the PCB acid etching waste liquid is electrolyzed directly and copper powder precipitated by electrolysis is reclaimed; reduced iron is added into a mixed solution after the electrolysis and copper sponge precipitated by replacement reaction is reclaimed; claimed crude copper is purified and prepared into copper powder products; the mixed solution after replacement reaction is added with ferric oxide or a substance containing Fe irons; the mixed solution mingled with the Fe irons is added respectively with a polymeric antioxidant and a stabilizer and simultaneously, the pH value of which is regulated with acid or alkali; and finally, the PFC is prepared. The method of the invention completely realizes reclamation and recycling of wastes and water environment treatment and finally 'zero' emission and has good environmental protection, simple preparation process, high economic benefit and wide application scope.
Owner:HUNAN VARY TECH
Catalyst for hyrogenating deoxidating and olefine saturating of Feather synthesizing oil and its mfg. process and application
ActiveCN1597859AImprove hydrogenation activityRefining by selective hydrogenationPtru catalystCopper oxide
The invention is a hydro-deoxidation and alkene-saturation catalyst of Fischer-Tropsch oil product and its components in weight percent: nickel oxide 5.0-18.0%, cobalt oxide 0-11.0%, copper oxide 0-6.0%, iron oxide 0-12.0%, titanium oxide 0-12.0%, lanthanum oxide 0-8.0% and carrier 46.0-85.0%. Its preparing method includes in turn carrier preprocessing and after-processing of supported active component and catalyst. It has higher activity to hydro-deoxidation and alkene saturation of the oil product, especially applied to the hydrofining process of the iron-base paste Fischer-Tropsch oil product with higher content of oxygen-containing compound and alkene.
Owner:SYNFUELS CHINA TECH CO LTD
Resin rough grinding wheel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103465179AImprove grinding efficiencyIncrease roughnessAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesPyriteAlumina zirconia
The invention relates to a resin rough grinding wheel and a preparation method thereof. The resin rough grinding wheel comprises a grinding body and reinforcing meshes, wherein the reinforcing meshes are arranged inside the grinding body to enhance the revolving strength of the grinding body. The grinding body is composed of 115-150 parts of grinding materials, 5-15 parts of liquid phenolic resin, 25-45 parts of phenolic resin powder and 15-35 parts of filling, wherein the grinding materials comprise 30-40 parts of microcrystal corundum, 80-100 parts of fused alumina zirconia and 5-10 parts of garnets, the filling is composed of 9-21 parts of pyrite, 1-3 parts of cryolite, 1-3 parts of ferric oxide, 1-3 parts of quick lime and 3-5 parts of fluorite. The resin rough grinding wheel is prepared through the steps of preparation, mixing, sifting, shaping, hardening, testing, packaging and storing, has high strength, good abrasive resistance and self-sharpening performance, high grinding efficiency, good roughness and low workpiece burning possibility; meanwhile, the surface of the grinding wheel is not easy to block and has good breathability, good tenacity and high security performance.
Owner:NINGBO DAHUA GRINDING WHEEL
Preparation method of furnace transmutation sorghum red-flower glaze
The invention relates to the technical field of ceramic glaze and particularly relates to a preparation method of furnace transmutation sorghum red-flower glaze. A ground coat is prepared from feldspar, quartz, Soochow soil, calcite, glass dust, dolomite, chromic oxide, cobaltous oxide, ferric oxide and vanadium pentoxide; overglaze is prepared from feldspar, quartz, zinc oxide, Soochow soil, boron frits, cadmium-selenium haematochrome, silicon carbide and copper oxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly applying the ground coat on a green body after biscuiting; then applying the overglaze; and firing by adopting oxidizing flames of a roller kiln. By adopting formulae of the ground coat which is matte black with metallic luster and the bright-red overglaze as well as a special firing process, particularly control of the temperature-raising rate, the ground coat which is matte black with metallic luster is low in initial melting point, the green body and the glaze are compactly combined, the glaze is level and smooth, and the product is smooth, flexible, vigorous and decent in surface.
Owner:江苏省宜兴彩陶工艺厂
Spinel type high-entropy oxide electrode material and preparation method thereof
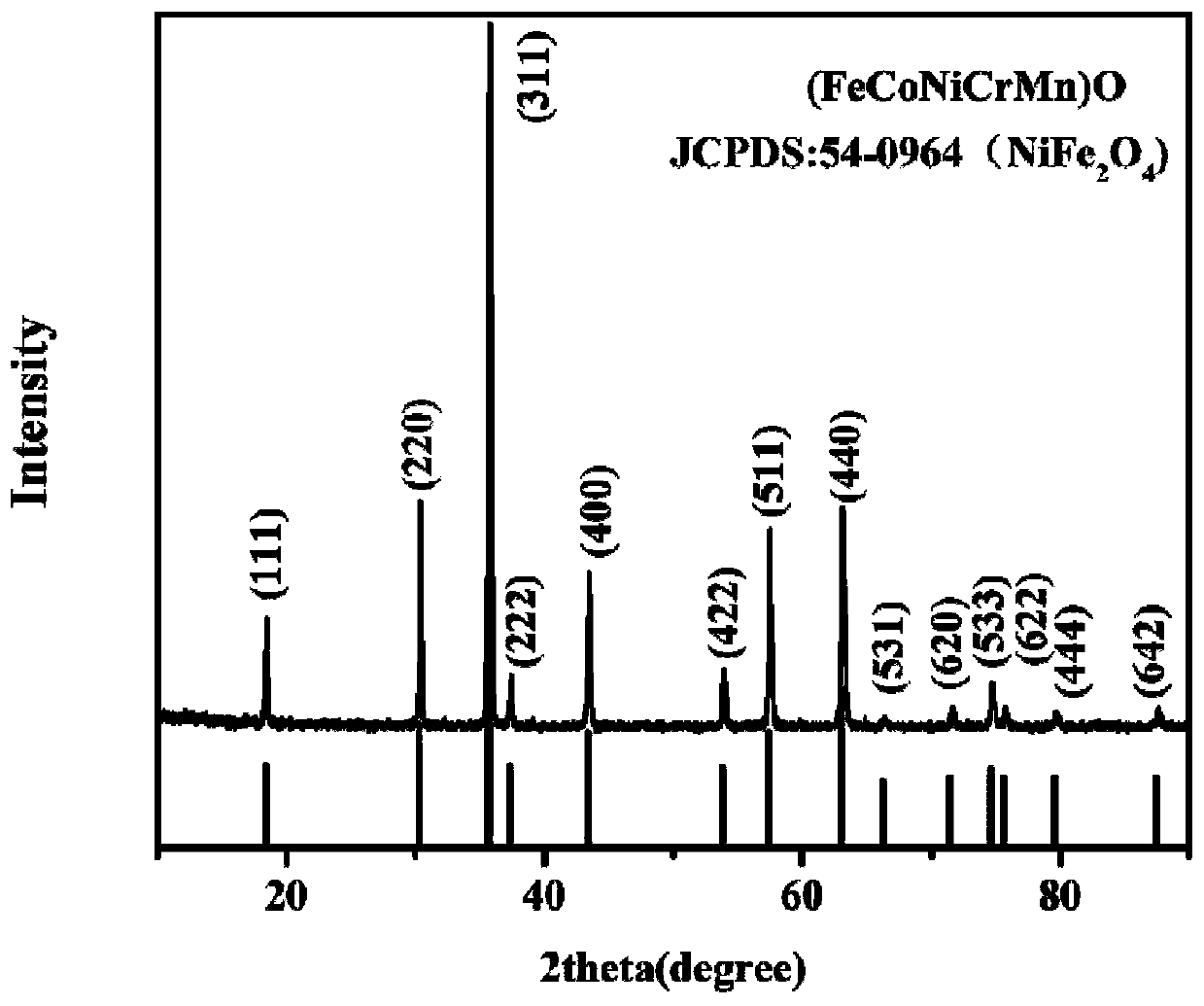
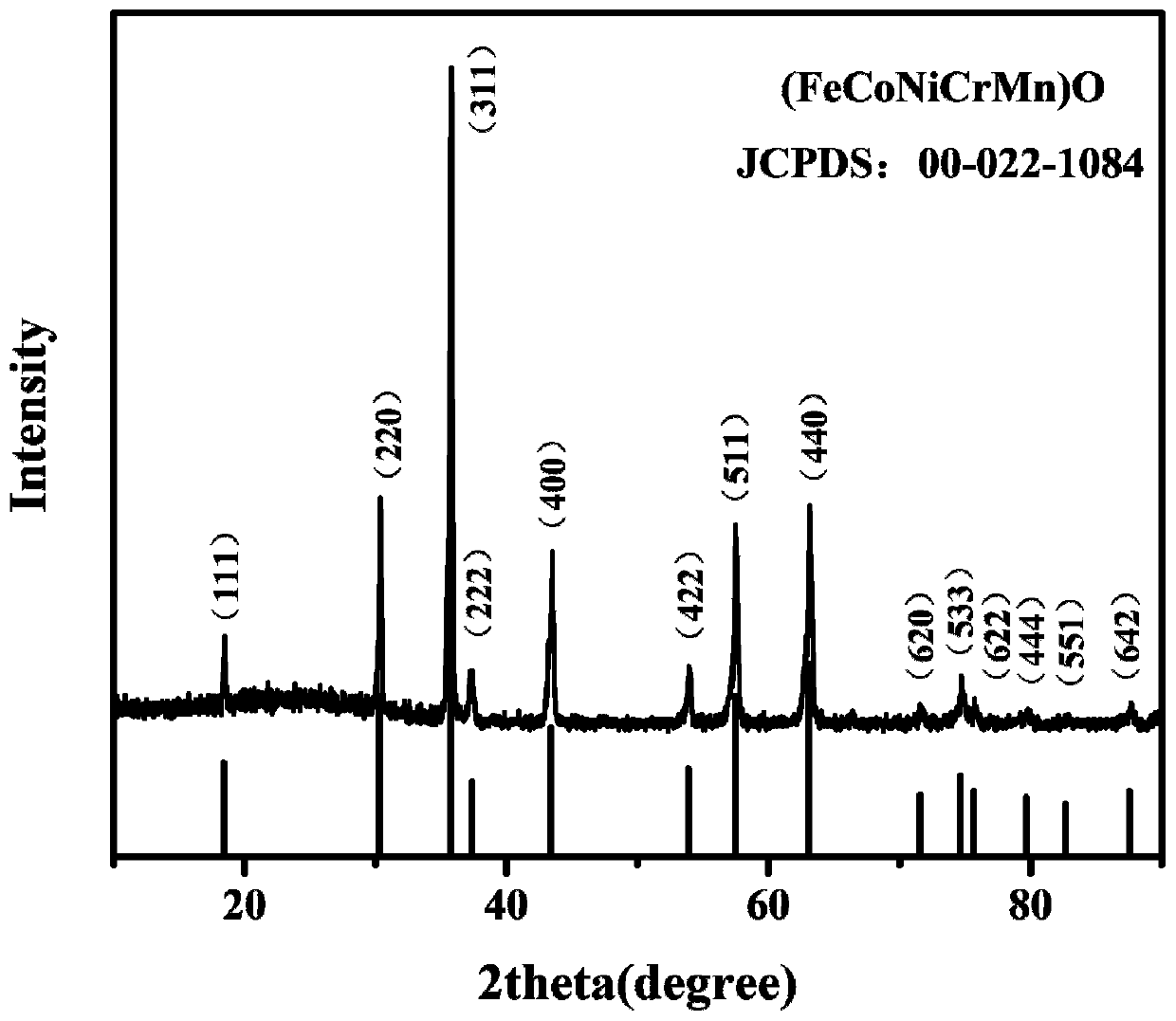
ActiveCN110364717AHigh specific capacityImprove cycle stabilityNegative electrodesSecondary cellsIron(II) oxideSpace group
The invention relates to a spinel type high-entropy oxide electrode material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of nanomaterial preparation and new energy. The chemical formulaof the high-entropy oxide electrode material is one of (FeCoNiCrMn)O, (FeZnNiCrMn)O, (FeCoZnCrMn)O and (FeCoNiCrMnCu)O. The preparation method includes the steps of 1) mixing and ball-milling iron oxide, chromium oxide, manganese oxide and M metal oxide, wherein the M metal oxide is two or more of nickel oxide, zinc oxide, copper oxide and cobalt oxide; and 2) carrying out high-temperature calcination, and obtaining the spinel type high-entropy oxide electrode material by adopting a cooling mode of furnace cooling, air quenching and liquid nitrogen quenching. The particle diameter of the high-entropy oxide is 100-500nm, and the high-entropy oxide is determined to be in a spinel structure according to XRD; and the space group of the material is Fd-3m, and the specific surface area is 5-100m<2>g<-1>.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
Method for treating acid-washing wastewater and metallic ions in iron and steel industry
InactiveCN102107963ALow running costGuaranteed uptimeWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFerric hydroxideZinc hydroxide
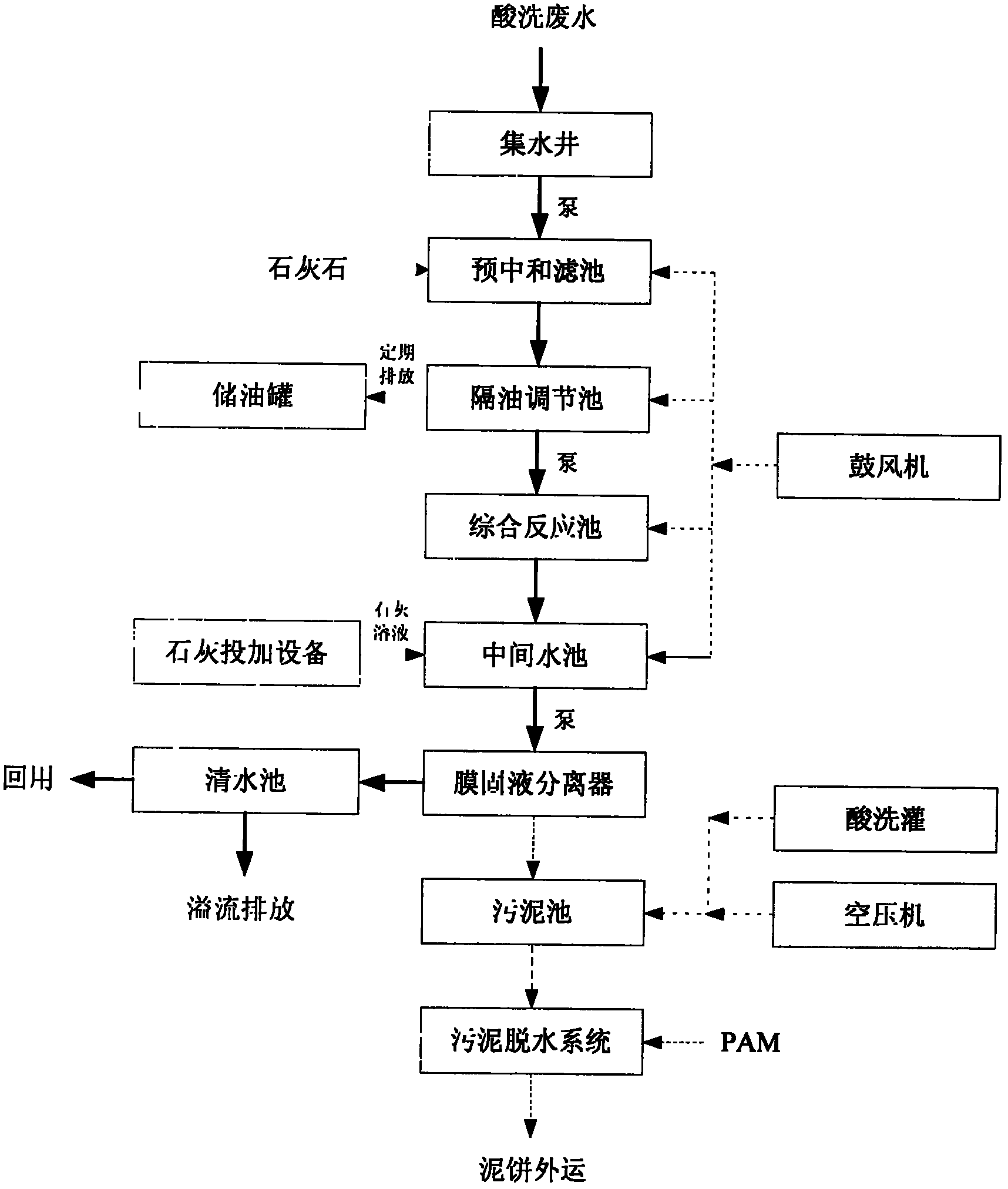
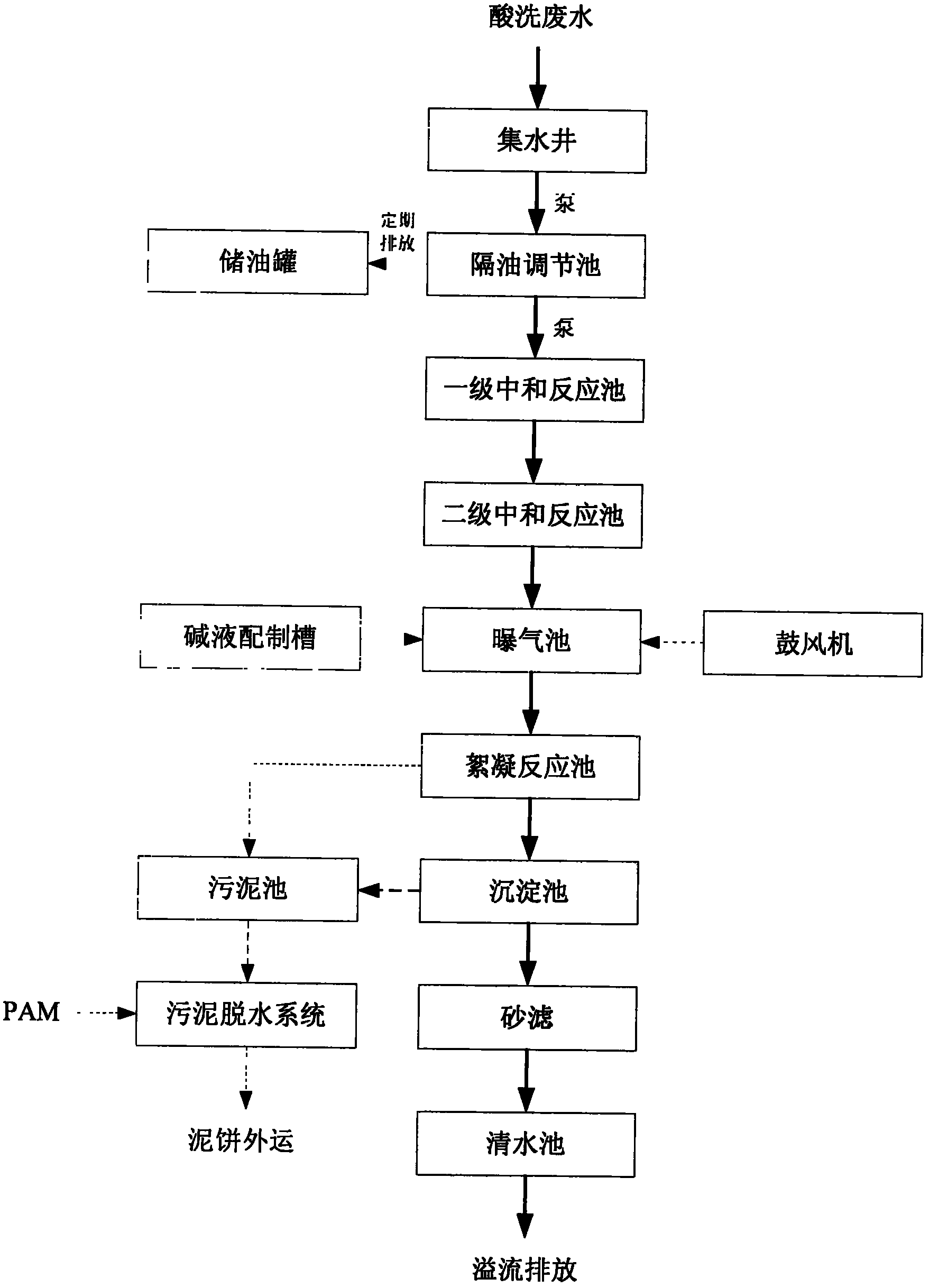
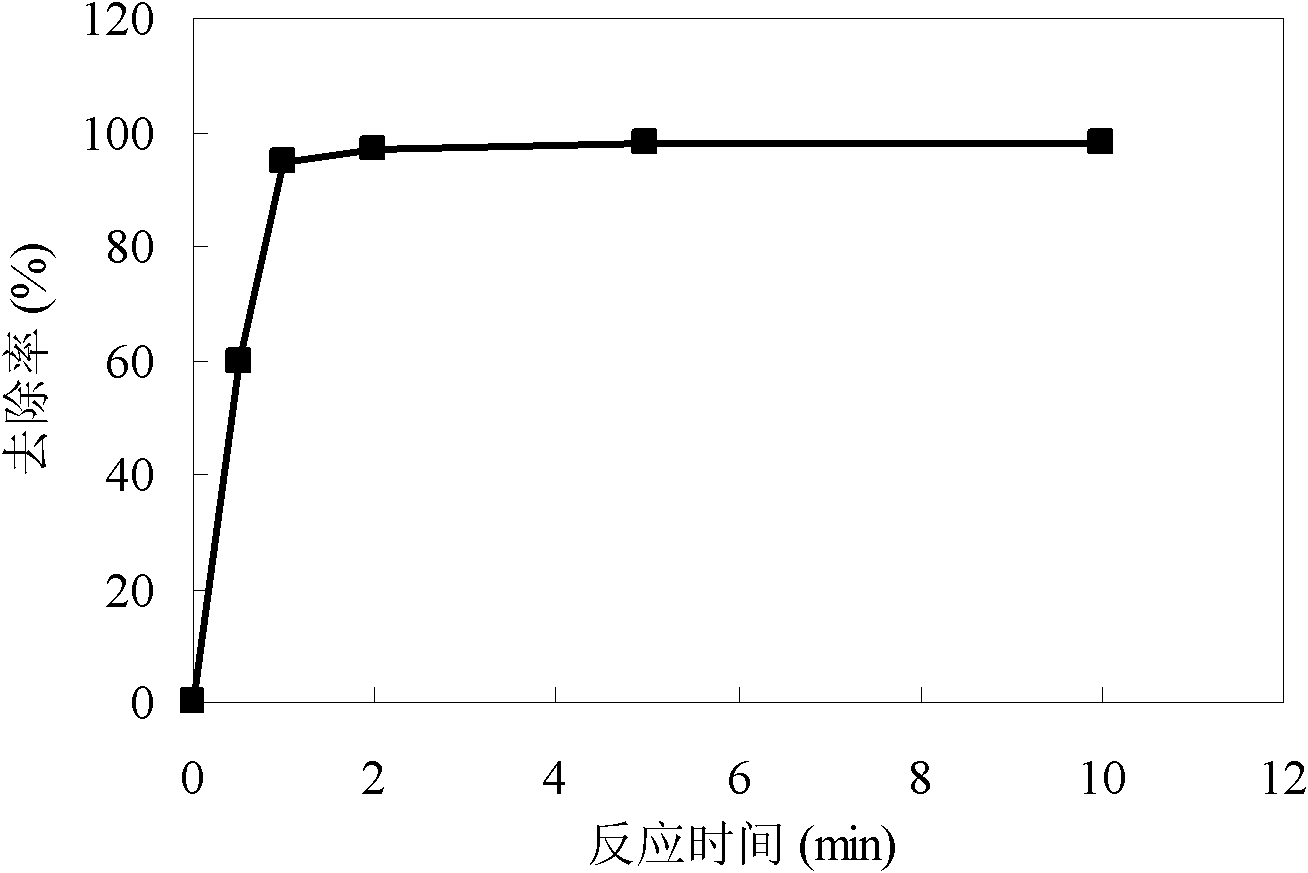
The invention provides a method for treating acid-washing wastewater and metallic ions in iron and steel industry, which comprises steps as follows: acid-washing wastewater naturally flows into a water collecting well and enters a preneutralization filter chamber under the elevation action of a pump, the preneutralization filter chamber is provided with 10-200mm limestone which is in a graded distribution mode, and after the acid-washing wastewater is preneutralized by the limestone, the pH value of the effluent water is controlled at 5-6, wherein the method provided by the invention greatly lowers the chemical expenses and operating cost as compared with the conventional method of directly adding an alkali solution; the acid-washing wastewater, which is subjected to initial pH value regulation, naturally flows into an oil separation regulating chamber, so that iron ions in the wastewater react with the alkali solution to form a precipitation mixture of ferric hydroxide, zinc hydroxide and the like; and the wastewater is elevated into a membrane solid-liquid separator to complete solid-liquid separation, so that the wastewater can be discharged after reaching the standard. The invention thoroughly solves the problems that the precipitate can not easily settle, the iron can not be easily removed, and the iron ions are dissolved out. The invention has the advantages of simple technique, high economy, low requirements for technical levels of workers, and high controllability, is reliable to operate, and has wide market prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Water treatment method for removing Tl<+> and/or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer iron and manganese oxides in situ
ActiveCN102145947AHigh electronegativityLarge specific surface areaWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFerric hydroxideWater source
The invention discloses a water treatment method for removing Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer iron and manganese oxides in situ, relating to a water treatment method of thallium and / or cadmium-containing source water and solving the problems of complex process, high running cost and low removing efficiency of thallium and / or cadmium existing in the conventional water treatment technology specific to thallium and / or cadmium-polluted source water. The method comprises the following steps of: adding permanganate and ferrous salt into Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+>-containing water; stirring to obtain a mixed solution; adding a coagulant; and performing conventional water treatment. A nanometer ferric hydroxide-manganese dioxide oxide composite adsorbent which has a large specific surface area and high electronegativity and is easy for precipitation separation is produced in situ by making permanganate react with the ferrous salt, so that Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> can be removed effectively andspecifications in the national Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water are met. The method has the advantages of high removing efficiency, simple process, flexibility and convenience for operation, no change of the original treatment process of a water plant, low running cost and the like, and can be applied to emergency treatment of a water pollution event.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation method of special low-density grinding ball for cement grinding mill
The invention relates to a preparation method of a special low-density grinding ball for a cement grinding mill. The preparation method comprises the steps of with bauxite, alumina powder and the like as main raw materials and chromium oxide, zirconium oxide, calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, ferric oxide, manganese oxide, titanium oxide, silicon dioxide and the like as modified raw materials, adding alumina sol, silica sol and metal salt into slurry at a grinding stage; molding by rolling, isostatic pressing or machine pressing to obtain a green body; and calcining after drying the green body to obtain the low-density grinding ball. By virtue of scientific proportion design, strict process control and unique calcining system, the special low-density grinding ball disclosed by the invention is low in cost, excellent in wear resistance, lower in power load as comparison with a high-density metal grinding body, suitable for substituting a metal grinding body in cement grinding, iron ore grinding and gold ore grinding and capable of reducing the electric consumption for grinding by 30-50%.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
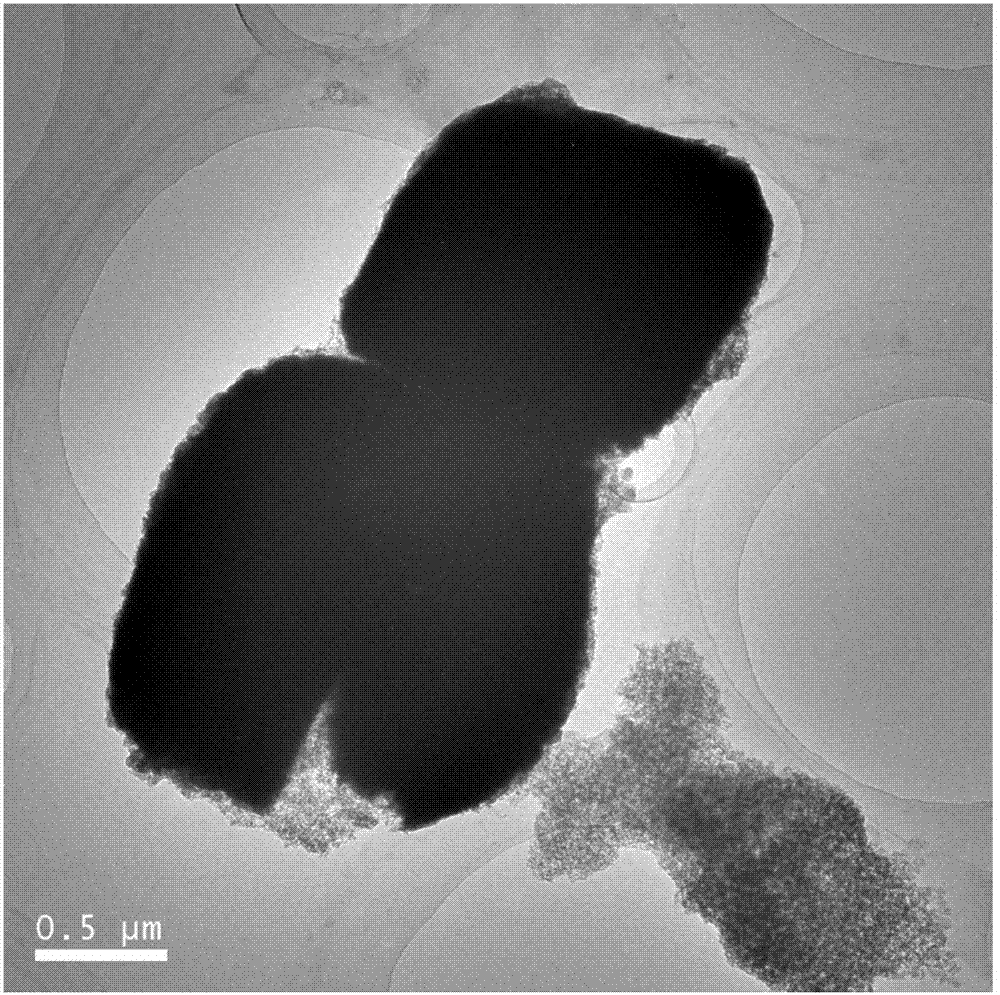
Carbon-coated hollow ferriferrous oxide and application thereof
The invention discloses carbon-coated hollow ferriferrous oxide and an application thereof. The preparation method of the carbon-coated hollow ferriferrous oxide comprises the following steps of: (1) adding a ferric salt into a solvent and dissolving the ferric salt, wherein the solvent is a mixture of water and ethanol; implementing a hydrothermal reaction in a sealed hydrothermal kettle for 20-30hours at 100-250 DEG C, and separating to obtain a ferric oxide deposit; and (2) uniformly mixing the ferric oxide deposit with a reducing carbon source, wherein the reducing carbon source is one substance or a combination of multiple substances selected from carbon powder, glucose, polyethylene, acetylene black and starch; and implementing an insulating reaction for 0.5-4hours in a muffle at 200-1000 DEG C, to obtain the carbon-coated hollow ferriferrous oxide. The carbon-coated hollow ferriferrous oxide, used as a lithium ion battery negative electrode material, can remarkably improve electrical conductivity and keeps a stable structure, so that a comparatively high capacity retention ratio is still guaranteed after several charge-discharge cycles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Raw material proportion of bice glaze and firing method thereof
The invention relates to a mixture ratio of raw materials of a grey blue glaze. The grey blue glaze comprises the following compositions by weight percentage: 30 to 35 percent of quartz, 32 to 38 percent of feldspar, 8 to 11 percent of talcum, 2 to 5 percent of clay, 6 to 9 percent of limestone, 3 to 5 percent of aluminum oxide, 7 to 9 percent of zirconium silicate, 0.01 to 0.05 percent of manganese oxide, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of ferric oxide, 0.01 to 0.05 percent of chromic oxide, 0 to 0.3 percent of cobalt oxide, 0 to 1 percent of dispersant and 0 to 1 percent of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium. The grey blue glaze is prepared by steps of drying, grinding, screening, iron removal, aging, glaze spraying and firing according to the mixture ratio of the grey blue glaze. The mixture ratio of raw materials of the grey blue glaze and the method for firing the grey blue glaze can improve the appearance quality of ceramic pieces and the performance of glaze layers and can meet requirements for batch production and ensure high qualification rate of products and good economic benefits due to the adoption of the prior equipment in the firing process.
Owner:CHINA XD ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Absorption liquid for gas desulfurization and its application
ActiveCN1621133AGood choiceHigh selectivityDispersed particle separationOrganic sulfide compoundLight irradiation
The present invention discloses one kind of gas desulfurizing absorption liquid and its desulfurizing method. The gas desulfurizing absorption liquid has nanometer alpha- or gamma-ferric oxide and iron chelate as catalyst. In the presence of organic compound and alkali compound and light irradiation, air is introduced and the absorption liquid absorbed inorganic and / or organic sulfide are oxidized into simple substance sulfur. The gas desulfurizing method of the present invention has the advantages of low catalyst consumption, fast regeneration of catalyst, no jamming of the absorption tower, etc.
Owner:BEIJING BAIAONA HI TECH
Catalyst for catalytic cracking mixed waste plastic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101284235AGood technical effectVersatilityMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCatalytic pyrolysisCatalytic reforming
The invention discloses a catalyst for manufacturing fuel oil through catalytic pyrolysis of mixed-waste plastics, and a preparation method thereof, and relates to catalytic thermal cracking for manufacturing the fuel oil through waste plastic cracking and a second stage catalyst in thermal cracking catalytic reforming. A first stage catalyst comprises a metallic oxide of 2.0wt percent to 30.0wt percent and carclazyte or montmorillonite of 70.0wt percent to 98.0wt percent; the first stage catalyst is innoxious and cheap, increases the reaction velocity of plastic cracking, reduces the temperature in the scission reaction, improves the selectivity of decomposition products, and is dechlorinated and transformed into innocuous substances. The second stage catalyst is composed of ferric oxide, molybdenum oxide, zinc oxide, cerium oxide, lanthana, nickel oxide or copper oxide, and ZSM-5, MCM-22, USY, REY, Beta or MOR molecular sieves; the second stage catalyst performs the second catalytic pyrolysis and isomerization and the aromatization reversion reactions on pyrolysis gas in the first stage, to increase the distillate rate of pyrolysis gasoline and gas oil. The catalyst and the preparation method thereof have good selectivity, and the raw material does not need classification, washing and drying; the operation is flexible, and the running cost is low; the method is particularly applied to the fuel oil manufacture through the cracking of the mixed-waste plastics in the urban and rural domestic refuse, the composition is complicated; the oil yield of the qualified fuel oil can reach up to more than 70 percent calculated on the basis of the waste plastic.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
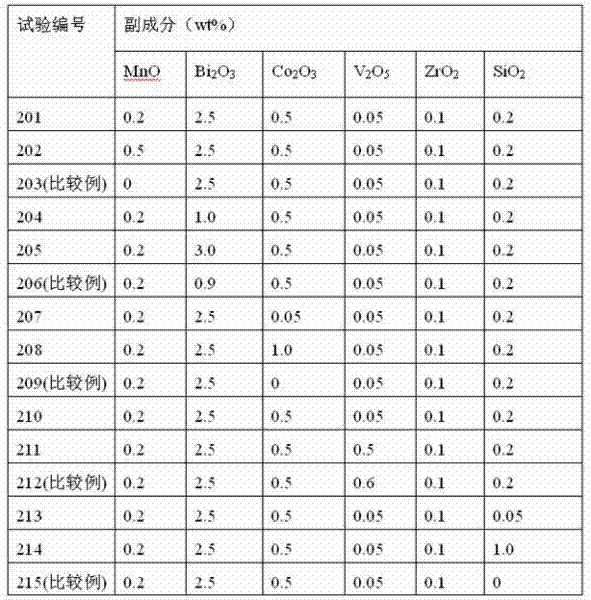
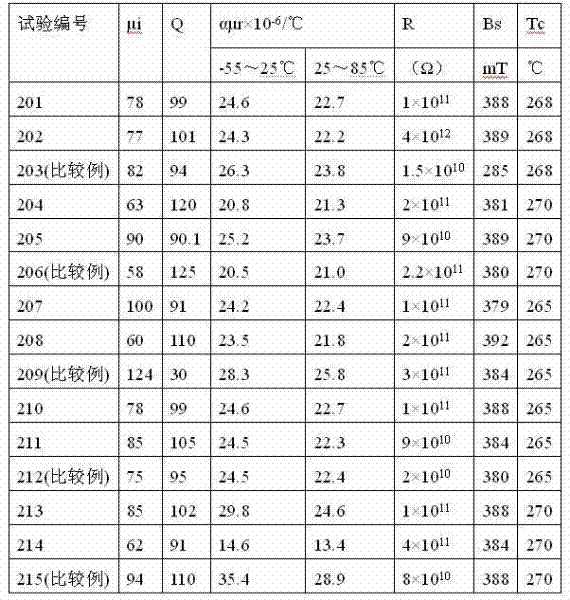
Soft magnetic ferrite material and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a soft magnetic ferrite material. Raw materials for preparing the soft magnetic ferrite material comprise composite materials and auxiliary materials. The composite materials comprise iron oxide, manganese oxide and zinc oxide. The auxiliary materials comprise 0-6000 ppm of nickel oxide, 100-800 ppm of calcium carbonate, 0-500 ppm of lithium carbonate, 20-120 ppm of silicon dioxide, 0-230 ppm of magnesium oxide, 0-180 ppm of niobium oxide, 700-2000 ppm of cobalt oxide, 0-350 ppm of bismuth oxide, 100-600 ppm of vanadium oxide, 0-2500 ppm of titanium dioxide, 0-500 ppm of copper oxide, and 100-500 ppm of zirconium oxide. The invention also discloses a preparation process of the soft magnetic ferrite material. The soft magnetic ferrite material has high initial magnetic permeability and low magnetic core loss.
Owner:ZHONGDE ELECTRONICS
High-strength, high-density porcelain granule support agent and method of producing the same
The invention discloses a high-strength high-density ceramic aggregate proppant and a method for preparing the same. In the proppant, 100 weight portions of bauxite raw mineral powder are taken as a base material, and the following auxiliary materials in weight portion are added: 0.5 to 5 portions of manganese oxide, 0.3 to 2 portions of magnesia and 0.1 to 3 portions of ferric oxide; and the base and auxiliary materials are milled by a Raymond mill into powder with grain size of less than or equal to 0.049 mm, mixed with each other, transferred to a granulator, and continuously added with atomized water under the condition that the granulator rotates at an uniform speed along one direction to prepare balls with roundness of more than or equal to 0.9, and the balls are sintered in a rotary kiln at a sintering temperature of between 1,000 and 1,400 DEG C for 0.5 to 4 hours to obtain the proppant. Under the closing pressure of 86MPa, the crashing ratio of the proppant is less than 10 percent, and the observed density is more than 3.30g / cm<3>. The proppant has the characteristics of high compressive strength, high observed density, good roundness, simple process, low production cost, high resource utilization rate, low energy consumption and the like, and the method is suitable for the production of the high-strength high-density ceramic aggregate proppant.
Owner:贵州鑫益能陶粒支撑剂有限公司
Mn-Zn ferrite material with wide temperature and high initial magnetoconductivity and preparation method thereof
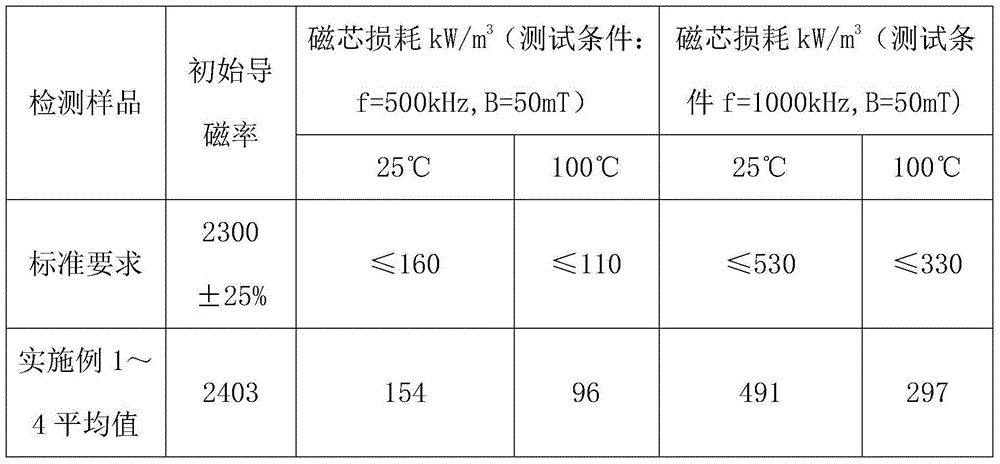
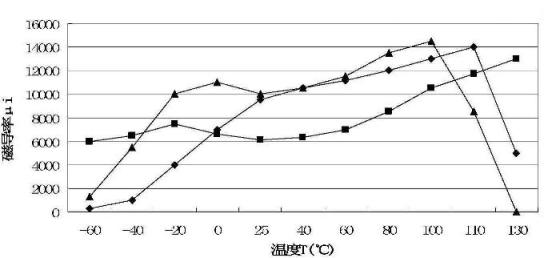
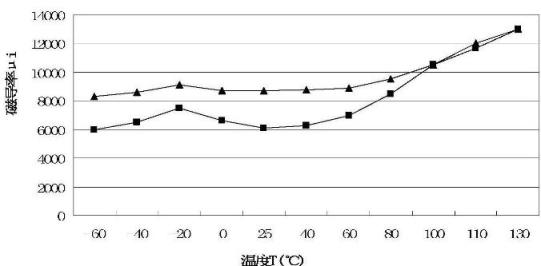
The invention belongs to the field of soft magnetic ferrite, particularly relates to a Mn-Zn ferrite material and provides a Mn-Zn ferrite material with a high initial magnetoconductivity in a wide temperature scope. The Mn-Zn ferrite material is prepared by main components and auxiliary components. The main components are as follows: 51-56 mol% of ferric oxide, 16-26 mol% of zinc oxide and the balance manganese oxide; the auxiliary components comprise one or a combination of more of 50-500ppm of calcium oxide, 50-1000ppm of bismuth oxide, 50-800ppm of molybdenum oxide, 50-800ppm of vanadium oxide or 50-800ppm of indium oxide based on the total weight amount of the main components. In a preferred proposal, one or a combination of more of zirconium oxide, titanium oxide, cobalt oxide or niobium oxide is further added in the auxiliary components. The Mn-Zn ferrite material of the invention is prepared according to a production process of a conventional drying method, and has the characteristic that the initial magnetoconductivity mui is above 5000 within a temperature zone of minus 60 DEG C-130 DEG C, thereby meeting the requirement of electronic devices on a magnetic core with high magnetoconductivity at a lower temperature.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
High-frequency nickel-copper-zinc ferrite and preparation thereof
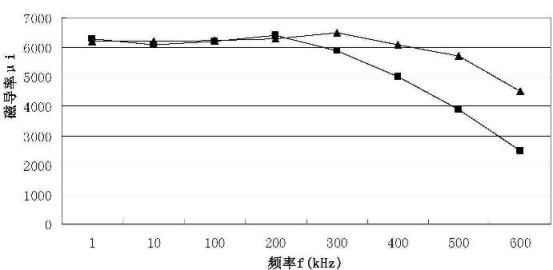
The invention relates to a high frequency nickel-copper-zinc ferrite and a method for preparing the same, which belong to the technical field of nickel series soft magnetism ferrite. The main components of the ferrite are ferric oxide, nickel oxide, zinc oxide, and copper oxide, the accessory components comprise cobalt oxide, bismuth oxide, and silicon oxide, and the ferrite is prepared by an oxide method. The invention adopts an iron deficiency formulation, a low calcination temperature, and a low sintering temperature so that the prepared high frequency nickel-copper-zinc ferrite has good performances of low initial permeability, low relative dissipation factor between 50MHz and 200MHz, and high Curie temperature, and can better satisfy the use requirement of communication electronic parts and components; besides, the preparation process is stable, and the production process has low energy consumption.
Owner:TDG HLDG CO LTD
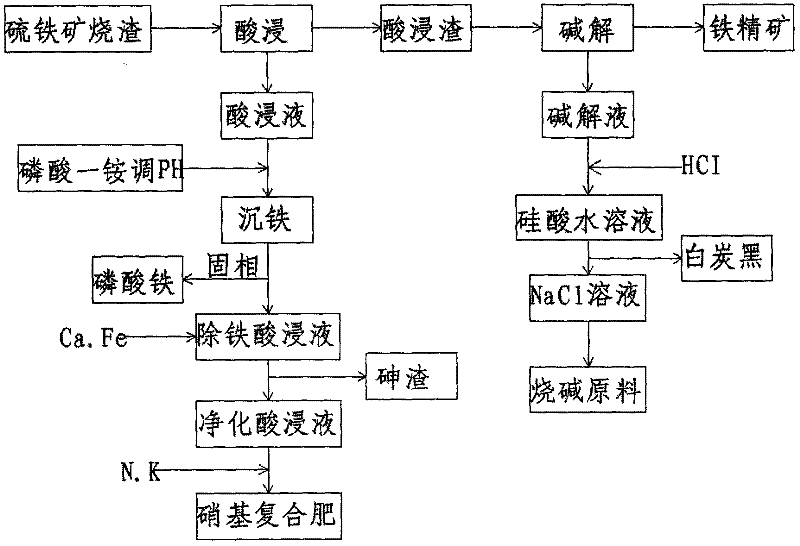
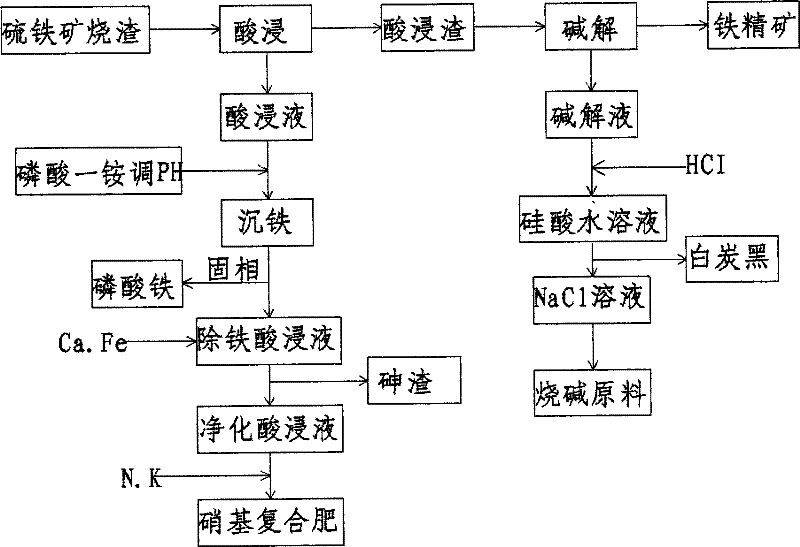
Method for treating pyrite cinder by combining acidic leaching with alkaline dissolving
ActiveCN102534187AEfficient enrichmentRealize cleaner productionProcess efficiency improvementNitro compoundResource utilization
The invention relates to a method for treating pyrite cinder by combining acidic leaching with alkaline dissolving. The method mainly comprises the following steps that: nitric acid is adopted to leach the pyrite cinder, so that alkaline oxide impurities containing sulfur and arsenic are desorbed, most of iron can still exist in a solid phase in the form of ferric oxide, and the iron is effectively enriched, wherein the iron enrichment ratio is more than 90%, the sulfur removal ratio is more than 98%, the arsenic removal ratio is more than 99%, the solid phase is acid-leached residue, and the liquid phase is acid-leached liquor; when the content of silicon dioxide is more than 15% and the total iron content can reach about 50% in the pyrite cinder, an alkaline dissolving treatment is needed, the alkaline-dissolved residue is iron ore concentrate, white carbon black is obtained after acidifying alkaline-dissolved liquor, and the liquid phase is a sodium chloride solution which can be used as a raw material of sodium hydroxide; the acid-leached liquor is added into ammonium dihydrogen phosphate to produce ferric phosphate which can be used as raw materials and ceramic raw materials of a lithium iron phosphate electromagnetic material; and purified acid-leached liquor is obtained after carrying out arsenic removal and can be applied to the production of nitro compound fertilizer. With the adoption of the method for treating the pyrite cinder by combining the acidic leaching with the alkaline dissolving, the pyrite cinder can be fully and comprehensively utilized, and thus, the resource utilization ratio is increased; and the energy-saving and emission-reduction effect is good, the method is beneficial to environment-friendliness, and the clean production in the acid making industry by using the pyrite cinder can be achieved.
Owner:师兆忠
NiCuZn soft magnetic ferrite material used for low temperature co-sintering and preparation method thereof
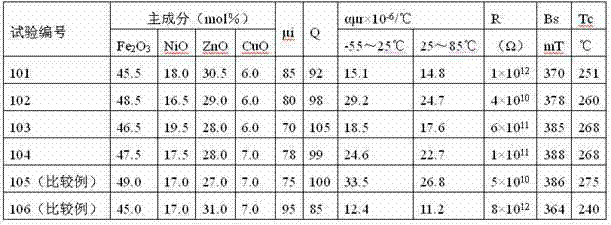
The invention belongs to the field of soft magnetic ferrite materials, and in particular, relates to a NiCuZn soft magnetic ferrite material used for low temperature co-sintering. The material comprises major constituents and accessory constituents, wherein: the major constituents consist of ferric oxide, nickel oxide, zinc oxide and copper oxide, the molar percentage content of each major constituent being Fe2O3 45.5-48.5 mol%, NiO 16.5-19.5 mol%, ZnO 28.0-30.5 mol% and CuO 6.0-8.0 mol%; the accessory constituents comprise manganic oxide and bismuth oxide, compared with the gross weight of the major constituents, the weight percentage gross of the accessory constituents being 1.1-3.5 wt% calculated by taking MnO and Bi2O3 as standard. The invention also provides a preparation method for the ferrite material. When used for preparing MLCI devices under high frequency usage, the material of the invention has advantages in that: the material has a relatively low sintering temperature and metallic silver is not easy to diffuse during co-sintering; and the material ensures that the MLCI devices can obtain excellent magnetic properties and have a relatively good consistency.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Method for dephosphorization and desulphurization in process of steel production in induction furnace
The invention provides a method for dephosphorization and desulphurization in the process of steel production in an induction furnace, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: during the smelting period and the initial period of total meltdown of charging materials, controlling the temperature of molten steel to below 1,450 EDG C, performing dephosphorization treatment on a liquid steel by using a dephosphorizing agent consisting of lime-ferric oxide-boron anhydrous, and controlling the phosphorous content in the liquid steel to below 0.01 percent; after finishing the dephosphorization, absolutely deslagging, then rapidly raising the temperature of the liquid steel to 1, 500 to 1, 600 DEG C; and performing pre-deoxidation and alloying on the liquid steel, and then adding the desulphurizing agent consisting of lime-calcium carbide-aluminum ash, performing the desulphuration on the liquid steel, and reducing the phosphorous content in the liquid steel to below 0.08 percent. The method has the advantages of combining the smelting characteristics of the induction furnace, fully utilizing favorable thermodynamic conditions of dephosphorization and desulphurization, realizing high-efficiency dephosphorization and desulphurization by slagging and greatly improving the quality of the liquid steel; and meanwhile, the method also has the advantages of low cost, less equipment investment, simple operation, easy implementation, and obvious economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
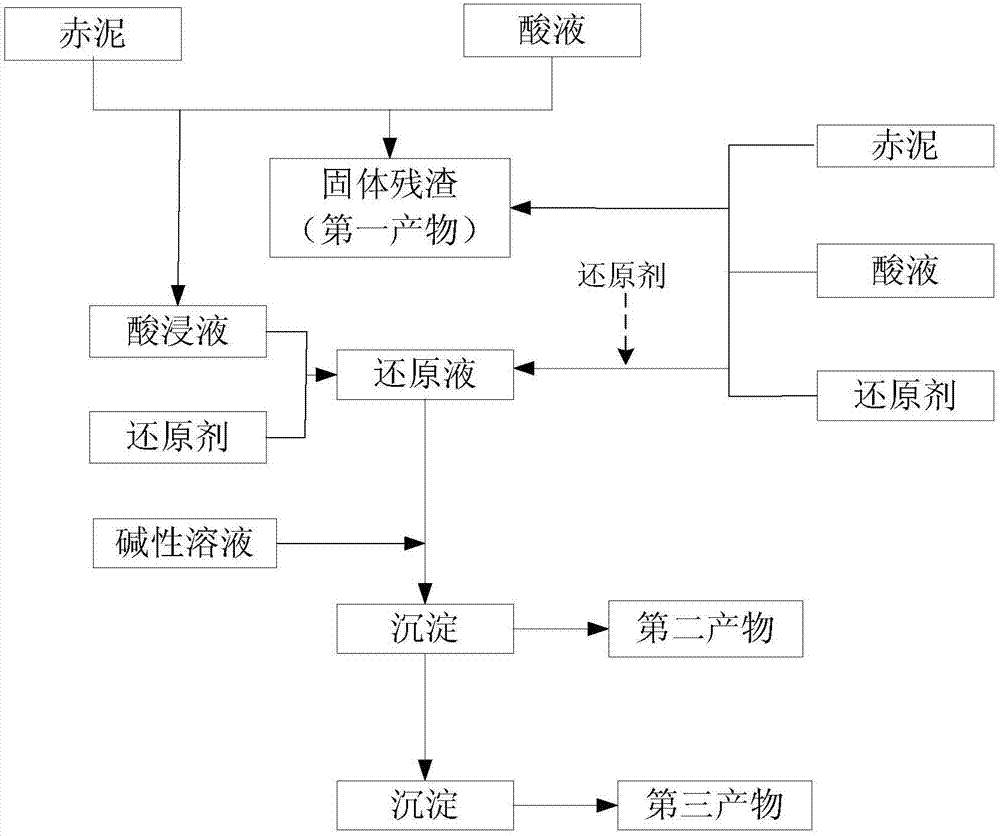
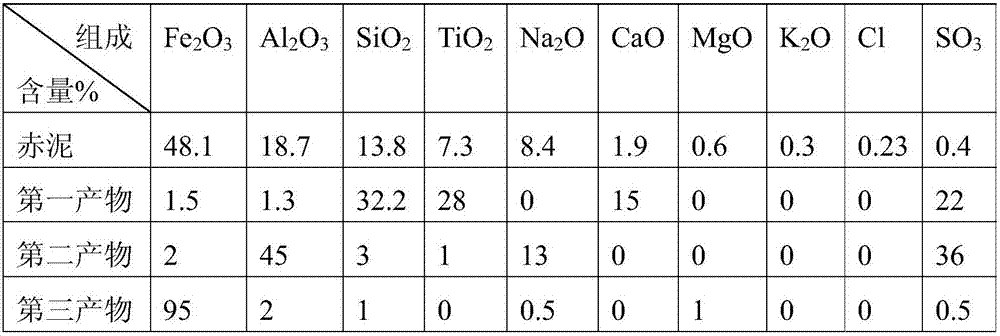
Method for separating iron and aluminum from red mud and/or iron-containing solid waste
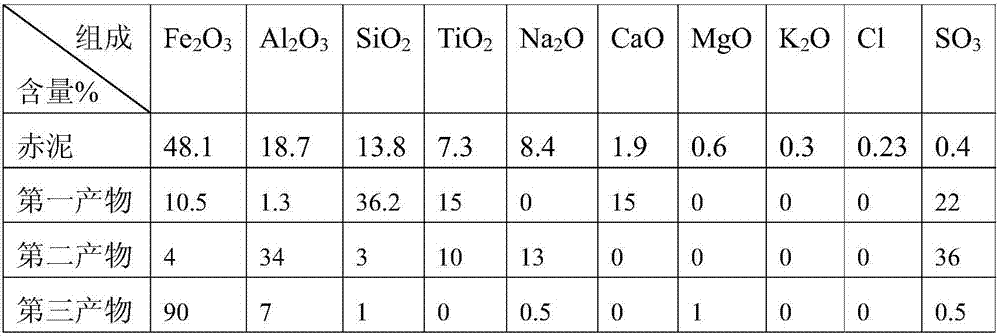
The invention provides a method for separating iron and aluminum from red mud and / or iron-containing solid waste. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out acid leaching and reduction treatment on the red mud and / or iron-containing solid waste to obtain residue and reduction solution; and 2, sequentially adjusting pH of the reduction solution to a precipitation pH interval of trivalent aluminium ions and ferrous ions to separate aluminum and iron. The method is moderate in condition, low in equipment requirements and high in iron separating efficiency; in addition, the purity of an obtained ferric oxide product is high; and harmless and high valve treatment of a large amount of red mud and / or iron-containing solid waste can be realized, so that the method has powerful industrial application potential.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Green Biodiesel
InactiveUS20070282119A1Significant energySignificant processing timeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationCalcium silicateBiodiesel
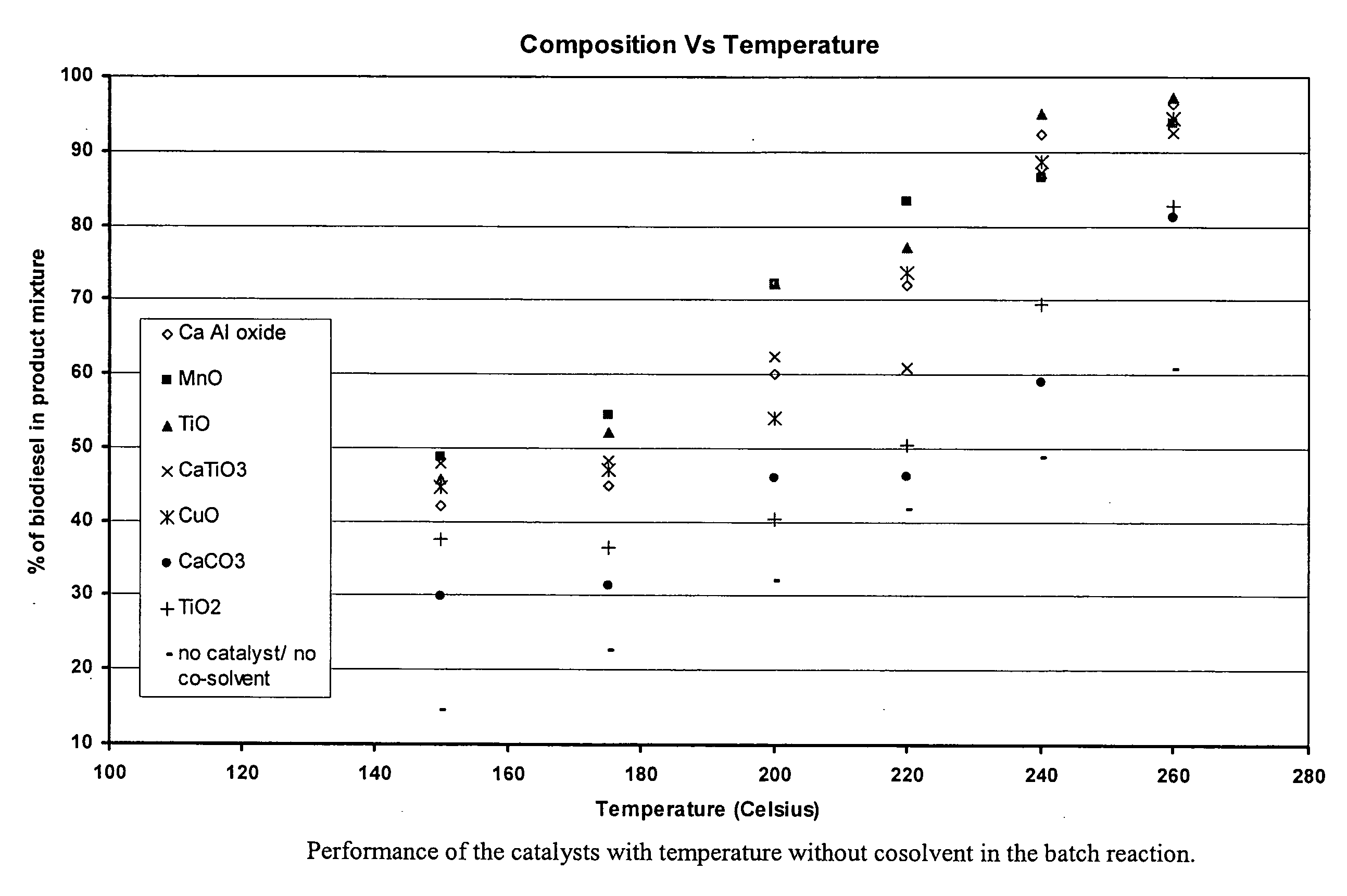
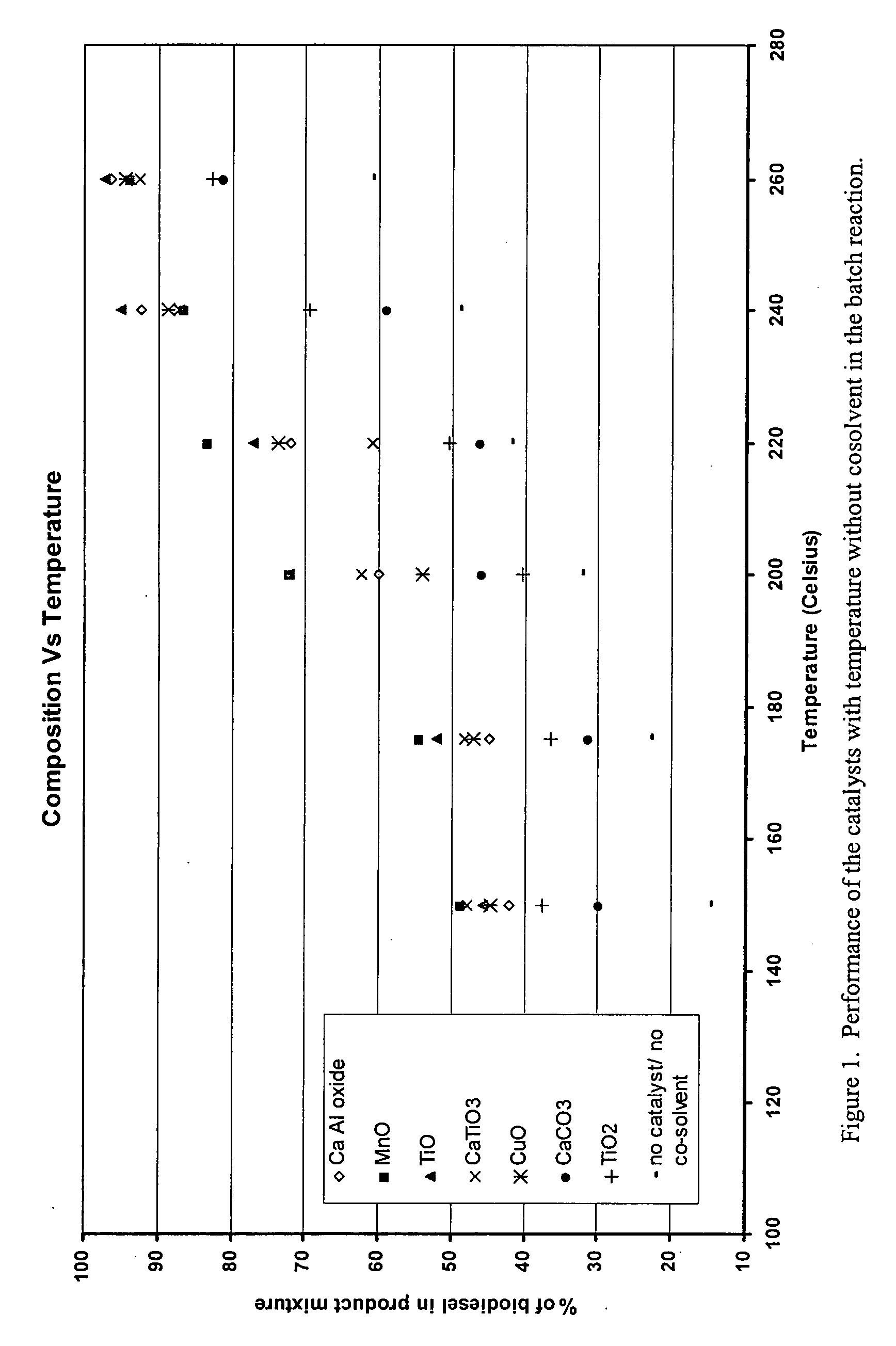
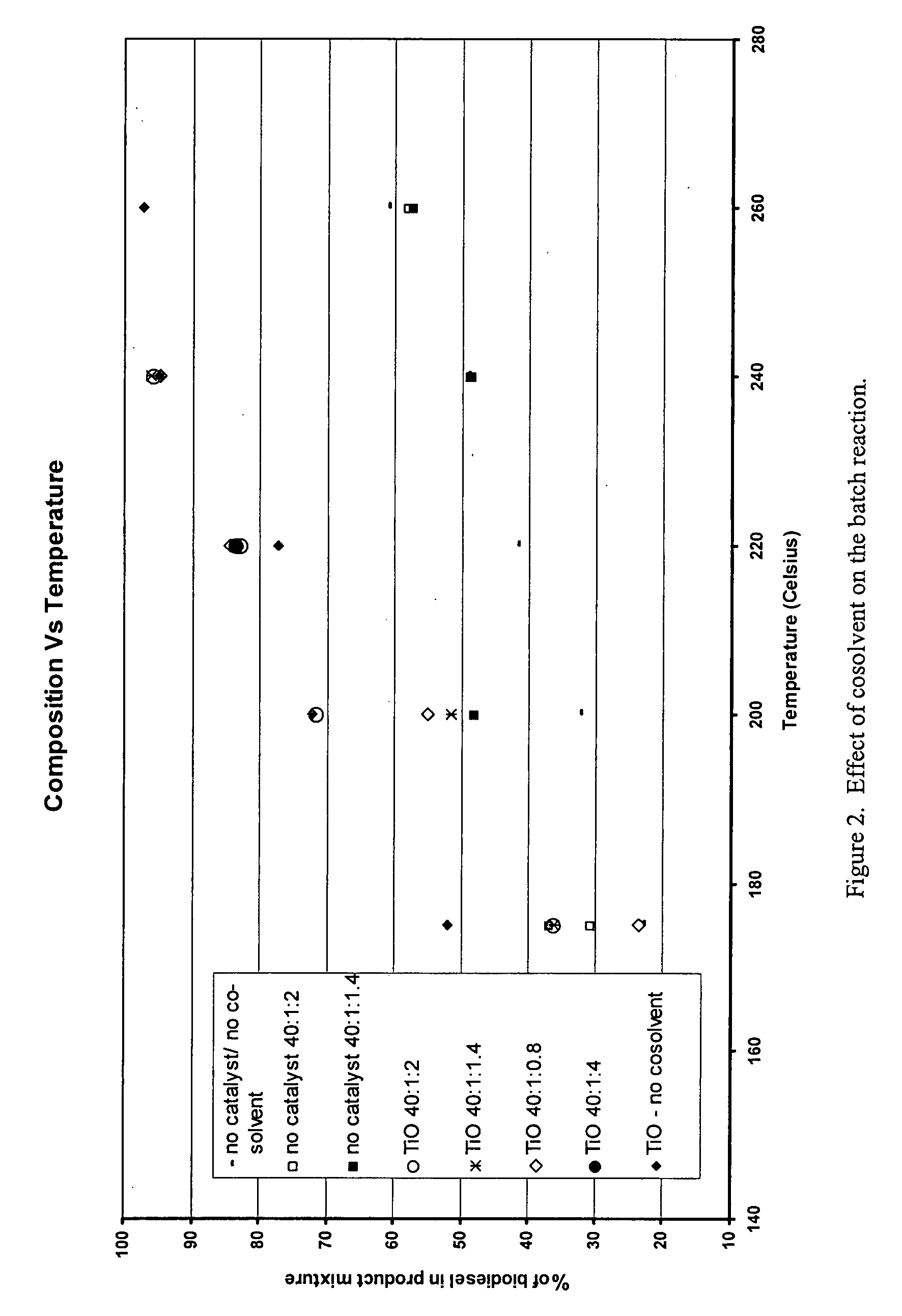
Methods for improved manufacture of green biodiesel focus on the selection and use of one or more solid metallic oxide base catalyst(s) selected from the group consisting of calcium oxide (CaO), calcium aluminum oxide (CaO—Al2O3), calcium titanate (CaTiO3), barium titanate (BaTiO3), magnesium aluminum oxide (MgO—Al2O3), zinc oxide (ZnO), copper (II) oxide (CuO), nickel oxide (NiO), manganese oxide (MnO), titanium oxide (TiO), vanadium oxide (VO), cobalt oxide (CoO), iron oxide (FeO), chromite (FeCr2O4), hydrotalcite (Mg6Al2(CO3)(OH)16.4(H2O), magnetite (Fe3O4), magnesium silicate and calcium silicate.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Stress-resistant nickel zinc ferrite with initial permeability of 120, and preparation method of stress-resistant nickel zinc ferrite
The invention relates to a stress-resistant nickel zinc ferrite which has the initial permeability of 120 and is applicable to a power inductor and a preparation method of the stress-resistant nickel zinc ferrite. The stress-resistant nickel zinc ferrite comprises the main components based on respective reference substance: 46.5-50mol% of ferric oxide (Fe2O3), 20-25mol% of nickel oxide (NiO), 20-25mol% of zinc oxide (ZnO) and 9-12mol% of copper oxide (CuO); and the nickel zinc ferrite comprises the accessory ingredient by respective reference substance: 0.1-0.3wt% of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), 0.035-0.10wt% of cobalt oxide (Co2O3), 0.05-0.45wt% of bismuth oxide (Bi2O3), 0.1-1.0wt% of talcum powder and 0.1-1.0wt% of mica powder. The stress-resistant nickel zinc ferrite is prepared by an oxide method and is sintered under a certain condition. After sintering, the product has the crystallized grain size of 20-30mu m, has obvious crystal boundary, and has the characteristic of less inductance change under the stress action, thus meeting the requirement of the power inductor needed to be packaged by resin on the stress resistance of the ferrite material.
Owner:TDG HLDG CO LTD
Boron-containing fluorine-free fluxing slag-melting agent for electric steelmaking
The invention provides a boron-containing fluorine-free fluxing slag-melting agent for electric steelmaking, belonging to the technical field of steelmaking. The slag-melting agent is made from the following components in parts of by weight: 30-50 parts of boron sludge, 20-40 parts of laterite, 20-40 parts of quicklime and 5-15 parts of ferric oxide. The preparation method of the slag-melting agent comprises the following steps: sufficiently drying and dehydrating the raw materials, and weighting and proportioning based on weight parts; and grinding, evenly mixing, and making block slag by a pelleting-drying-sintering method or premelting-cooling-crushing-sieving method. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the following beneficial effects: the product provided by the invention is used as the fluxing agent instead of fluorite, calcium aluminate and ferriferous oxide, thereby eliminating fluorine pollution and relieving the corrosion action of the slag-melting agent on the furnace lining; and particularly, the waste boron sludge are recycled, and high-cost calcium aluminate is replaced with low-cost laterite with abundant reserves, thus the boron-containing fluorine-free fluxing slag-melting agent provided by the invention has important meanings for reasonably and comprehensively utilizing mineral resources, lowering the steelmaking cost, and realizing high-efficiency low-cost low-pollution green steelmaking.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
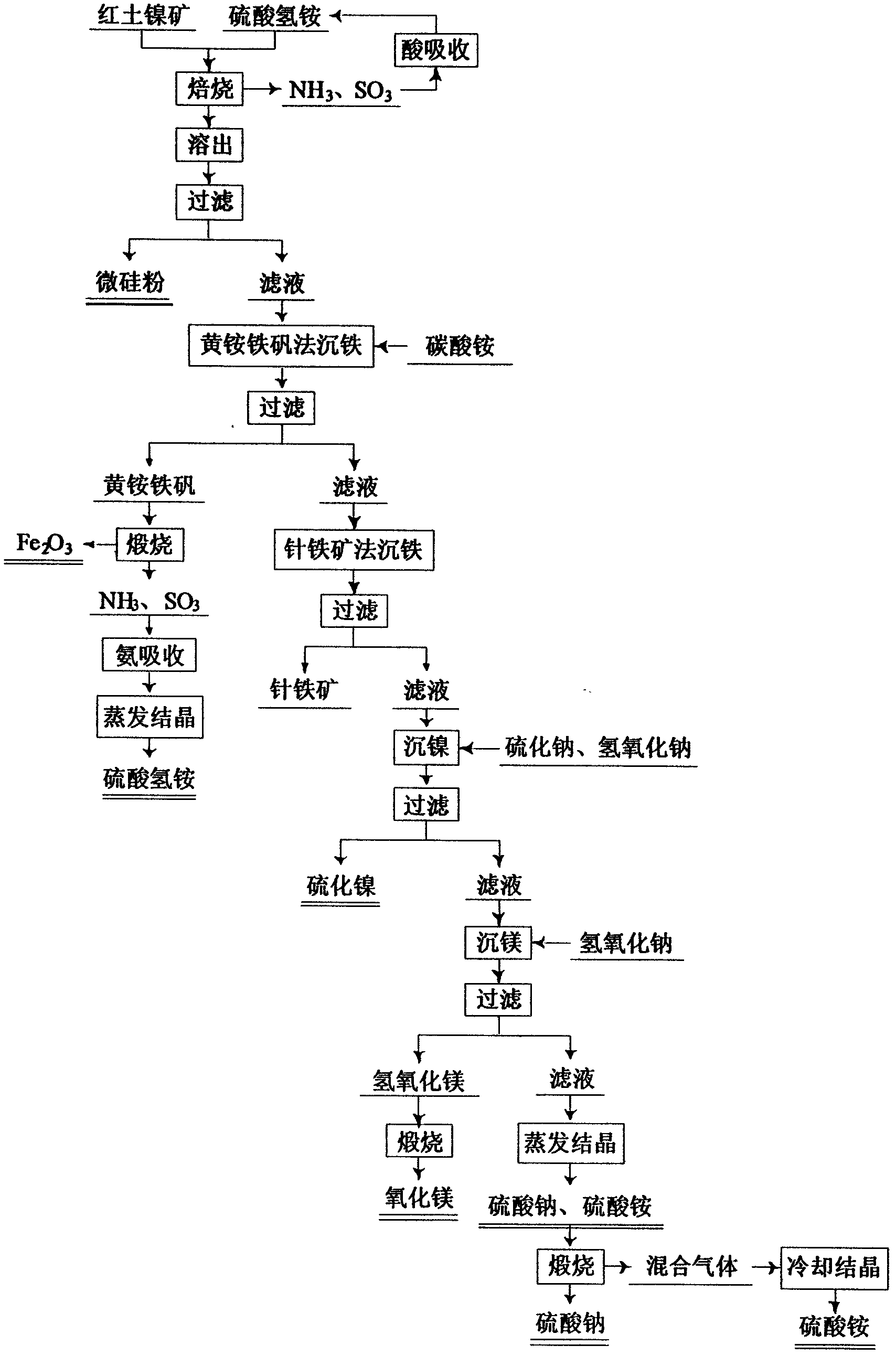
Method for comprehensive utilization of laterite nickel ore
A method for comprehensive utilization of laterite nickel ore comprises the following steps: (1) pulverizing laterite nickel ore, grinding, mixing with ammonium bisulfate, and roasting; (2) dissolving and filtering the roasted clinker to obtain a filtrate, depositing iron by an ihleite method, and depositing iron by a goethite method; (3) performing nickel deposition of the filtrate obtained after iron deposition by sodium sulfide, preparing a nickel sulfide product; (4) performing magnesium deposition of the filtrate obtained after nickel deposition by sodium hydroxide to obtain magnesium hydroxide; (5) washing, drying and calcining magnesium hydroxide to prepare a magnesium oxide product; (6) using the roasted clinker dissolved slag as a microsilica fume product directly, wherein the main component of the slag is silica; (7) calcining ammonium jarosite to obtain an iron oxide product.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for controlling phosphorus content of end point molten steel smelted by a top-bottom combined blowing converter to be less than 30 ppm
InactiveCN103103308ASimple and fast operationEasy to masterManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSlagMolten steel
The invention relates to a method for controlling the phosphorus content of the end point molten steel smelted by a top-bottom combined blowing converter to be less than 30 ppm, and belongs to the field of a steel smelting control method. The method is mainly used for controlling the phosphorus content of the end point molten steel of the top-bottom combined blowing converter to be less than 30 ppm. The method comprises the following steps of: tapping low-phosphorus steel which is smelted last time and has the phosphorus content being less than or equal to 100 ppm and remaining 25%-35wt% of oxidizing slag in the converter; controlling the phosphorus content of molten iron added to the converter to be less than or equal to 0.13%, wherein slag content of the molten iron is less than or equal to 5 kg / t, and the temperature of the molten iron added to the converter is stable and higher than 1300 DEG C; controlling the phosphorus content of steel scrap used for the converter to be less than 0.030%, and controlling the scrap ratio to be 12%-13%; adding slag materials to the converter, wherein the use amount of the slag materials is 115-125 kg per ton of steel materials; controlling the bottom-blowing strength of the converter by adopting a double slag method; controlling the end point carbon of the converter to be less than or equal to 0.06%, the end point temperature to be less than or equal to 1640 DEG C and the end point slag basicity to be 4.2-4.5, and controlling the iron oxide content of the slag to be 18%-25%, thus obtaining the molten steel with the phosphorus content being less than 30 ppm. The method disclosed by the invention is easy and convenient to operate and easy to control.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Soft magnetic ferrite material containing magnesium, nickel and zinc element as well as manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101354941AHigh initial permeabilityMagnetically stableInorganic material magnetismCopper oxideInductor
The invention discloses a soft magnetic ferrite material containing magnesium element, nickel element and zinc element, which comprises the following compositions in mol portion: 60 to 66 mol percent of ferric oxide Fe2O3, 7 to 10 mol percent of nickel oxide NiO, 7 to 10 mol percent of magnesia MgO, 10 to 15 mol percent of zinc oxide ZnO and 3 to 6 mol percent of copper oxide CuO. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of the processing of raw material, batching, primary ball milling, drying, pulverization or sifting, preburning, secondary batching, secondary ball milling, secondary drying and secondary pulverization or sifting, in a preburning condition, the soft magnetic ferrite material is presynthesized in an air furnace at a temperature of between 800 and 900 DEG C. The prepared soft magnetic ferrite material has the initial magnetic conductivity of about 100, stable magnetic performance and low production cost when the soft magnetic ferrite material is used to produce a laminated sheet type inductor.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com