Method for evaluating ecotoxicity of uranium by utilizing ostracoda
An ecotoxic, ostracodal technology, applied in measuring devices, instruments, testing water, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, less scientific, and more time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
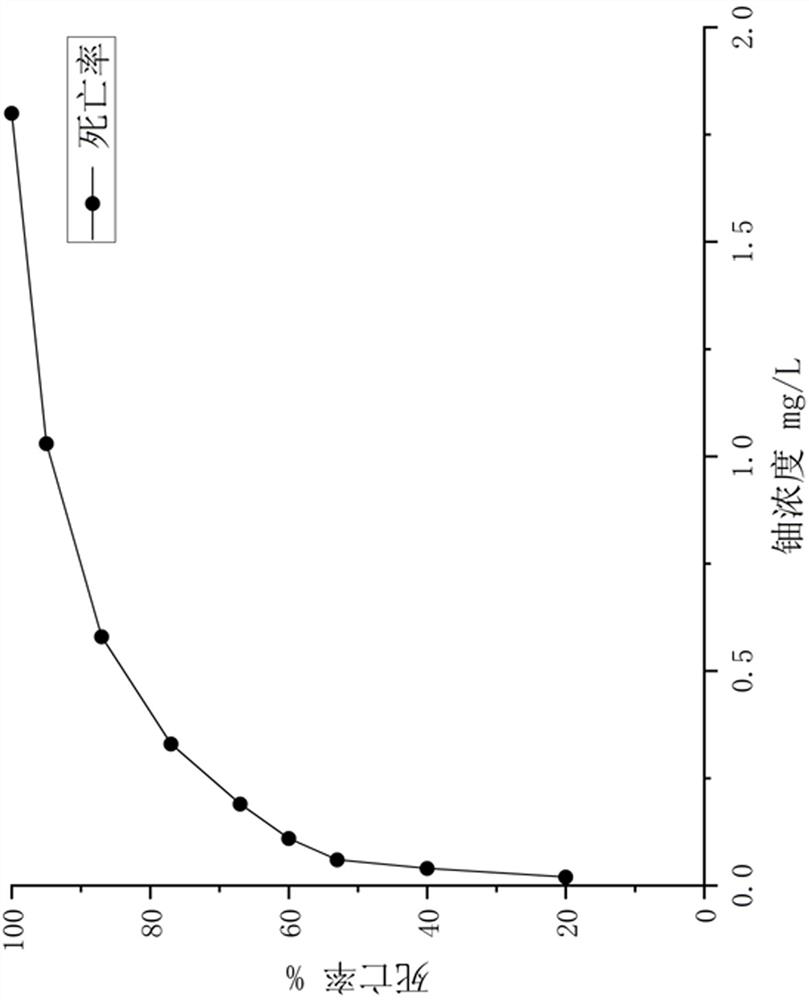
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1, the method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of uranium by using ostracods, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0024] A. Collection of ostracods
[0025] The ostracods were collected in ponds or lakes with a hand-operated net bag with a net aperture of 280 mesh, and then the collected ostracods were stored in a refrigerator at 3°C for 7 days. Choose to collect ostracods in the wild from March to April every year, because at this time the species are the most abundant and generally have a strong reproductive capacity; the water bodies collected are generally ponds and lakes, and these water bodies are generally quiet, and the abundance of ostracods is often relatively high. high.
[0026] B. The cultivation of ostracods
[0027] Put the ostracods stored in the refrigerator in the mineral water culture water body, cultivate chlorella in the water and feed the ostracods, set the water body temperature to 22°C, pH to 7, and dissolved oxygen to grea...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2, using ostracods to assess the method for uranium ecotoxicity, specifically includes the following steps:
[0041] A. Collection of ostracods
[0042] The ostracods were collected in ponds or lakes with a hand-operated net bag with a net diameter of 300 mesh, and then the collected ostracods were stored in a refrigerator at 5°C for 10 days. Choose to collect ostracods in the wild from March to April every year, because at this time the species are the most abundant and generally have a strong reproductive capacity; the water bodies collected are generally ponds and lakes, and these water bodies are generally quiet, and the abundance of ostracods is often relatively high. high.
[0043] B. The cultivation of ostracods
[0044]Put the ostracods stored in the refrigerator in the mineral water culture water body, cultivate chlorella in the water and feed the ostracods, set the water body temperature to 25°C, pH to 8, and dissolved oxygen to be greater than 6 ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment three, the method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of uranium by using ostracods, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0058] A. Collection of ostracods
[0059] The ostracods were collected in ponds or lakes with a hand-operated net bag with a net aperture of 290 mesh, and then the collected ostracods were stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for 9 days. Choose to collect ostracods in the wild from March to April every year, because at this time the species are the most abundant and generally have a strong reproductive capacity; the water bodies collected are generally ponds and lakes, and these water bodies are generally quiet, and the abundance of ostracods is often relatively high. high.
[0060] B. The cultivation of ostracods
[0061] Put the ostracods stored in the refrigerator in the mineral water culture water body, cultivate chlorella in the water and feed the ostracods, set the water temperature at 27°C, pH at 7.6, and dissolved oxygen greater ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com