Crispr effector system based multiplex diagnostics
A detection system and motif technology, applied in genetic engineering, recombinant DNA technology, microbial assay/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as expensive, low-sensitivity applications, limited availability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1- 1
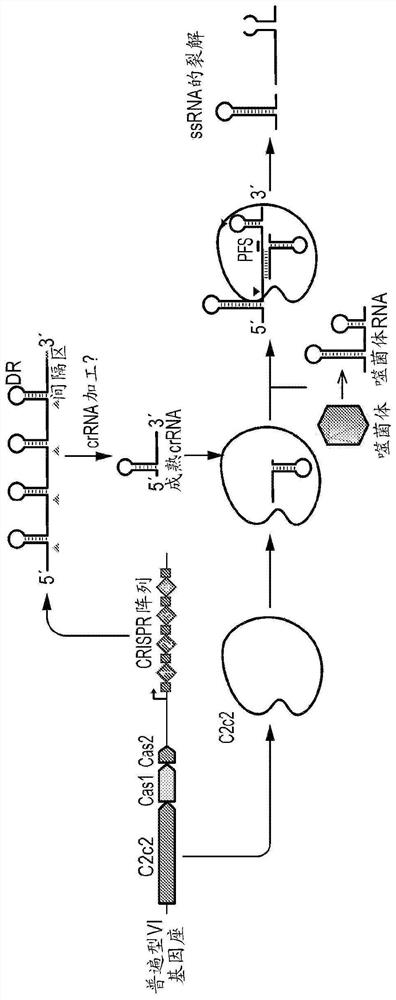
[0691] Example 1 - General Scheme
[0692] Two ways are provided to perform the C2c2 diagnostic test for DNA and RNA. This approach can also be used with protein detection variants following delivery of detection aptamers. The first is a two-step reaction in which amplification and C2c2 detection are done independently. The second is where everything is combined in one reaction and this is called a two-step reaction. It is important to keep in mind that amplification may not be necessary for higher concentration samples, so it is good to have a separate C2c2 protocol that does not have amplification built in.
[0693] Table 11. CRISPR effectors only - no amplification:
[0694] components Volume (μL) Protein (final 44nM) 2 crRNA (final 12nM) 1 Background target (100ng total) 1 target RNA (variable) 1 RNA sensor probe (125nM) 4 MgCl 2 (final 6mM)
[0695] The reaction buffer is: 40mM Tris-HCl, 60mM NaCl, pH 7.3
[0696] This ...
Embodiment 2
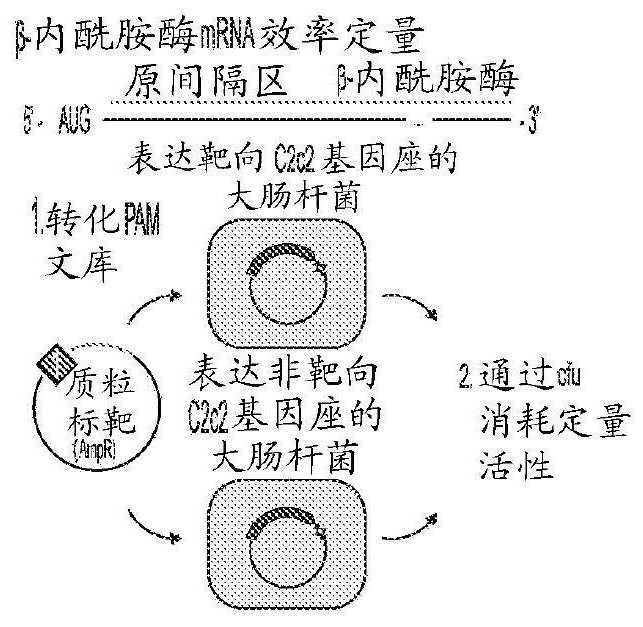
[0710] Example 2 - Highly Sensitive and Specific Detection of C2C2-Mediated DNA and RNA from Ciliophora videides
[0711]Rapid, cheap, and sensitive nucleic acid tests can aid point-of-care pathogen detection, genotyping, and disease surveillance. The RNA-guided RNA-targeting CRISPR effector Cas13a (previously known as C2c2) exhibits "side effects" of promiscuous RNase activity following target recognition. Applicants combine the collateral effect of Cas13a with isothermal amplification to establish a CRISPR-based diagnostic (CRISPR-Dx), providing rapid DNA or RNA detection with attomolar sensitivity and specificity for single-base mismatches. The applicant used this Cas13a-based molecular detection platform, called SHERLOCK (Specific High Sensitivity Enzymatic Reporter Unlocking), to detect specific strains of Zika and Dengue viruses, and to distinguish pathogens bacteria, genotyping human DNA, and identifying mutations in cell-free tumor DNA. In addition, SHERLOCK reagents...
Embodiment 3
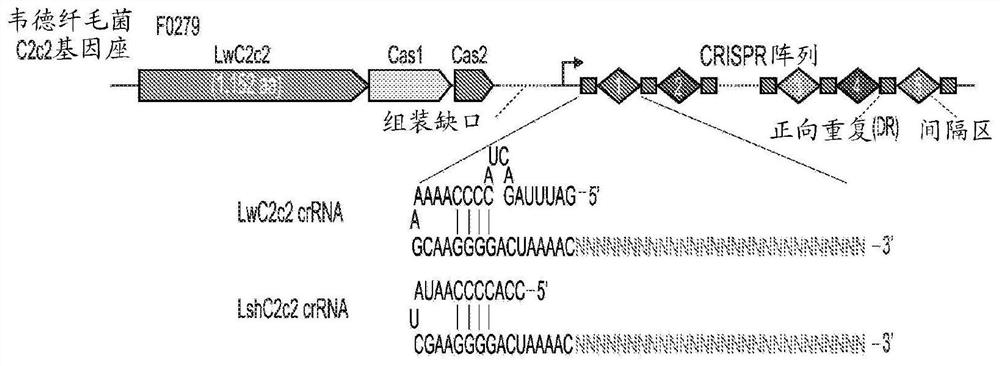
[0828] Example 3 - Characterization of Cas13b Orthologs with Orthogonal Base Preferences
[0829] Applicants biochemically characterized fourteen orthologs of the recently defined Type VI CRISPR-Cas13b family of RNA-guided RNA-targeting enzymes to find new candidates for improved SHERLOCK assay technology ( Figure 83A and Figure 85 ). Applicants were able to heterologously express fourteen Cas13b orthologs in E. coli and purify the proteins for in vitro RNase activity assays ( FIG. 86 ). Because different Cas13 orthologs may have different base preferences for optimal cleavage activity, Applicants generated a fluorescent RNase homopolymer sensor consisting of 5 A, G, C, or U to estimate orthogonal cleavage preference. Applicants incubated each ortholog with its cognate crRNA targeting the synthetic 173nt ssRNA 1 and measured incidental cleavage activity using a homopolymer fluorescent sensor ( Figure 83B and Figure 87).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com