Application of rice potassium ion transport protein gene OsHAK9 in improving seed germination capacity under salt stress
A technology for rice seeds and transporters, which can be used in applications, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., and can solve problems such as fewer clones
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Gene Mapping
[0043] (1) Materials and methods
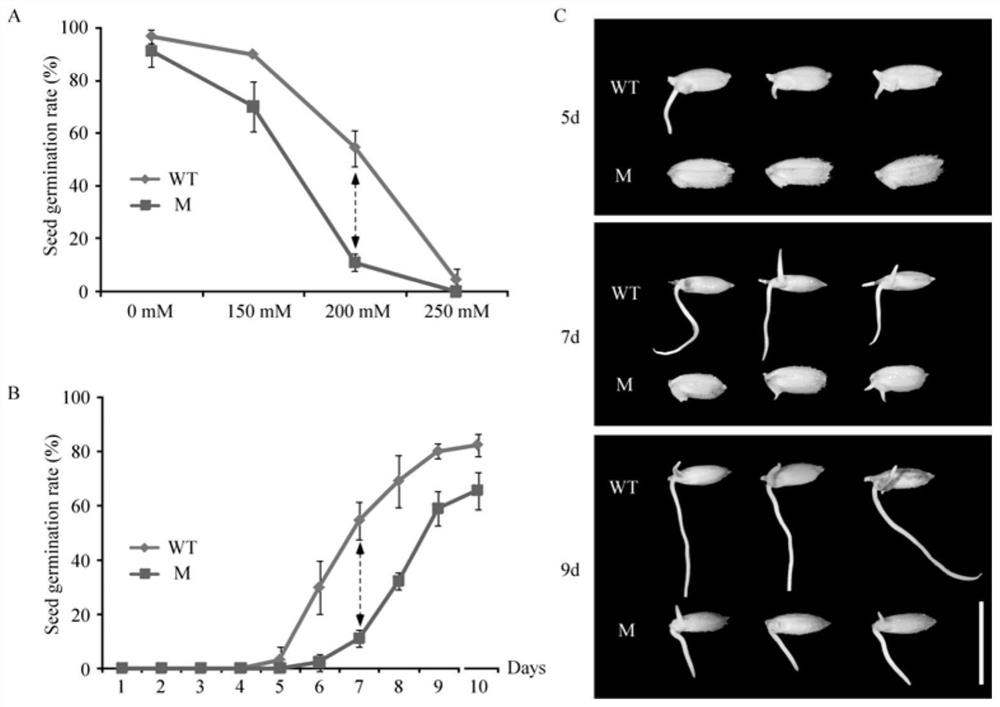
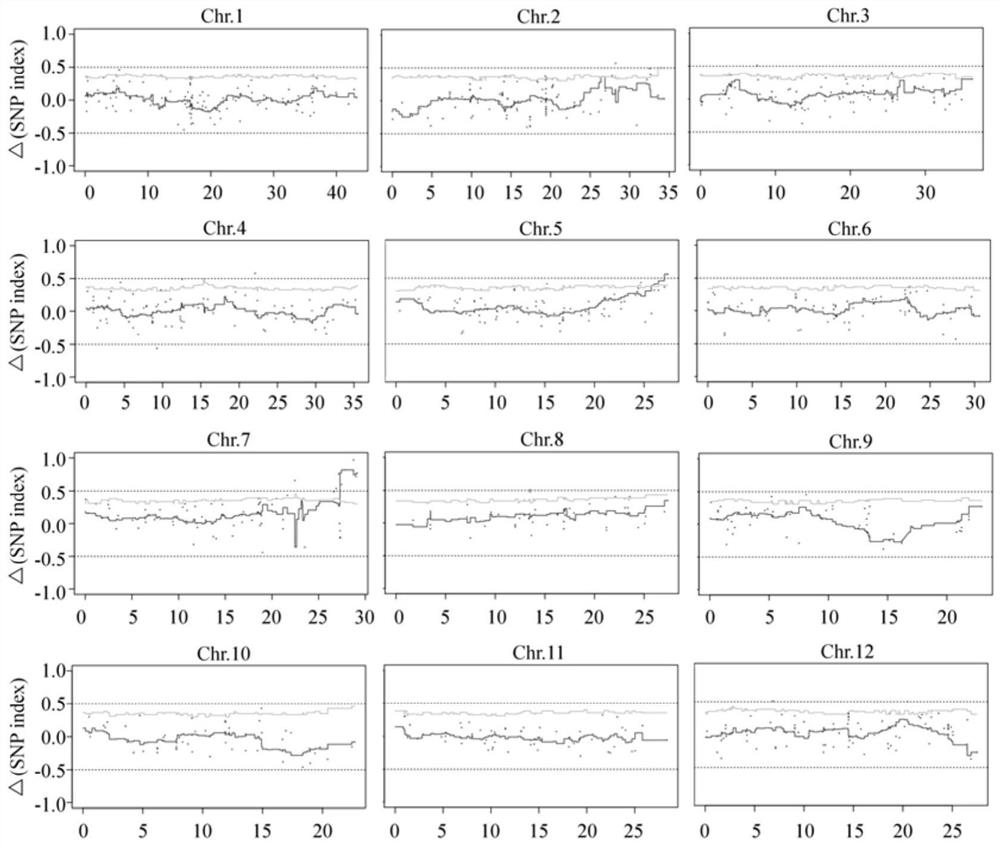
[0044] 1. Materials: The salt-sensitive mutant gss1 (attached figure 1 shown), and crossed with wild-type Nipponbare (WT) to construct F 2 The isolated population was used for the detection and localization of salt-tolerant loci during seed germination using the MutMap method based on the resistance-sensitivity pool (BSA). Depend on figure 1 A. figure 1 B. figure 1 C It can be seen that the seed germination rate, germination speed or seedling growth of the gss1 mutant seeds under salt stress is significantly lower than that of the control japonica Nipponbare seeds.
[0045] 2. Screening of individual plants in resistant and susceptible pools: in F 2 In the segregation population, 150 progeny seeds of individual plants were randomly selected for identification of seed germination under 200mM salt stress, and 20 individual plants of extreme salt resistance and salt sensitivity were selected according to th...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: gene cloning
[0050] Using the cDNA of the japonica rice variety Nipponbare seedling leaves as a template, the sequence of the OsHAK9 gene was cloned by using touchdown PCR amplification technology. The sequence of the upstream primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.3 in the sequence table, and the sequence of the downstream primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.4 in the sequence table. Show. The nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence of the rice OsHAK9 gene are obtained, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2.
[0051] OsHAK9-F1: 5'-GCTGATTCTCTCGATTGATTAC-3' (SEQ ID NO.3)
[0052] OsHAK9-R1: 5'-AGCAGAGAGATTTGATTTTGAA-3' (SEQ ID NO.4)
[0053] The PCR reaction system is:
[0054]
[0055] The reaction program is: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5min, denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing at 60°C for 30s, extension at 72°C for 90s, 8 cycles, denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing a...
Embodiment 3
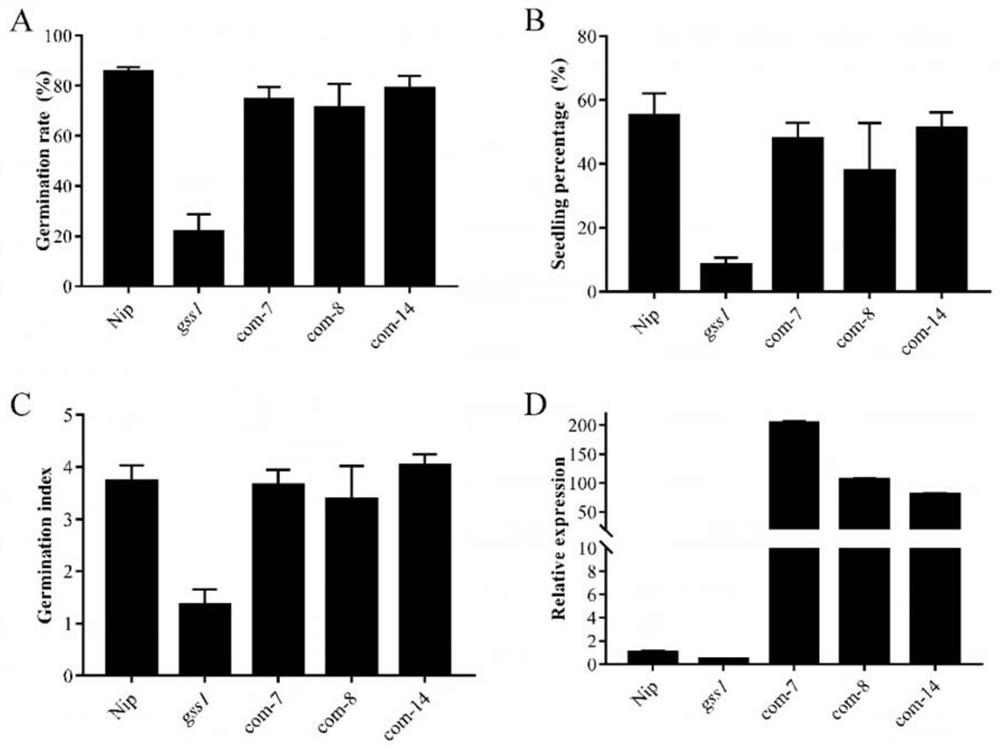
[0056] Example 3: Complementary transgenic plants
[0057] (1) Amplification of the promoter sequence: Using Nipponbare genomic DNA as a template, PCR amplification technology was used to amplify the sequence about 2.4kb upstream of the OsHAK9 initiation code. The upstream primer sequence is shown in the sequence table as SEQ ID NO.5, The downstream primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.6 in the sequence table, and the OsHAK9 gene promoter sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.7 is obtained.
[0058] OsHAK9-F2: 5'-GCAACAGCAAAGGTCACTCT-3' (SEQ ID NO.5)
[0059] OsHAK9-R2: 5'-ACCAGTGGATCGGATAGTCC-3' (SEQ ID NO.6)
[0060] The PCR reaction system is:
[0061]
[0062]
[0063] The reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 56°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 90 s, 30 cycles, complete extension at 72°C for 10 min, 32 cycles, and storage at 4°C.
[0064] (2) Construction of recombinant plasmids: Based on the principle of ov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com