Active power distribution network multi-terminal fault identification method and system based on transient signals
A transient signal and fault identification technology, which is applied in the direction of fault location, measurement of electrical variables, and detection of faults according to conductor types, etc., can solve the problem of not having synchronous data channels or GPS equipment, affecting the accuracy of fault direction judgment, and the existence of fault lines Problems such as through current, achieve high sensitivity and anti-transition resistance, reduce costs, and achieve good economical effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
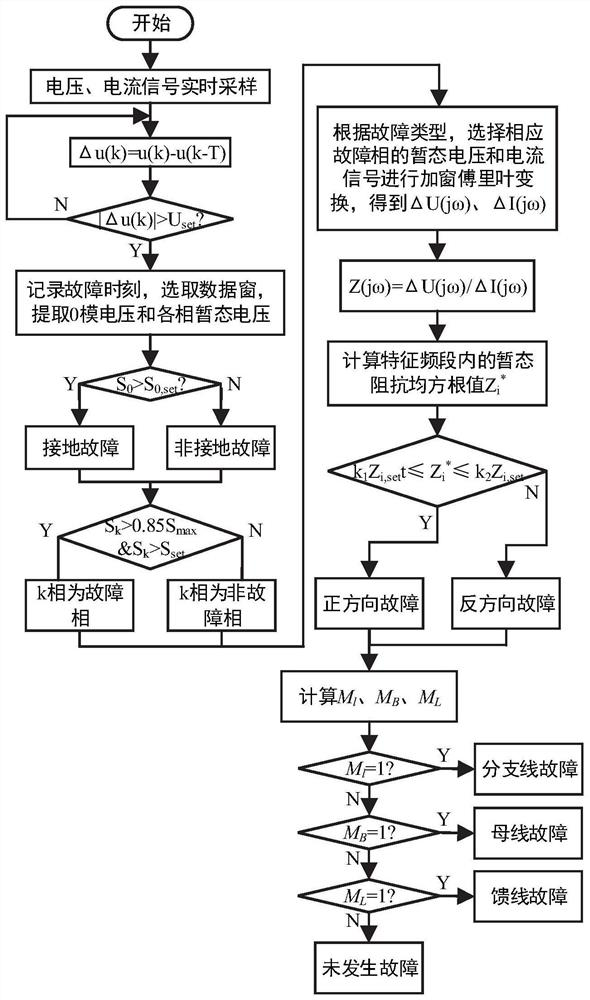
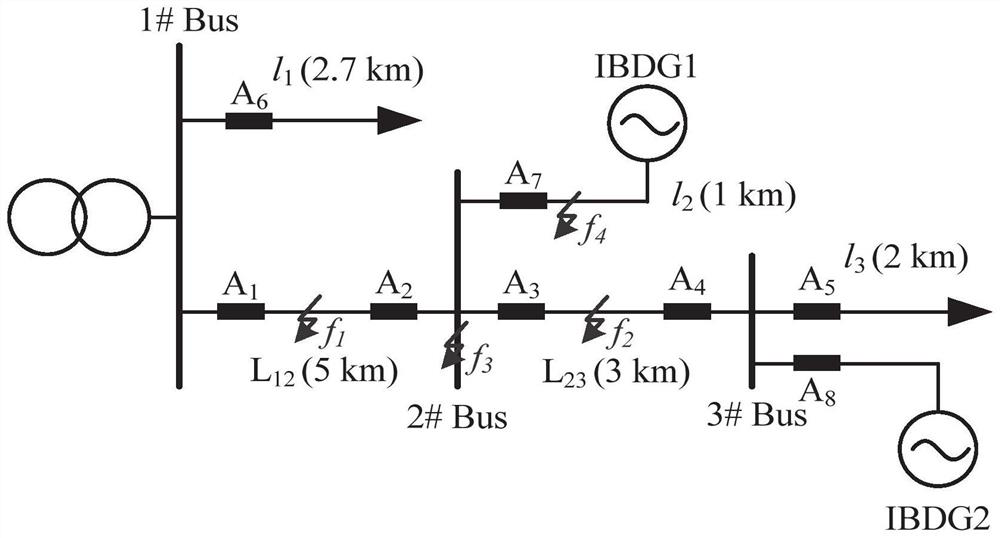
[0038] In the technical solutions disclosed in one or more embodiments, such as figure 1 As shown, the multi-terminal fault identification method of active distribution network based on transient signals includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1. Obtain the transient voltage of the busbar at each measurement point and the three-phase current of each incoming and outgoing line of the busbar;
[0040] Step 2. For each measurement point, identify the fault phase and fault type according to the bus transient voltage;
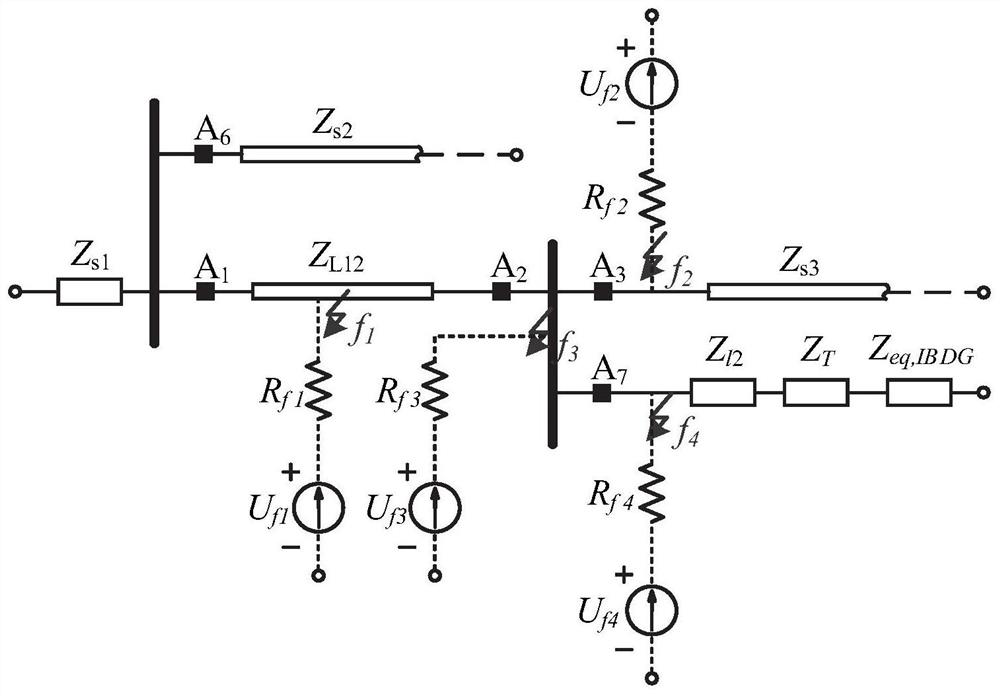
[0041] Step 3. Calculate and judge the transient impedance based on the transient voltage and current signals of each measurement point, and obtain the fault direction of each measurement point;
[0042] Step 4. Fusing the fault direction of each measurement point to determine the fault section.
[0043] In this embodiment, the judgment of the transient signal by each measurement point is based on the fault direction of each measurement point, and the judgment...
Embodiment 2
[0149] The multi-terminal fault identification system for active distribution network based on transient signals provided in this embodiment includes: a protection device installed at each inlet and outlet of the busbar, and the protection device implements the transient state-based fault identification system described in Embodiment 1. The multi-terminal fault identification method of the active distribution network of the signal identifies the fault direction at the protection device, obtains the fault signal of the adjacent protection device, and compares the fault direction of the relevant measurement point to determine whether the section connected to the protection device has Fault.
Embodiment 3
[0151] This embodiment provides an active distribution network multi-terminal fault identification system based on transient signals, including:
[0152] Obtaining module: configured to obtain the transient voltage of the bus at each measurement point and the three-phase current of each incoming and outgoing line of the bus;
[0153] Fault phase and fault type judging module: configured to identify fault phase and fault type according to bus transient voltage for each measurement point;
[0154] Fault direction identification module: configured to calculate and judge the transient impedance based on the transient voltage and current signals of each measurement point, and obtain the fault direction of each measurement point;
[0155] Comparison identification module: configured to fuse the fault direction of each measurement point to determine the fault section.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com