Three-period minimal curved surface variable density lattice structure design method for additive manufacturing
A technology of minimal curved surface and lattice structure, which is applied in the field of three-period minimal curved surface variable density lattice structure design in additive manufacturing, can solve problems such as low efficiency and unstable topological structure values, so as to improve structural strength, solve Numerical instability of topological structure, effect of improving structural strength and specific stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
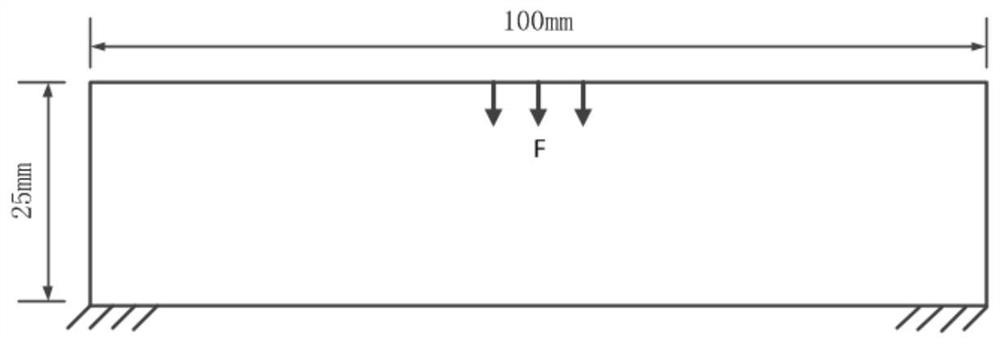
[0091] Taking a rectangular plate with a length of 100 mm and a width of 50 mm as an example, the restraint load is as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0092] The specific operation steps are as follows:
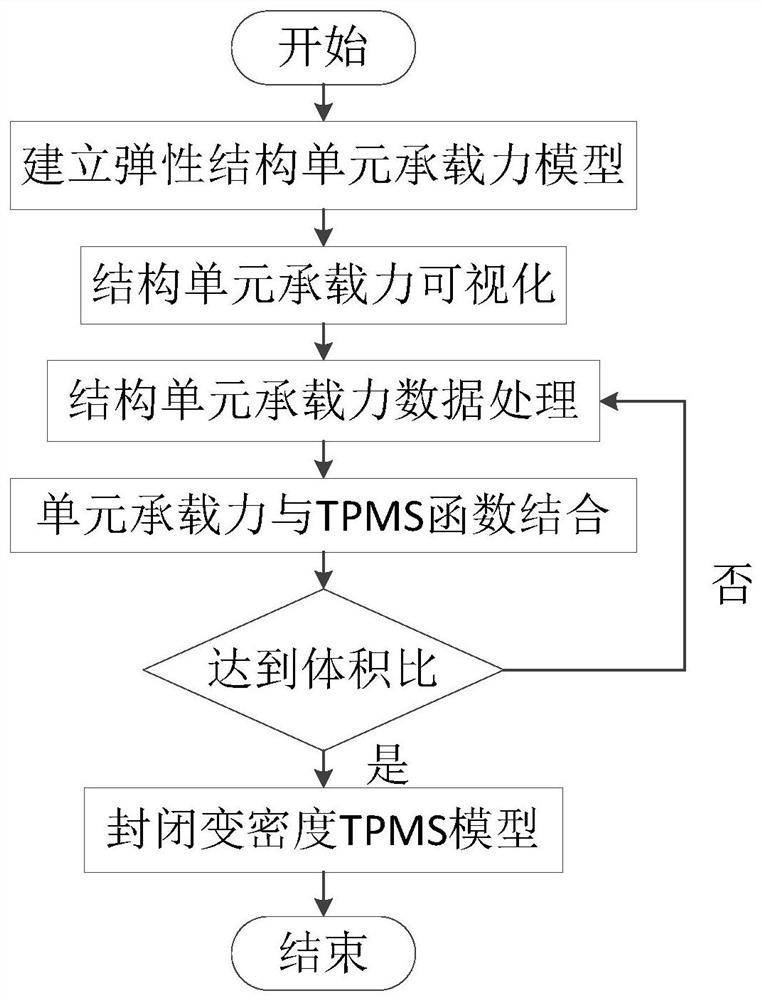
[0093] S1. Establish a finite element model of a rectangular flat elastic structure, divide the mesh size into 5mm×5mm, and apply constraints and loads.
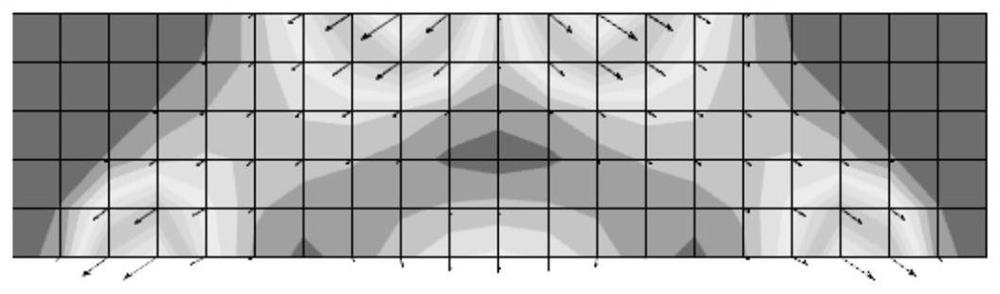
[0094] S2. Based on the static balance principle of elastic structure and the "life and death" state technology of the unit, design the method of extracting the bearing capacity of the unit;
[0095] S21. Determine the load boundary and constraint boundary of the elastic continuum, and calculate the anti-support force f of the constraint boundary i and the nodal displacement δ at the load boundary 1 ;
[0096] S22. Remove the attention area of the elastic continuum, and set the load boundary by node displacement δ 1 load, and calculate the constraint boundary anti-support force at this time again as
[0097] S23. The ...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Taking a cuboid with a length of 100mm, a width of 50mm, and a height of 25mm as an example, the restraint load is as follows: Figure 6 shown.
[0111] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0112] S1. Establish the finite element model of the cuboid elastic structure, divide the mesh size into 5mm×5mm×5mm, and apply constraints and loads.
[0113] S2. Based on the static balance principle of elastic structure and the "life and death" state technology of the unit, design the method of extracting the bearing capacity of the unit;
[0114] S21. Determine the load boundary and constraint boundary of the elastic continuum, and calculate the anti-support force f of the constraint boundary i and the nodal displacement δ at the load boundary 1 ;
[0115] S22. Remove the attention area of the elastic continuum, and set the load boundary by node displacement δ 1 load, and calculate the constraint boundary anti-support force at this time again as
[0116] S23. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com