Quantum key sharing method based on discrete modulation non-orthogonal state
A quantum key and non-orthogonal technology, which is applied in the field of quantum key sharing based on discrete modulation non-orthogonal states, can solve the problem that remote users cannot recover key information alone, cannot guarantee the key sharing requirements of multiple users, and cannot To ensure the reliability of remote users and other issues, to achieve the effect of easy preparation and measurement, good anti-interference ability and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
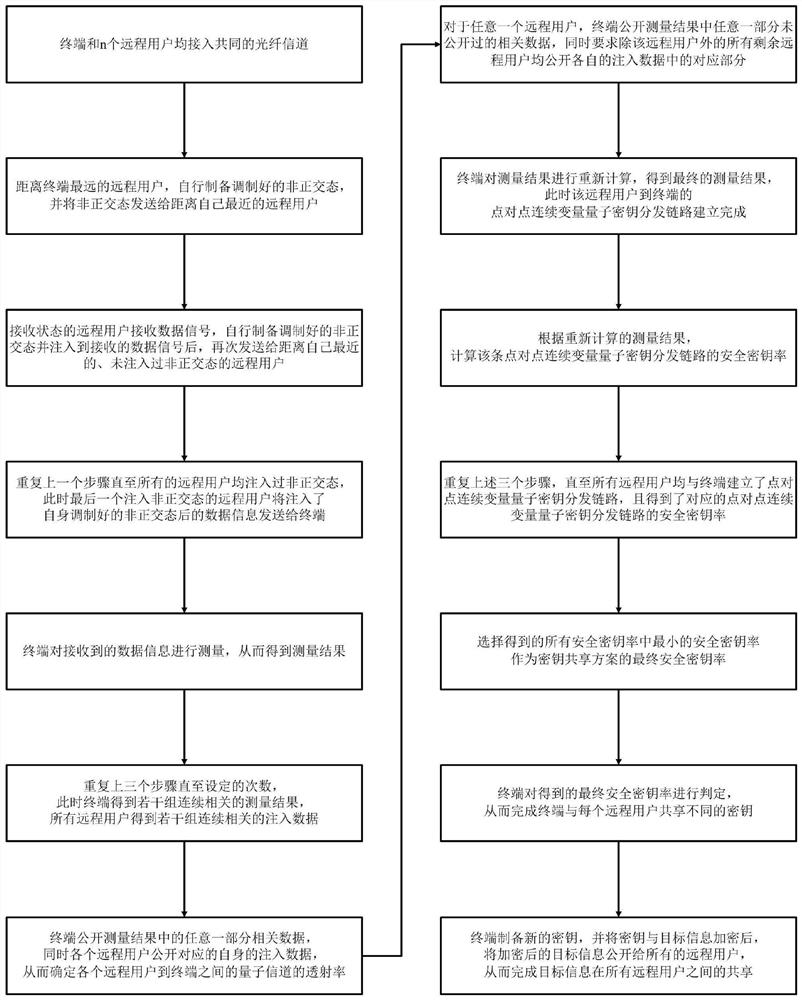
[0040] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic flow chart of the method of the present invention: the quantum key sharing method based on the discrete modulation non-orthogonal state provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0041] S1. Both the terminal and the n remote users access a common optical fiber channel;
[0042] S2. The remote user farthest from the terminal prepares the modulated non-orthogonal state by itself, and sends the non-orthogonal state to the remote user closest to him;
[0043]S3. The remote user in the receiving state receives the data signal, prepares the modulated non-orthogonal state by itself, and injects the non-orthogonal state into the received data signal (such as using a highly asymmetric fractionator), and injects the non-orthogonal state into the received data signal. The data signal is sent to the nearest remote user who has not injected non-orthogonal state again;
[0044] S4. Step S3 is repeated until all remote us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com