Exon splicing enhancer related to Duchenne muscular dystrophy, sgRNA, gene editing tool and application
A Duchenne muscular nutrition, gene editing technology, applied in genetic engineering, DNA/RNA fragments, applications, etc., can solve rare problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 AAV virus carrying gene editing tool
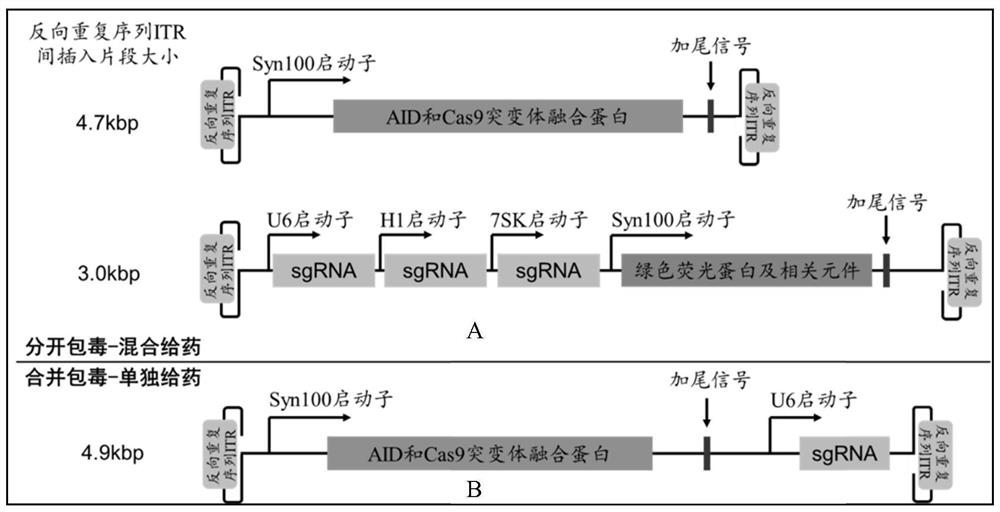
[0046] Gene editing tools designed according to the present invention such as figure 1 As shown, taking AID as an example, we cloned the corresponding sequence into the AAV plasmid, including the following steps:
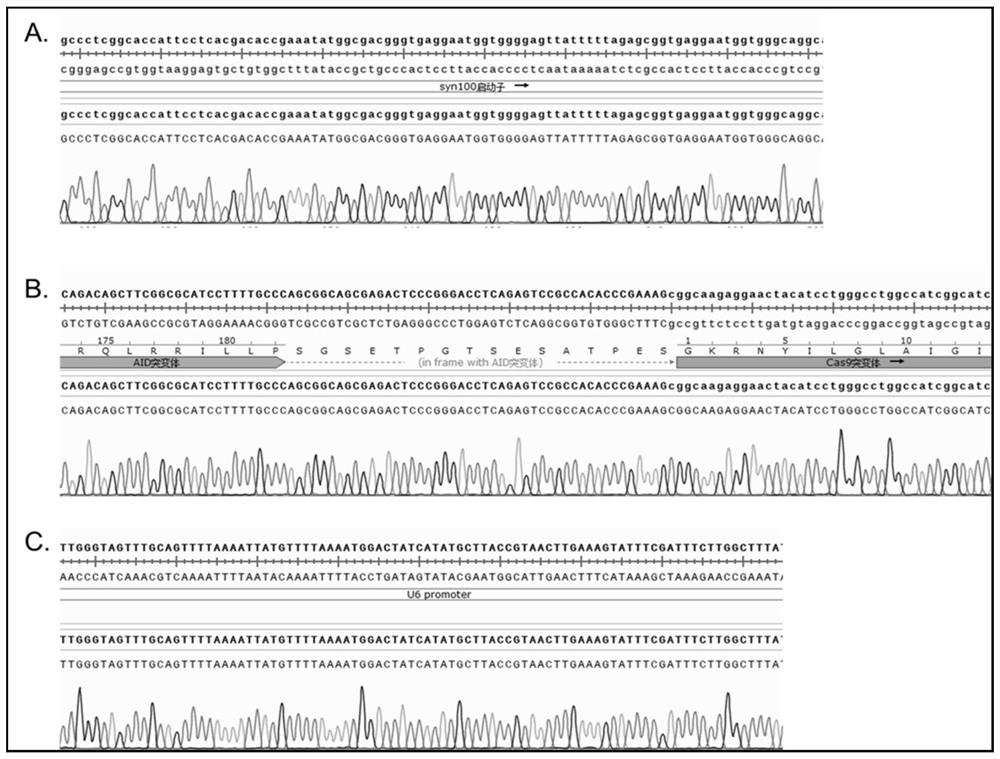
[0047] First, the pAAV2 backbone vector (purchased from addgene, but not limited thereto) was double-digested based on the restriction sites of XhoI and NotI. Simultaneously design the amino acid sequence of AID and Cas9 fusion protein in the gene editing tool, the amino acid sequence and nucleic acid sequence are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. After codon optimization, double-stranded DNA fragments were directly synthesized, and elements such as the Syn100 promoter and tailing signal were connected to the AAV backbone vector to obtain an AAV vector plasmid expressing the AID-Cas9 mutant fusion protein. Its sequence is SEQ ID NO.3 shown. In addition, using primer synthesis and PCR methods...
Embodiment 2
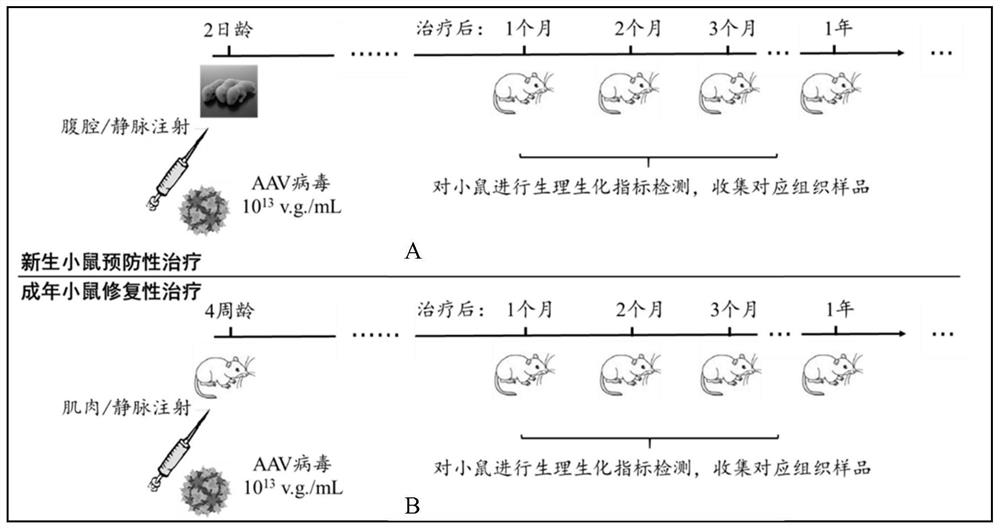
[0049] Embodiment 2 Utilizes AAV carrying gene editing tools to treat DMD model mice in vivo
[0050] In this example, Dmd-E4, a novel DMD mouse disease model with abnormal cardiac function, was selected. This model can be purchased from Jiangsu Jicui Yaokang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., but is not limited thereto. Dmd-E4 showed myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis and other phenotypes in the heart at 6-8 weeks, and showed severe degeneration of cardiac function at about 8 months. This process simulates the cardiac pathological process of DMD patients well. For this model, we applied cytosine deaminase and Cas9 to design gene editing tools, targeting exons carrying pathogenic mutations, and inducing mutations near their 5' splicing sites, causing them to skip reads. On the basis of not affecting the open reading frame of the protein, the expression of Dystrophin protein is retained to the maximum extent, and its biological function is restored.
[0051] Specifically, the method of E...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 The gene editing of human induced pluripotent stem cell iPSC DMD model successfully restored the expression of Dystrophin protein
[0066] At the same time, the present invention has successfully implemented the gene editing therapy of human cells. First, we constructed induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and then used the CRISPR-cas9 method to specifically delete exon 50 Exon50 of the Dystrophin-encoding gene DMD, making the Dystrophin protein encoding The sequence produces a frameshift mutation, thereby constructing a mutation type that simulates a DMD patient, and becomes a good DMD disease model cell. For this cell, we designed the sequence of AID and Cas9 fusion protein and the corresponding sgRNA, which is used to target a series of potential regulatory exon splicing elements of exon 51 Exon51 of the DMD gene, which was used in this example The sgRNA is sgRNA-12 as shown in SEQ ID No.19 and sgRNA-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com