In-vitro monolayer culture and representing method for constructing mouse intestinal epithelium by using Transwell
A technology of intestinal epithelium and monolayer, applied in artificial cell constructs, biochemical equipment and methods, gastrointestinal cells, etc., can solve the problems of limited in vitro test time, poor experimental repeatability and stability, and lack of cell-cell interaction to overcome the slow formation of intestinal epithelial monolayer, improve the activity of intestinal stem cells, and optimize the in vitro identification method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
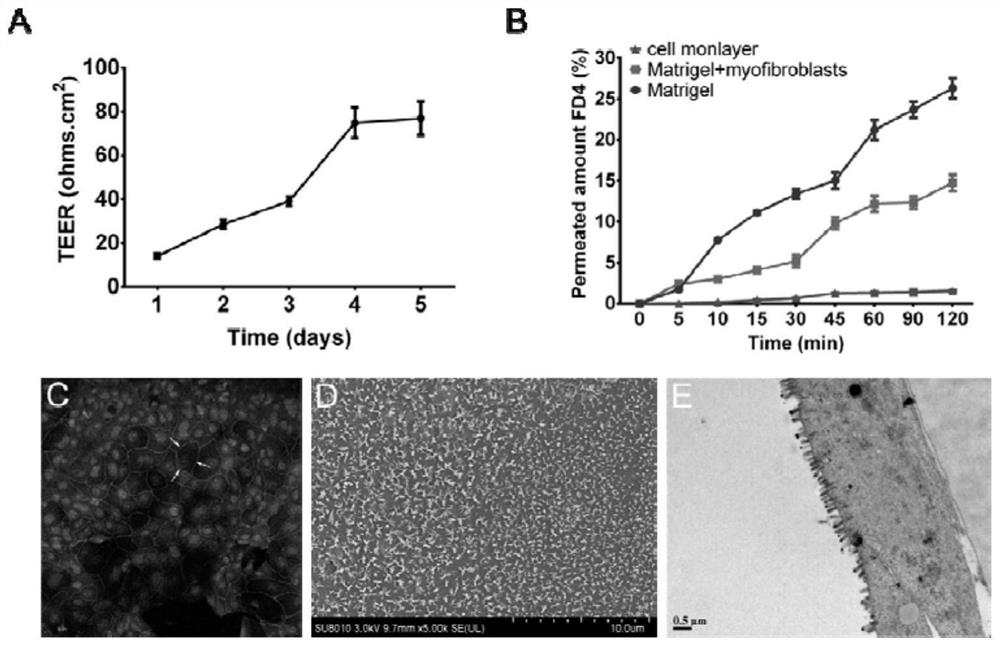
[0030] Step 1. Isolation of intestinal crypt structure: collect 7-8cm small intestine of 8-week-old ICR mice, and use a 10ml syringe containing phosphate buffer solution without calcium and magnesium ions pre-cooled on ice to wash until no visible to the naked eye in the cleaning solution. Residue; cut the intestinal tract along the longitudinal axis and place it in a 100mm Petri dish 1 containing calcium- and magnesium-free phosphate buffer solution placed on ice, use ophthalmic scissors to cut the intestinal tract into 0.5-1cm intestinal segments, and cut the intestinal tract into 0.5-1cm intestinal segments. Transfer the good intestinal segment to 15ml centrifuge tube 1 containing 10ml of phosphate buffer solution without calcium and magnesium ions pre-cooled on ice, turn the centrifuge tube 1 upside down 10-20 times, and then let it stand until the intestinal segment sinks in the centrifuge tube 1 Remove the supernatant after the bottom, and wash repeatedly 3 times to remov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com