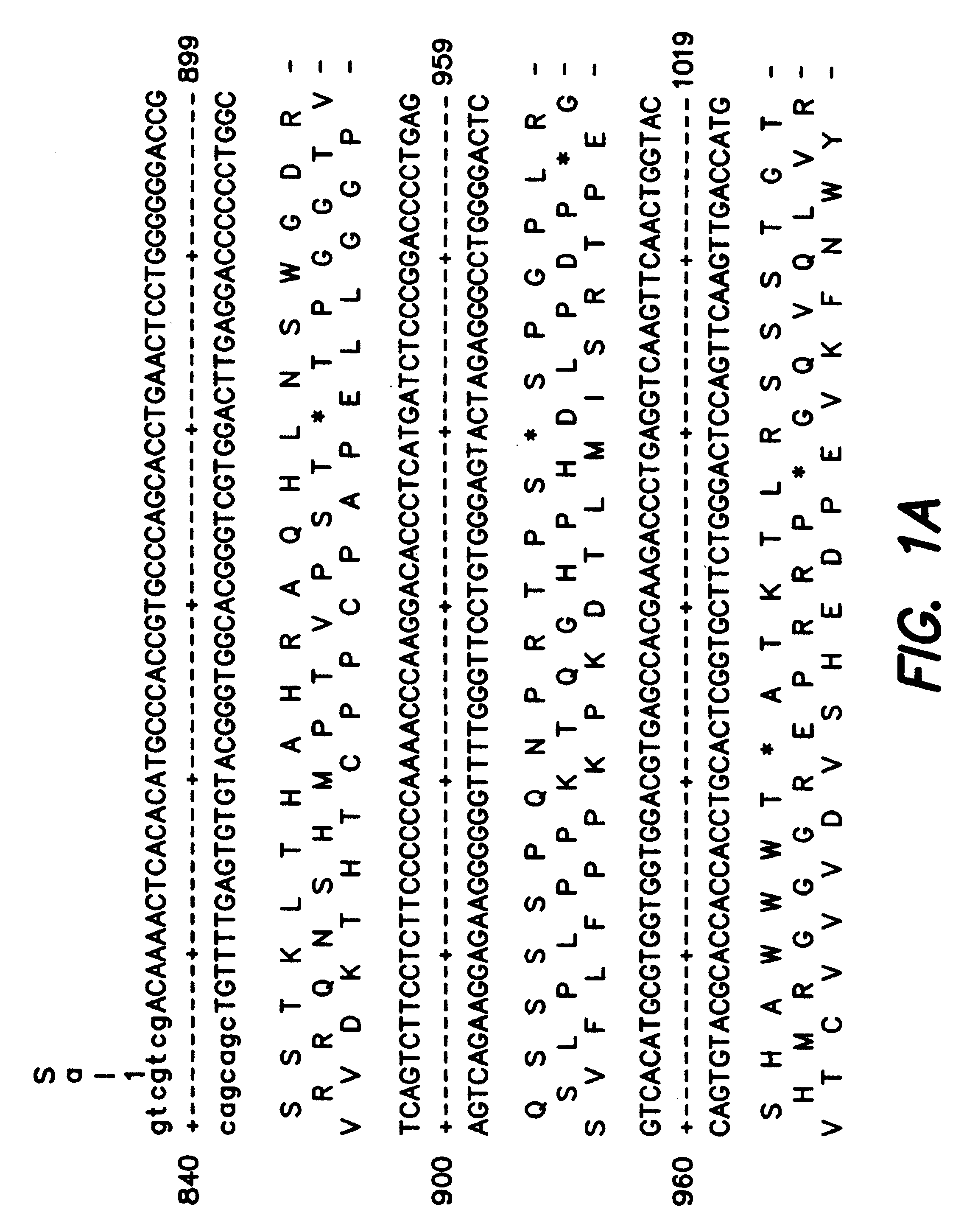
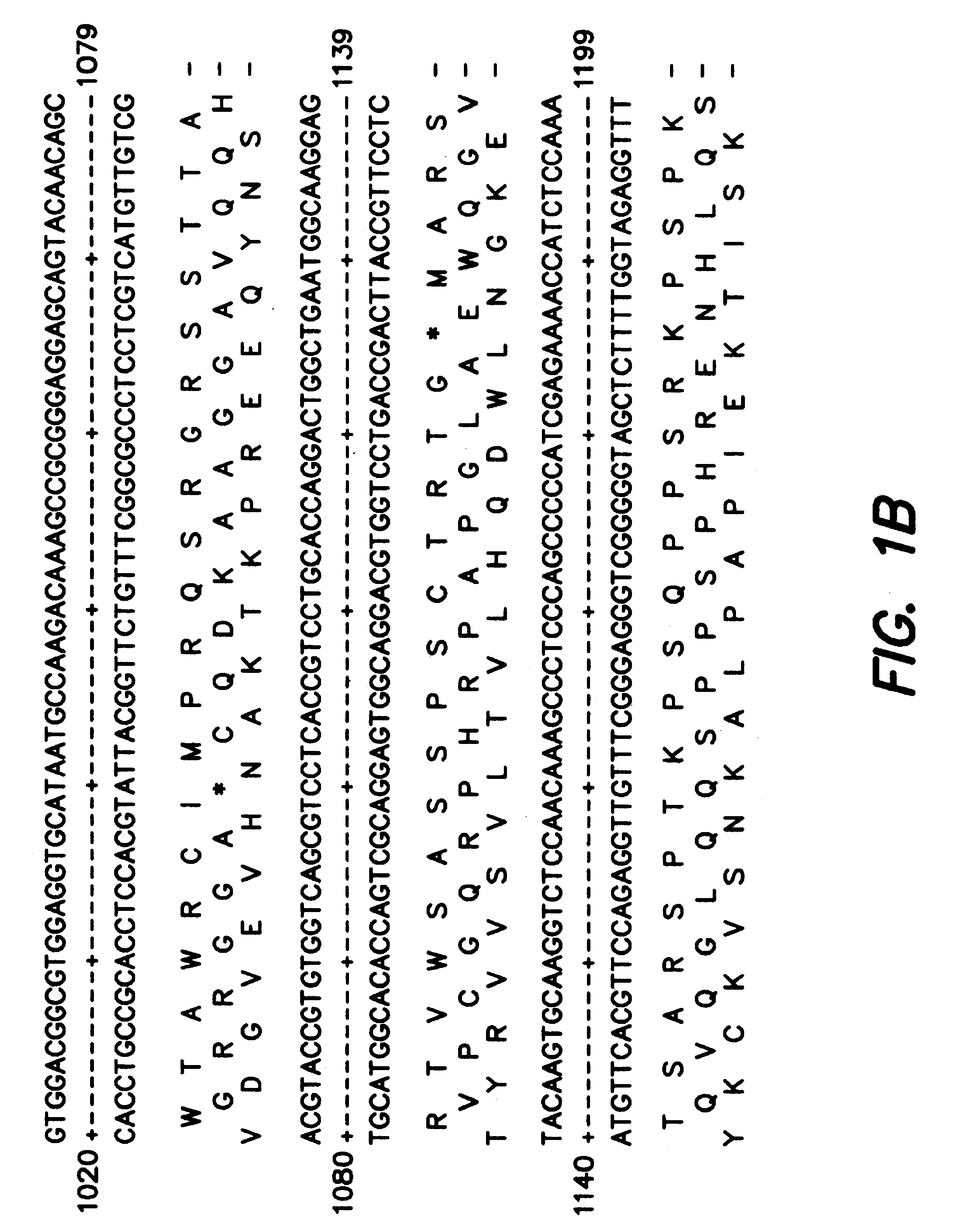
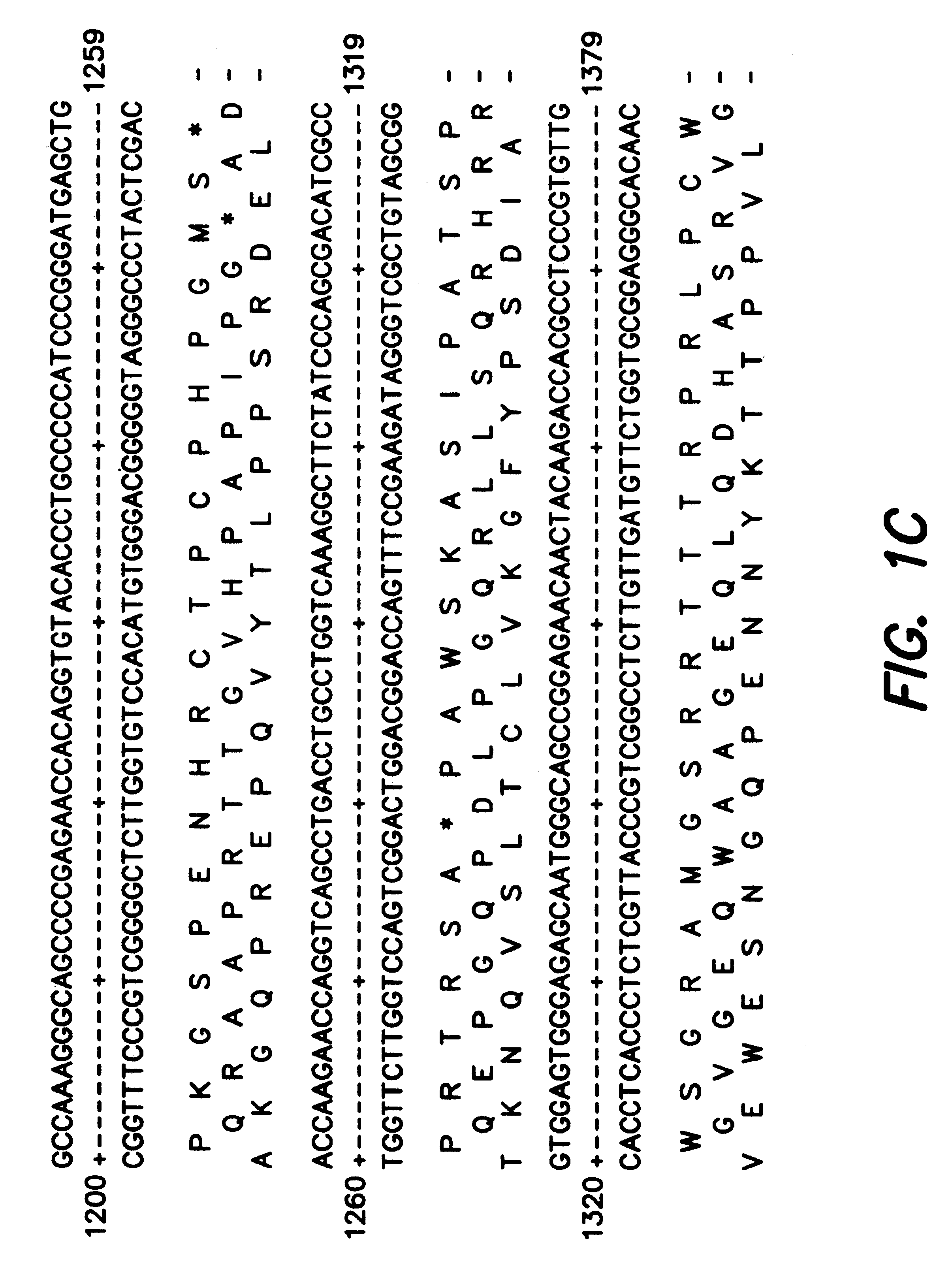
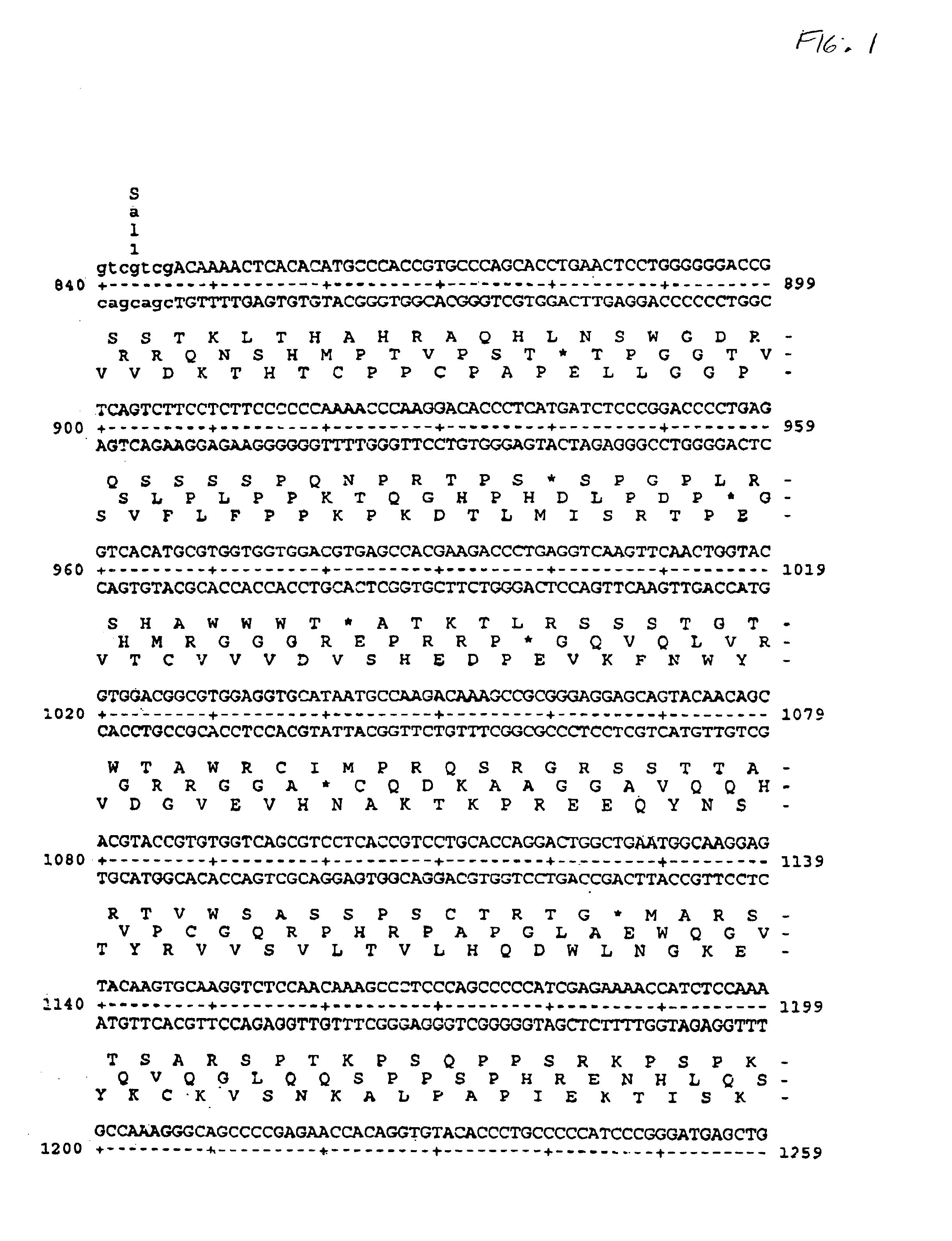
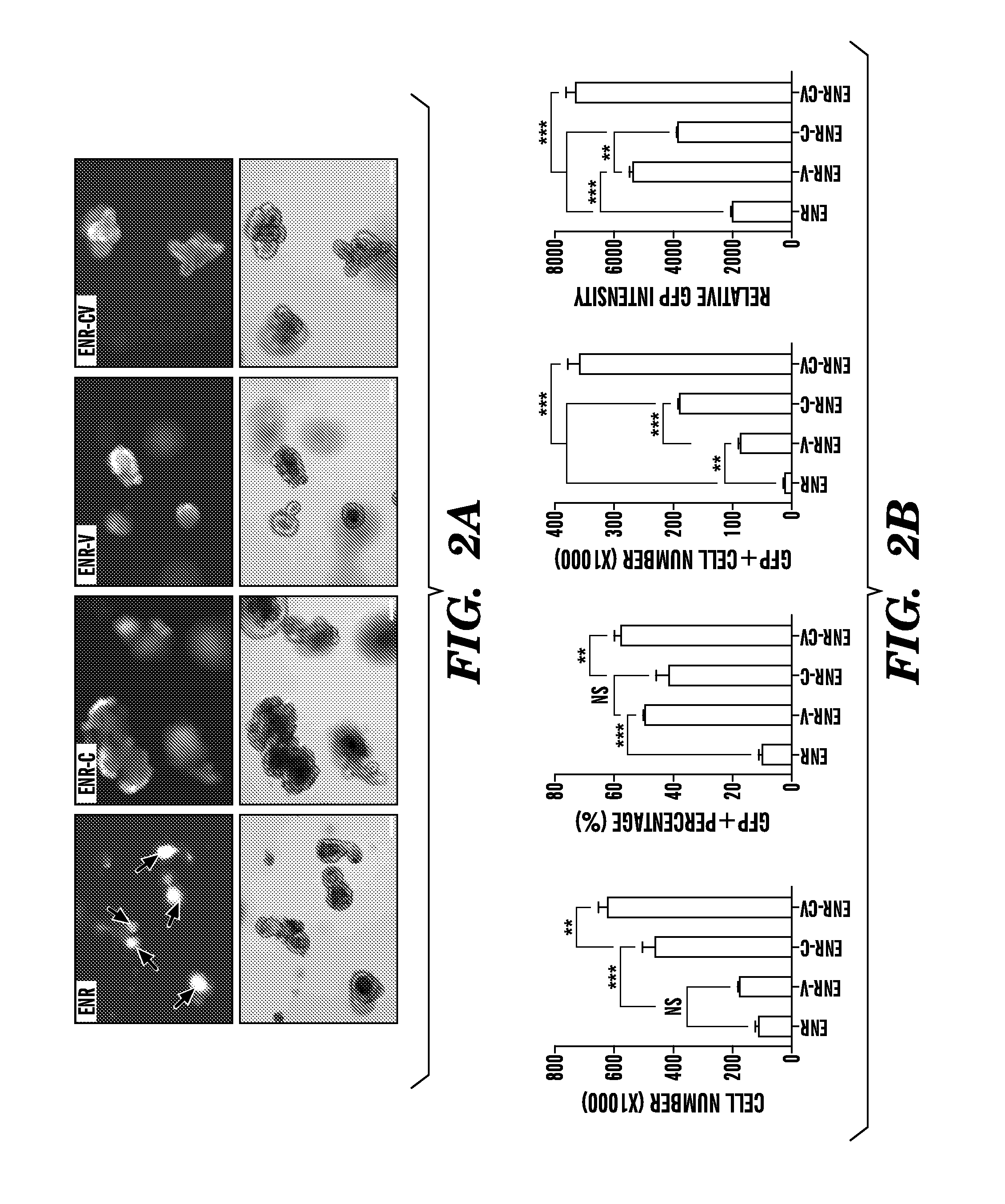
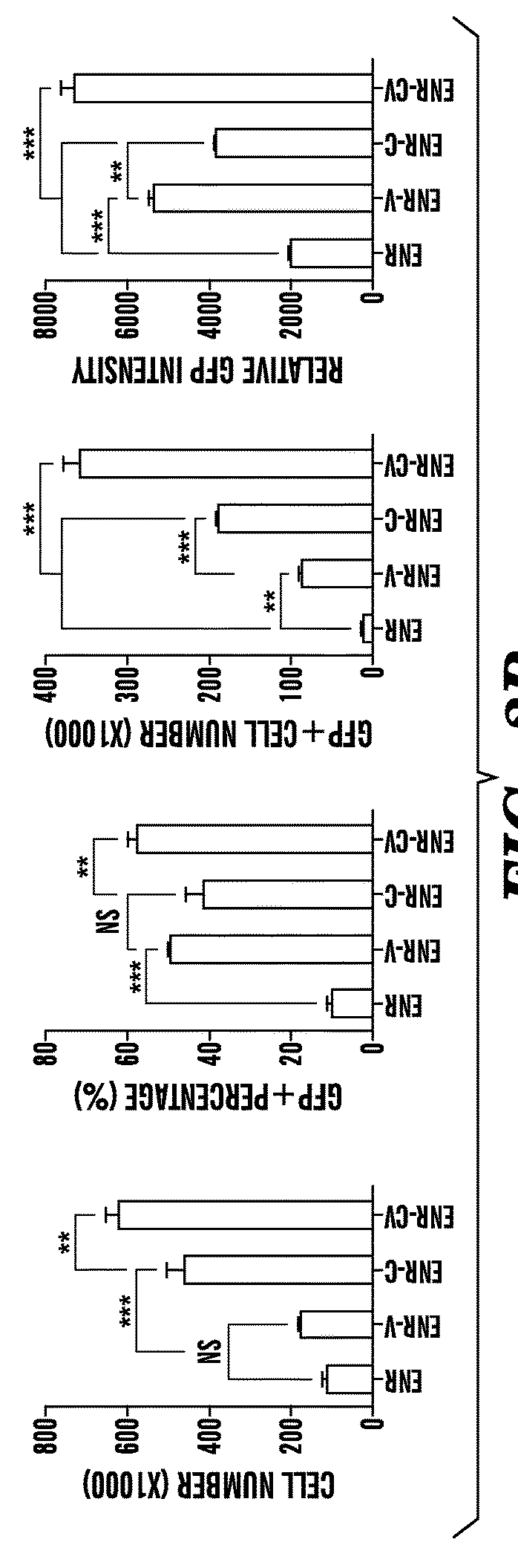
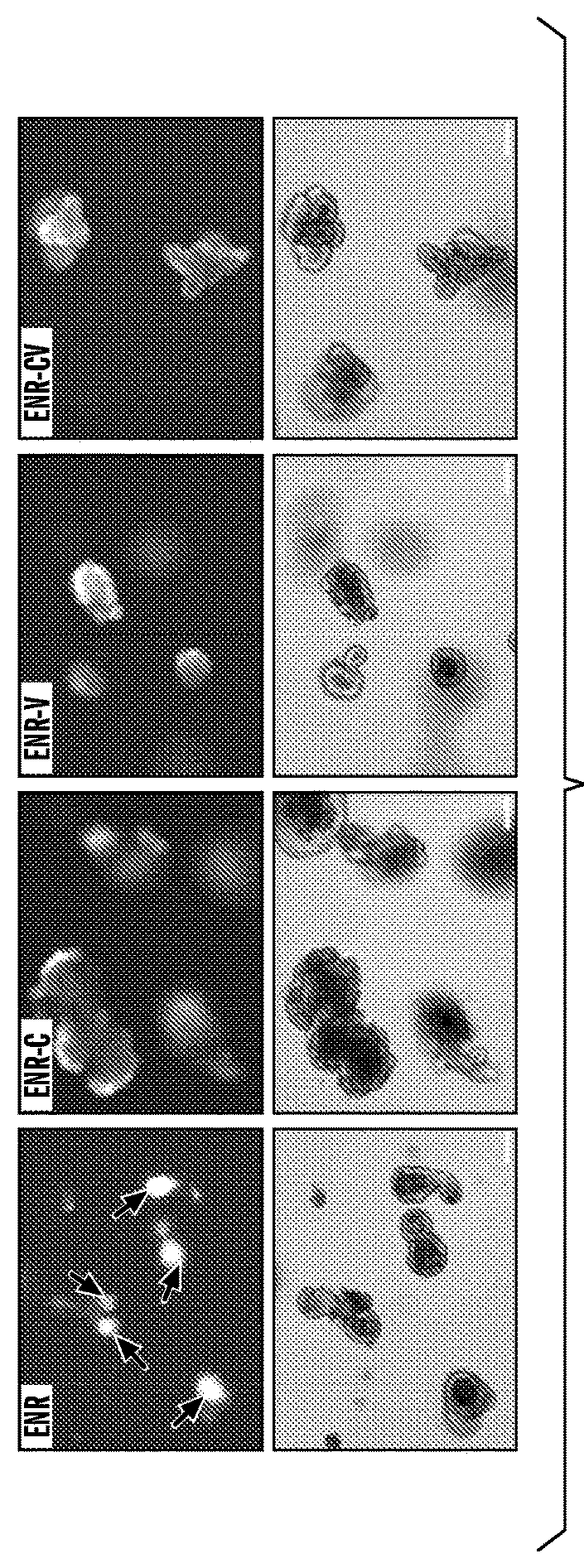
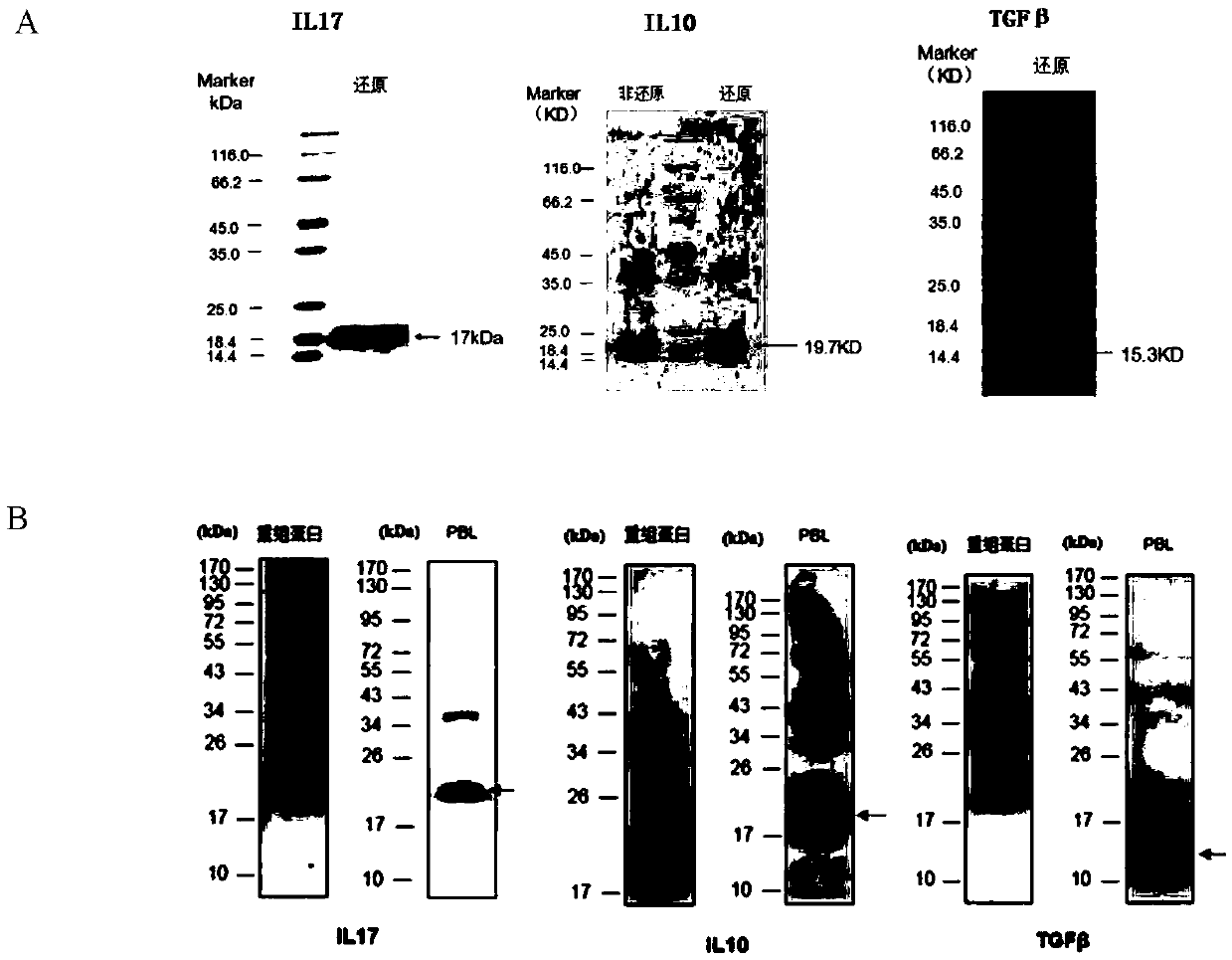
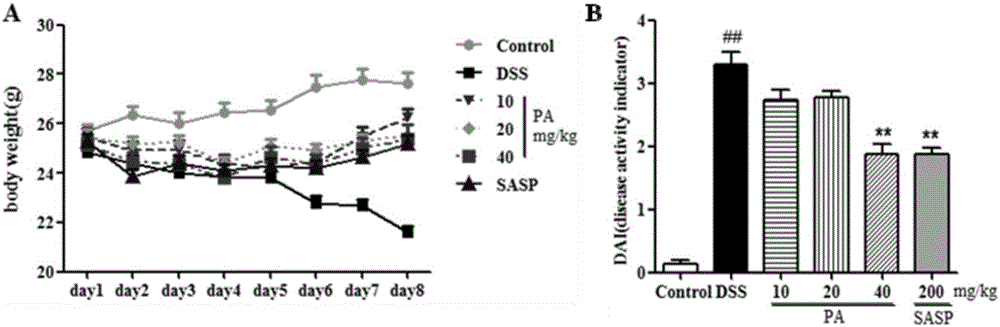
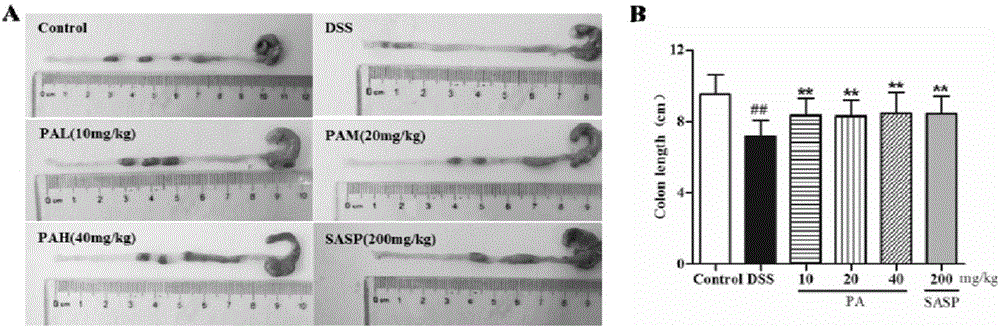
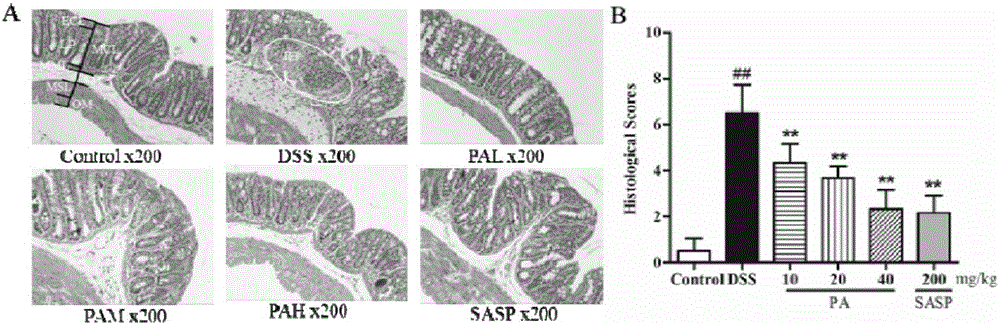
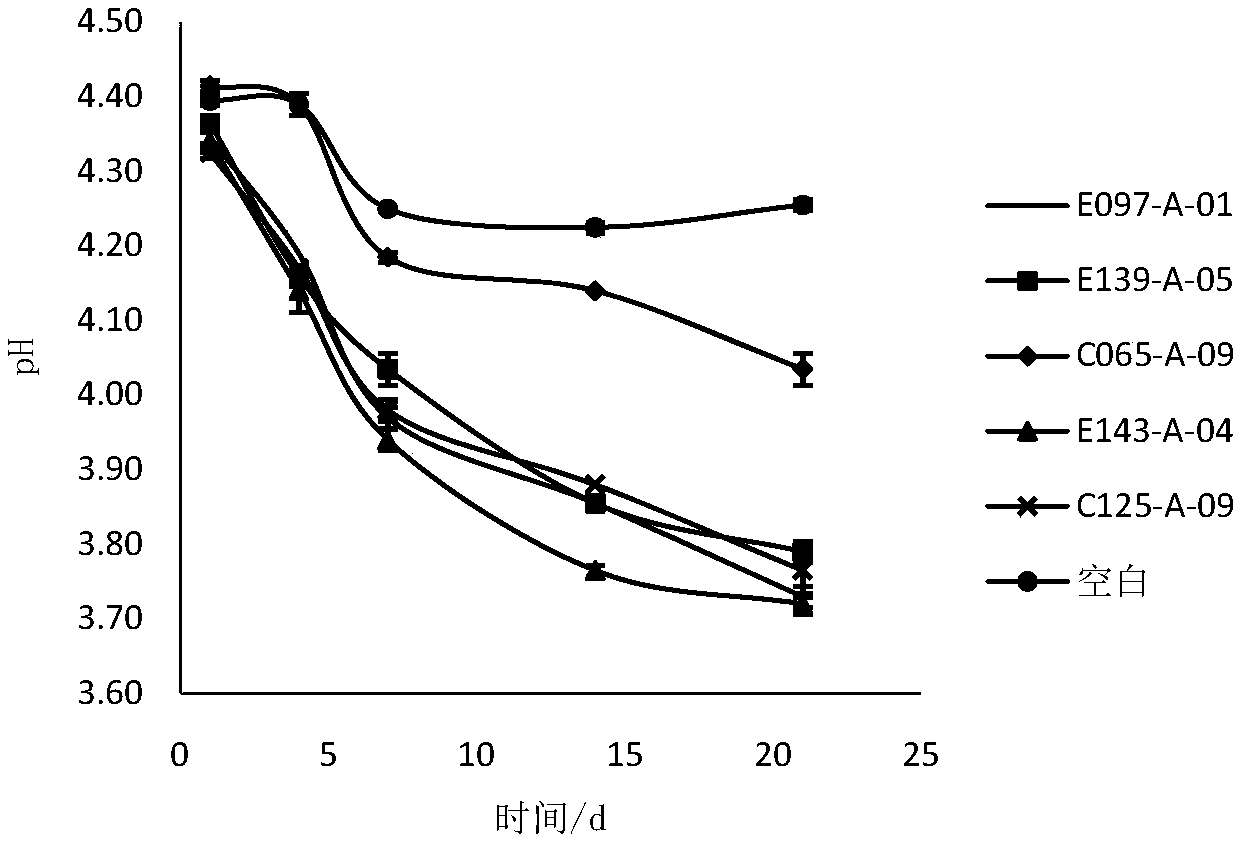
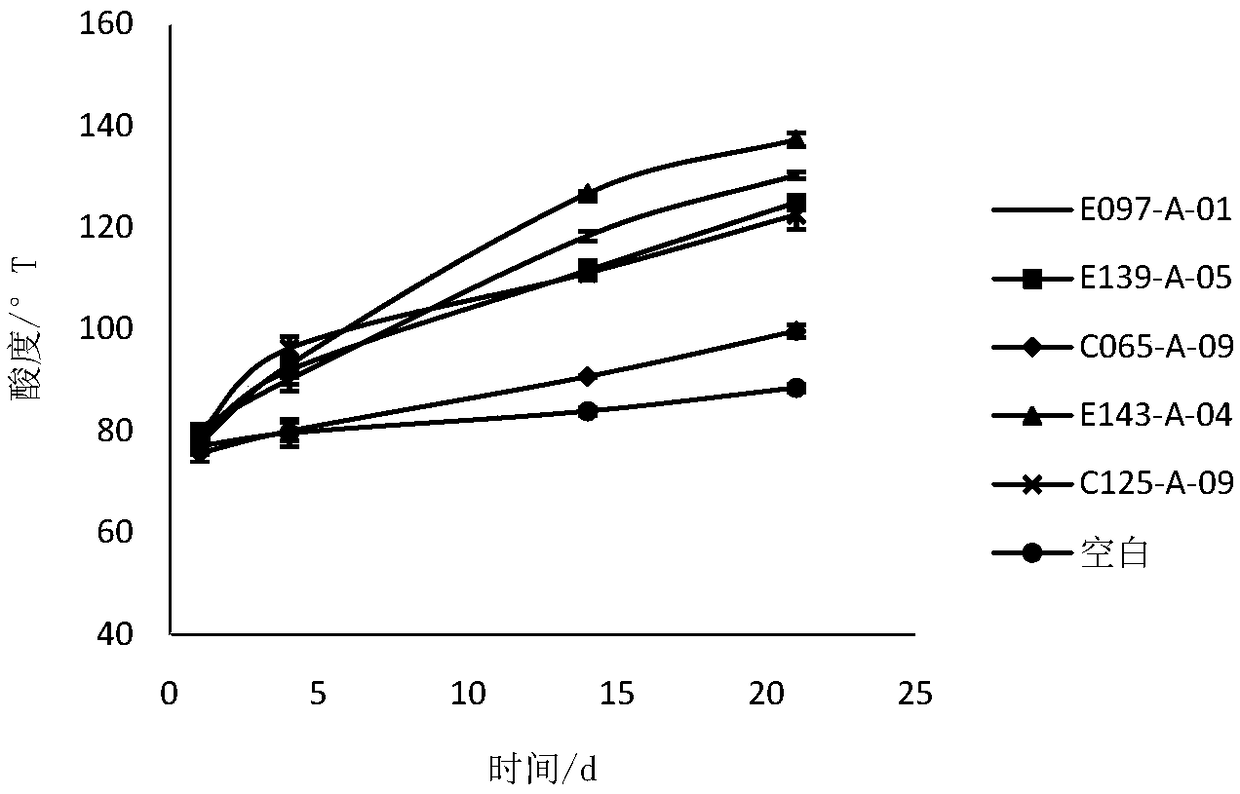
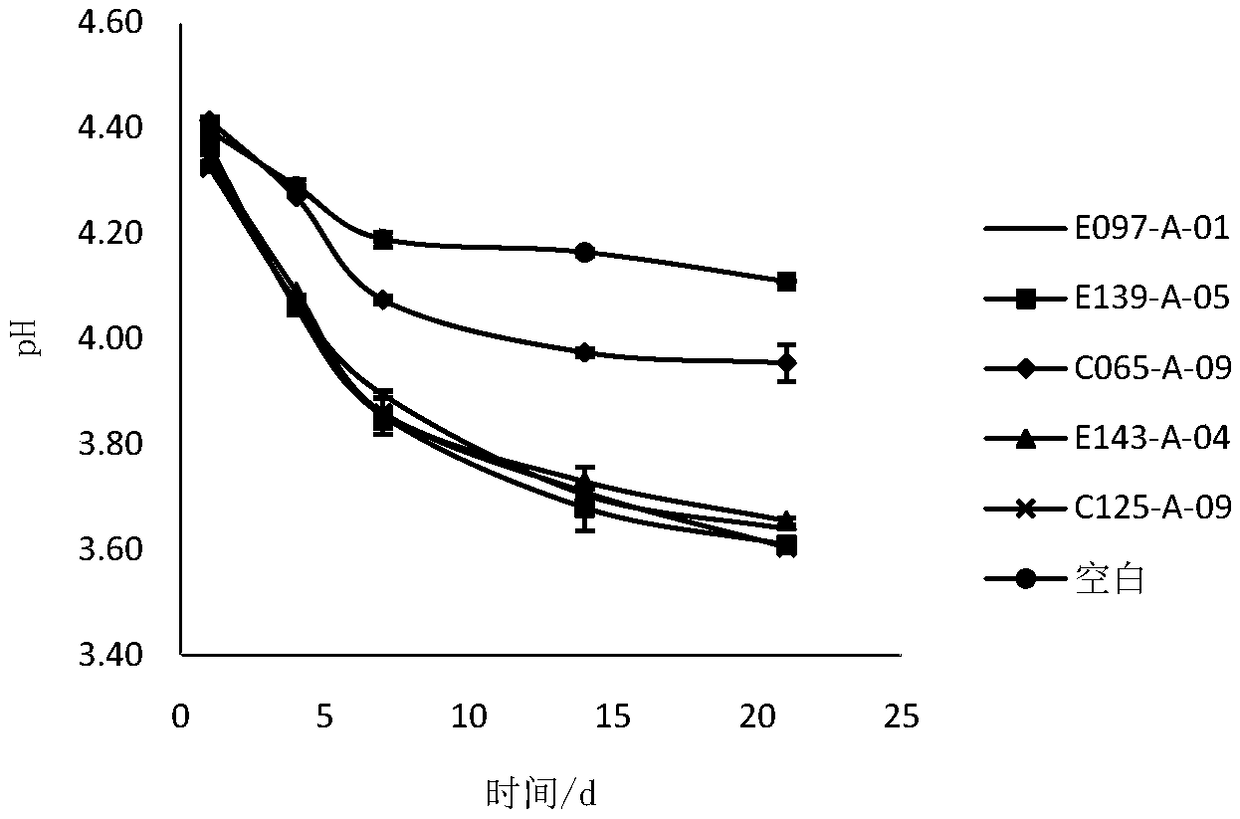
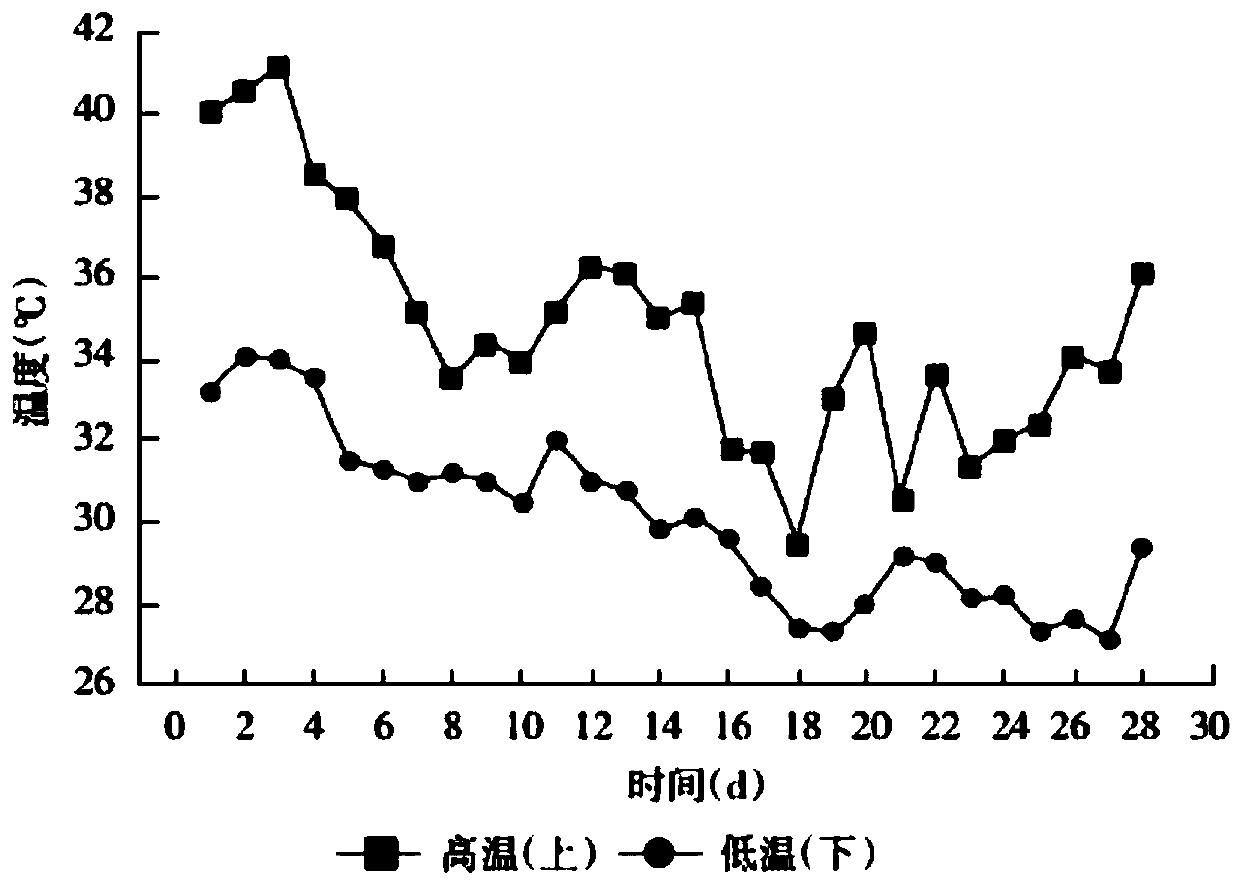
Patents
Literature
90 results about "Intestinal epithelium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
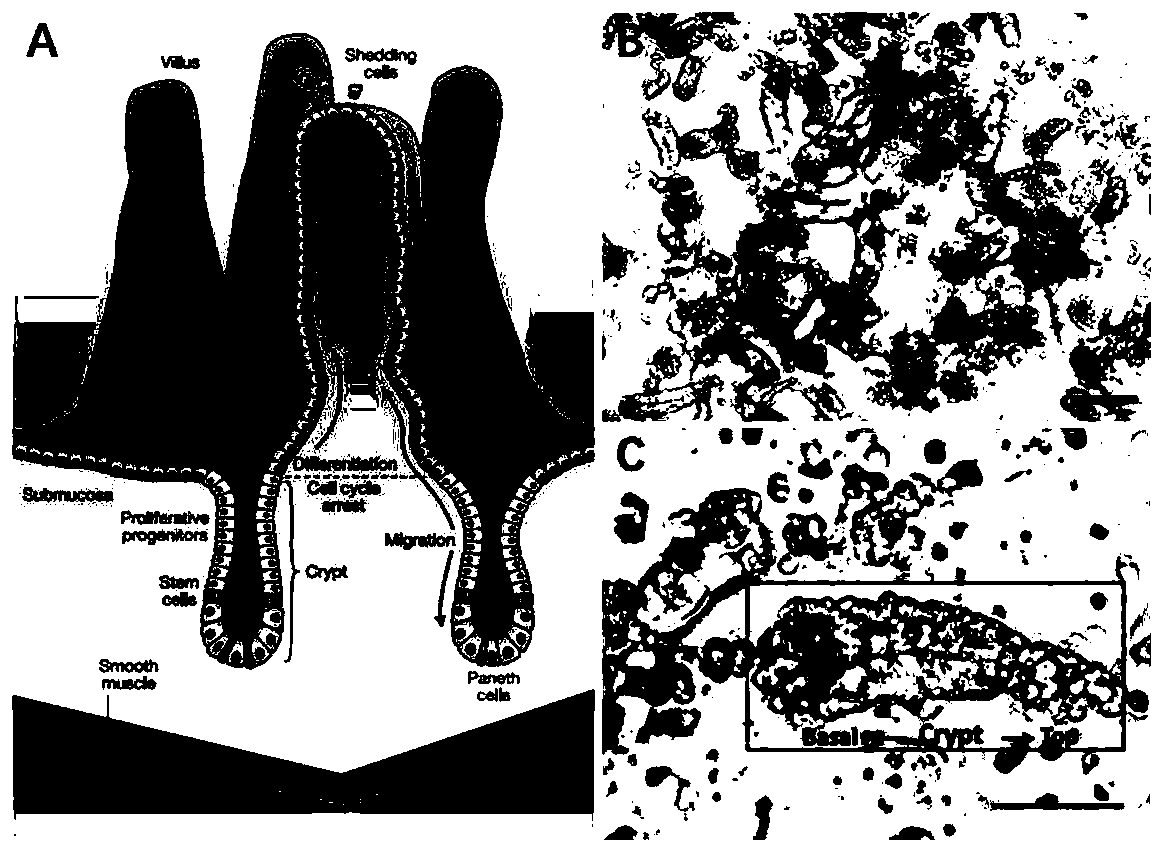
The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that form the luminal surface (lining) of both the small and large intestine (colon) of the gastrointestinal tract. Composed of simple columnar epithelial cells, it serves two main functions: absorbing useful substances into the body and restricting the entry of harmful substances. As part of its protective role, the intestinal epithelium forms an important component of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Certain diseases and conditions are caused by functional defects in the intestinal epithelium. On the other hand, various diseases and conditions can lead to its dysfunction which, in turn, can lead to further complications.
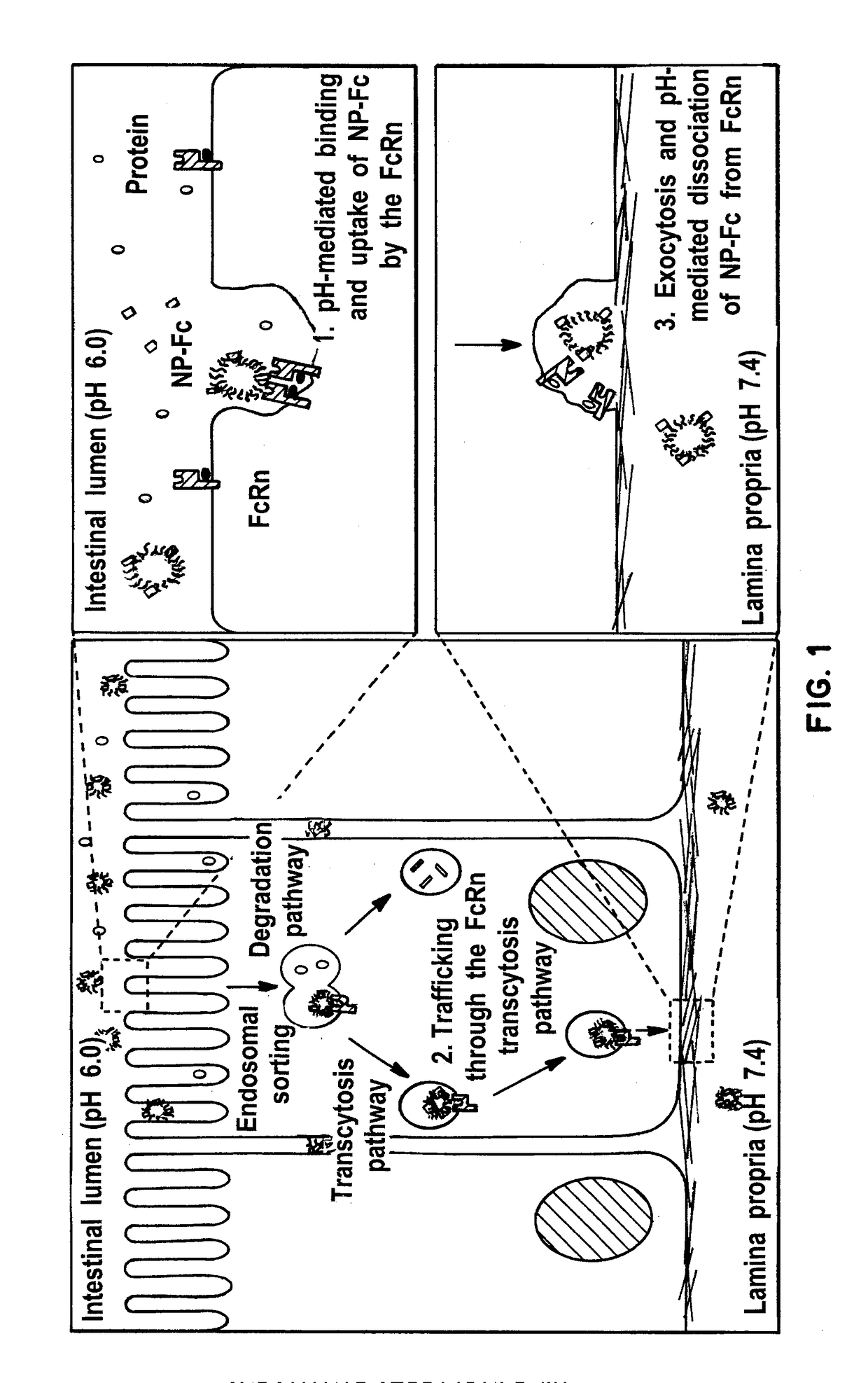
Receptor specific transepithelial transport of therapeutics
InactiveUS6030613AEffective strategyImprove abilitiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenTolerability
The present invention relates in general to methods and products for initiating an immune response against an antigen, and in particular relates to transepithelial delivery of antigens to provoke tolerance and immunity. The present invention further relates to methods and products for the transepithelial delivery of therapeutics. In particular, the invention relates to methods and compositions for the delivery of therapeutics conjugated to a FcRn binding partner to intestinal epithelium, mucosal epithelium and epithelium of the lung. The present invention further relates to the synthesis, preparation and use of the FcRn binding partner conjugates as, or in, pharmaceutical compositions for oral systemic delivery of drugs and vaccines.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV +1
Receptor specific transepithelial transport of therapeutics
InactiveUS6485726B1Effective strategyImprove abilitiesBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenTolerability
The present invention relates in general to methods and products for initiating an immune response against an antigen, and in particular relates to transepithelial delivery of antigens to provoke tolerance and immunity. The present invention further relates to methods and products for the transepithelial delivery of therapeutics. In particular, the invention relates to methods and compositions for the delivery of therapeutics conjugated to a FcRn binding partner to intestinal epithelium, mucosal epithelium and epithelium of the lung. The present invention further relates to the synthesis, preparation and use of the FcRn binding partner conjugates as, or in, pharmaceutical compositions for oral systemic delivery of drugs and vaccines.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV +1
Receptor specific transepithelial transport of therapeutics
The present invention relates in general to methods and products for initiating an immune response against an antigen, and in particular relates to transepithelial delivery of antigens to provoke tolerance and immunity. The present invention further relates to methods and products for the transepithelial delivery of therapeutics. In particular, the invention relates to methods and compositions for the delivery of therapeutics conjugated to a FcRn binding partner to intestinal epithelium, mucosal epithelium and epithelium of the lung. The present invention further relates to the synthesis, preparation and use of the FcRn binding partner conjugates as, or in, pharmaceutical compositions for oral systemic delivery of drugs and vaccines.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
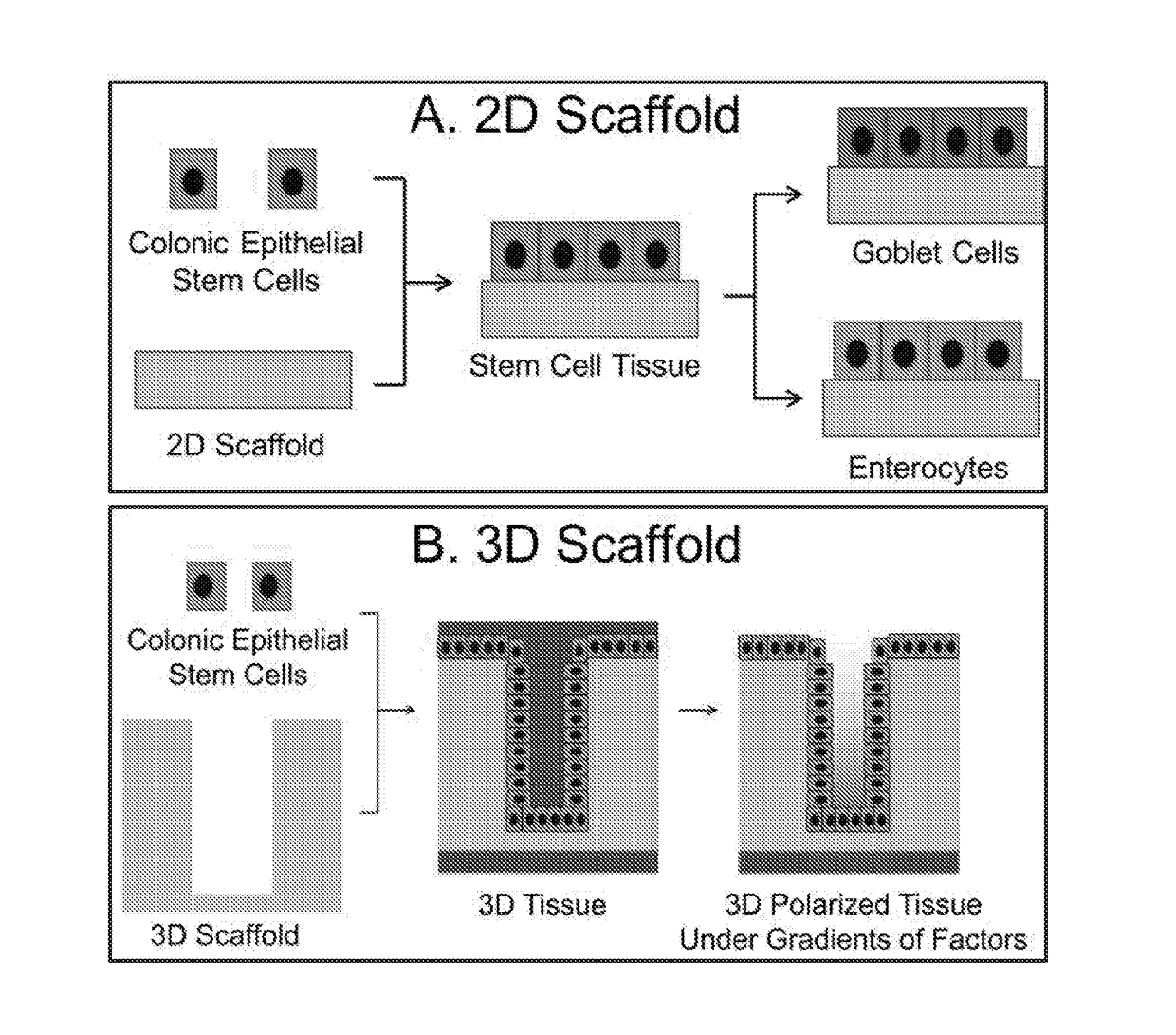
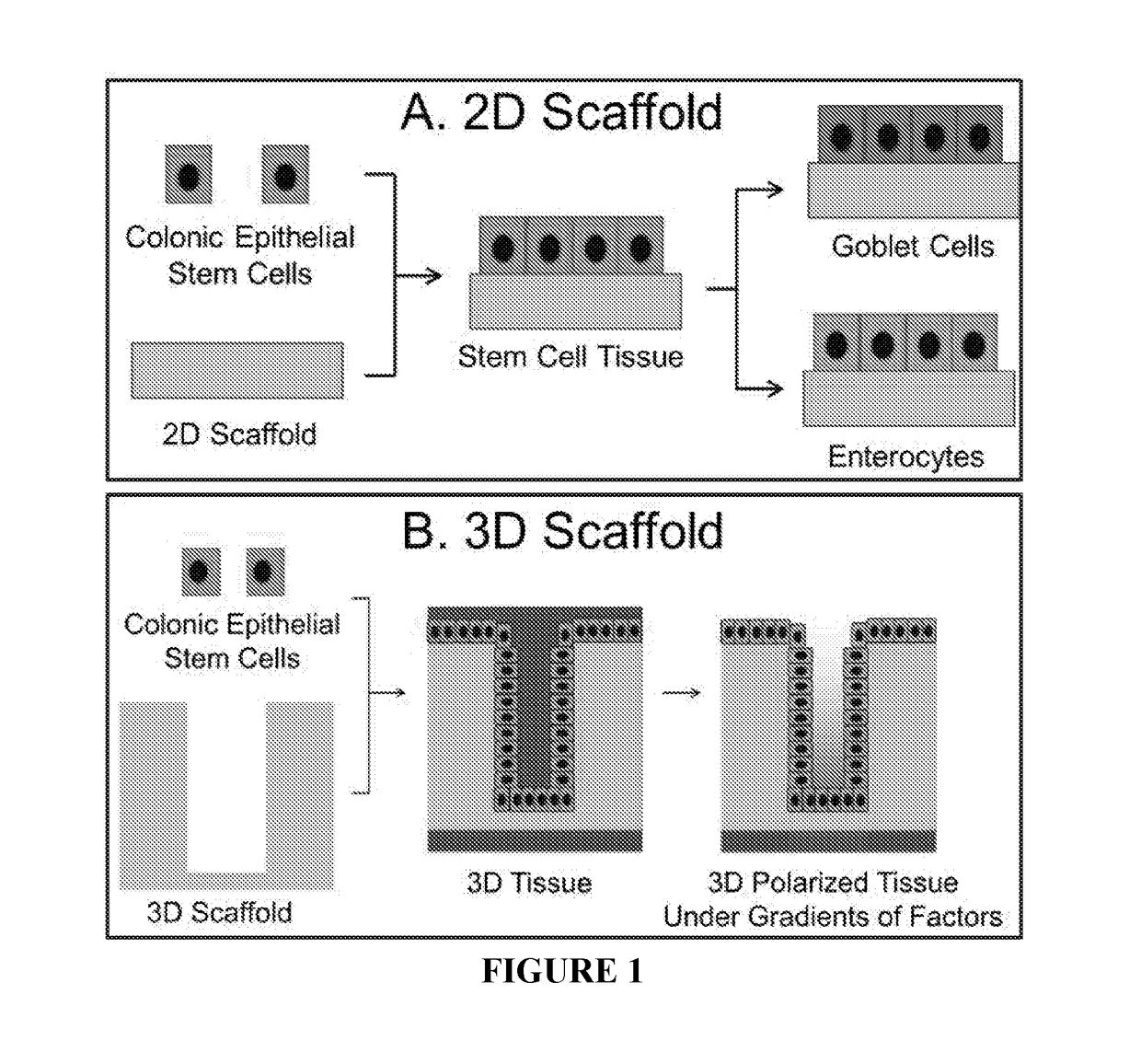
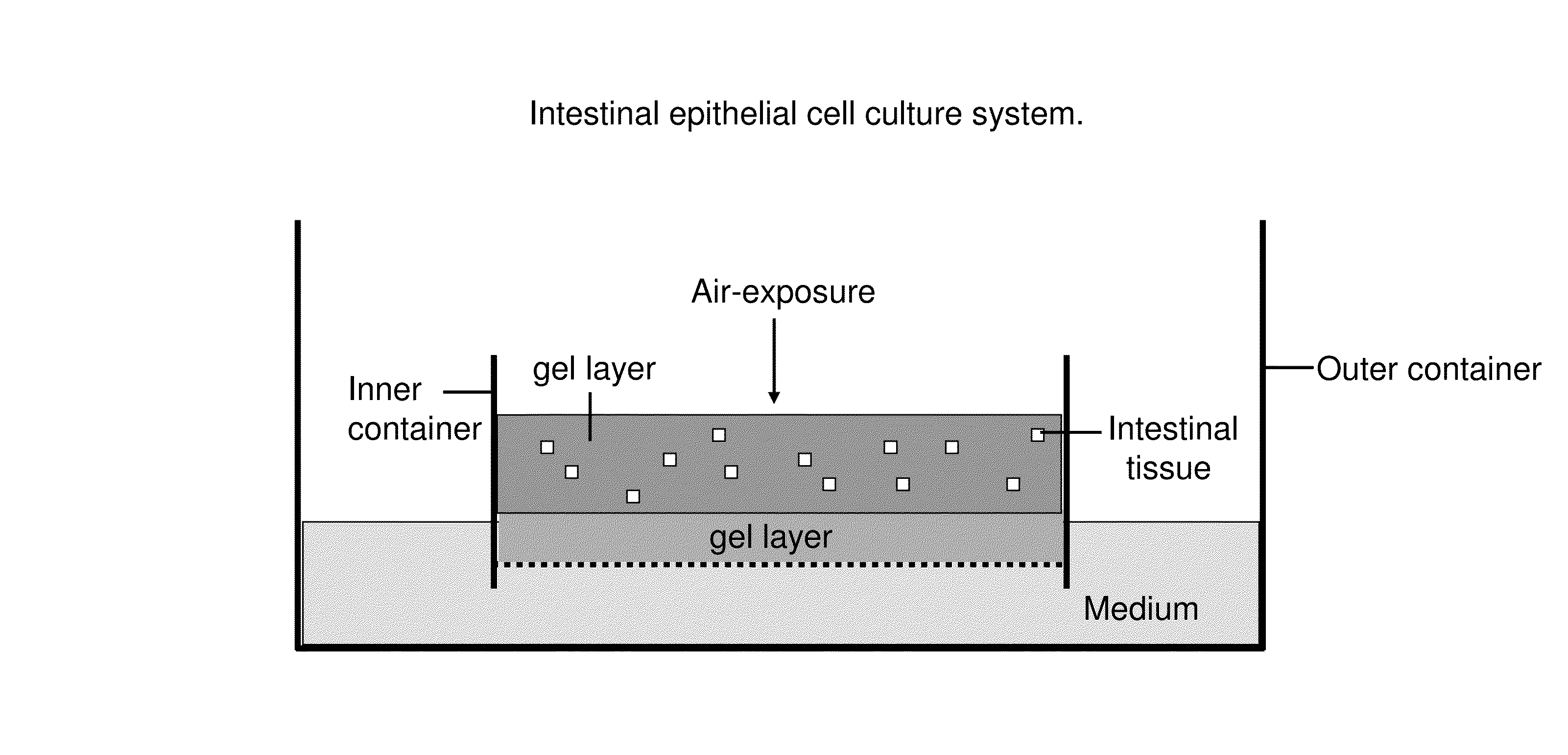
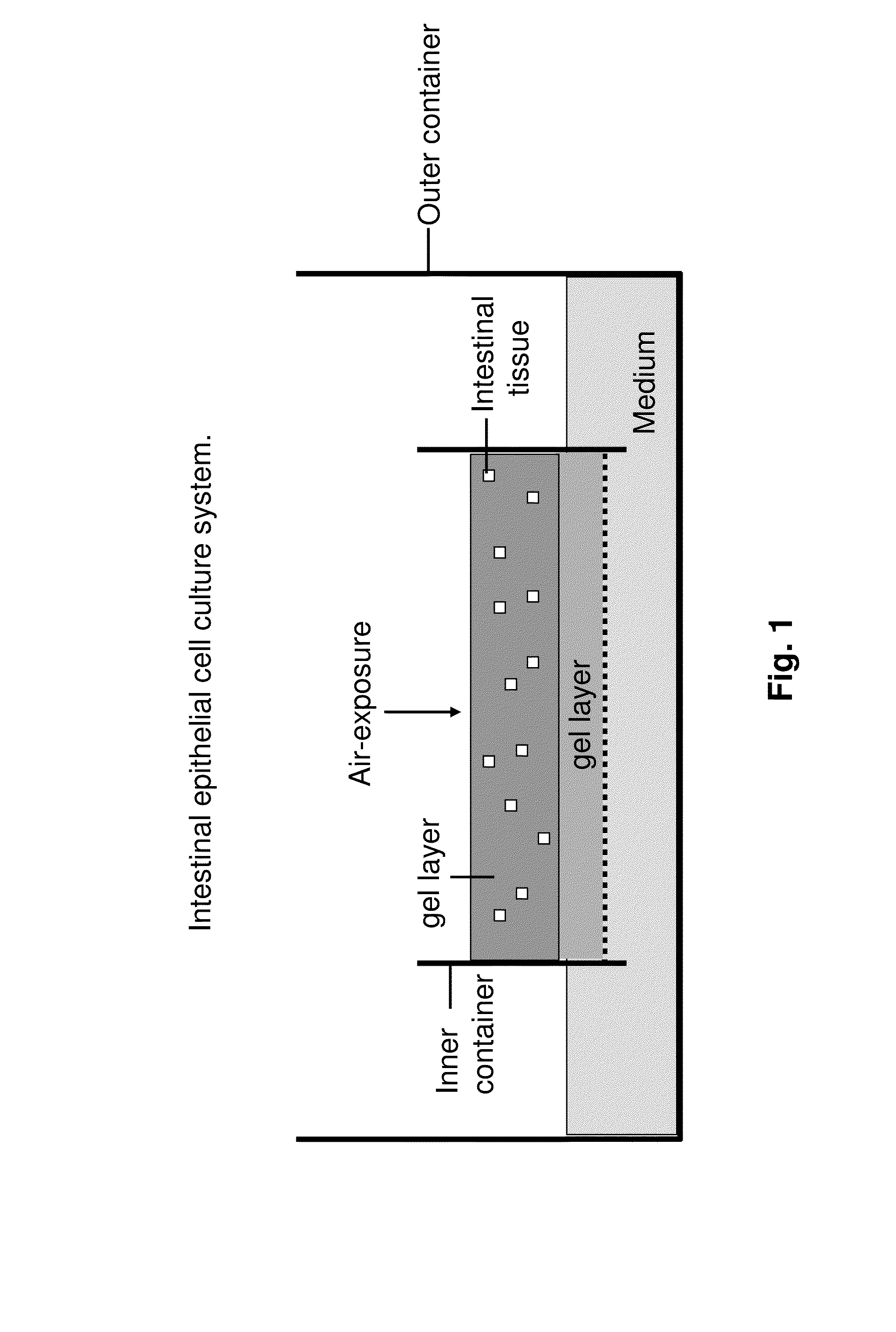
Ex Vivo Culture, Proliferation and Expansion of Intestinal Epithelium
ActiveUS20100047853A1Induce pluripotencyAlter differentiationGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementAir liquid interfaceMammal
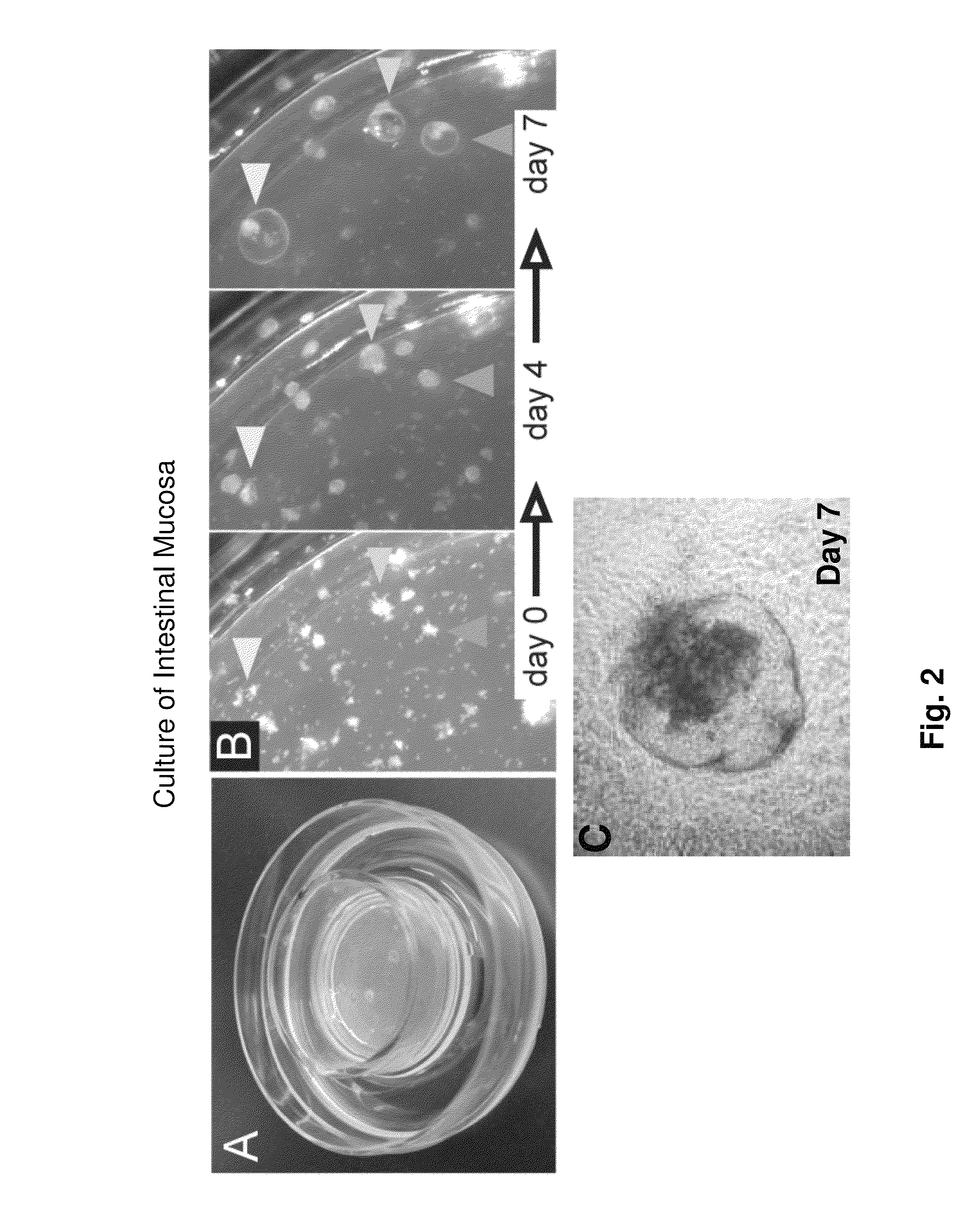
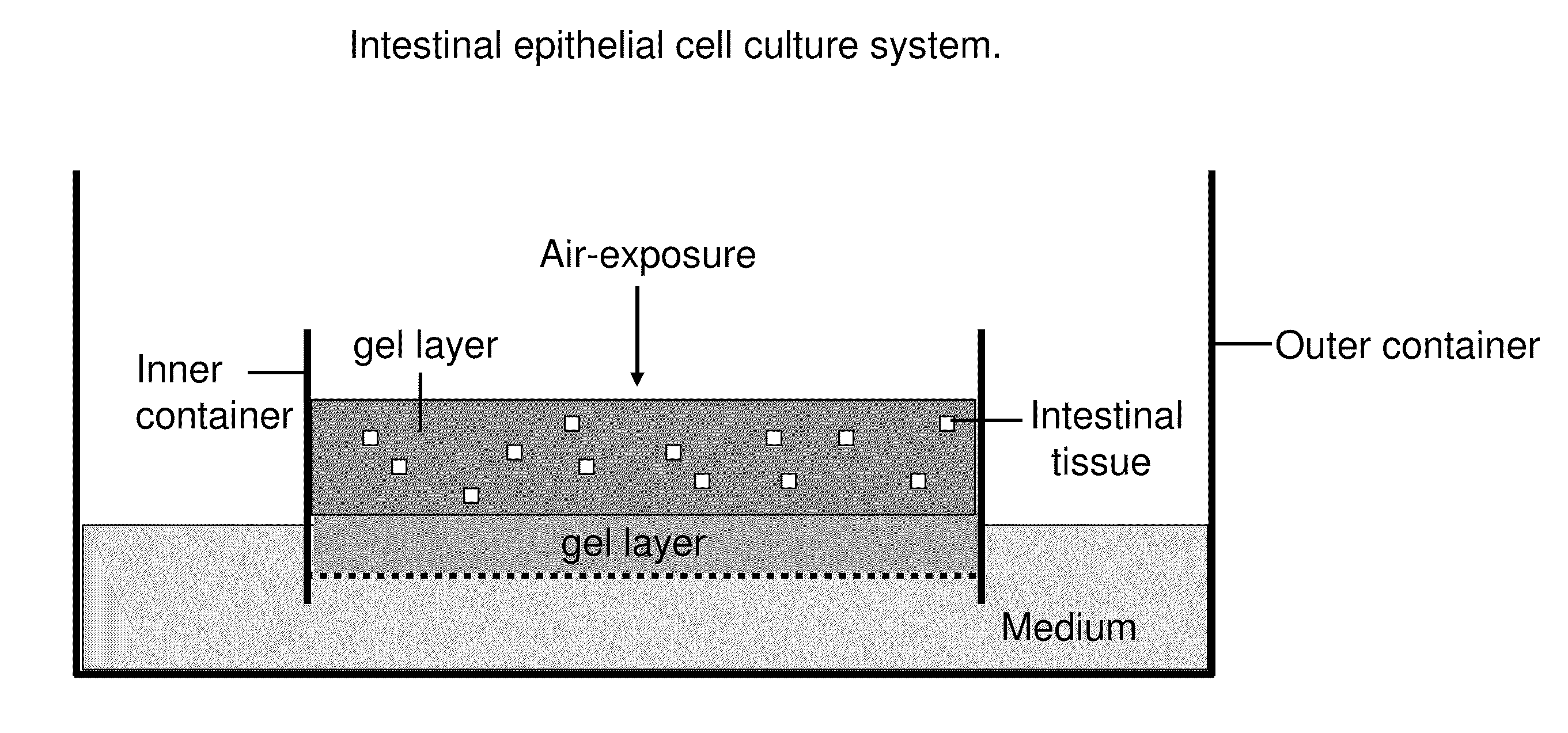
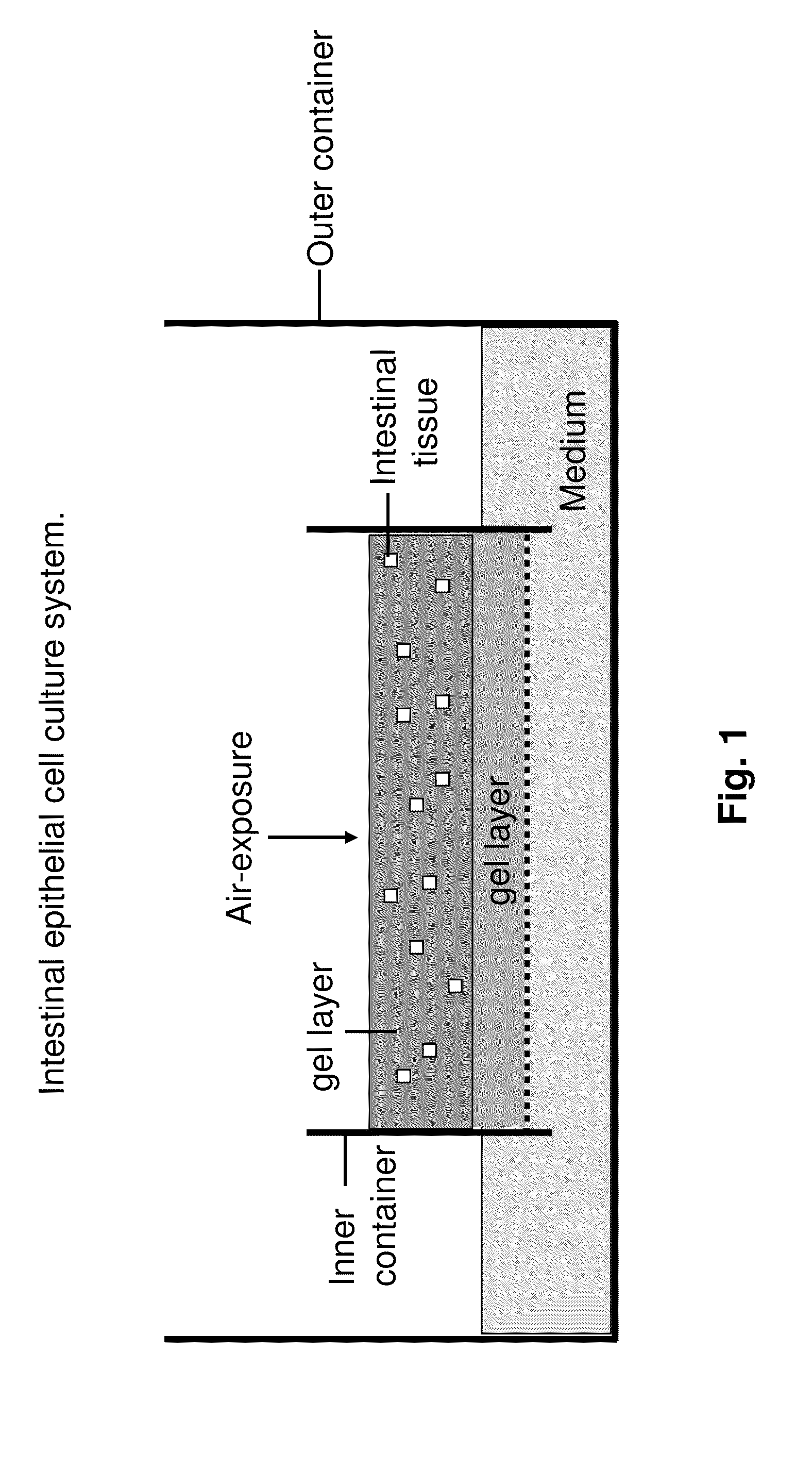
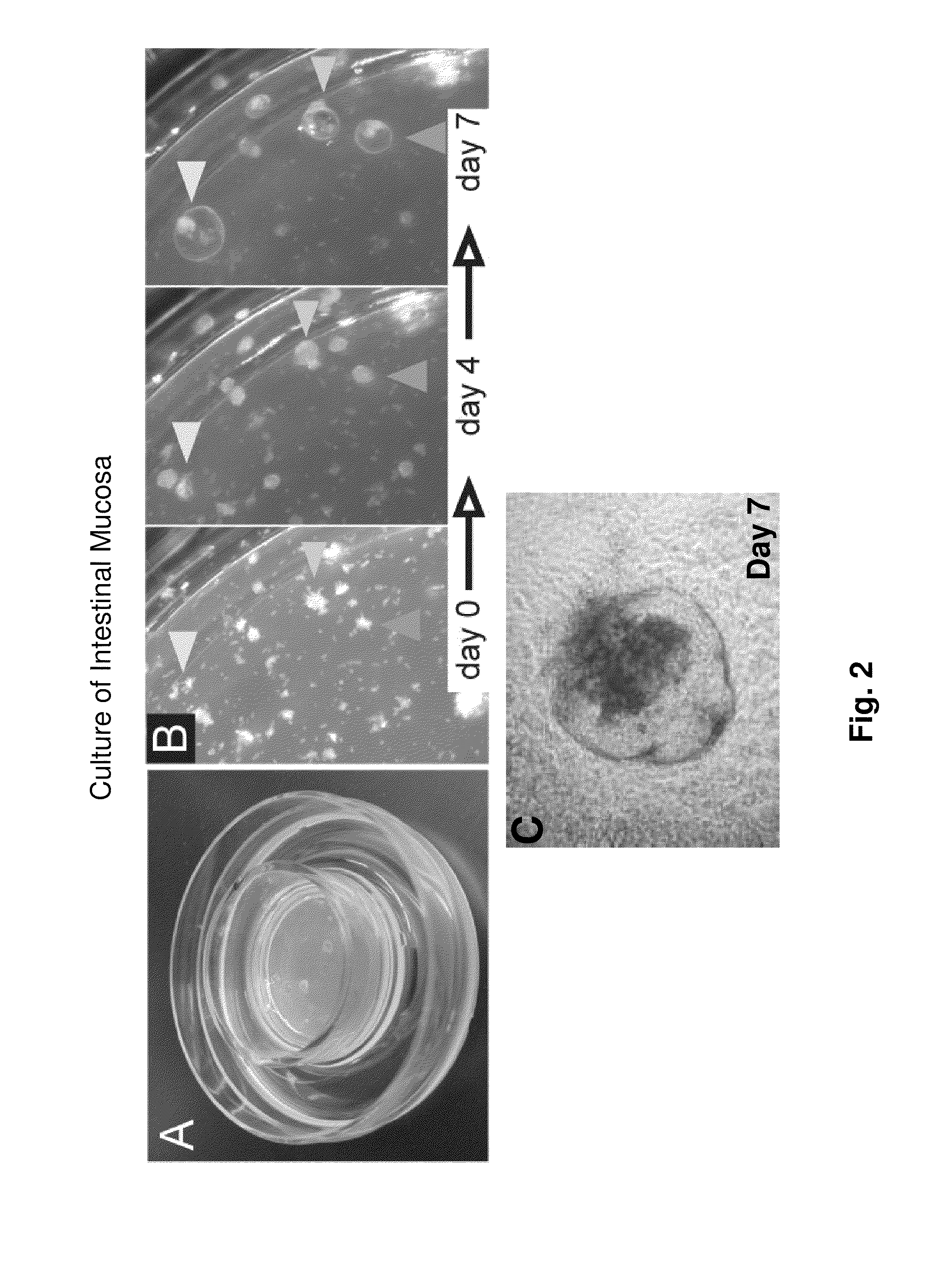
Methods are provided for long term culture of mammalian intestinal cells. Cultures are initiated with fragments of mammalian intestinal tissue, which are then maintained embedded in a gel substrate that provides an air-liquid interface. Intestinal epithelium in cultures of the invention can be continuously grown for extended periods of time. Mammalian intestinal cells cultured by the methods of the invention recapitulate features of intestinal growth in vivo.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
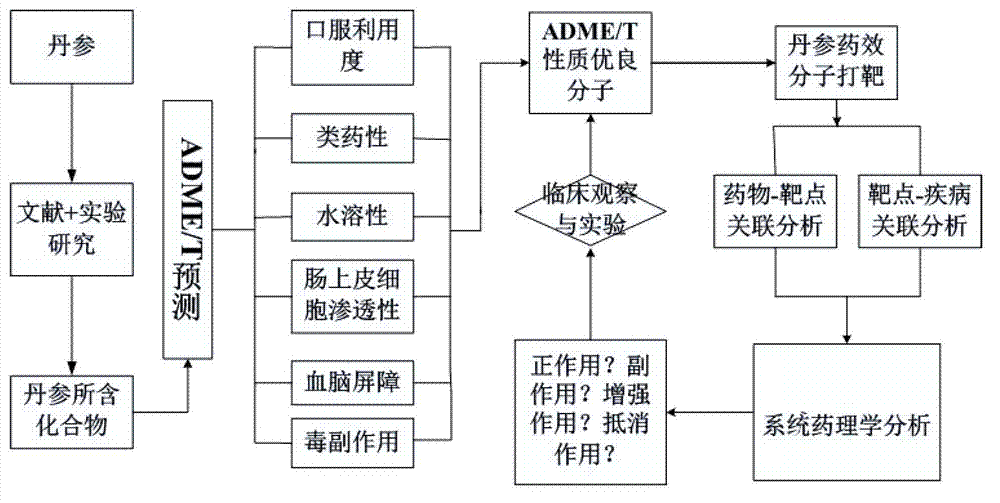
Analysis platform and analysis method of pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine system
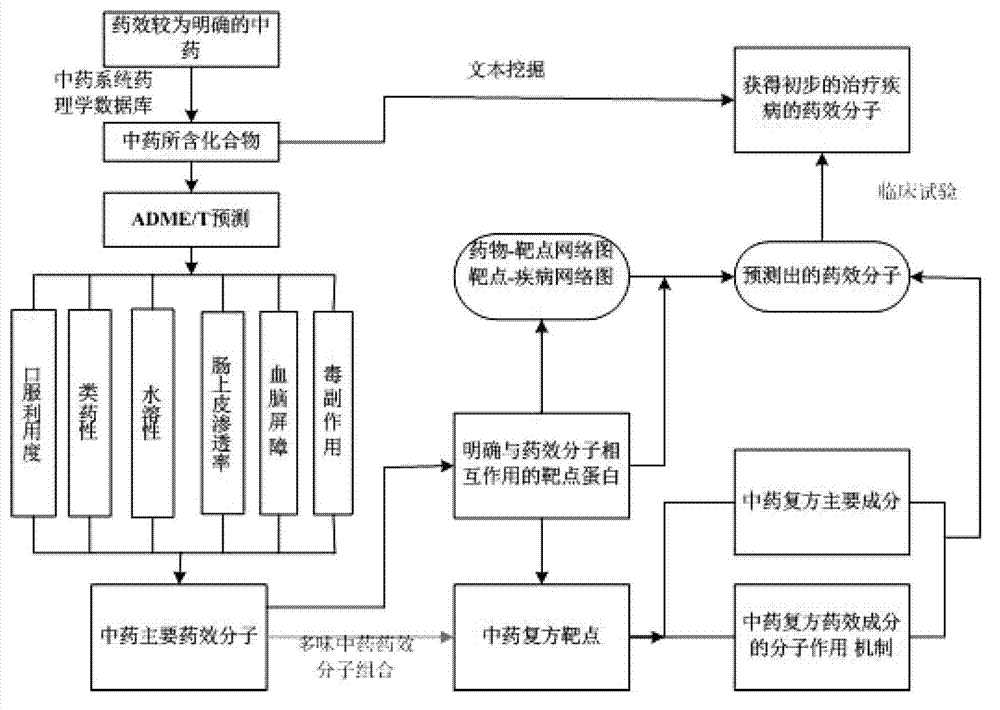
The invention provides an analysis platform and an analysis method of pharmacology of a traditional Chinese medicine system. The analysis platform comprises a database module of the pharmacology of the traditional Chinese medicine system, a target point prediction software package module and a network construction module. The database module of the pharmacology of the traditional Chinese medicine system comprises text mining, drug-likeness prediction, intestinal epithelium permeability prediction, water-solubility prediction, blood brain barrier prediction, toxic and side effect prediction, and the like. The network construction module comprises a drug and target point prediction technology, a network construction analysis technology and a target point and disease network construction technology. From the positive direction, the invention provides a prediction method from traditional Chinese medicine, active compound to a target and relevant diseases. Meanwhile, from the negative direction, the invention provides a prediction and analysis method from the diseases, searching of the target, to active ingredients and belonged traditional Chinese medicine. Convenience is brought for research of the modern pharmacology of the traditional Chinese medicine, modification of old drugs, design of new drugs, components of the new drugs, and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Compositions And Methods For Epithelial Stem Cell Expansion And Culture
ActiveUS20160194604A1Sufficient amountGastrointestinal cellsDigestive systemIntestinal structureUnilaminar epithelium
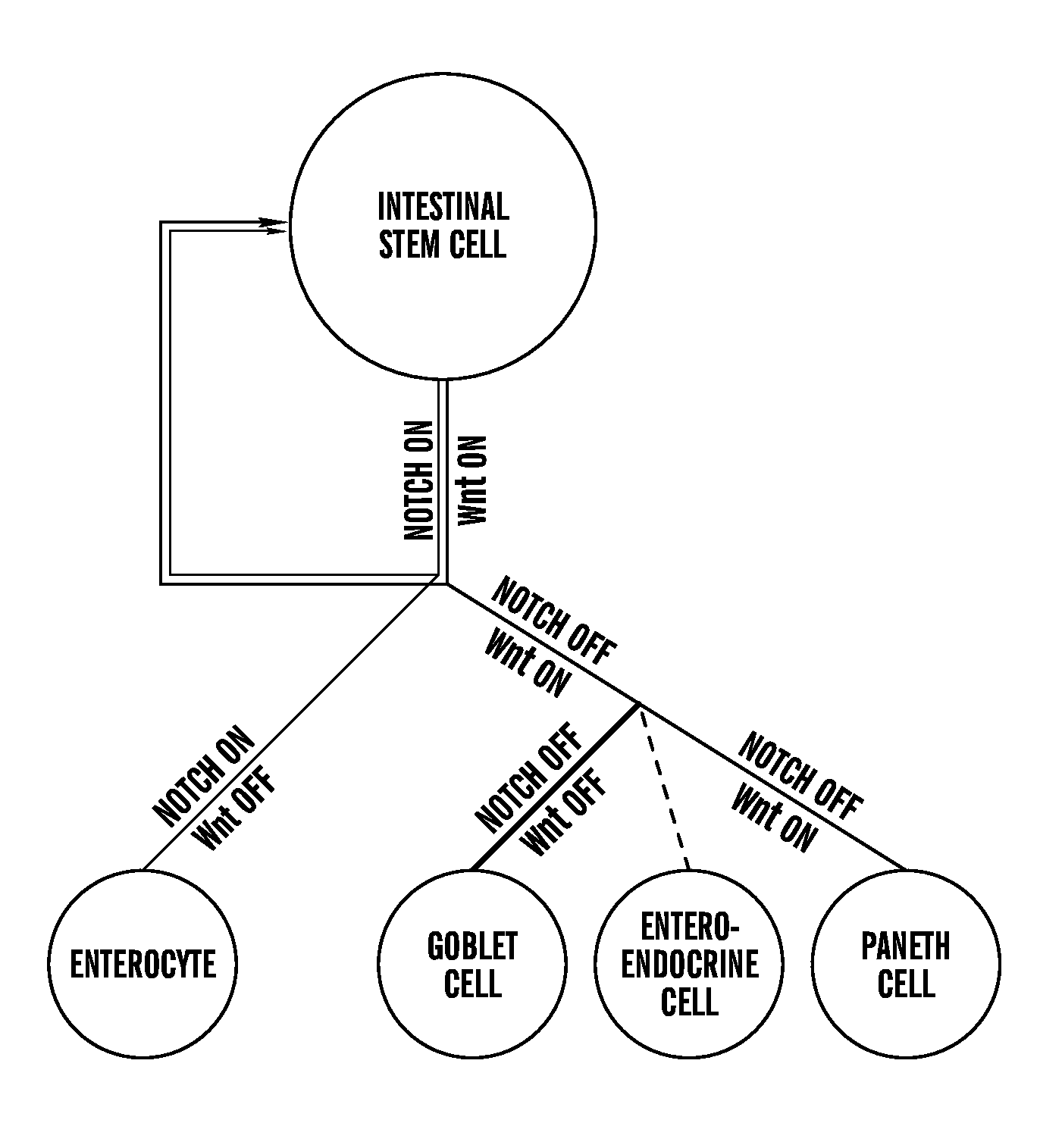
Described are cell culture solutions and systems for epithelial stem cell and organoid cultures, formation of epithelial constructs and uses of the same in transplantation. A single layer of epithelial cells that actively self-renews and is organized into crypts and villi clothes the intestine. It has been recently shown that the renewal of intestinal epithelium is driven by Lgr5+ intestinal stem cells (ISC) that reside at the base of these crypts (Barker et al., 2007). Lgr5+ stem cells can be isolated and cultured in vitro to form organoids containing crypt-vcllus structures that recapitulates the native intestinal epithelium (Sato et al., 2009).
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Compositions and methods for epithelial stem cell expansion and culture
Described are cell culture solutions and systems for epithelial stem cell and organoid cultures, formation of epithelial constructs and uses of the same in transplantation. A single layer of epithelial cells that actively self-renews and is organized into crypts and villi clothes the intestine. It has been recently shown that the renewal of intestinal epithelium is driven by Lgr5+ intestinal stem cells (ISC) that reside at the base of these crypts (Barker et al., 2007). Lgr5+ stem cells can be isolated and cultured in vitro to form organoids containing crypt-vcllus structures that recapitulates the native intestinal epithelium (Sato et al., 2009).
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Methods to generate gastrointestinal epithelial tissue constructs
ActiveUS20180002672A1Maintain their viabilityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProgenitorGoblet cell
A method of making a live cell construct is carried out by: (a) providing a non-cellular support having a top surface and a bottom surface, (b) contacting live undifferentiated cells to the non-cellular support, and then (c) propagating a gastrointestinal epithelial cell monolayer on said top surface. In some embodiments, the live cells in the monolayer include: (i) undifferentiated cells (e.g., stem or progenitor cells); and (ii) optionally, but in some embodiments preferably, differentiated cells (e.g., enterocytes, Paneth cells, enteroendocrine cells, tuft cells, microcells, intra-epithelial lymphocytes, and / or goblet cells). Constructs formed by such methods and methods of using the same (e.g., in high through-put screening) are also described.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
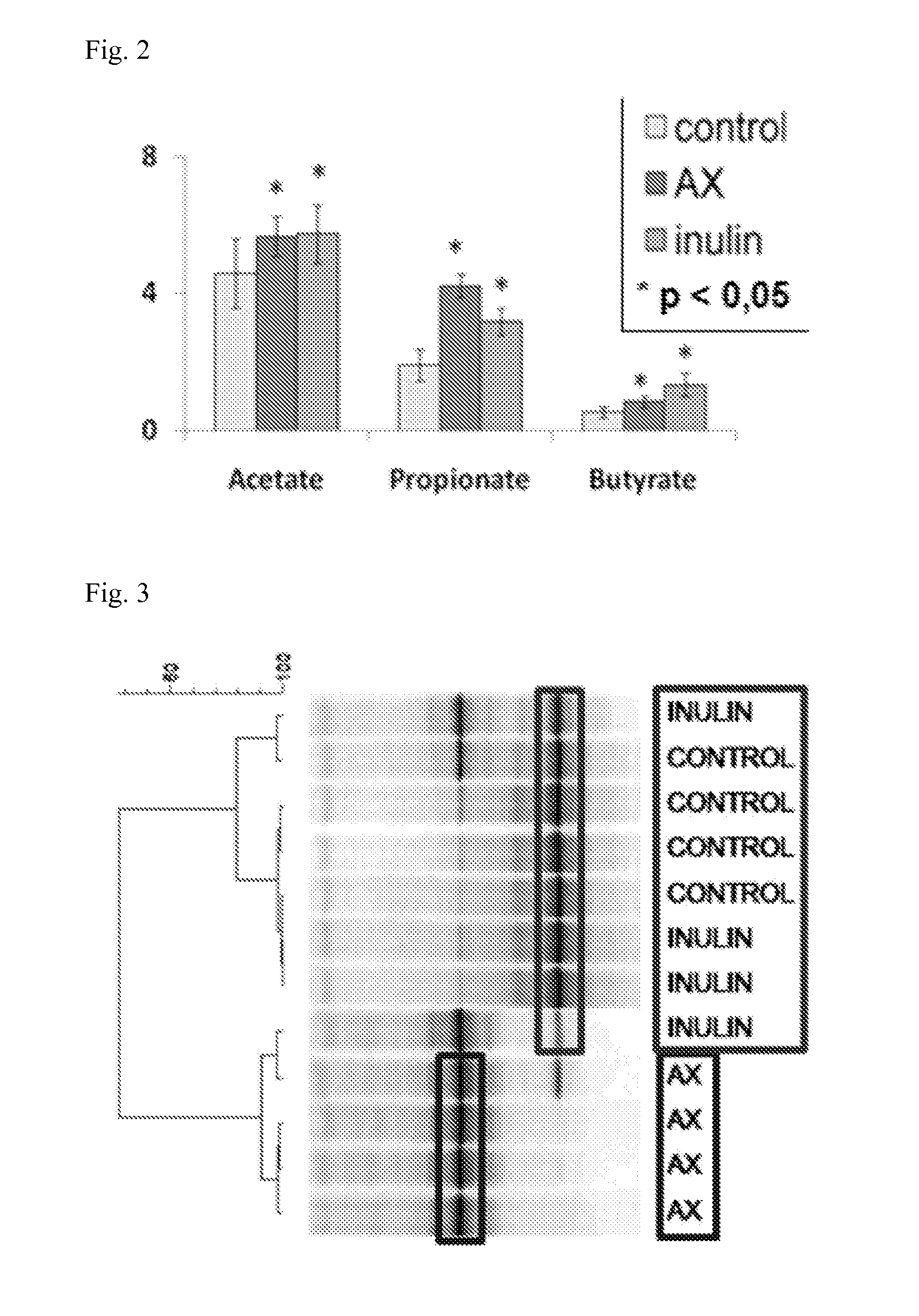
Arabinoxylans for modulating the barrier function of the intestinal surface
ActiveUS20120230955A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsIntestinal surfaceIntestinal microorganisms
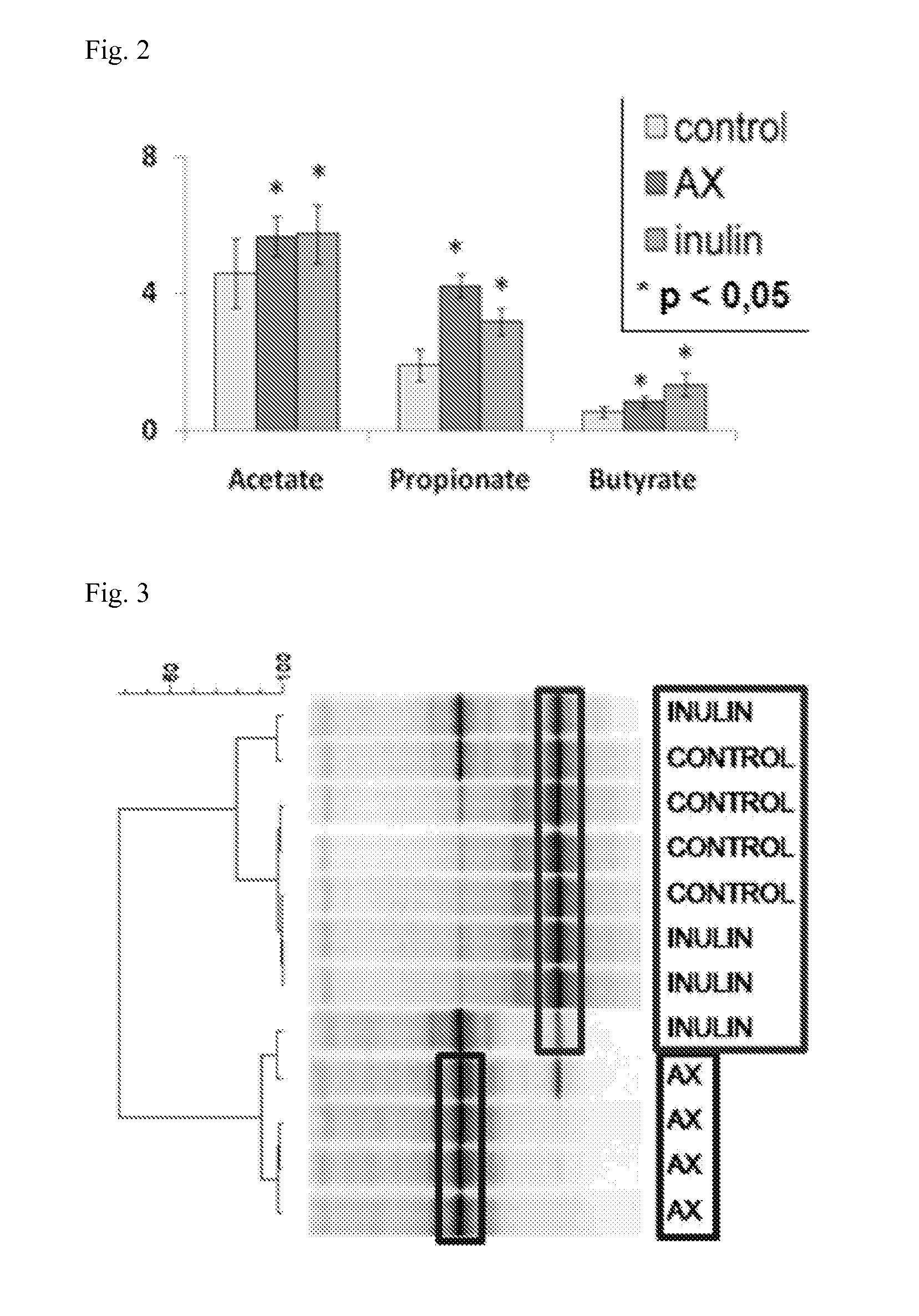
The present invention is directed to a particular arabinoxylan (“AX”) preparation and the finding that this preparation has a beneficial effect on the organization of the intestinal microbial community in the lumen and in particular at the site of the gut mucosa, where it modulates the barrier function of the intestinal surface, primarily by modulating the mucosa-associated microbial community towards a relative increase of health beneficial bacteria, such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. It is accordingly a first aspect of the present invention to provide said arabinoxylan preparation characterized in comprising isolated water-soluble arabinoxylans and the use thereof to improve functioning (e.g. barrier function) of the intestinal epithelium. Thus, in a further aspect the present invention provides compositions, both pharmaceutical and nutritional compositions, comprising said arabinoxylan preparations; in particular pharmaceuticals, medical foods, food supplements or food compositions, such as infant formula products, dairy products, bakery products or pastry products. The compositions optionally comprise probiotics such as Bifidobacterium or Lactobacillus.
Owner:BIOACTOR
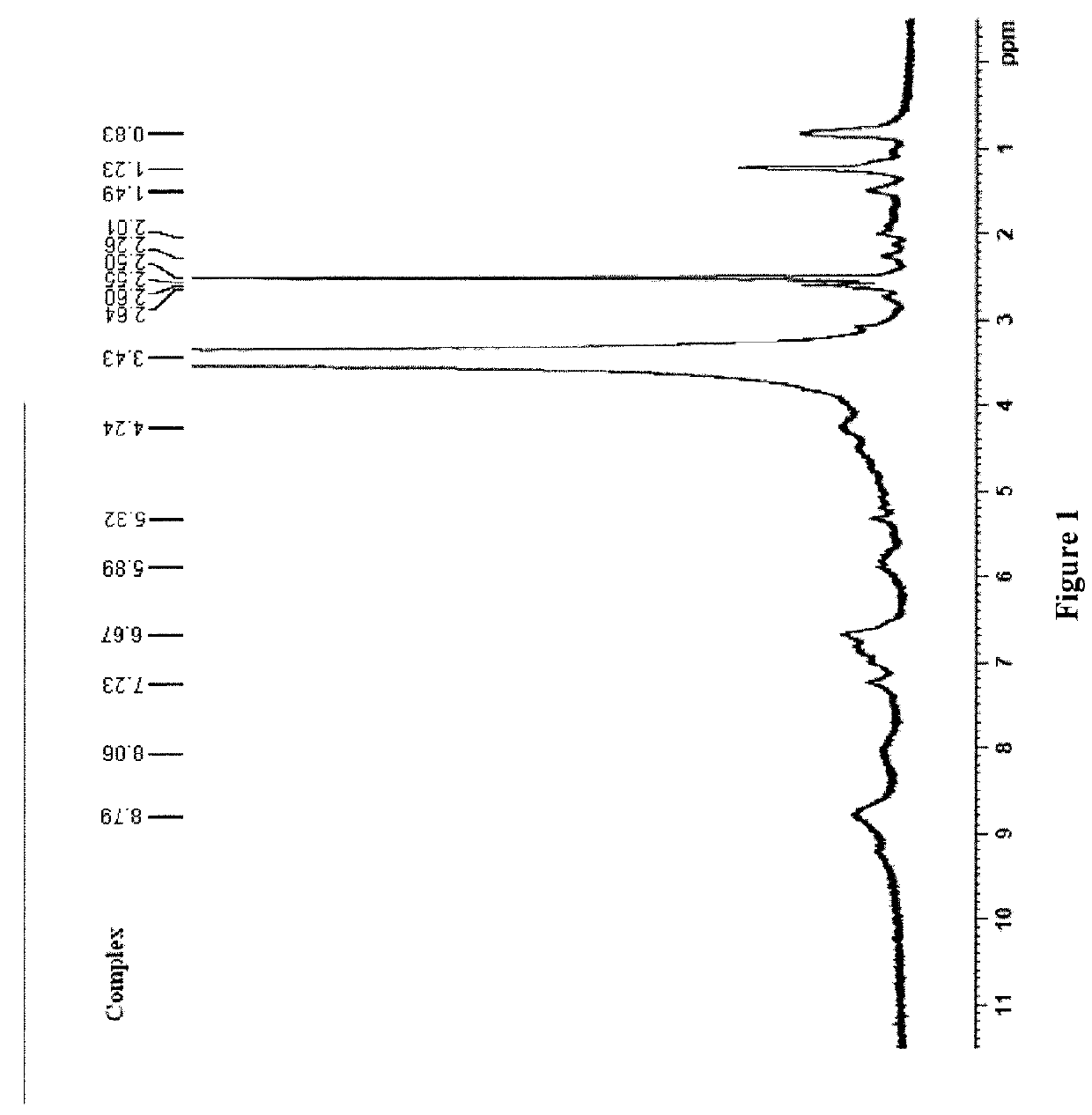
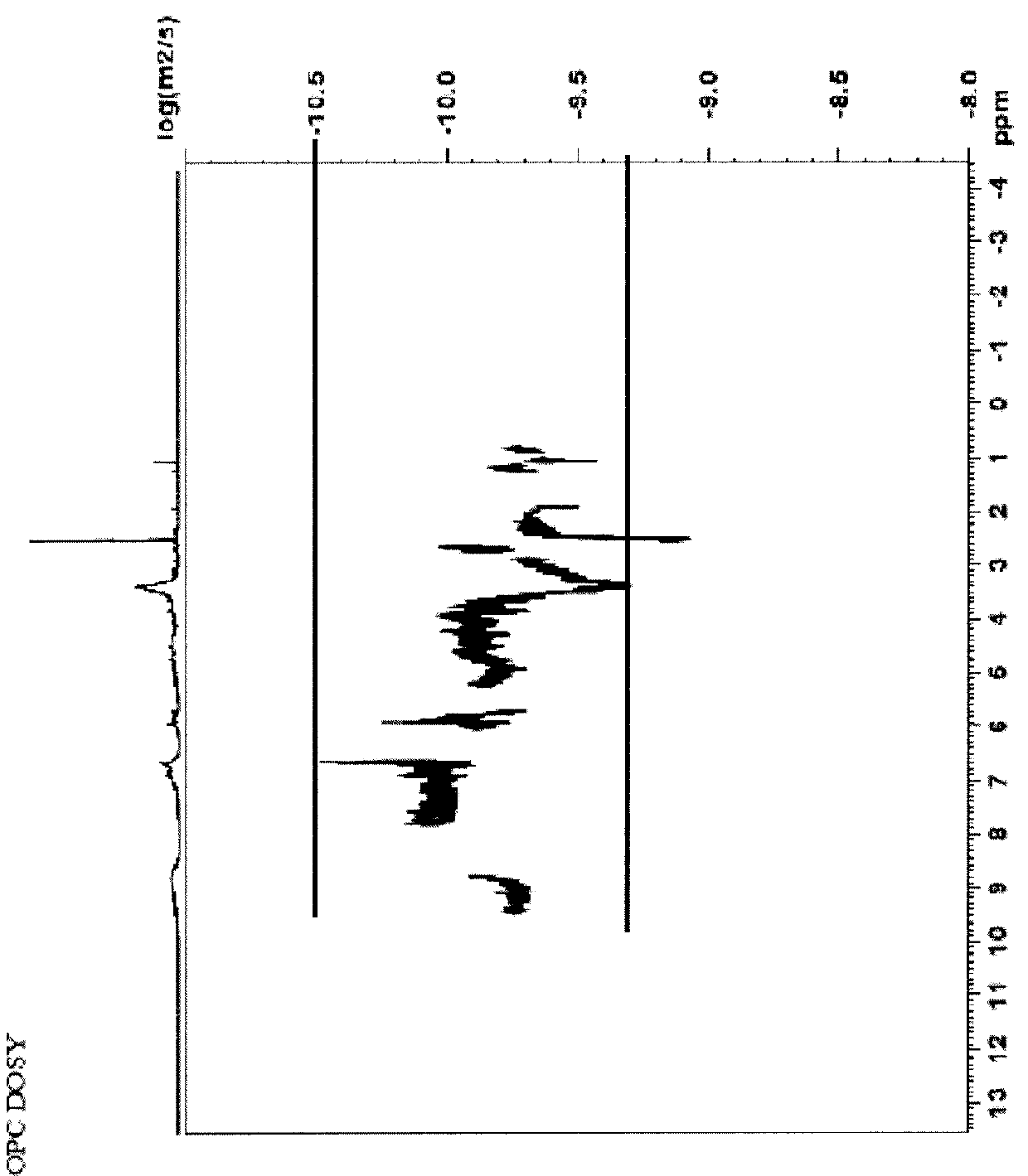
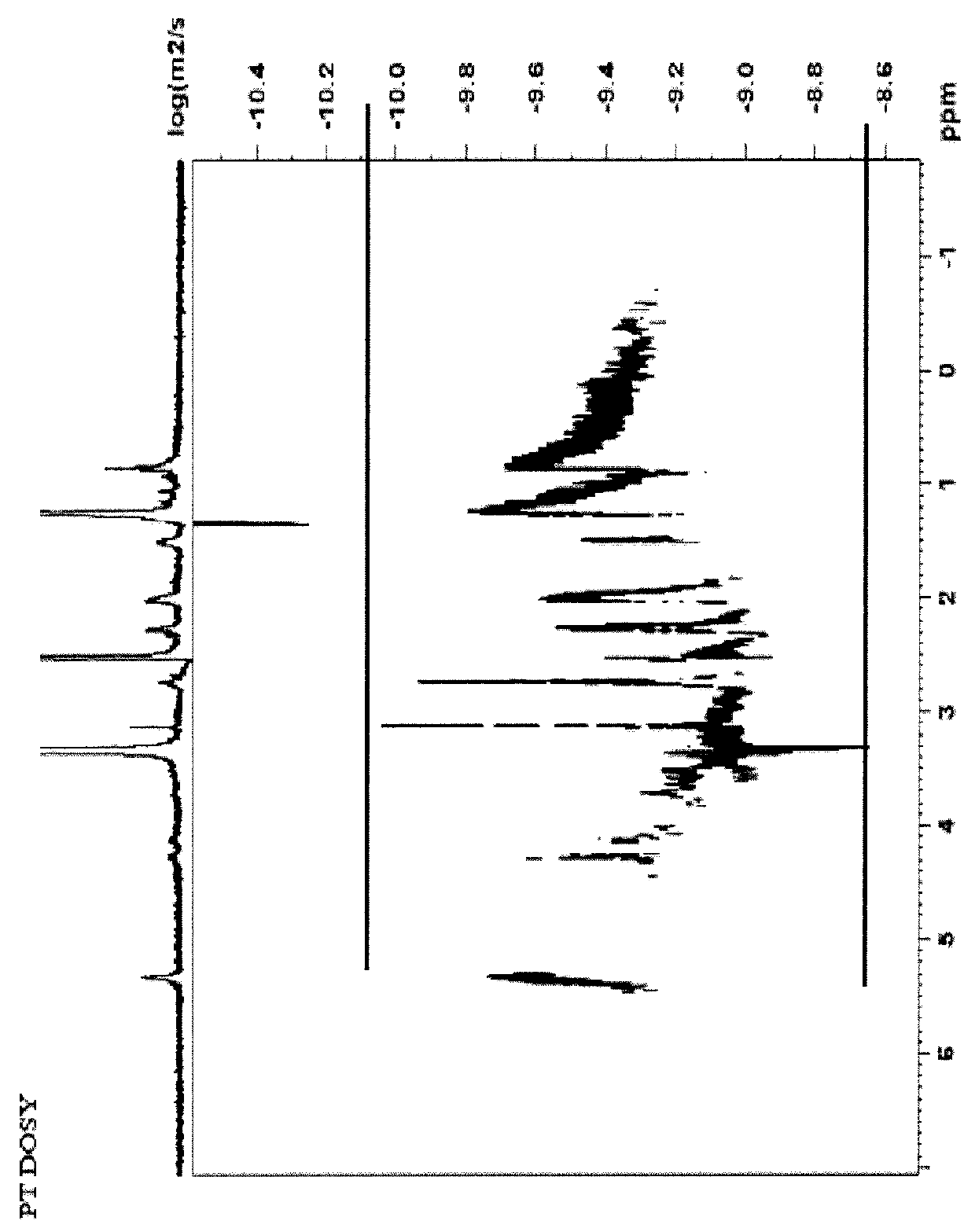
Compositions comprising complexes of proanthocyanidins with vegetable proteins
Disclosed is a complex of pea protein and proanthocyanidins for use in the treatment of disorders caused by alterations of the intestinal epithelial tissue.
Owner:NOVINTETHICAL PHARMA
Probiotic lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparation of low-salt fermented meat food
ActiveCN114231473AFast growthGrowth inhibitedBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyNutritive values
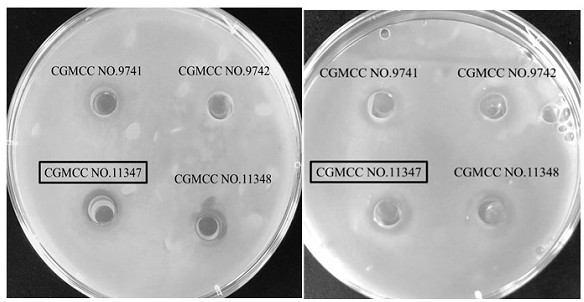
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to probiotic lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparation of low-salt fermented meat food. The invention provides a strain of lactobacillus plantarum CMRC 19L, which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11347. The lactobacillus plantarum CMRC 19L is high in growth speed, capable of inhibiting growth of pathogenic bacteria, excellent in meat fermentation performance, resistant to the gastrointestinal tract environment, high in adhesiveness to intestinal mucus protein and intestinal epithelioid cells and good in probiotic performance. As a leavening agent, the strain can ensure the edible safety and flavor quality of the low-salt fermented meat food, and significantly improve the nutritional value of the fermented meat food.
Owner:FOODSTUFF INST BEIJING
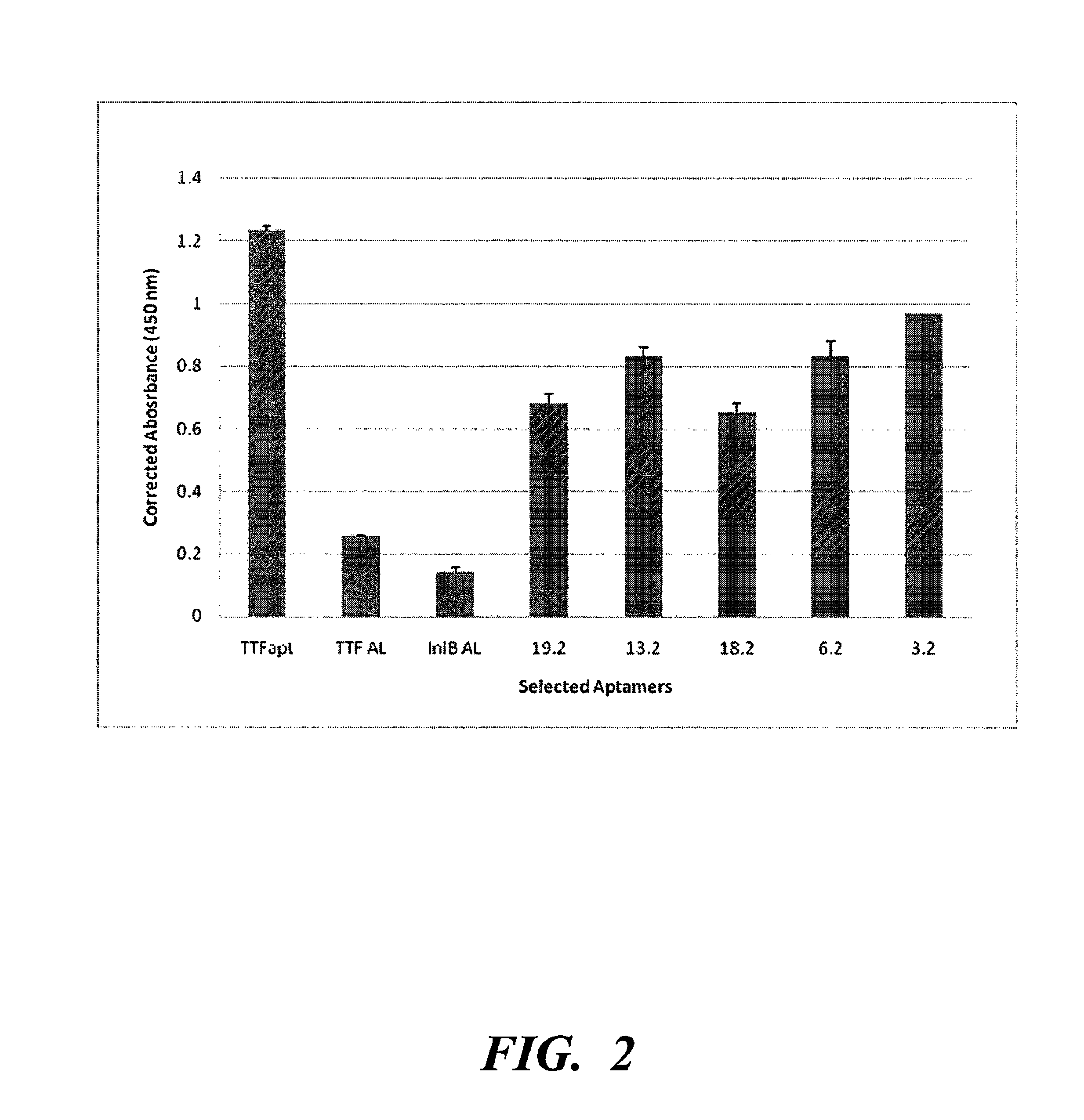
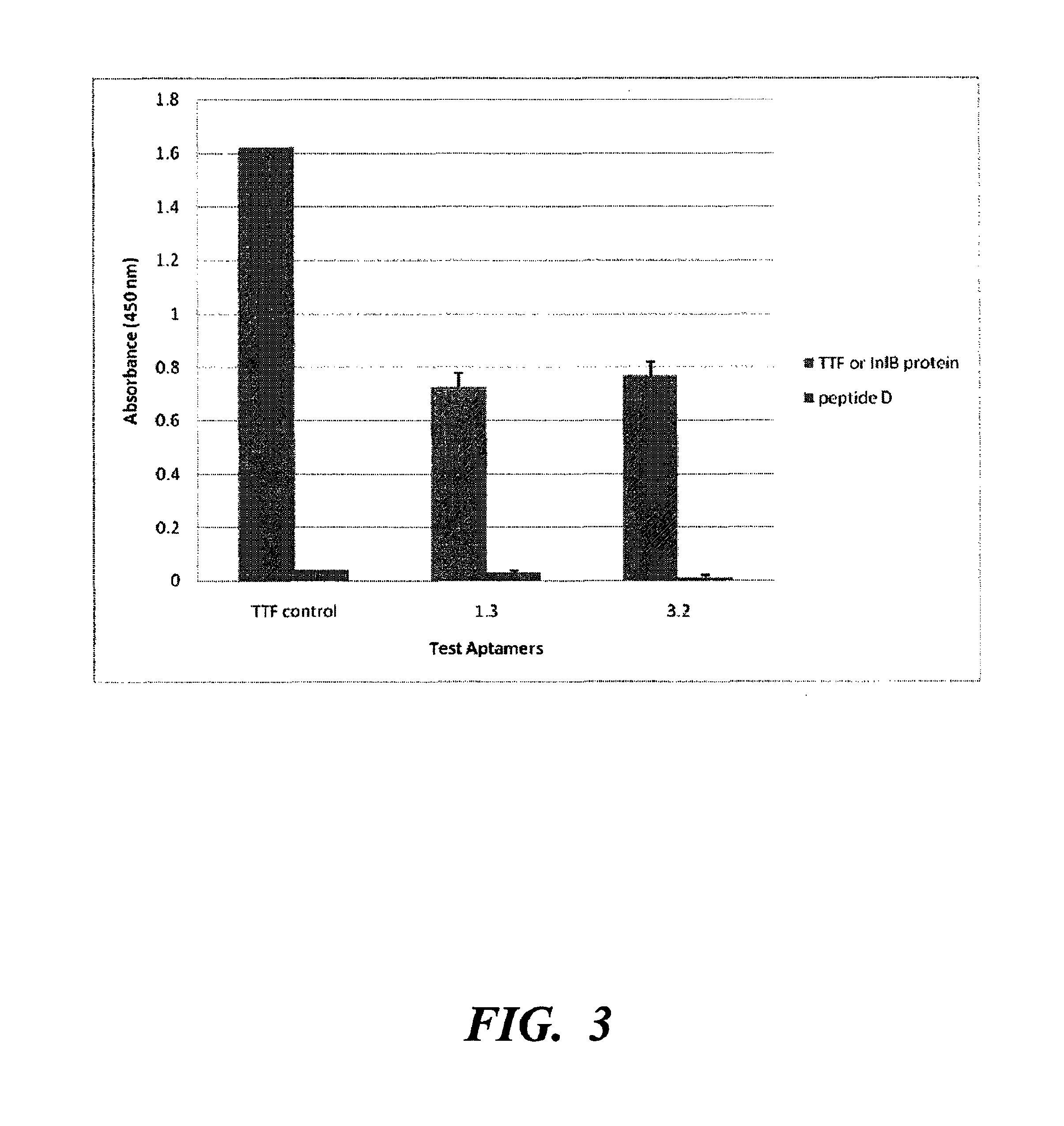
Nucleic acid ligands capable of binding to internalin B or internalin A
The present disclosure relates to the isolation of a novel reagent selected for its binding characteristics to the proteins internalin B or internalin A. InIB is a surface-localized protein of Listeria monocytogenes that binds and activates the receptor tyrosine kinase Met. InIB promotes invasion of a number of cells including hepatocytes, endothelial and epithelial cell lines and causes activation of the actin-mediated internalization of the bacterium. InIA belongs to a large group of surface-localized leucine-rich repeat (LRR) proteins identified in the Listeria genome. InIA enables Listeria monocytogenes to invade non-phagocytic cells such as those of the human intestinal epithelium and is sufficient for adhesion to and inducing uptake into epithelial cells. The disclosed nucleic acid ligands to internalin B and internalin A may be useful for determining the presence or absence of internalin B, internalin A, or Listeria in food, clinical or environmental samples; they may also be useful as an agent for combating Listeria infection by binding to and inactivating the infection-promoting inlB or inlA proteins. One object is to incorporate these nucleic acid ligands into an in vitro diagnostic or biosensor platform designed to detect the presence or absence of internalin B, internalin A, or Listeria in food, clinical or environmental samples. Another object is to employ these nucleic acid ligands in methods for treating or preventing Listeria infection.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION +1
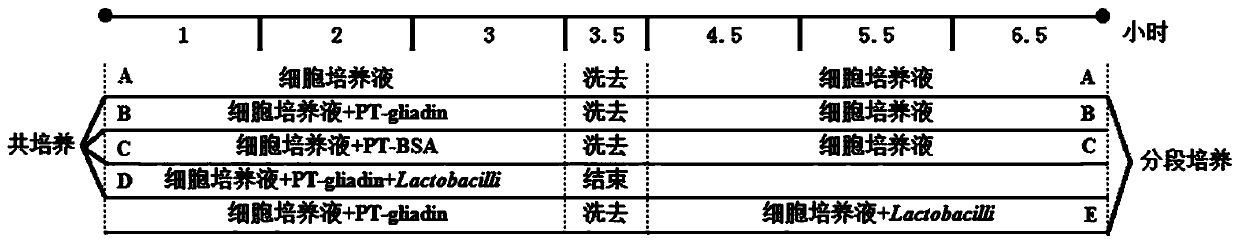
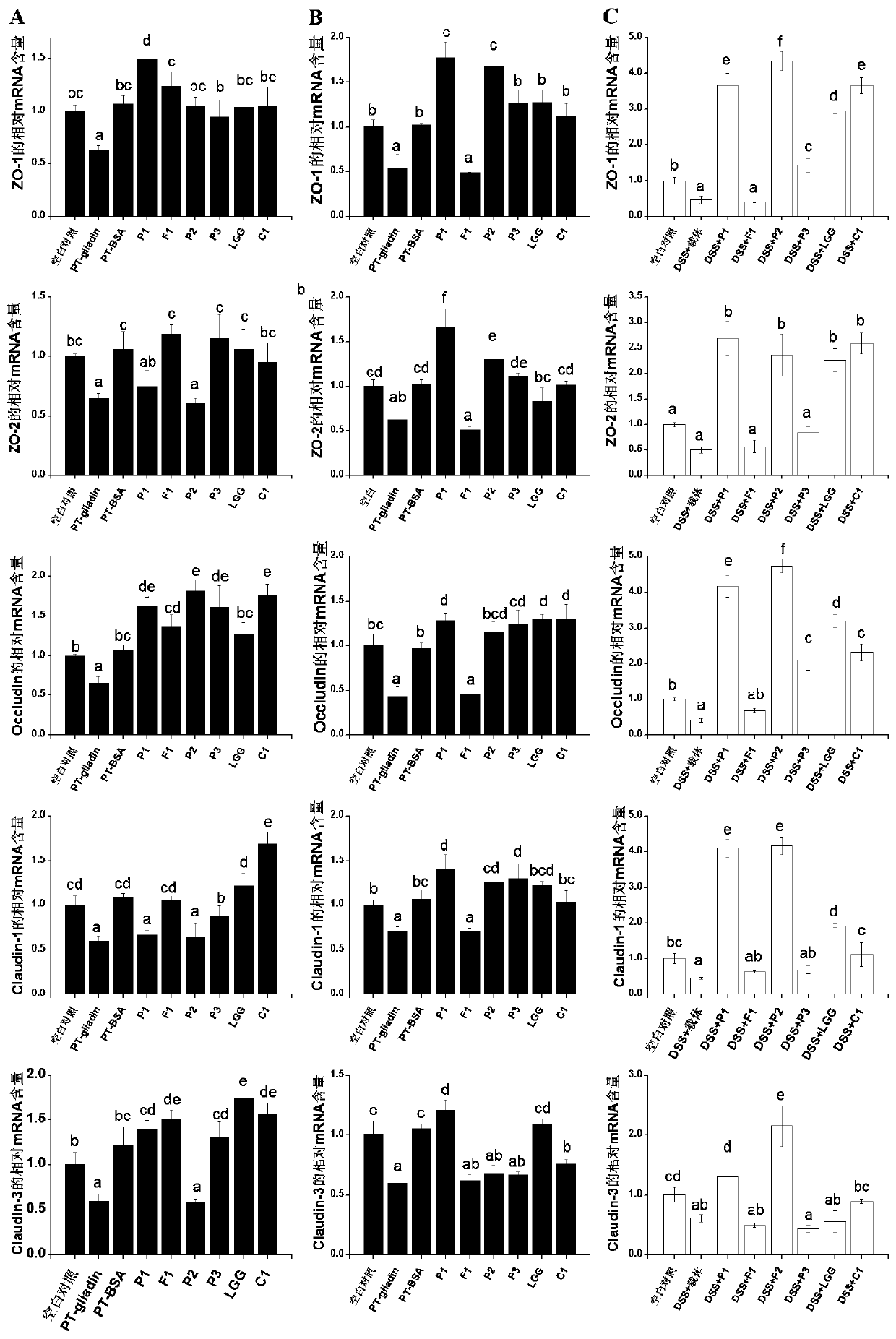
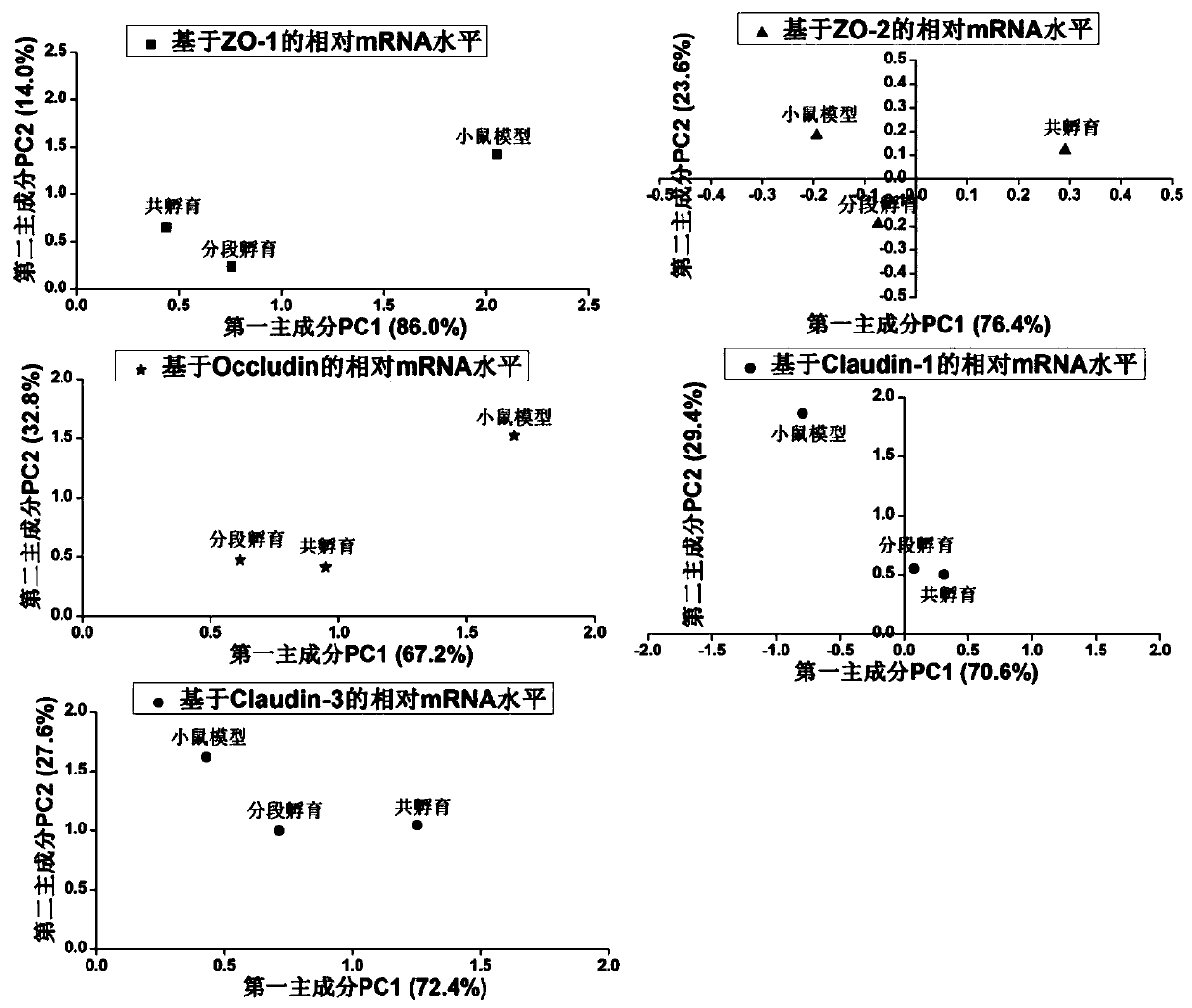
A method for screening probiotics with the function of enhancing intestinal cell tight junction at the cellular level
ActiveCN106520603BReflect the real roleMeet the repair abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismProbiotic bacteria
The invention discloses a method for screening probiotics with the function of enhancing intestinal cell tight junction at the cell level. The method includes: firstly utilizing digested protein to treat cells, washing off residual digested gliadin, then adding a certain amount of probiotics to conduct co-incubation for a certain period of time, and then washing off the probiotics so as to determine the probiotics' ability of improving cell tight junction destroyed by digested gliadin. An in vitro experimental model involved in the invention can reflect the actual repair effect of probiotics on gliadin caused intestinal epithelial injury, and the obtained result is in line with probiotics' ability of repairing intestinal barrier damage already formed in the intestinal tract, thereby providing a more convenient and accurate detection method for determining whether probiotics and other microorganisms can enhance intestinal cell tight junction at the cell level.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of galanthamine in prevention and treatment for fish enteritis caused by soybean meal feed
ActiveCN110447787AAvoid residueAvoid environmental securityAntipyreticFood processingDiseaseInformation analysis
The invention discloses application of galanthamine in prevention and treatment for soybean meal-induced enteritis of fishes. According to a neuroregulation theory of intestinal mucosal immunity, in combination with two methods of disease modeling and biological information analysis, it is inferred that the galanthamine is a potential medicine for preventing and treating the soybean meal-induced enteritis; it is proved by an experiment that the galanthamine can activate expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines in intestinal tracts of bred fishes through addition into feed or intramuscular injection in backs, inhibit intestinal inflammations, maintain tight junctions of intestinal epithelium barriers, and inhibit intestinal epithelium apoptosis, therefore the enteritis caused by a soybeanmeal feed is relieved, recovery of growth of the fishes can be achieved, and therefore the galanthamine can be taken as a novel feed additive with an anti-inflammatory effect or an injection with an anti-inflammatory effect for injection operation.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Separation and purification method of mouse intestinal epithelium mucosa lamina propria dendritic cells
InactiveCN102382802AEfficient removalThe experiment process is simpleBlood/immune system cellsPurification methodsDendritic cell
The invention relates to a separation and purification method of mouse intestinal epithelium mucosa lamina propria dendritic cells, which comprises the following specific steps: (1) the acquisition of mixed cells; (2) the acquisition of individual karyocytes: preparing cells acquired after the digestion of collagenase into a suspension, slowly adding into a mouse lymphocyte separation liquid according to a volume ratio of 1:1, and centrifuging at 1800 rpm for 25 minutes; sucking the middle buffy coats, adding into 1-2 milliliters of MACS buffer, and centrifuging at 1200 rpm for 5 minutes; and removing the supernate, and suspending the cells again, wherein the MACS buffer is a PBS (phosphate buffer solution) containing 2mM mol / milliliter EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) and 0.5% FCS (fetal calf serum); and (3) the acquisition of intestinal epithelium mucosa lamina propria dendritic cells. By using the separation and purification method, a large number of high-purity and high-activity intestinal epithelium mucosa lamina propria dendritic cells can be conveniently, economically and efficiently acquired in short time; and the acquired cells keep a good antigen presentation capability under in vitro conditions, thereby providing favorable conditions for the in vitro simulation of in vivo antigen presenting cell induced lymphocyte differentiation.
Owner:梁廷波
Application of bacteroides fragilis to preparation of enhancing agent for enhancing intestinal mucosal barrier function
InactiveCN109481475AEasy to eatReduce permeabilityMilk preparationDigestive systemIntestinal mucosal permeabilityMedicine
The invention relates to application of bacteroides fragilis to preparation of an enhancing agent for enhancing an intestinal mucosal barrier function. According to a great quantity of experiments, the bacteroides fragilis has functions of repairing intestinal epithelium mucus barrier and reducing intestinal mucosal permeability and is capable of effectively enhancing the intestinal mucosal barrier function to protect human health.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ZHIYI PHARMA INC
Arabinoxylans for modulating the barrier function of the intestinal surface
ActiveUS8465788B2Antibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsIntestinal microorganismsIntestinal surface
Owner:BIOACTOR
Method to Increase the Growth Velocity of Human Infants
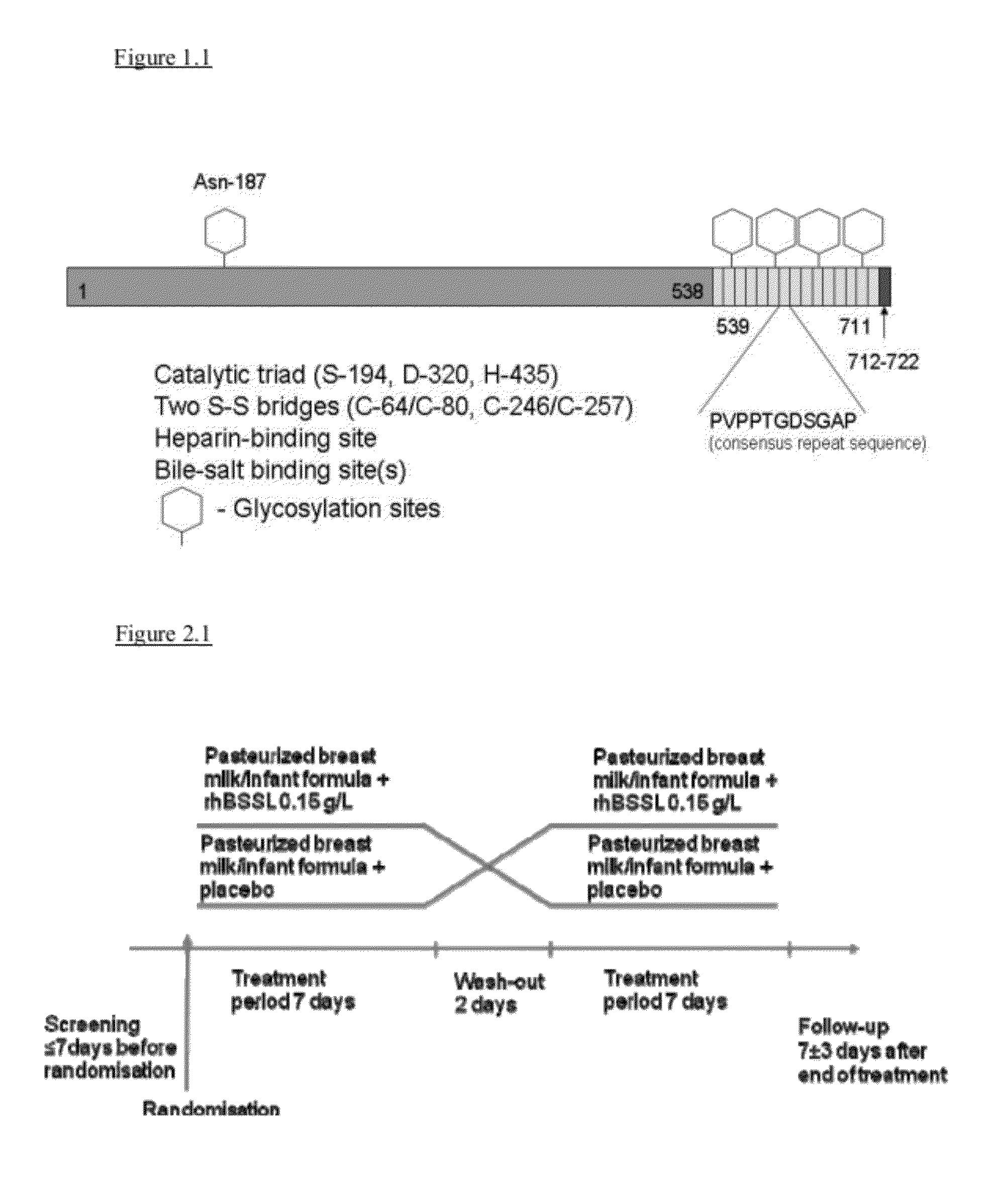
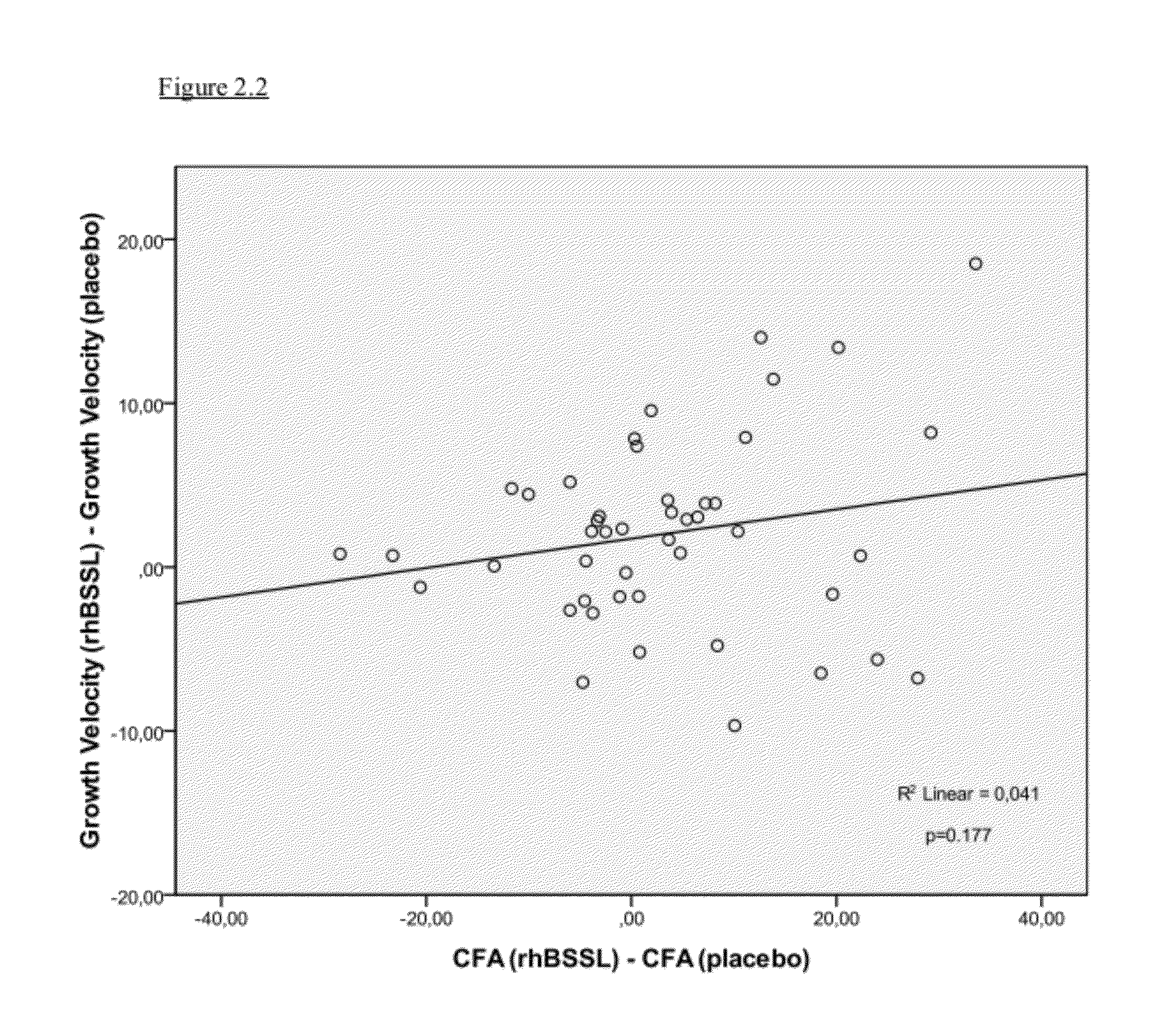
The present invention relates to a method to increase the growth velocity of a human infant, said method comprising the enteral administration to said infant of recombinant human bile-salt-stimulated lipase (rhBSSL). Such method has particular utility for underweight or preterm human infants, particular those in medical need of increasing their growth velocity. The invention also relates to compositions, including infant feeds, kits, packaged-pharmaceutical-products and pharmaceutical compositions, and also to methods to prepare infant feeds. In another aspect, the present invention relates to methods to: (X) protect the small bowel mucosa of a human infant from damage; to (Y) protect an immature intestinal epithelium of a human infant from the deleterious effects of incompletely digested and / or excess fat and / or lipid; and / or to (Z) limit accumulation of incompletely digested and / or excess fat and / or lipid in the ileum of a human infant; said methods in each case comprising the step of enteral administration of rhBSSL.
Owner:SWEDISH ORPHAN BIOVITRUM AB
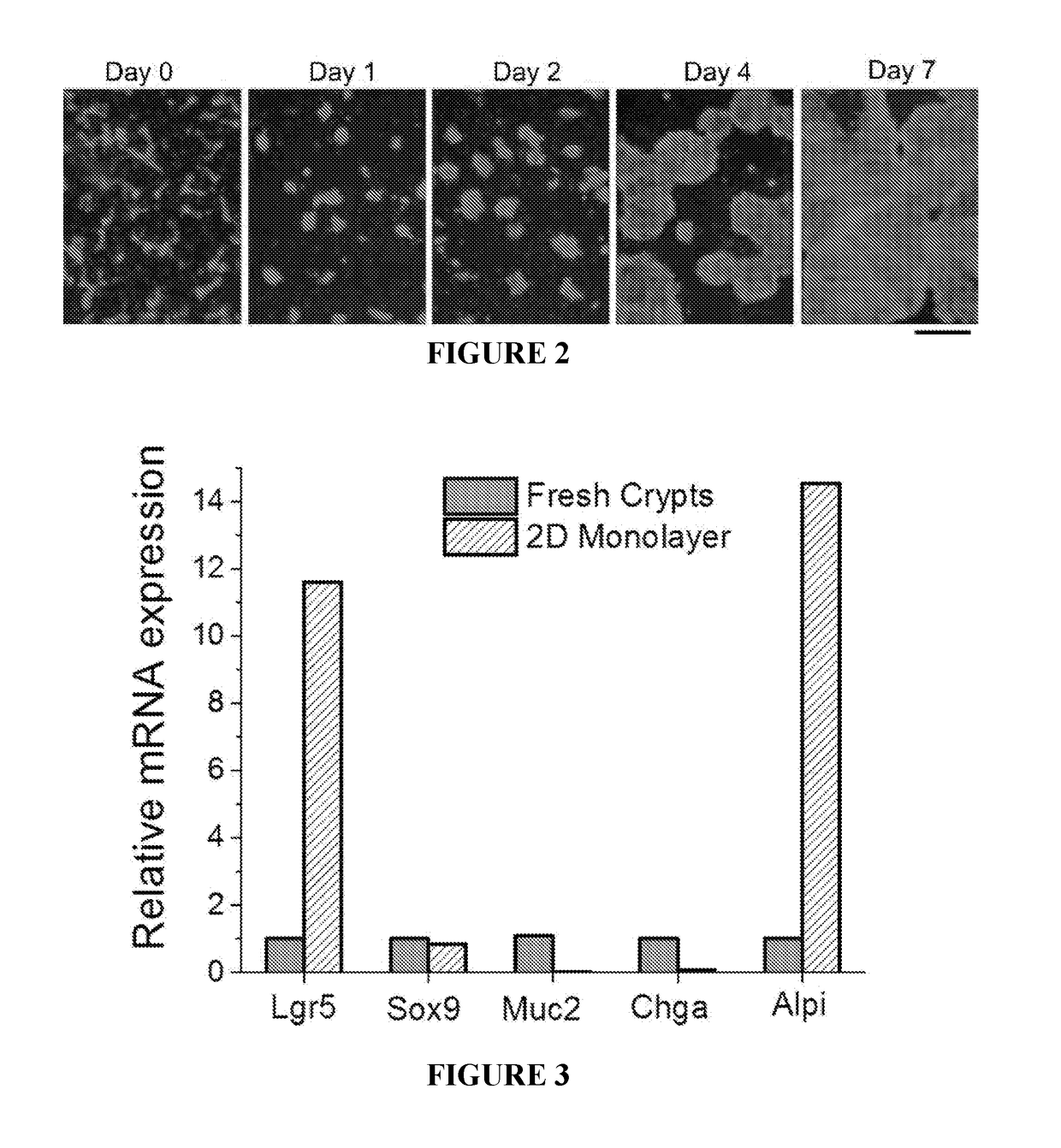
Intestinal epithelium monolayer culture and characterization method based on mouse intestinal stem cells
InactiveCN109679893ASignificant progressEasy to handleGastrointestinal cellsArtificial cell constructsSmall intestineMicrobiology
The invention discloses an intestinal epithelium monolayer culture and characterization method based on mouse intestinal stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) monolayer culture ofmouse intestinal epithelium; (2) characterization of monolayer culture of the intestinal epithelium. Compared with the prior art, the method is based on small intestinal crypts containing stem cells,optimizes the monolayer in-vitro culture system and culture medium of the intestinal epithelium, and includes a complete culture and characterization method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Application of patchoulicalcohol to preparing medicines for preventing and treating ulcerative colitis
ActiveCN106511323AImprove securityNo toxicityHydroxy compound active ingredientsDigestive systemUlcerative colitisExcipient
The invention relates to application of patchoulicalcohol to preparing medicines for preventing and treating ulcerative colitis. The medicines comprise the patchoulicalcohol and medically acceptable excipients. The application has the advantages that the vitality of myeloperoxidase (MPO) which reflects the degrees of colitis diseases can be reduced by the patchoulicalcohol in the medicines, expression of tight junction proteins (TJs) and mucoproteins can be promoted, effects of protecting intestinal epithelium mucous membrane barriers can be realized, and obvious effects of preventing and treating the ulcerative colitis can be realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Lactobacillus paracasei and application thereof
InactiveCN109456919AGuaranteed quantityEnhanced tight junction protein expressionMilk preparationBacteriaMicroecosystemCholesterol
The invention relates to microbes and particularly relates to lactobacillus paracasei. The lactobacillus paracasei is characterized in that lactobacillus paracasei is lactobacillus paracasei CG-C1, the collection number is CGMCCNo. 12941, the collection date is September 8th, 2016, the collection unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the collection site is Instituteof Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. The product is from the intestinal tract of a healthy centenarian. Proved by test, the lactobacillus paracasei CG-C1 is used for producingprobiotic fermented milk; the method is safe, low in risk, and easy in implementation, can ensure the quantity of strains and is lower in cost; compared with other methods, the method has obvious advantages. Therefore, the fermented milk product has the effects of regulating the intestinal flora, maintaining the balance of the intestinal microecological system, enhancing the expression of intestinal tight junction protein, improving the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium, reducing the level of cholesterol and relieving the problems of constipation and diarrhea.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHENGUANG DAIRY IND CO LTD
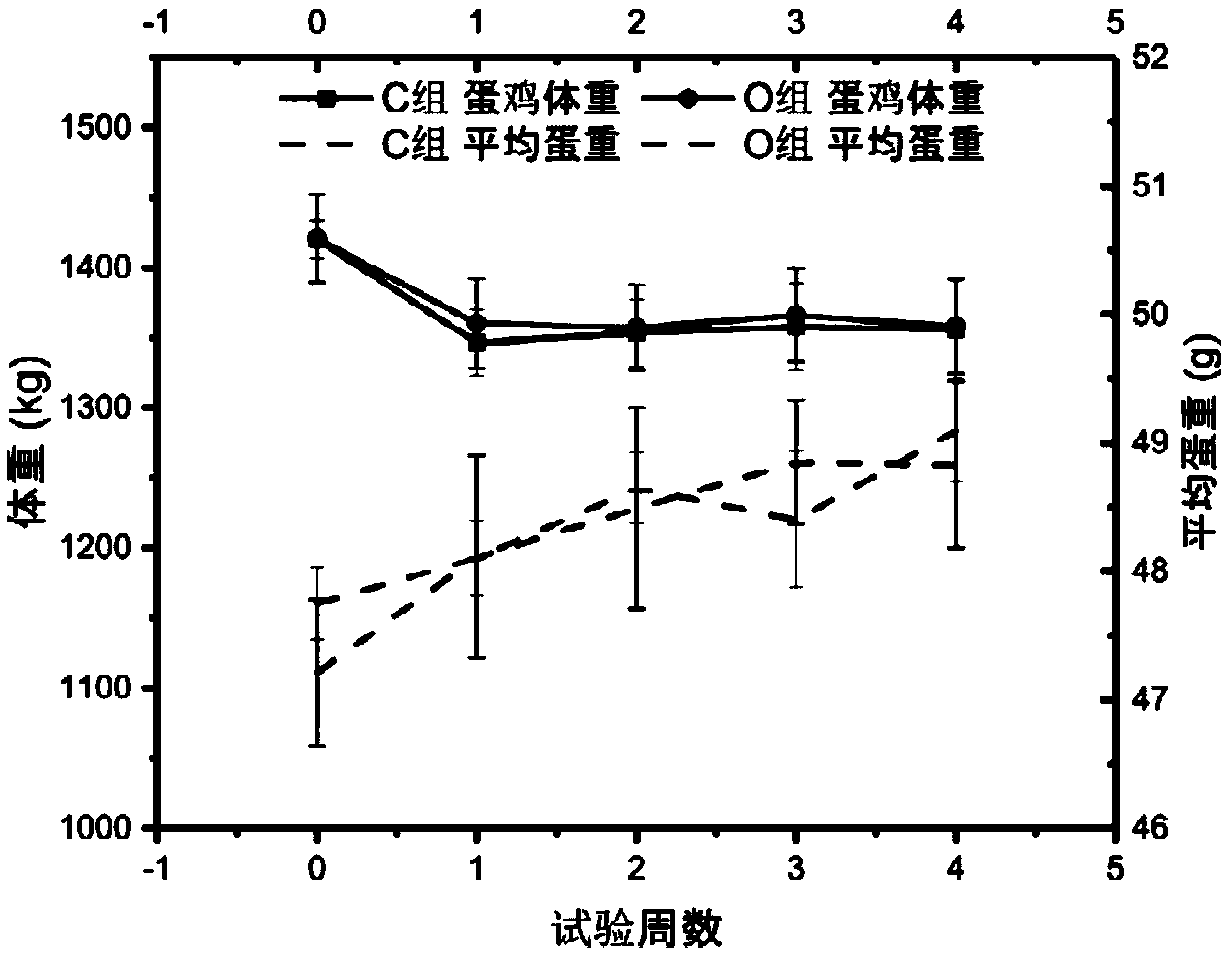
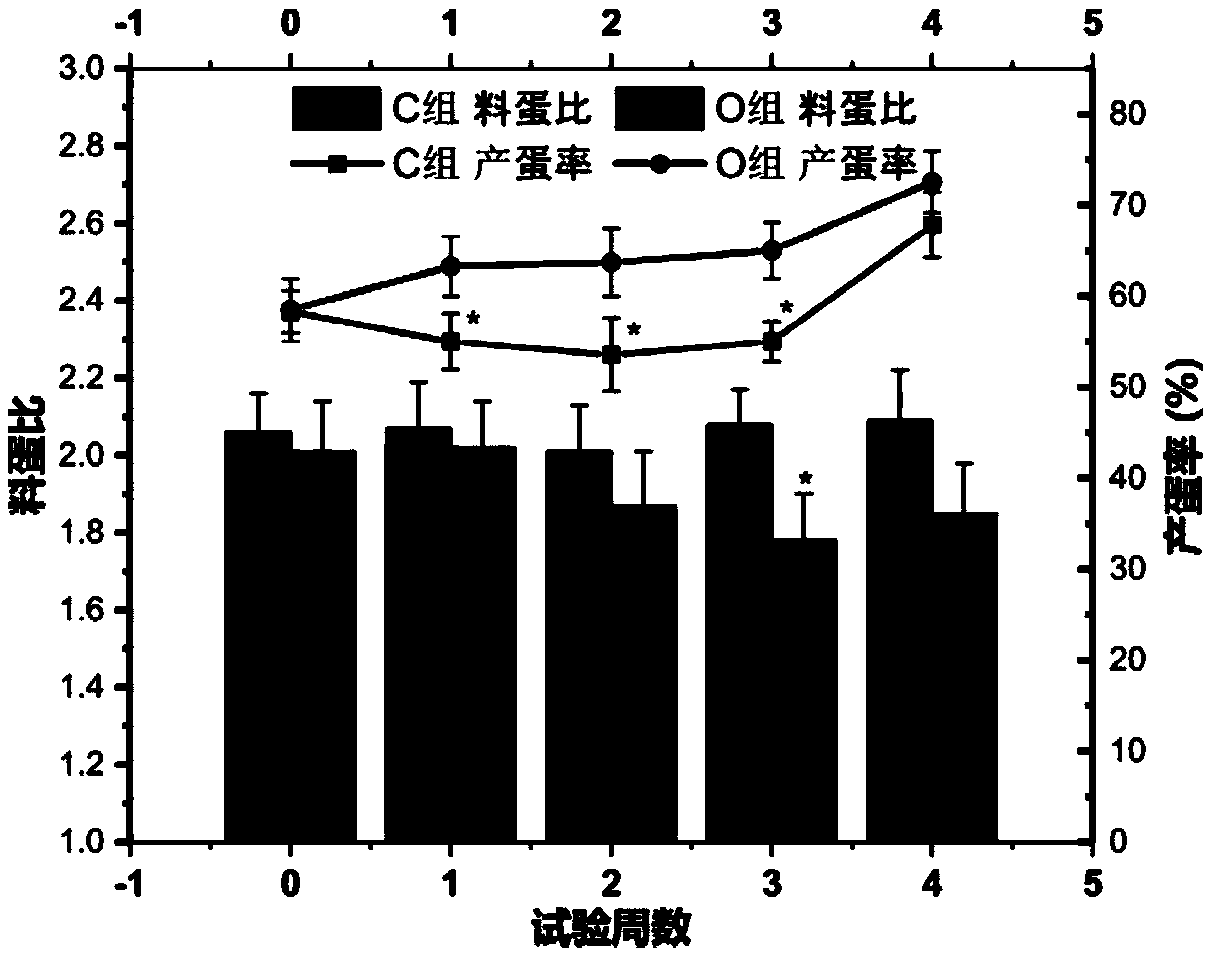
Heat-stress-resistant premix used for laying hen feed
InactiveCN109566899ABoost energy levelsIncrease the content of essential fatty acidsFood processingAnimal feeding stuffManganeseChromium
The invention discloses a heat-stress-resistant premix used for laying hen feed. The heat-stress-resistant premix is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 5-8% of amino acid,10-15% of a vitamin mixture, 16-20% of a trace element mixture, 20-25% of a carrier, 30-35% of emulsified oil powder, 0.30-0.60% of salt and 0.10-0.80% of a spicate clerodendranthus herb extract, wherein trace elements in the trace element mixture comprise manganese, copper, zinc, iron, copper, zinc, iodine, selenium and chromium. The spicate clerodendranthus herb extract is adopted as a poultryadditive, the good antioxidant capability and intestinal epithelium protection effect are achieved, the egg yield of laying hens during heat stress is increased, and the egg quality is improved; the physiological index of the laying hens during heat stress is improved, and the laying hens are promoted to keep healthy; and the working procedure during heat stress is simplified, economic benefits are increased, and using is easy, convenient, safe and effective.
Owner:上海申丰畜牧兽医科技有限公司 +1
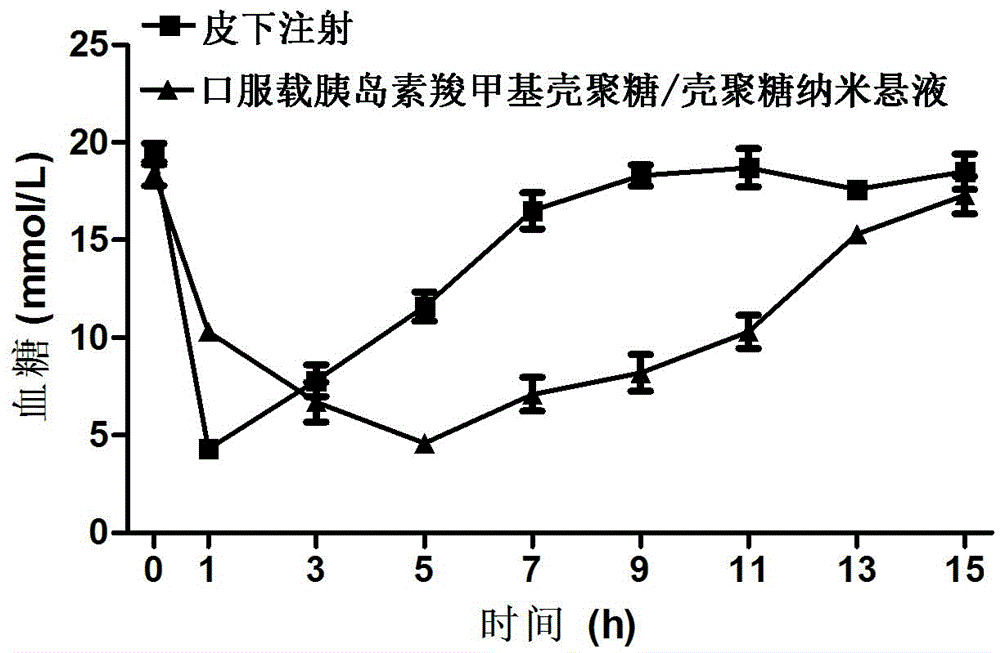
Preparation method of insulin-supporting carboxymethyl chitosan/chitosan nanometer preparation
InactiveCN106421807AImprove biological activityPromote absorptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsChitosan nanoparticlesFreeze-drying
The present invention relates to a preparation method of an oral insulin preparation insulin-supporting carboxymethyl chitosan / chitosan nanometer preparation. The preparation method comprises: 1) forming core nanoparticles from carboxymethyl chitosan and insulin; 2) adding chitosan to a core nanometer suspension, and forming the outer layer of the nanoparticles on the surface of the core nanoparticles through the chitosan and the part of the carboxymethyl chitosan; and 3) stirring the obtained mixture until completely performing the cross-linking, carrying out high speed centrifugal separation, and carrying out freeze-drying to obtain the insulin-supporting carboxymethyl chitosan / chitosan nanoparticles. According to the present invention, the preparation conditions are mild, such that the insulin can be effectively protected from the influence caused by the gastrointestinal tract acid environment and the protease; the chitosan and the carboxymethyl chitosan can further promote the intestinal epithelium to absorb the insulin; and the results of the in vivo tests using diabetes rats as model animals show that the insulin-supporting carboxymethyl chitosan / chitosan nanometer preparation can effectively reduce the blood glucose of the rats.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
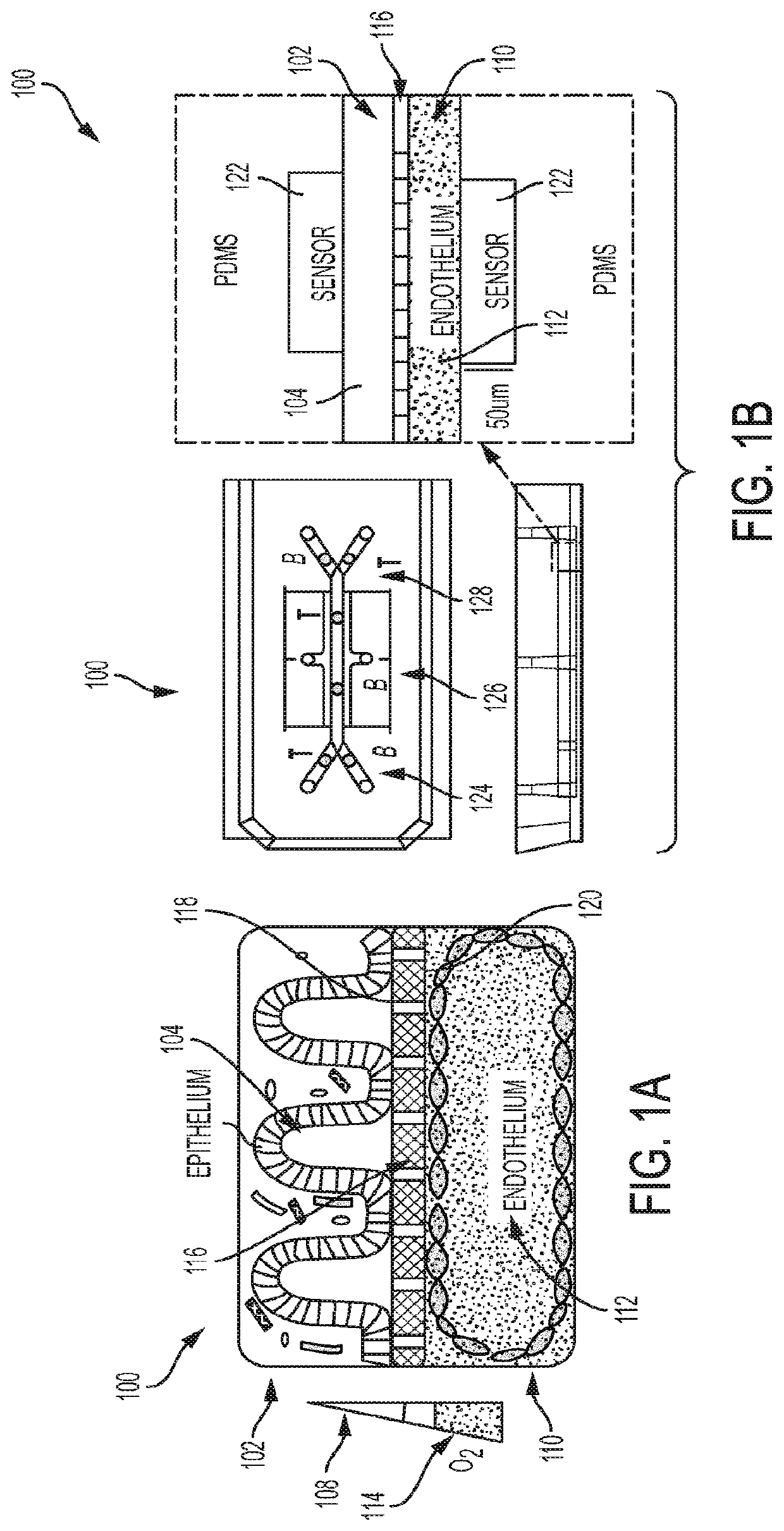
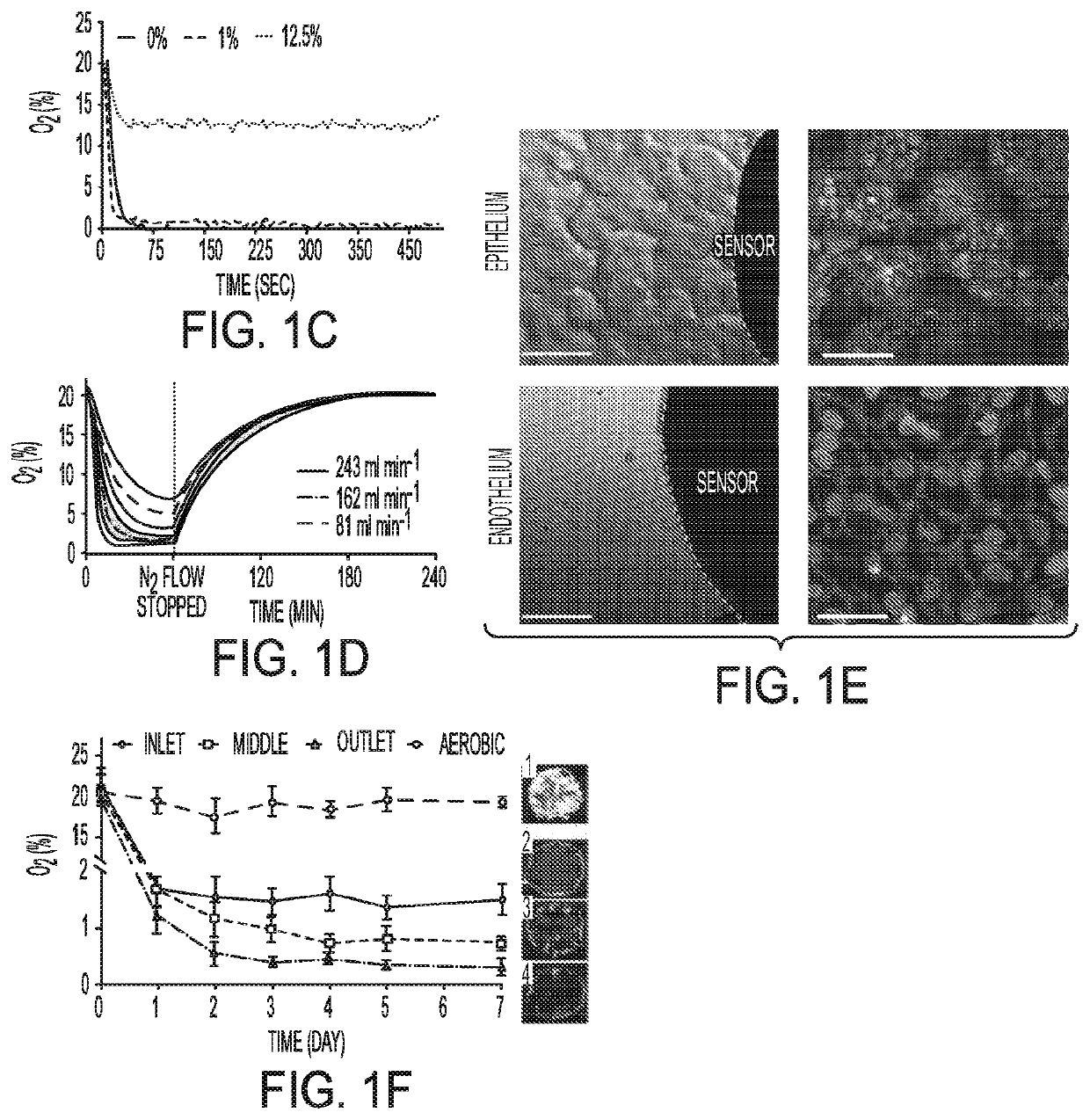
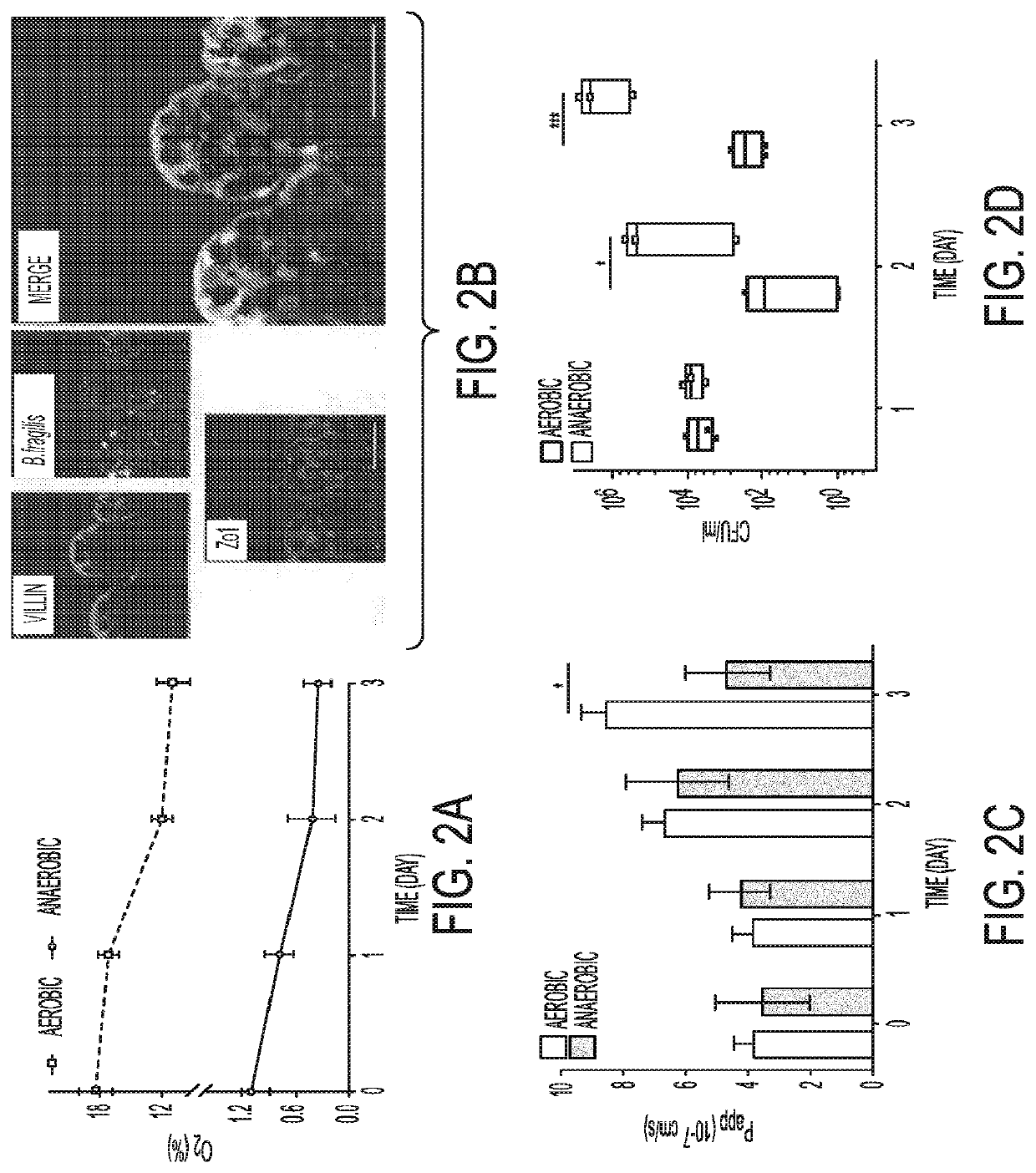
Complex Human Gut Microbiome Cultured In An Anaerobic Human Gut-On-A-Chip
A microfluidic device is directed to sustaining a complex microbial community in direct and indirect contact with living human intestinal cells in vitro. The device includes a first microchannel having cultured cells of a human intestinal epithelium and microbiota, the first microchannel further having a first level of oxygen. The device further includes a second microchannel having cultured cells of a vascular endothelium, the second microchannel further having a second level of oxygen. The device also includes a membrane located at an interface region between the first microchannel and the second microchannel, the membrane being composed of an oxygen-permeable material or further having pores via which oxygen flows between the first microchannel and the second microchannel to form a physiologically-relevant oxygen gradient.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
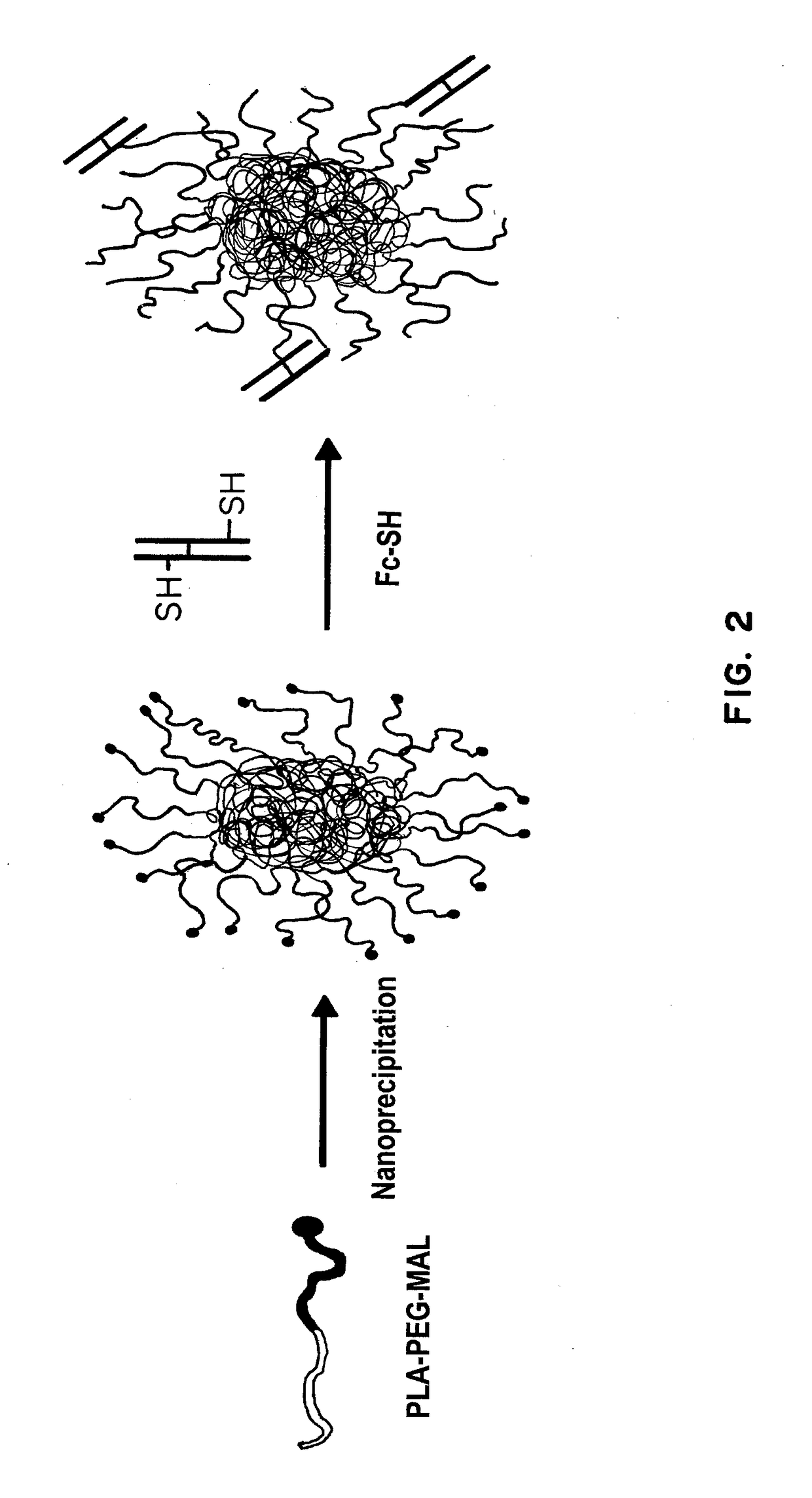
Receptor-targeted nanoparticles for enhanced transcytosis mediated drug delivery
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Method for separating, identifying and preliminary screening of probiotic yak-derived lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN108441434AEnhanced barrier functionRegulate immunityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementFecesOxygen
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a method for separating, identifying and preliminary screening of probiotic yak-derived lactic acid bacteria. The separation steps comprise: taking about 1 g of the middle portion of a manure sample, adding into a sterilized and refrigerated peptone buffer solution, sucking 1 mL of the manure supernatant under a sterile condition,inoculating into a MRS liquid culture medium, respectively carrying out aerobic culture and anaerobic culture for 24 h at a temperature of 37 DEG C, taking 200 [mu]l of the bacterial suspension, coating a MRS plate with the bacterial suspension, respectively carrying out aerobic culture and anaerobic culture for 24 h, selecting single suspected colony, inoculating into a corresponding plate culture medium, carrying out streak culture, respectively carrying out aerobic culture and anaerobic culture for 24 h at a temperature of 37 DEG C, re-selecting single colony, inoculating into a corresponding plate culture medium, respectively carrying out aerobic culture and anaerobic culture at a temperature of 37 DEG C, purifying twice, selecting single colony, inoculating into a corresponding slopeculture medium, respectively carrying out aerobic culture and anaerobic culture for 24 h at a temperature of 37 DEG C, and storing in a 4 DEG C a refrigerator so as to be spare. According to the present invention, the probiotic yak-derived lactic acid bacteria can protect the intestinal mucosa so as to reduce intestinal epithelium inflammation and diarrhea.
Owner:TIBET AGRI & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY COLLEGE
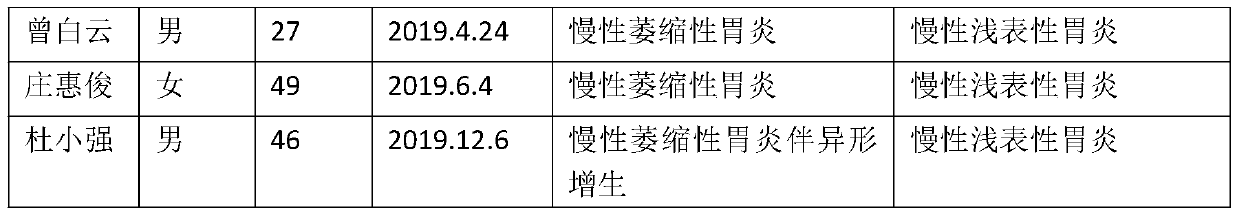
Pharmaceutical composition for treating chronic atrophic gastritis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111494583ANo damageMedication safetyAnthropod material medical ingredientsDigestive systemLiver and kidneyLicorice roots
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating chronic atrophic gastritis, and belongs to the technical field of Chinese herbal medicines. The pharmaceutical composition disclosed bythe invention is prepared from the following raw materials, by weight: 18-24 parts of root of hairy asiabell, 12-16 parts of poria cocos, 12-16 parts of bighead atractylodes rhizome, 13-18 parts of figs, 10-16 parts of dried tangerine or orange peel, 9-13 parts of vinegar-processed nutgrass galingale rhizome, 9-13 parts of vinegar-processed zedoray rhizome, 8-12 parts of perilla stems, 11-17 parts of officinal magnolia bark processed with ginger, 12-16 parts of salvia the root of red-rooted salvia, 13-16 parts of ground beeltle, 13-17 parts of fried inner membrane of chicken gizzard, 9-12 parts of fried hawthorn fruit and 3-6 parts of honey-fried licorice root. The pharmaceutical composition is safe to use, does not cause damage to gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidney functions of a patient, can reverse atrophy of gastric mucosa glands and metaplasia of intestinal epithelium, and has a good curative effect on treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis.
Owner:SHENZHEN HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
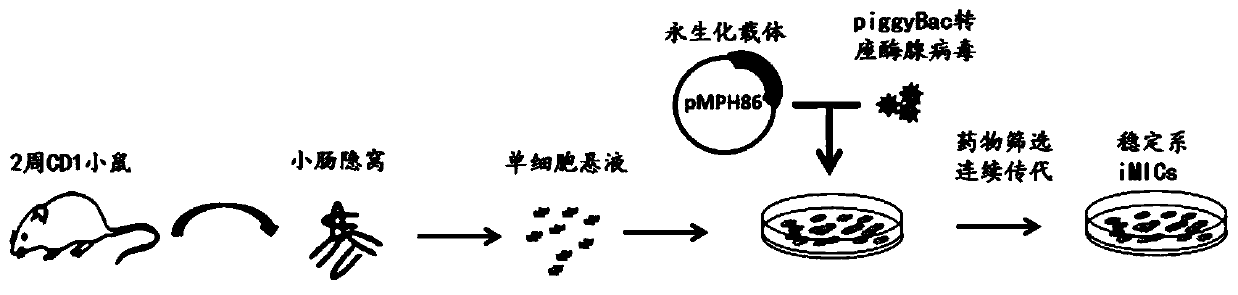
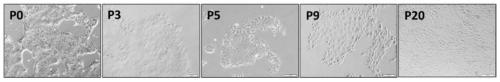
Mouse intestinal epithelium pit cell line and constructing and culturing method thereof
ActiveCN109750065AKeep shapeImprove proliferative abilityFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyTreatment targets
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecules and cellular biology, and particularly relates to a constructing method of a mouse intestinal epithelium pit cell line. The method comprises the steps that a single cell suspension of pit epithelium cells is prepared through a special separation method, cellular immortality is conducted after cell adherence. The form of intestinal epithelium primary cells is well maintained by the cell line, and high proliferation capability is achieved. Characteristic organ structures can be formed in three-dimensional culturing conditions, it is indicated by specific staining that cells which form the structure comprise multiple intestinal epithelium differentiated progeny. Pit cells of an established line can only grow in primary culturing conditions still, and the pit cells can be applied to the establishing of a mouse intestinal epithelium in vitro multi-dimensional study model which is used for studying intestinal physiologic functions andpathological mechanisms including infection, carcinogenesis and the like, and tools and platforms are provided for treatment targets and medicine screening and evaluating of intestinal diseases including intestinal cancer.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Ex vivo culture, proliferation and expansion of intestinal epithelium
ActiveUS9464275B2Gastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementIntestino-intestinalCell biology
Methods are provided for long term culture of mammalian intestinal cells. Cultures are initiated with fragments of mammalian intestinal tissue, which are then maintained embedded in a gel substrate that provides an air-liquid interface. Intestinal epithelium in cultures of the invention can be continuously grown for extended periods of time. Mammalian intestinal cells cultured by the methods of the invention recapitulate features of intestinal growth in vivo.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Feeding method capable of improving growth performance of broiler chicken 1-21 days old
InactiveCN107494987AImprove immunityPromote growthFood processingAnimal feeding stuffIntestinal wallsNutrient solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of chicken cultivation and in particular relates to a feeding method capable of improving growth performance of broiler chicken 1-21 days old. The feeding method comprises the following concrete steps: (1) feeding young chicken with feed everyday, namely feeding the young chicken with feed for five times everyday; and (2) feeding the young chicken with nutrient solution everyday, namely feeding the young chicken with the nutrient solution twice everyday. The feeding method provided by the invention has the advantages that content of proteins, DNA and RNA of intestinal mucosae is increased, intestinal villi are heightened, intestinal walls are thickened, small intestinal mucosa enzyme activity is improved, intestinal development is further promoted, growth of the intestinal villi is promoted, villi are heightened, and recesses are shallowed, so that quantity of mature cells of intestinal epitheliums is increased, and maturation rate is increased, capability of digesting and absorbing nutrient substances is enhanced, feed utilization rate is improved, and the broiler chicken can be grown rapidly; meanwhile, metabolism of microorganisms is accelerated, structure of a flora is adjusted, intestinal microecological balance is effectively maintained, intestinal conditioned pathogens are inhibited, nutrition is provided, body immunity is enhanced, and robust growth of the young chicken is promoted.
Owner:JIESHOU DONGYONG ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com