A CNC Machining Method for Controlling Machining Deformation of Large Aluminum Alloy Wall Panel Parts
A technology of part processing and processing method, which is applied in the field of numerical control processing to control the processing and deformation of large aluminum alloy wall plate parts, and can solve the problems of no distinction between the initial deformation of the blank, the difficulty of processing large warpage deformation, and the low efficiency of roll forming. , to achieve the effect of reducing machining allowance, reducing machining difficulty and improving rolling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This embodiment provides a numerical control machining method for controlling machining deformation of large aluminum alloy wall panel parts, which specifically includes the following steps:
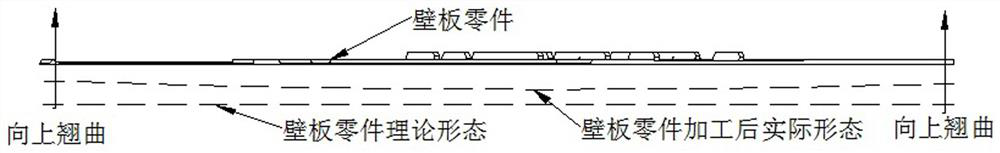
[0034] (1) Before processing, measure the deformation of the part blank to determine the concave and convex surfaces of the part blank;
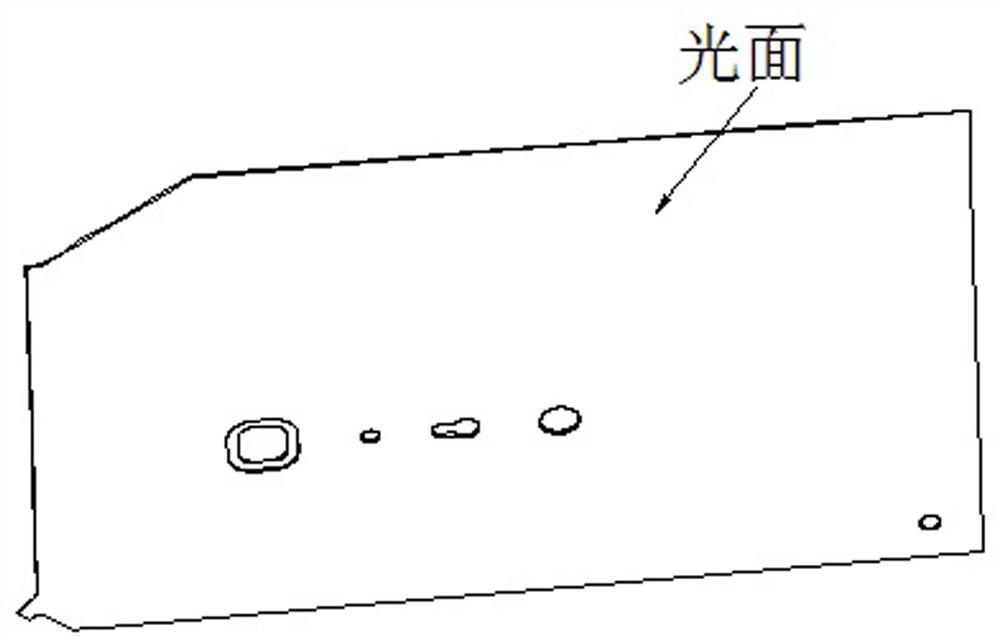
[0035] (2) Repair the concave surface of the part blank, so that the concave surface of the part blank has a slight rebound, and use the concave surface of the part blank as the smooth surface of the large aluminum alloy wall panel part;
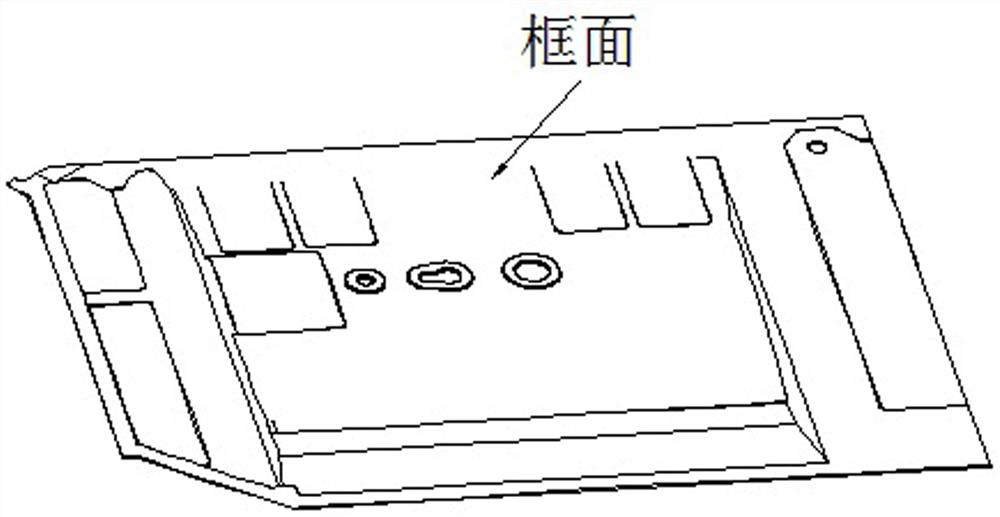
[0036] (3) Use the convex surface of the part blank as the frame surface of the large aluminum alloy siding part, and then process it to form the frame of the convex surface of the part blank, thereby obtaining a large aluminum alloy siding part with greatly improved deformation.
[0037] The specific implementation process, such as Figure 4 As shown, the concave surface (A surface) is selected as the smooth...
Embodiment 2
[0039] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment further defines that in the step (2), before trimming the concave surface of the part blank, it is necessary to allocate the machining allowance of the smooth surface and the frame surface of the part blank, Such as Figure 5 As shown, under the premise of satisfying the processing, increase the machining allowance of the smooth surface of the part blank, and reduce the machining allowance of the frame surface of the part blank.
[0040] When distributing the machining allowance on both sides, under the premise of satisfying the processing, increase the smooth surface machining allowance D1, reduce the frame surface machining allowance D2, make the smooth surface machining allowance D1 larger than the frame surface D2, and reduce the material removal amount on both sides The gap between them, thereby reducing the warping deformation of the parts to the frame surface after processing. Other parts of this e...
Embodiment 3
[0042] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment further defines that in the step (3), before machining the convex surface of the part blank into a frame surface, it is necessary to process a plurality of interlaced stress relief grooves on the convex surface of the part blank. Such as Figure 6 As shown, when roughing the frame surface of the part. At the beginning of rough machining, multiple interlaced stress relief grooves are processed on the frame surface to release the residual stress of the blank. Other parts of this embodiment are the same as those of the foregoing embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com