Machining process for high-speed steel surface-replaceable blade
A processing technology and high-speed steel technology, which is applied in the field of high-speed steel exchangeable blade processing technology, can solve the problems of high raw material cost and high machining cost, and can reduce the cutting edge strength, reduce the machining cost, and be less prone to chipping. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
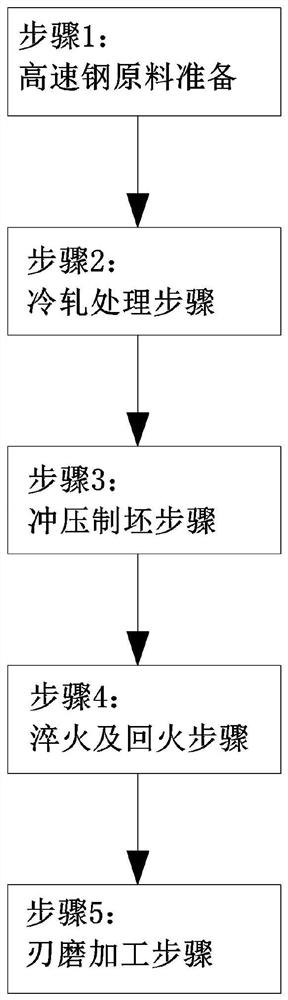
[0038] The process flow of a kind of high-speed steel replaceable face type insert in embodiment 1 is basically as attached figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1: Prepare high-speed steel plate raw material, the type of high-speed steel plate raw material is high-speed steel W6Mo5Cr4V2;
[0040] Step 2: cold-rolling the high-speed steel plate raw material in step 1 to form a high-speed steel plate;
[0041] Step 3: stamping the high-speed steel plate in step 2 to form a rough blade; the surface of the rough blade after punching the blank is in a square shape, and at the same time, vertically set a mounting hole 101 at the center of the rough blade;
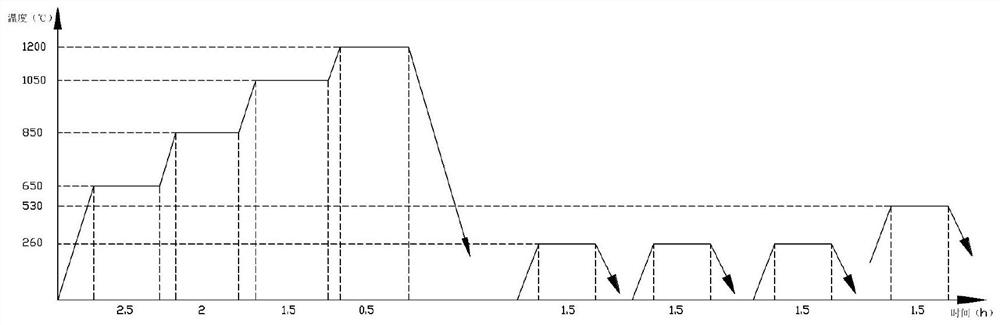
[0042] Step 4: Carry out vacuum quenching to the rough blade in step 3, and quench and heat the rough blade in stages; figure 2 As shown, in the first stage of quenching, the rough blade is heated to 640-660°C at a uniform speed, and the temperature is maintained for 2.4-2.5h; in the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com