Experimental device and method for simulating gully head drop hole development
A technology of experimental device and experimental method, applied in measurement device, fluid dynamics test, testing of machine/structural components, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in accurately simulating the development process of burrowing, lack of traceable erosion prediction model of gully head, and the number of gully heads. limited issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
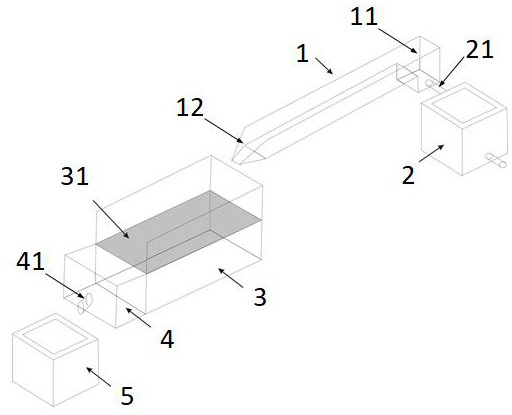
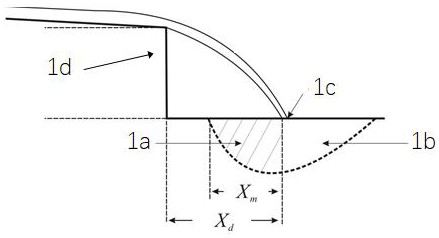
[0054] (1) Adjustment of water drop dynamic conditions: adjust the flow rate of tank 1 to 30 L / min, the slope to 2°, and the height of the water drop to 0.2 meters. Each group of experiments should be washed for 80 minutes, and every 8 minutes is a round of washing;
[0055] (2) Treatment of furrow bed soil: fill the dry red soil into the filling area 31 to form a furrow bed;
[0056] (3) Parameter monitoring:
[0057] Hydraulic parameters: monitor the flow velocity of the runoff in the water tank 1 every 3 minutes, and the 1.5m upward from the outlet 12 is the flow velocity monitoring section. The flow velocity is measured by the dyeing method, and the average value is obtained by repeating 3 times;
[0058] Runoff sediment data: use a 0.25 liter runoff bottle to collect the runoff sediment at 41 sand collection outlets every 1 min, repeat 3 times, and record the total amount of runoff in the grit chamber 5. After fully stirring the grit chamber 5 water sand, Use a runoff bo...
Embodiment 2
[0062] (1) Adjustment of water drop dynamic conditions: adjust the flow rate of tank 1 to 100 L / min, the slope to 15°, and the height of the water drop to 0.6 meters. Each set of experiments is washed for 90 minutes, and every 10 minutes is a round of washing;
[0063] (2) Treatment of furrow bed soil: fill the red soil to the filling area 31 to form a furrow bed;
[0064] (3) Parameter monitoring:
[0065] Hydraulic parameters: monitor the flow velocity of the runoff in the water tank 1 every 5 minutes, and the 2m above the outlet 12 is the flow velocity monitoring section. The flow velocity is measured by the dyeing method, and the average value is obtained by repeating 3 times;
[0066] Runoff sediment data: use a 0.5 liter runoff bottle to collect the runoff sediment at 41 places of the sand collection port every 3 minutes, repeat 3 times, and record the total amount of runoff in the grit chamber 5. After fully stirring the water sand in the grit chamber 5, Use a runoff b...
Embodiment 3
[0070] (1) Adjustment of water drop dynamic conditions: adjust the flow rate of tank 1 to 280 L / min, the slope to 35°, and the height of the drop to 1.0 meters. Each group of experiments is scouring for 100 minutes, and every 10 minutes is a round of scouring;
[0071] (2) Trench bed soil treatment: fill the brick red soil to the filling area 31 to form a ditch bed;
[0072] (3) Parameter monitoring:
[0073] Hydraulic parameters: monitor the flow velocity of the runoff in the water tank 1 every 8 minutes, and the flow velocity monitoring section is 2.5m up from the outlet 12. The flow velocity is measured by the dyeing method, and the average value is obtained by repeating 3 times;
[0074] Runoff sediment data: use 0.5 liter runoff bottle to collect the runoff sediment at 41 places of the sand collection port every 5 minutes, repeat 3 times, and record the total amount of runoff in the grit chamber 5, after fully stirring the water sand in the grit chamber 5, Use a runoff b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com