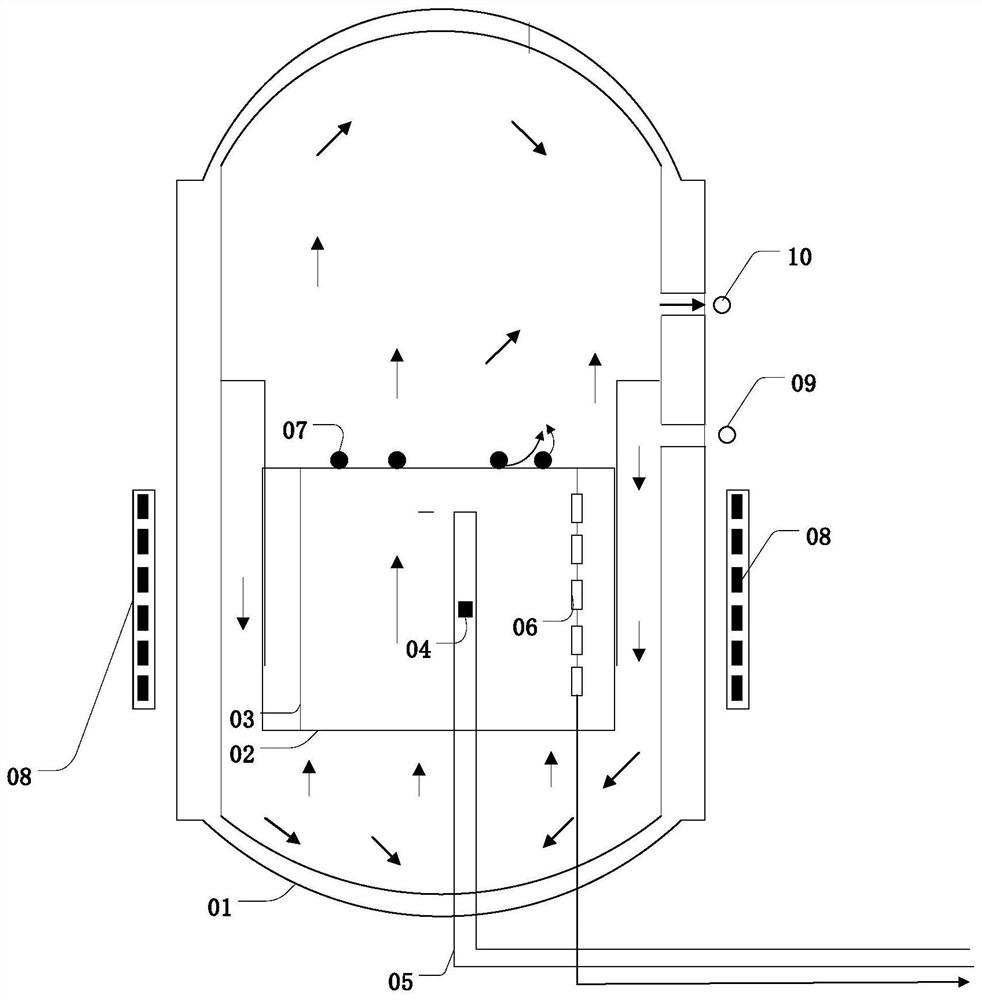
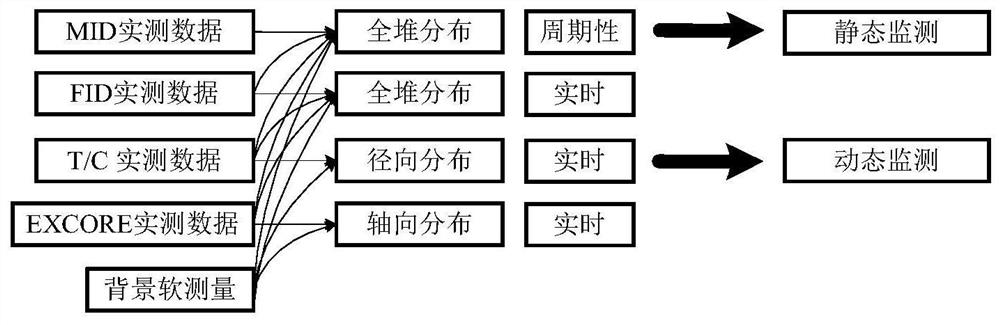
Reactor three-dimensional power probability distribution monitoring method based on information fusion theory
A technology of three-dimensional power and probability distribution, which is applied in nuclear reactor monitoring, reactor, probability network, etc., can solve the problems that cannot be measured, it is difficult to expand the random position of the whole reactor, and the uncertainty of fuel consumption distribution, etc., to achieve high reliability, informative effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
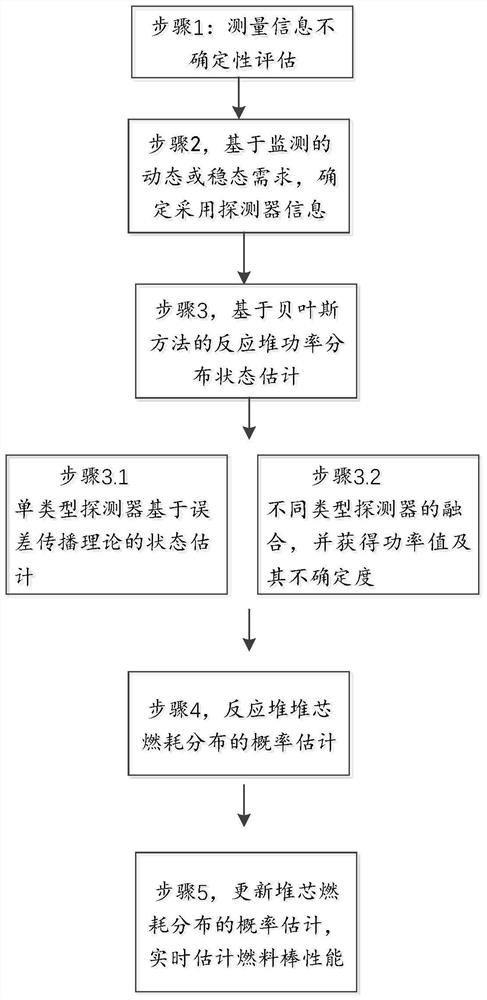
[0062] In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present application clearer, the present application will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present application, not to limit the present application.
[0063] Step 1: Measurement information uncertainty assessment.
[0064] The influence weight w of the detector on the power value i determines the power value. while w i The precision part of is related to the uncertainty assessment of the measurement information of all detectors. For this purpose, a quantitative evaluation of the uncertainty of each position detector of each type is required. The final uncertainty of the power value is also related to the uncertainty of the information of each detector, for which the uncertainty of each detector also needs to be evaluated.
[0065] A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com