Double-stator excitation full-degree-of-freedom bearingless motor and active control method thereof
A bearingless motor and active control technology, which is applied in the direction of winding excitation motor control, current controller, synchronous motor with stationary armature and rotating magnet, etc., can solve the problem of complex mechanical structure and anti-disturbance of bearingless motor system Poor ability and other problems, to achieve good machinability, improve poor anti-disturbance ability, and improve poor stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
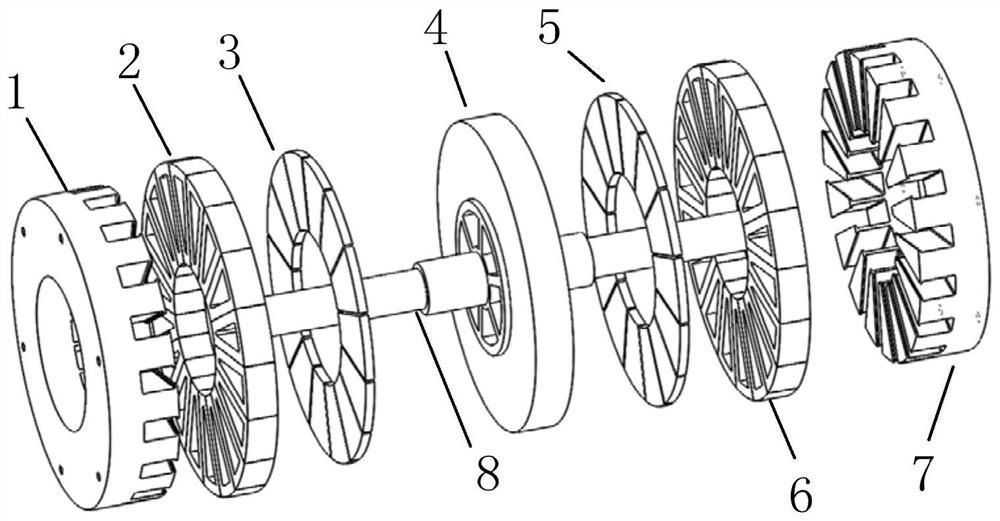
[0045] A double-stator excitation full-degree-of-freedom bearingless motor, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes: a rotating shaft 8, and two stators and a rotor disk arranged along the rotating shaft 8, and the rotor disk is located between the two stators;
[0046] The rotor disk includes a rotor core 4, and permanent magnet modules 3 and 5 that are surface-attached to the rotor core; Magnetic field; in this embodiment, the number of pole pairs of the rotor permanent magnetic field produced by the permanent magnet module is 7;
[0047] The stator includes stator cores 1, 7, and stator windings 2, 6 arranged on the stator cores 1, 7; in this embodiment, each stator core has 18 teeth, and the teeth of the two stator cores are aligned with each other. The stator winding is a suspension and torque integrated winding structure;
[0048] When working, the first armature magnetic field and the second armature magnetic field are generated after the stator windings 2 and 6 are fe...
Embodiment 2
[0059] A double-stator excitation full-degree-of-freedom bearingless motor. This embodiment is similar to the above-mentioned embodiment 1. The difference is that in this embodiment, the stator winding is a suspension winding and the torque winding is separated. Specifically, the stator winding includes mutual Independent suspension winding and torque winding, the first armature magnetic field is generated after the current is passed into the suspension winding, and the second armature magnetic field is generated after the current is passed into the torque winding;
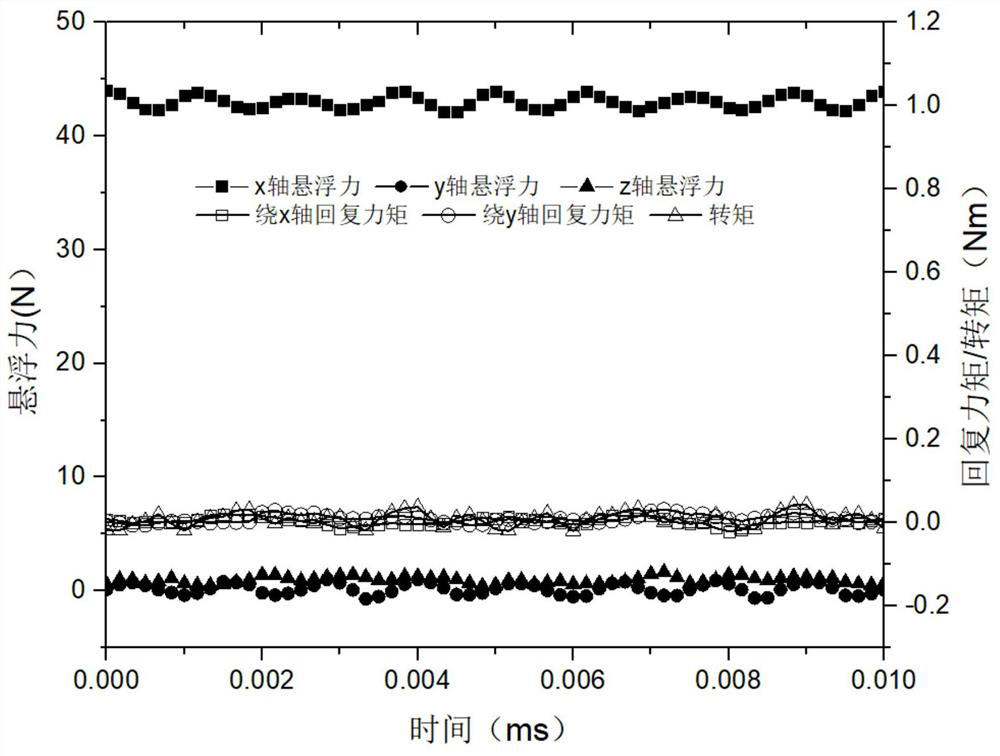
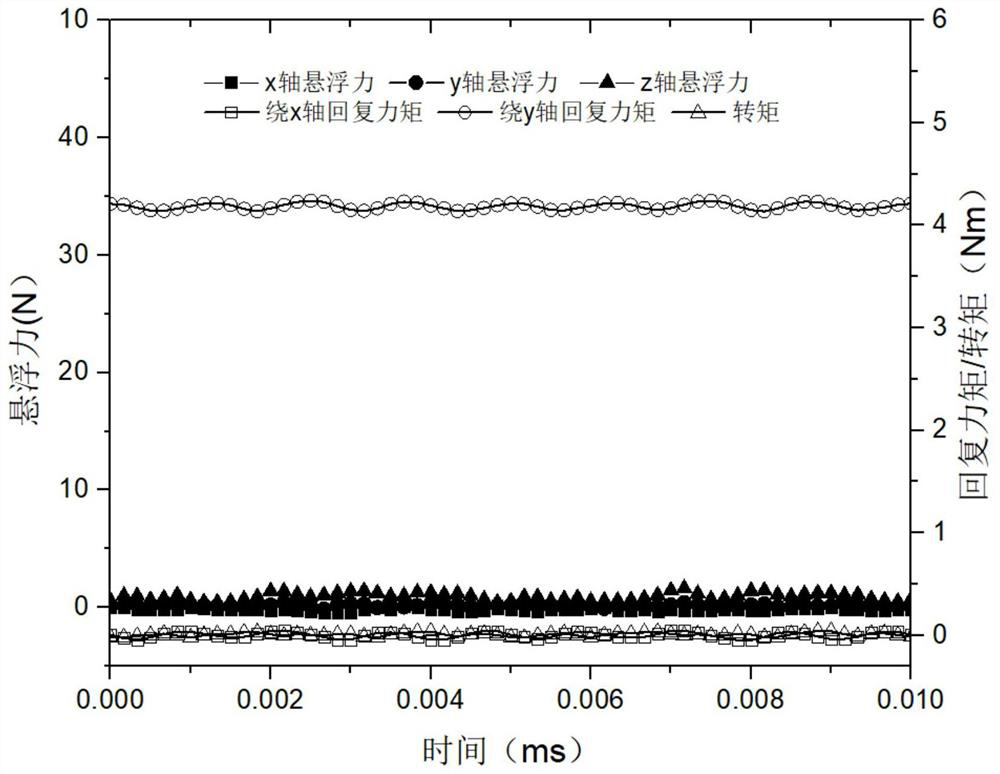
[0060] When the suspension windings of the two stators are fed with the same-phase direct-axis suspension current, the motor generates a suspension force along the radial x direction; The levitation force; when the suspension windings of the two stators are fed with the anti-phase direct-axis suspension current, the motor will generate a restoring torque around the radial direction in the y direction; The return t...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The active control method of the double-stator excitation full-degree-of-freedom bearingless motor provided in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 includes:
[0064] Active control of the four degrees of freedom of the rotor disk, namely two degrees of freedom in radial translation and two degrees of freedom in radial rotation, is achieved by controlling the magnitude and phase relationship of the suspension current components on the two stators in the mid-point and direct axis currents;
[0065] By controlling the torque current components of the two stators, the magnitude and phase relationship of the mid-phase and direct-axis currents, the active control of the two rotor degrees of freedom, the axial translational degree of freedom and the axial rotational degree of freedom of the rotor disk, is realized.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com